Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
SUSPENSION STRUCTURE FOR AN ELECTRIC WHEELCHAIR
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a suspension structure, and more
particularly to a suspension structure for an electric wheelchair.
Description of the Prior Art
A conventional electric wheelchair disclosed in Taiwan Patent Application
number 098214606 generally comprises a frame connected with a small front
wheel,
a big front wheel, and a small rear wheel. Between the frame and the small
front
wheel are connected a connecting member, a shock absorber and a front arm. The
connecting member is pivoted to the frame, the front arm is pivoted to the
connecting member, the shock absorber is connected between the connecting
member and the front arm, and the big front wheel is connected to a motor and
the
front arm. A rear arm is connected to the small rear wheel and pivoted to the
frame,
and between the frame and he rear arm is also connected a shock absorber. The
shock absorbers can reduce shocks and enhance sitting comfort, when the small
front
and rear wheels run across bumpy roads. However, this conventional suspension
structure of the electric wheelchair is very complicated and difficult to
assemble, and
complicated structure further reduces the structural strength of the
suspension
structure. Besides, the conventional suspension structure only provides shock
absorbing effect but is unable to prevent rollover.
Another conventional suspension structure for an electric wheelchair
disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 8408598 has been simplified in structure, but is
still
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
=
unable to prevent rollover.
The present invention has arisen to mitigate and/or obviate the
afore-described disadvantages.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
One aspect of the present invention is to provide a simply structured
suspension structure for an electric wheelchair which is easy to assemble, and
capable of enhancing sitting comfort and safety of the wheelchair.
To achieve the above, a suspension structure for an electric wheelchair in
accordance with the present invention, comprises: a frame with an. upper side,
a
lower side, a front end and a rear end, a chair seat mounted on the upper
side, a
direction extending from the front end to the rear end being defined as a
first
direction, and a direction perpendicular to the first direction being defined
as a
second direction; two drive units located at both sides of the frame and each
including a bogie and a transmission device fixed to the bogie, one end of
each of
the bogies being pivoted to the frame via a transmission pivot unit, and each
of the
transmission devices extending toward another end of each of the bogies, the
suspension structure is characterized in that:
each of the bogies is further provided with an assembling section extending
along in the second direction;
two drive wheels are connected to and rotated by the transmission devices;
two front guide units are located at both sides of the frame and each include
a front guide wheel, a front suspension arm and a torsion spring, the front
guide
wheels are pivoted to one end of the front suspension arms, respectively, and
another
2
CA 02877922 2016-03-21
end of each of the front suspension arms is pivoted to the frame via a front
suspension arm pivot shaft and located close to the front end, each of the
torsion
springs is sleeved onto the front suspension arm pivot shaft;
two front shock absorbers each have one end pivoted between the two ends
of each of the front suspension arms and another pivoted to the assembling
section of
each of the bogies, and extend in a direction which has a front-shock-absorber
angle
with respect to the first direction;
two anti-roll units are located at both sides of the frame and each include an
anti-roll wheel and a rear suspension arm, each of the anti-roll wheels is
pivoted to
one end of each of the rear suspension arms, and another end of each of the
rear
suspension arms is pivoted to the frame via a rear suspension arm pivot shaft;
and
two rear shock absorbers each have one end pivoted between two ends of
each of the rear suspension arms and another end pivoted to the frame, and
extend in
a direction which has a rear-shock-absorber angle with respect to the first
direction,
the rear-shock-absorber angle is defined between an edge of each of the rear
shock
absorbers close to the front shock absorbers and the first direction, the
front-shock-absorber angle is defined by an edge of each of the front shock
absorbers close to the rear shock absorbers with respect to the first
direction, and the
front-shock-absorber angle is larger than the rear-shock-absorber angle.
3
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
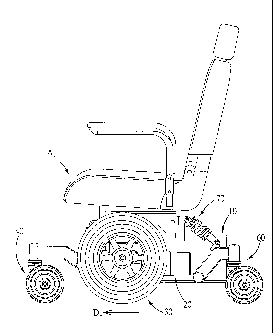
Fig. 1 shows that a suspension structure for an electric wheelchair in
accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention is assembled
on
the electric wheelchair;
Fig. 2 is a perspective view of the suspension structure for the electric
wheelchair in accordance with the present invention;
Fig. 3 is a top view of the suspension structure for the electric wheelchair
in
accordance with the present invention;
Fig. 4 is a cross sectional view of the suspension structure for the electric
wheelchair in accordance with the present invention;
Fig. 5 shows the transmission unit, the front guide unit and the front shock
absorber of the suspension structure for the electric wheelchair in accordance
with
the present invention;
Fig. 6 shows that the suspension structure for the electric wheelchair in
accordance with the present invention is placed on a flat bearing surface;
Fig. 7 shows that the suspension structure for the electric wheelchair in
accordance with the present invention is climbing a convex obstacle; and
Fig. 8 shows that the suspension structure for the electric wheelchair in
accordance with the present invention runs across a concave obstacle.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The present invention will be clearer from the following description when
viewed together with the accompanying drawings, which show, for purpose of
=
illustrations only, the preferred embodiment in accordance with the present
4
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
invention.
Referring to Figs. 1-8, a suspension structure for an electric wheelchair in
accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises: a
frame
10, two drive units 20, two drive wheels 30, two front guide units 40, two
front
shock absorbers 50, two anti-roll units 60, and two rear shock absorbers 70.
The frame 10 includes an upper side 11, a lower side 12, a front end 13 and
a rear end 14. A chair seat A is mounted on the upper side 11. A direction
extending
from the front end 13 to the rear end 14 is defined as a first direction D1,
and a
direction which is perpendicular to the first direction DI is defined as a
second
direction D2.
The two drive units 20 are located at both sides of the frame 10 and each
include a bogie 21 and a transmission device 22 fixed to the bogie 21. One end
of
each of the bogies 21 is pivoted to the frame 10 via a transmission pivot unit
211,
and each of the transmission devices 22 extends toward another end of each of
the
bogies 21. Each of the bogies 21 is further provided with an assembling
section 212
extending along in the second direction D2.
The two drive wheels 30 are connected to and rotated by the transmission
devices 22.
The two front guide units 40 are located at both sides of the frame 10 and
each include a front guide wheel 41, a front suspension arm 42 and a torsion
spring
43. The front guide wheels 41 are pivoted to one end of the front suspension
arms 42,
respectively, and another end of each of the front suspension arms 42 is
pivoted to
the frame 10 via a front suspension arm pivot shaft 421 and located close to
the front
5
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
end 13. Between the two ends of each of the front suspension arms 42 is formed
a
first front extension section 422 and a second front extension section 423. In
this
embodiment, the first front extension section 422 is a flat and straight
section
extending along the first direction DI, and the second front extension section
423 is
an oblique section which extends toward the lower side 12 and defines an angle
with
respect to the first direction Dl. Each of the torsion springs 43 is sleeved
onto the
front suspension arm pivot shaft 421 and has one end fixed to the second front
= extension section 423 and another end abutted against the lower side 12
close to the
front end 13 of the frame 10.
Each of the two front shock absorbers 50 has one end pivoted between the
two ends of each of the front suspension arms 42 and another pivoted to the
assembling section 212 of each of the bogies 21, and extends in a direction
which
has a front-shock-absorber angle 01 with respect to the first direction Dl.
The two anti-roll units 60 are located at both sides of the frame 10 and each
includes an anti-roll wheel 61 and a rear suspension arm 62. The anti-roll
wheel 61 is
pivoted to one end of the rear suspension arm 62, and another end of the rear
suspension arm 62 is pivoted to the frame 10 via a rear suspension arm pivot
shaft
621. Between two ends of each of the rear suspension arms 62 are formed a
first rear
extension section 622 and a second rear extension section 623. The first rear
extension section 622 is straight and flat section extending in the first
direction D1,
and the second rear extension section 623 is an oblique section which extends
toward the lower side of the frame and has an angle with respect to the first
direction
Dl.
6
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
The two rear shock absorbers 70 each have one end pivoted between two
ends of each of the rear suspension arms 62 and another end pivoted to the
frame 10,
and extend in a direction which has a rear-shock-absorber angle 02 with
respect to
the first direction Dl. The rear-shock-absorber angle 02 is defined between
the edge
of each of the rear shock absorbers 70 close to the front shock absorbers 50
and the
first direction D1. The front-shock-absorber angle 01 is defined by the edge
of each
of the front shock absorbers 50 close to the rear shock absorbers 70 with
respect to
the first direction D1, and 01>02.
Referring then to Figs. 6-8, when the suspension structure of the electric
wheelchair in accordance with the present invention is placed on a horizontal
bearing
surface G, the drive wheels 30, the front guide wheels 41 and the anti-roll
wheels 61
are all pressed against the ground.
When the suspension structure runs across a convex obstacle, as shown in
Fig. 7, the drive wheels 30 will move the wheelchair forward until the front
guide
wheels 41 come into contact with the obstacle. At this moment, the drive force
from
the drive units 20 make the front guide wheels 41 drive the front suspension
arms 42
to pivot upward around the front suspension arm pivot shaft 421, so that the
front
guide wheels 41 can easily climb the obstacle. Meanwhile, the pivoting motion
of
the front suspension arms 42 makes the torsion springs 43 compressed, so that,
once
the front guide wheels 41 climb onto the obstacle, the torsion springs 43 will
press
the front guide wheels 41 against the obstacle via the front suspension arms
42, so as
to improve the grip of the front guide wheels 41.
The upward pivoting motion of the front suspension ann pivot shafts 421
7
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
also compress the front shock absorbers 50, then the front shock absorbers 50
push
the bogies 21 to pivot toward the lower side 12 of the frame 10 by moving
around
the transmission pivot units 211, so that the front shock absorbers 50 absorb
the
upward pushing force from the front guide units 40, so as to prevent the frame
10
from rolling over backwards. After the front guide units 40 pass through the
obstacle,
the transmission devices 22 continue driving the front drive wheels 30 to
rotate
forward, meanwhile, the anti-roll units 60 compress and decompress the rear
shock
absorbers 70, making the rear suspension arms 62 pivot around the rear
suspension
arm pivot shafts 621 to change the position of the anti-roll wheels 61, so
that the
anti-roll wheels 61 can pass through the obstacle successfully.
When the suspension structure runs across a concave obstacle, as shown in
Fig. 8, the drive wheels 30 will move the wheelchair forward until the front
guide
wheels 41 come into contact with the concave obstacle. At this moment, the
front
guide wheels 41 lower down to the surface of the obstacle which is at
different
heights with respect to the anti-roll wheels 61, the front shock absorbers 50
will
extend to maintain the frame 10 and the anti-roll wheels 61 at their original
height,
so as to stabilize the wheelchair.
After lowering down to the surface of the obstacle, the front guide wheels
41 will drive the front suspension arms 42 to pivot downward around the front
suspension arm pivot shafts 421, making the second front extension sections
423 of
the front suspension arms 42 compress the torsion springs 43, then the torsion
springs 43 push against the frame 10, making the frame 10 produce a reaction
force
toward the front suspension arms 42, ensuring that the frame 10 and the anti-
roll
8
CA 02877922 2015-01-13
units 60 are all truly pressed against the surface of the bearing surface G,
and
preventing the frame 10 from rolling over forward. The reaction force of the
front
guide units 40 and the anti-roll units 60 improves the grip performance while
substantially reducing the possibility of rollover of the wheelchair. After
the front
guide units 40 successfully pass through the concave obstacle, the
transmission
devices 22 continue driving the drive wheels 30 to move forward, meanwhile,
the
anti-roll units 60 compress and decompress the rear shock absorbers 70, making
the
rear suspension arms 62 pivot around the rear suspension aim pivot shafts 621
to
change the position of the anti-roll wheels 61, so that the anti-roll wheels
61 can pass
through the obstacle successfully.
In general, when the front guide arms 42 drive the front guide wheels 41 to
pivot, the torsion springs 43 can produce a reaction force to prevent the
frame 10
from rolling over, improving safety. When the suspension structure runs across
an
uneven bumpy road, the front and rear shock absorbers 50, 70 can ease the
shock
imposed on the frame 10, enhancing sitting comfort.
While we have shown and described various embodiments in accordance
with the present invention, it is clear to those skilled in the art that
further
embodiments may be made without departing from the scope of the present
invention.
9