Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
RAM SHAFT ASSEMBLY FOR BLOWOUT PREVENTER
FIELD
The present disclosure relates in general to ram actuation assemblies for
blowout
preventers, and further relates to methods for assembling ram actuation
assemblies and
components of such assemblies.
BACKGROUND
This section is intended to introduce the reader to various aspects of art
that may be
related to various aspects of the presently described embodiments. This
discussion is believed to
be helpful in providing the reader with background information to facilitate a
better
understanding of the various aspects of the present embodiments. Accordingly,
it should be
understood that these statements are to be read in this light, and not as
admissions of prior art.
In order to meet consumer and industrial demand for natural resources,
companies
often invest significant amounts of time and money in finding and extracting
oil, natural gas, and
other subterranean resources from the earth. Particularly, once a desired
subterranean resource
such as oil or natural gas is discovered, drilling and production systems are
often employed to
access and extract the resource. These systems may be located onshore or
offshore depending on
the location of a desired resource. Further, such systems generally include a
wellhead assembly
through which the resource is extracted. These wellhead assemblies may include
a wide variety
of components, such as various casings, valves, fluid conduits, and the like,
that control drilling
or extraction operations.
More particularly, wellhead assemblies often include a blowout preventer, such
as a
ram-type blowout preventer that uses one or more pairs of opposing rams that
press toward one
another to restrict flow of fluid through the blowout preventer. Many rams
include main bodies
(or ram blocks) that receive sealing elements (or ram packers) that press
together when a pair of
opposing rams close against one another. Often, the rams are driven into and
out of a main bore
- 1 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
of a blowout preventer by operating pistons coupled to the rams by connecting
rods (or ram
shafts).
BRIEF SUMMARY
Embodiments in accordance with the present disclosure generally relate to ram
actuation assemblies for blowout preventers. In some embodiments, a ram
actuation assembly
includes a ram shaft and a removable piston connected to the ram shaft by
means of intermediate
mounting members. The mounting members, which in one embodiment may be
segments of a
split mounting ring, are positioned radially about the ram shaft, such as
within an external groove
of the shaft. The piston is fastened to the mounting members to retain the
piston on the ram shaft.
Various refinements of the features noted above may exist in relation to
various
aspects of the disclosed embodiments. Additional features may also be
incorporated in these
various aspects as well. Such refinements and additional features may exist
individually or in any
combination. For instance, various features discussed below in relation to one
or more of the
illustrated embodiments may be incorporated into any of the above-described
aspects of the
present disclosure alone or in any combination. This brief summary is intended
only to
familiarize the reader with certain aspects and contexts of some embodiments
without limitation
to the scope of the claimed subject matter.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
These and other features, aspects, and advantages of certain embodiments will
become
better understood when the following detailed description is read with
reference to the
accompanying drawings in which like characters represent like parts throughout
the drawings,
and in which:
FIGURE 1 generally depicts a drilling system for forming a well, where the
drilling
system has wellhead equipment including a blowout preventer.
FIGURE 2 is an isometric view of a ram-type blowout preventer having
embodiments of ram actuation assemblies in accordance with the present
disclosure.
- 2 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
FIGURE 3 is a cross-section through the blowout preventer of FIG 2, depicting
the
ram actuation assemblies.
FIGURES 4 and 5 are isometric views of a ram actuation assembly as in FIG. 3,
having a piston coupled to a ram shaft by means of one or more intermediate
mounting elements, with one end of the ram shaft having a ram button.
FIGURE 6 is an end view of the ram button end of the ram shaft of the ram
actuation assembly of FIG 5.
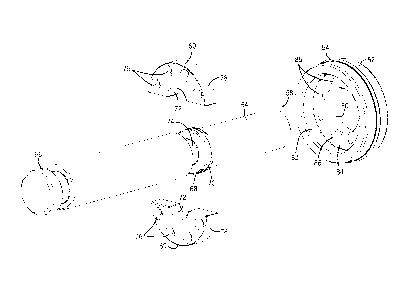
FIGURE 7 is an exploded isometric view generally illustrating the positioning
of
mounting elements in a groove of the ram shaft in accordance with one
embodiment.
FIGURE 8 is an exploded isometric view generally depicting the fastening of
the
piston to the mounting elements positioned radially about the ram shaft in
accordance
with one embodiment.
FIGURE 9 is a longitudinal cross-section of the ram actuation assembly of
FIGS. 4
and 5.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
When introducing elements of various embodiments herein, the articles "a",
"an",
"the", and "said" are intended to mean that there are one or more of the
elements. The terms
"comprising", "including", and "having" are intended to be inclusive and to
mean that there may
be other elements additional to the listed elements. Any use of directional or
relational terms
such as but not limited to "top", "bottom", "above", "below", and variations
of these terms is
made for convenience, but does not require any particular orientation of the
components.
Ram actuation assemblies in accordance with the present disclosure can be used
in
various blowout preventers, and such blowout preventers can be used in a
variety of systems. By
way of example, a drilling system 10 including a blowout preventer is
illustrated in FIG 1 in
accordance with one embodiment. Notably, the system 10 may be operated to
drill a well 12 to
access a subterranean resource, such as oil or natural gas. As depicted, the
system 10 includes an
- 3 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
onshore drilling rig 14, although the system 10 could instead be an offshore
system in other
embodiments. The drilling rig 14 uses a drill string 16 and a drill bit 18 to
form the well 12.
The drilling rig 14 also includes a mast 20 and a hoisting system (shown in
FIG 1 as
including a traveling block 22, a crown block 24, and drawworks 26) to enable
a top drive 28 to
be raised and lowered with respect to a drill floor 30. The drill string 16 is
suspended from the
top drive 28, and extends through a hole in the drill floor 30 and through
wellhead equipment 32
(comprising, for example, a blowout preventer installed on a wellhead). The
drill string 16 can be
rotated by the top drive 28 and can be raised and lowered with the top drive
28 (by means of the
traveling block 22) to facilitate drilling operations. Although the drilling
system 10 is depicted as
including the top drive 28, some other embodiments do not include a top drive,
such as
embodiments using a kelly and a rotary table for rotating the drill string 16.
One example of a blowout preventer forming part of the wellhead equipment 32
is
generally depicted in FIGS. 2 and 3 and indicated by reference number 34. In
the illustrated
embodiment, the blowout preventer 34 includes a hollow main body 36 having a
bore 38 that
allows fluid or devices (e.g., the drill string 16) to pass through the
blowout preventer 34. A plate
40 is provided on the main body 36 and can be removed to allow an operator to
easily access the
inside of the blowout preventer 34. The depicted blowout preventer 34 can be
mounted on a
wellhead or another component by way of a lower connection flange. Additional
equipment may
be installed on the blowout preventer 34 by means of studs on top of the
blowout preventer.
Bonnet assemblies 42 secured to the main body 36 include various components
that
facilitate control of rams 48 disposed in the blowout preventer 34. More
specifically, in the
depicted embodiment, ram actuation assemblies 50 are disposed in housings
between bonnets 44
and end caps 46 of the bonnet assemblies 42. The ram actuation assemblies 50
include pistons 52
coupled to ram shafts 54. In operation, a force (e.g., from hydraulic
pressure) may be applied to
the pistons 52 to drive the rams 48, by means of the ram shafts 54, into the
bore 38 of the
blowout preventer 34. The rams 48 can be pipe rams (as depicted in FIG. 3)
that are driven
together to seal about a tubular member (e.g., drill string 16) and to inhibit
flow through the
blowout preventer 34. Such pipe rams could also include variable-bore pipe
rams. The rams 48
could take other forms as well, such as blind rams or shear rams. Further, the
rams 48 can have
- 4 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
any desired size, which may vary depending on the intended application. For
example, various
pipe rams 48 may be sized for use with blowout preventers having different
bore diameters, such
as bores of seven and one-sixteenth inches or nine inches. In the depicted
embodiment, the end
caps 46 include locking stems that can be threaded through the end caps 46 to
engage the ram
shafts 54 and to lock the rams 48 into place within the bore 38.
Various ram actuation assemblies can be used to control movement of rams in a
blowout preventer. For example, it is known for a ram actuation assembly to
include a separable
ram shaft with two shaft portions that could be coupled together by means of a
threaded
connection (e.g., pin) to retain a piston between the two shaft portions.
However, a threaded
connection between the two shaft portions increases manufacturing expense
(e.g., from
machining the threads) and can be susceptible to galling. Further, if the two
shaft portions are
made of a soft material, like stainless steel, care must be taken by an
assembler to properly align
and connect the two shaft portions. Otherwise, the threaded surfaces of the
two shaft portions
could be scarred, and the actuation assembly could be misaligned (e.g., out-of-
round) when
connected. It is also known for a ram actuation assembly to have a piston
formed integrally with
the ram shaft. While this arrangement may avoid certain alignment issues,
manufacturing costs
may be undesirably high from increased machining time and material expense
(e.g., by removing
material from stainless steel bar stock, sized to accommodate the larger-
diameter piston, to form
the smaller-diameter shaft).
In some embodiments of the technique taught herein, however, the ram actuation
assemblies 50 include separate pistons 52 that can be installed on ram shafts
54 without threaded
surfaces. Additional details of such ram actuation assemblies 50 may be better
understood
through reference to FIGS. 4-9, which depict a ram actuation assembly 50 in
accordance with
certain embodiments. Isometric views of this example of a ram actuation
assembly 50 are
provided in FIGS. 4 and 5, while an elevational view of one end of the ram
actuation
assembly 50 is provided in FIG. 6. These Figures show the piston 52 installed
on the ram shaft
54. One end of the ram shaft 54 (the end depicted in FIG 6) includes a ram
button 56 sized to fit
within a slot in a ram 48 to facilitate coupling of the ram shaft 54 to the
ram 48, as generally
- 5 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
depicted in FIG 3. The other end of the shaft 54 includes a recess 58 for
receiving a locking stem
through an end cap 46 as shown in FIG. 3 and discussed above.
In the embodiment depicted in the Figures, the ram shaft 54 is formed from a
single
piece of material (such as metal); alternatively, however, the ram shaft 54
could be formed with
multiple pieces. More specifically, in at least some embodiments the ram shaft
54 is made from
stainless steel bar stock (e.g., type 304 or type 316 stainless steel). In
accordance with certain
embodiments, the depicted ram shaft 54 does not have threaded surfaces.
Compared to certain
arrangements known in the prior art, the absence of threaded connections on
the ram shaft 54 in
some embodiments allows the ram shaft 54 to reduce or avoid the problems of
alignment,
scarring, and galling discussed above. By avoiding the need to cut threads on
the shaft, such ram
shafts 54 may also be less expensive to manufacture.
The ram actuation assembly 50 also includes one or more mounting members 60
for
coupling the piston 52 to the ram shaft 54. In the particular embodiment
illustrated in FIG 5,
these mounting members 60 are provided in the form of segments of a split
mounting ring
positioned radially about the ram shaft 54. Fasteners 62, such as cap screws,
couple the piston 52
to the mounting members 60. Once the piston 52 is coupled in this manner, it
is retained on the
ram shaft 54 by means of the mounting members 60. The piston 52 also includes
a seal 64 for
inhibiting fluid flow between interior portions of a bonnet assembly 42
separated by the
piston 52.
The piston 52 and the mounting members 60 can be made from the same material
as
the ram shaft 54 (e.g., stainless steel). In at least some embodiments,
however, the piston 52 and
the mounting members 60 are made from different material than the ram shaft
54. For instance,
in certain embodiments the ram shaft 54 is made from stainless steel and the
piston 52 and the
mounting members 60 are made from non-stainless steel, such as a chromoly
steel (e.g., type
4130 steel) or a carbon steel. Because the piston 52 and mounting members 60
are separate from
the ram shaft 54, they can be made from less expensive materials than the ram
shaft 54, thereby
reducing manufacturing expense compared to arrangements with ram shafts having
integral
pistons. Maintenance costs may also be lower, as the separate components could
be individually
replaced as needed.
- 6 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
To assemble the piston 52 and the mounting members 60 on the ram shaft 54, the
mounting members 60 are first positioned about the ram shaft 54 as generally
depicted in FIGS.
7 and 8. The mounting members 60 include inner edges 72, holes 76, and outer
edges 78. In this
illustrated embodiment, the mounting members 60 are received in an external
groove 74 of the
ram shaft 54.
The piston 52 includes an aperture 80 that allows the piston 52 to be slipped
over an
end of the ram shaft 54. Once the mounting members 60 are positioned about the
ram shaft 54,
the piston 52 may be moved along the ram shaft 54 to engage the mounting
members 60. In this
position, the piston 52 abuts a seal 70 within a seal groove 68 of the ram
shaft 54. Like the seal
64, the seal 70 inhibits fluid from passing between interior portions of the
bonnet assembly 42
separated by the piston 52. In at least some embodiments, the ram actuation
assemblies 50 are
constructed to use the same seals 64 and 70 as certain known ram actuation
assemblies. This
enables a blowout preventer to be retrofit with ram actuation assemblies 50
that use the same
seals as the known ram actuation assemblies.
In the depicted embodiment, the piston 52 includes a recess 82 that allows the
piston
52 to receive the mounting members 60 within the recess 82 such that the
piston 52
circumscribes or otherwise encompasses the outer edges 78 of the mounting
members 60. The
piston 52 includes a shoulder 84 having threaded mounting recesses 86. In the
depicted
embodiment, after the mounting members 60 are received in the recess 82, the
piston 52 can then
be coupled to the mounting members 60 by threading the fasteners 62 into
mounting recesses 86
through the holes 76, as generally depicted in FIGS. 8 and 9.
The recess 82 generally facilitates assembly of the piston 52 on the ram shaft
54 by
allowing the piston 52 to encircle the split mounting ring segments or other
mounting members
60 and to hold them in place about the ram shaft 54 while the fasteners 62 are
installed. In other
embodiments, the recess 82 could be omitted. For example, instead of having a
recessed surface,
the piston 52 could have a flat transverse surface that abuts the mounting
members 60.
- 7 -
CA 02847153 2014-03-21
While aspects of embodiments in accordance with the present disclosure may be
susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific
embodiments have been
shown by way of example in the drawings and have been described in detail
herein. However, it
should be understood that embodiments in accordance with the present
disclosure are not
intended to be limited to the particular forms disclosed. Persons skilled in
the art will appreciate
that various modifications to embodiments in accordance with the present
disclosure may be
devised without departing from the present teachings, including modifications
that may use
structures or materials later conceived or developed. Accordingly, embodiments
in accordance with
the present disclosure are intended to cover all modifications, equivalents,
and alternatives
falling within the scope of the invention as defined by the following appended
claims, which
should be given the broadest interpretation consistent with the disclosure as
a whole.
- 8 -