Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
A
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 1 -
2012P11641W0US
Description
Component, in particular for an outside cladding of a path-
bound vehicle
The invention relates to a component, more particularly for an
outside cladding of a path-bound vehicle, an arrangement, more
particularly for a path-bound vehicle, and a method for
manufacturing a component, more particularly for an outside
cladding of a path-bound vehicle.
It is known from practice that profiled components which are
part of an outside cladding of a path-bound vehicle formed as a
railed vehicle have to be installed with precision fit between
adjacent components of the outside cladding of the railed
vehicle. To this end the component has to be made with
precision dimensions, thus with small or negligible error
tolerances. Furthermore it is necessary that the component has
a high mechanical stability in order where necessary to safely
divert power flows between further components of the outside
cladding adjoining the component, which can represent force-
conducting components.
One method of manufacturing a component of this kind can be
based on a three-dimensional (3D) milling process in which a
compact three-dimensional plate is milled to the required
dimensions of the component. This method of manufacture can
however be linked to a great time expense with the machine
hours necessary for the 3D milling device used and a high
material consumption owing to the stock-removing manufacturing
process. Consequently the method of manufacture can be cost-
intensive.
,
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
,
PCT/EP2013/062468 - la -
2012P11641WOUS
* A further method of manufacturing the component can be based on
a casting process in which the component can be cast in one
work step by way of example from aluminium. This method of
manufacture can however also be laborious and cost-intensive.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 2 -
212P11641WOUS
It is an object of the present invention to provide measures by
means of which a simple and cost-effective manufacture of a
component is possible, more particularly for an outside
cladding of a path-bound vehicle.
This is achieved by a component, more particularly for an
outside cladding of a path-bound vehicle, an arrangement, more
particularly for a path-bound vehicle and a method for
manufacturing a component, more particularly for an outside
cladding of a path-bound vehicle, according to the independent
claims. Preferred developments of the invention are provided in
the dependent claims.
According to the invention a component, more particularly for
an outside cladding of a path-bound vehicle, is provided
wherein the component is made by means of extrusion molding
from a solid material, wherein the component has an outside
profiling on an outer surface of the component, wherein a first
end face and a second end face of the component opposite the
first end face extend crosswise, more particularly
perpendicularly, to the outer surface and wherein the first end
face and the second end face are formed by means of milling or
sawing.
In the context of the present application the term "path-bound
vehicle" can designate in particular a vehicle which is fixed
in its drive direction or its track. More particularly, the
vehicle can be moved (exclusively) bi-directionally.
The term "outside cladding" can more particularly designate an
outer cover whose wall can be formed more particularly by means
of the component.
The term "outside profiling" of the component can more
particularly designate a shaping of a surface of the component.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 2a -
2@l2P11641WOUS
The outside profiling can be by way of example a recess, a
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 3 -
2412P11641WOUS
groove, a hole and/or inclined or chamfered surfaces.
During manufacture or production of a component according to
the invention, the in particular three-dimensionally formed
component can be made with its outside profiling arranged on an
outer surface by means of extrusion molding from a solid
material. This can enable a particularly cost-effective and
simple manufacture of the component in only one work step
without any unnecessary material consumption. In a following
work step which can be simple to execute, the component can be
cut to length with precision measurements on a first and second
end face by means of milling or sawing, thus can be cut off in
one of its dimensions, by way of example in its length, width
or height, in order to adapt in particular the component
accurately sized to its measurements which are required for an
installation. The cutting process takes place by a two-
dimensional (2D) machining process which can be carried out at
low cost. The component can thereby be provided with the
necessary connections or connection faces for adjoining
component parts.
The component can be made overall simply and particularly cost-
effectively, and a cost-intensive casting process or a cost-
intensive three-dimensional milling process can be avoided more
particularly when manufacturing the component.
Furthermore, particularly in comparison with a casting process,
as a result of the extrusion molding process used, the
component can have easy-handling material properties, by way of
example a sufficient bending flexibility, for its further
machining and/or assembly.
More particularly, the first and second end faces can extend
crosswise, more particularly perpendicularly, to a base surface
of the outer surface of the component, which by way of example,
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
POT/EP2013/062468 -4 -
2G12P11641WOUS
seen in the cross section of the component, can be defined by
an outside border, more particularly an edge, of the outer
surface.
The component can have an oblong body wherein the outer surface
can be a longitudinal surface of the body, wherein the first
end face and the second end face can be transverse faces of the
body. Alternatively, the first end face and the second end face
can represent further longitudinal faces of the body which can
extend crosswise, more particularly perpendicularly, to the
outer surface.
The outside profiling can have a recess which can be inserted
into the outer surface and extend from the first end face up to
the second end face. The first and second end faces can
consequently have lateral apertures which can form lateral
openings for the recess. The recess can be introduced into the
component by way of example for optical reasons, for
aerodynamic reasons and/or for stability reasons. An extension
of the recess from the first end face up to the second end face
can produce a uniform outside profiling of the component along
an extension direction of the component so that the component
can be made in a longer length by means of extrusion molding in
order then to be cut off accordingly by means of sawing or
milling.
The recess can taper towards an interior of the component
wherein a first boundary wall of the recess extending from the
first end face up to the second end face can be curved
concavely and a second boundary wall of the recess extending
from the first end face up to the second end face can be formed
flat. This measure can enable a particularly simple production
of the component by means of extrusion molding since the first
and second boundary walls can be shaped geometrically simply.
=
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 5 -
2:)12P11641WOUS
' A first depth of the recess which can be measured from a first
outer edge section of an edge defining the recess to a bottom
of the recess can be different from a second depth of the
recess which is measured from a second outer edge section of
the edge to the bottom of the recess. By the term "edge" can be
understood in particular a rim or rim surface. By the term
"bottom" can be understood in particular a point, a line or a
surface area which can be arranged at the furthest distance
from the first and second edge sections seen along a depth
direction of the recess. More particularly, the first and
second depths can be measured along a common direction. The
first depth can be smaller or greater than the second depth.
This measure can have the effect that the component, seen
relative to a direction which can run crosswise, more
particularly perpendicularly to the depth direction of the
recess, can have different width sections. The component can
thereby enable an adjustment in width between adjoining
different width components, more particularly of the outside
cladding of the path-bound vehicle. Furthermore, the component
can enable a diversion of a power flow between the different
width sections of the component and/or the components adjoining
these sections.
More particularly, a first section of the outer surface can be
arranged adjoining the first boundary wall of the recess and
comprise the first edge section, and a second section of the
outer surface can be arranged adjoining the second boundary
wall of the recess and comprise the second edge section. The
first and second sections can in particular be designed flat
and have different inclines relative to a common reference
surface. The component can thereby be designed uniform along
the extension of the recess so that the extrusion molding of
the component can be carried out particularly cost-effectively.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 6
2c,)12P11641WOUS
The component can have a further outside profiling along a
third end face of the component, wherein the further outside
profiling can comprise a welding structure which can have a
chamfer on an outer edge section of the third end face and a
grooved further recess which can be introduced in the first end
face adjacent the chamfer, wherein the chamfer and the grooved
further recess can extend from the first end face up to the
second end face. The welding structure can serve more
particularly as a welding seam preparation for a subsequent
welding process by means of which the component can be bonded
by welding to an adjoining component. Welding material of a
welded seam which is to be formed can thereby be introduced
into the grooved further recess in order to enable a root
formation for the welded seam which is to be formed. More
particularly, the welding material for the welded seam which is
to be formed can be placed on the chamfer in order to enable
the component to be welded to the adjoining component in the
region of the chamfer. A used welding device can apply heat in
the region of the chamfer to the third end face in order to
produce a sufficient heat transfer to the material of the
welded seam which is to be formed, the component and the
adjoining component. A particularly stable bonding of the
component to the adjoining component can thereby be achieved.
The welding structure can have still one more recess in the
third end face, wherein the still one more recess can be
introduced into the third end face on a side of the grooved
further recess remote from the chamfer, and can extend from the
first end face up to the second end face. The one more recess
can have by way of example a rectangular cross section which
can be substantially constant along a depth extension of the
one more recess. The heat necessary for the welding process can
thereby be contained in the region of the chamfer and the
grooved further recess, and not
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 7 -
2.012P11641WOUS
" diverted into an interior of the component so that the risk of
faults in the welded seam along the joins can be severely
reduced.
More particularly, the component can have one more outside
profiling along a fourth end face of the component, which can
be designed according to one or more of the embodiments
described above for the further outside profiling of the third
end face. More particularly, the fourth end face can be
opposite the third end face. The component can thereby be
connected on each side to the relevant adjoining components.
More particularly, the outside profiling and the welding
structure of the further outside profiling or welding structure
of the one more outside profiling can be arranged adjacent one
another on a common side half of the component.
More particularly, the further outside profiling and/or the one
further outside profiling can have one further welding
structure which can be arranged on the third end face and/or
the fourth end face and can be designed according to one of the
embodiments described above. More particularly, the further
welding structure and the one further welding structure can be
free of the one further recess of the outside profiling.
More particularly, the component can comprise or be formed of
metal, more particularly aluminium or an aluminium alloy. In
particular, the component can be extrusion molded in one piece.
The invention relates further to an arrangement, more
particularly for a path-bound vehicle, with a component which
is described above, wherein the component is welded to a first
support element and to a second support element of the path-
bound vehicle.
,
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 8 -
2G12P11641WOUS
More particularly, the first and second support elements can be
formed as longitudinal supports which can be interrupted in the
region of a door pillar of the path-bound vehicle in order to
free up the entry area to the path-bound vehicle.
Alternatively, the first and second support elements can be
formed as longitudinal supports and as a door pillar which
define the entry area to the path-bound vehicle. The first and
second support elements can also be formed as longitudinal
supports which can be arranged in a roof area of the path-bound
vehicle and allow by way of example a width profiling of a roof
of the path-bound vehicle. In these three cases, more
particularly the outer surface can represent an exposed outer
surface and form a closure for the corresponding support
elements. It is likewise possible that the component can be
part of an outside cladding of the path-bound vehicle and can
be installed between adjacent components and can be covered by
these components.
The invention further relates to a path-bound vehicle, with an
arrangement, which is described above. More particularly, the
path-bound vehicle can be designed as a railed vehicle, more
particularly as a train or high-speed train. Alternatively, the
path-bound vehicle can be designed as a magnetic monorail or as
a hover train.
The invention further relates to a method for manufacturing a
component, more particularly for an outside wall cladding of a
path-bound vehicle, with extrusion molding of the component
from solid material and with an outside profiling on an outer
surface of the component and sawing or milling of a first end
face and a second end face of the component opposite the first
end face, wherein the first end face and the second end face
extend crosswise, more particularly perpendicularly to the
outer surface.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 9 -
2g12P11641WOUS
More particularly, the first and second end faces can be sawn
or milled simultaneously or in any sequence one after the
other.
The method can furthermore comprise machining the outside
profiling, the further outside profiling and/or the one further
outside profiling of the extrusion-molded component, more
particularly before or after sawing or milling the first and
second end faces. By way of example, during machining, the
corresponding surface of the component can be smoothed,
polished or shaped by means of filing.
More particularly, the method can comprise further machining at
least one end face of the group consisting of the first end
face, the second end face, the third end face and the fourth
end face, more particularly by means of one of the
aforementioned measures.
The embodiments described above with reference to the component
according to the invention, the arrangement according to the
invention, the path-bound vehicle according to the invention
and the method according to the invention, also apply for the
respective other objects according to the invention.
The properties, features and advantages of this invention
described above as well as the manner in which these are
achieved will become clearer and more comprehensible in
conjunction with the following description of the embodiments
which are explained in further detail in conjunction with the
drawings. The features outlined below represent both each
individually and also in combination one aspect of the
invention. The drawings show:
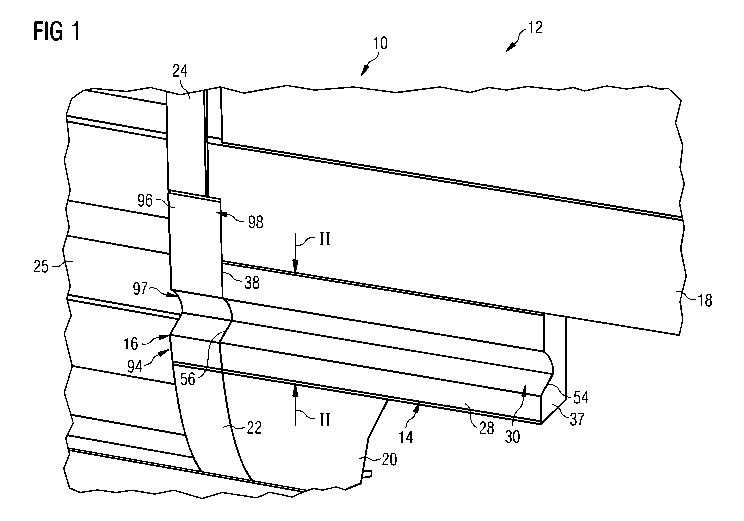
Fig. 1 an arrangement for a high-speed train according to
one embodiment; and
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 9a -
2Q12P11641WOUS
Fig. 2 a cross-sectional view of the arrangement along a
line II-II in Figure 1.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 10 -
2 12P11641WOUS
An arrangement 10 of a high-speed train 12 according to one
embodiment has a first component 14, a second component 16,
first to third support elements 18, 20, 22 and a door pillar
24. The first and second support elements 18, 20 are designed
in the form of longitudinal beams which extend along a
longitudinal extension of the high-speed train 12 and are
interrupted in an entry area 25 to the high-speed train 12
which is shown diagrammatically in Figure 1 by means of steps.
The first and second longitudinal supports 18, 20 abut the door
pillar 24 or the third support element 22 likewise designed as
a longitudinal beam and defining the entry area 25.
The first component 14 shown in detail in Figure 2 comprises a
substantially block-shaped body 26 of solid aluminium material
and is made by means of extrusion molding. A first outer
surface 28 of the body 26 has an outside profiling 30 which is
formed by a first section 32 and a second section 34 of the
first outer surface 28 and a recess 36 of the outside profiling
30. The first section 32, the second section 34 and the recess
36 extend along a complete longitudinal extension of the first
component 14 from a flat first end face 37 of the first
component 14 up to a flat second end face 38 of the first
component 14 which are both produced by milling.
The first section 32 and the second section 34 extend in
different planes and are inclined respectively by an angle a of
about 1 degree and an angle P, of about 2 degrees relative to a
second outer surface 39 of the body 26 opposite the first outer
surface 28. The second outer surface 39 runs approximately
perpendicular to a longitudinal extension of the first and
second longitudinal supports 18, 20.
s
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 11 -
212P11641WOUS
The recess 36 tapers toward an interior 40 of the body 26 and
has a first boundary wall 42 and a second boundary wall 44
which are arranged adjacent to the first section 32 and to the
second section 34 respectively. The first boundary wall 42 is
curved concavely in the direction of the interior 40, whilst
the second boundary wall 44 is flat and is inclined at an angle
y of about 48 degrees relative to a vertical which runs
substantially parallel to the second outer surface 39. A depth
Ti of the recess 36 is measured perpendicular between a bottom
45 of the recess 36 which is approached by a reference plane 46
running parallel to the second outer surface 39, and a first
outer edge section 48, formed as a rim, of an outer edge 50 of
the recess 36. The depth Ti is smaller than a second depth T2
of the recess 36 which is measured perpendicular between the
bottom 45 or reference plane 46 and a second edge section 52,
formed as a rim, of the edge 50 of the recess 36. The edge 50
has in addition to the first and second edge sections 48, 52, a
third and fourth edge section 54, 56 which represent the rims
of the first and second end faces 37, 38 of the component 14.
A third end face 62 of the body 26 is designed flat and extends
at about 90 degrees to the second outer surface 39. An outside
profiling 63 with a first and second welding structure 64, 66
is introduced in the third end face 62. The first and second
welding structures 64, 66 are arranged adjacent the first
section 32 of the outer surface 28 and the second outer surface
39 respectively. The first welding structure 64 has a chamfer
68 which is part of the third end face 62 and defines the third
end face 62 from the second section 32 of the first outer
surface 28. A grooved first recess 70 is inserted into the end
face 62 adjacent the chamfer 68. A second recess 72 which has a
rectangular cross section which is constant along its depth, is
inserted into the end face 62 adjacent the grooved first recess
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 12 -
212P11641WOUS
on a side of the grooved first recess 70 remote from the
chamfer 68. A width of the recess 72 measured perpendicular to
a longitudinal extension of the first and second surfaces 28,
39 and parallel to the depth direction of the recess 36,
corresponds roughly to the depth Ti and is half as large as a
width of the recess 36 measured between the first and second
edge sections 48, 52. The second welding structure 66 has a
chamfer 74 which represents a part of the third end face 62 and
defines the third end face 62 from the second outer surface 39.
A grooved recess 76 is inserted into the third end face 62
between the chamfer 74 and the recess 72.
A fourth end face 78 of the body 26 opposite the third end face
62 is designed flat and extends at an angle of about 90 degrees
to the second outer surface 39. Furthermore, the fourth end
face 78 has an outside profiling 79 with a first and second
welding structure 80, 82 which, seen relative to a width
direction of the first component 14, lie opposite one another
and which, relative to a height direction of the first
component 14, lie opposite the welding structures 64 and 66
respectively of the third end face 62. The welding structure 80
has a chamfer 84 which forms a part of the end face 78 and
closes the fourth end face 78 from the second section 34 of the
first outer surface 28. A grooved first recess 86 is inserted
in the fourth end face 78 between the chamfer 84 and a second
recess 88 formed in the fourth end face 78. A chamfer 90 of the
welding structure 82 is arranged adjacent a grooved recess 92
of the welding structure 82 and defines the fourth end face 78
from the second outer surface 39. The grooved recess 92 is
arranged directly adjacent the recess 88. A width of the recess
88 corresponds to a width of the recess 72. A depth of the
recess 88 is about double the size of a depth of the recess 72.
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 13 -
212P11641WOUS
The second component 16 of the arrangement 10 is formed
similarly to the component 14 of the arrangement 10. However a
body 94 of the component 16 tapers in the direction of the
entry area 25 of the high-speed train 12 by about 4 degrees
relative to the longitudinal direction of the first component
14. A first section 96 of the first outer surface 98 of the
second component 16 provided with an outside profiling 97 has a
greater width than the section 32 of the first outer surface 28
of the first component 14. A length of the second component 16
measured along the longitudinal extension of the high-speed
train 12 is less than a corresponding length of the first
component 14 and less than the width of the second component
16.
In a method for manufacturing the first component 14, according
to one embodiment the body 26 of the component 14 is extrusion-
molded from aluminium. The outside profilings 30, 63, 79 of the
first component 14 are created during the extrusion process.
Following this, the first component 14 is cut to length, with
the first and second end faces 37, 38 of the first component 14
being cut by means of milling. The outside profilings 30, 63,
79 are made free of further machining or in other words the
outside profilings 30, 63, 79 are not machined further.
Following this, the first component 14 is arranged between the
first longitudinal support 18 and the second longitudinal
support 20 so that the first outer surface 28 represents an
exposed surface of the first component 14 and the second outer
surface 39 represents a rear concealed surface of the first
component 14 in its installed position. The third end face 62
of the first component 14 corresponds in the installed state of
the first component 14 to an upper end face of the first
component 14, and the fourth end face of the component 14
corresponds to a lower end face of the first component 14. The
first component 14 is welded to the first and second
longitudinal supports 18, 20 whereby
=
CA 02879764 2015-01-22
PCT/EP2013/062468 - 14 -
2912911641WOUS
welding material is filled into the grooved recesses 70, 76,
86, 92 of the welding structures 64, 66, 80, 82 and applied to
the chamfers 68, 74, 84, 90 of the welding structures 64, 66,
80, 82, and then heated.
A method for manufacturing the second component 16 according to
a further embodiment is carried out in a similar way to the
method for manufacturing the first component 14. The component
16 is however extrusion-molded from an aluminium alloy with the
corresponding outside profilings 79. The second component 16 is
then welded between the door pillar 22 and the third support
element 20 by using corresponding welding structures of the
second component 16.
Although the invention is illustrated and described in detail
through the preferred embodiment, the invention is not
restricted by the disclosed examples and other variations can
be derived therefrom by the person skilled in the art without
departing from the protection scope of the invention.