Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164 - 1, -
2012P11623W0US
Description
Single-shell floor profile for a rail vehicle
The present invention relates to a single-shell floor profile
for a rail vehicle. In particular, the present invention
relates to a floor profile, which has a floor plate and at
least one reinforcement element, wherein the reinforcement
element extends parallel with the longitudinal axis of the
vehicle and forms a hollow-chamber profile with the floor
plate.
Prior Art
Rail vehicles form complex multi-component systems whose
material composition and structural configuration are limited
by a large number of very different peripheral conditions. For
instance, particularly the demands which are made in the field
of rail vehicle construction with regard to safety,
reliability, functionality and not least also the economic
viability of the technical implementation constitute a complex
challenge, which in other fields of vehicle construction of
this type may not be encountered at all or may be encountered
only in a reduced form.
Previously in the construction of floors in rail vehicles,
there were used hollow-chamber profiles which have a
significant construction height over the entire vehicle width
of the rail vehicle shell. In particular in the region of the
bogies of rail vehicles, the entire structural space available
was thus occupied by the structural height of the floor
profiles.
A bogie is a drive mechanism of a rail vehicle in which two or
more sets of wheels are resiliently supported in a frame which
can turn with respect to the carriage chassis on bends. This
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164 - l -
2012P11623W0US
so-called dual turntable steering enables the construction of
longer vehicles or line laying of the rails with a tighter
radius of curvature.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164 - 2, - .
2012P11623W0US
Modern bogies in this instance have dual spring-mounting. On
the one hand, the wheel sets are spring-mounted by means of the
so-called primary spring-mounting with respect to the bogie
frame. On the other hand, the bogie is spring-mounted by means
of a cradle in the region of the bogie pivot which forms the
connection between the carriage body and the bogie with respect
to the carriage body of the rail vehicle by means of the so-
called secondary spring-mounting.
The spring-mounting of the bogie with respect to the carriage
body by the secondary spring-mounting in this instance improves
the travel comfort of the rail vehicle. At high speed, the
rigidity of the primary spring-mounting and the damping of the
rotary movement by means of so-called rolling dampers becomes
highly significant for the stability of the sine run of the
wheel sets.
A sine run occurs with wheel/rail systems having conically
profiled and rigidly coupled wheels in which the wheel profile
tapers outward. On bends, the wheel which is outwardly
displaced travels with a larger periphery on the rail than the
wheel which is offset toward the track center. This remains
recessed with respect to the outer wheel so that the axle
steers into the bend. A sine run occurs in the event of a
deviation of the rail guide from the ideal line which is
overcompensated by the wheel profiling and thus leads to a
rolling movement. This movement is at small amplitudes
sinusoidal with a constant wavelength, the frequency increasing
with the travel speed. At high speeds, additional dynamic
forces occur and may occur to the extent of zig-zag travel with
an abutment of the wheel flanges of the wheel sets on the rails
so that measures for damping have to be taken in order to
prevent excessive wear and significant impairments of comfort.
It is therefore necessary in the region of the bogies to
provide corresponding damping and spring-mounting components.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164 - 2a -
2012P11623WOUS
However, these require sufficiently free structural space, both
for the installation thereof and for the maintenance thereof.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164
2012P11623W0US
Furthermore, in the region of the bogies, there are also the
drive motors of modern rail vehicles, which in turn take up a
corresponding amount of structural space.
The control and supply lines which are intended to be guided
through the region of the bogies are currently either guided
through the hollow-chamber profile or laid in cable ducts which
are mounted separately below the hollow-chamber profile,
whereby the free structural space available is, however,
significantly further reduced. Laying the supply and control
lines through the hollow-chamber profile is in this instance
extremely complicated in terms of assembly and very time-
consuming since in this instance care has to be taken that the
hollow-chamber profiles in which the lines are intended to be
laid are free from any occurrences of contamination, such as,
for example, welding defects, in order to prevent damage to the
lines during assembly or during operation of the rail vehicle.
An object of the present invention is therefore to provide
sufficient free structural space for assembling modern drive
and spring-mounting systems in the region of bogies of rail
vehicles.
This object is achieved according to claim 1. Specific
embodiments of the invention are set out in the dependent
claims.
To this end, there is provided according to the invention a
floor profile, which has a floor plate and at least one
reinforcement element, wherein the reinforcement element
extends parallel with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle and
forms a hollow-chamber profile with the floor plate.
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, consequently,
there is proposed a floor profile which has a substantially
reduced structural height with respect to the previously used
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
TCT/EP2013/065164 - 3,. - .
,
2012P11623W0US
hollow-chamber profiles at least in the region of the bogies of
a rail vehicle, and consequently provides more free structural
CA 081331 2015-10
PCT/EP2013/065164 - 4 - .
2012P11623W0US
space for the components which are intended to be provided in
the underfloor region of the rail vehicle.
The floor plate has in this instance localized reinforcements
for transmitting the longitudinal forces which occur. In
particular, there may be provision for the hollow-chamber
profile in the region of the cross-section center of the rail
vehicle to have at least one reinforcement element in order to
take up the coupling forces which occur in the rail vehicle and
to be able to reliably discharge them.
The remaining structural space under the floor plate, in
particular in the edge region of the cross-section of the rail
vehicle, is available as free assembly space, within which
supply and control lines can be guided in cable ducts, without
this leading to an increase in the entire structural height of
the floor.
This simplifies the assembly of control and supply lines in
this region since these no longer have to be laid through the
chambers of the hollow-chamber profile in order to be able to
dispense with the assembly of cable ducts which are mounted
below the hollow-chamber profile to the benefit of the assembly
space. A time-consuming and costly endoscopic examination of
the hollow-chamber profiles is thereby prevented. Cables and
pipes may be prefabricated and laid in cable ducts which are
secured in the region of the tapered hollow-chamber profile.
This enables pipe and cable guiding within the structural space
height of the originally used hollow-chamber profiles with at
the same time easy accessibility and thereby a high level of
ease of assembly.
The hollow-chamber profile formed by the floor plate and the
reinforcement element may have a rectangular, trapezoidal or
triangular cross-section. It is particularly preferable for the
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
.PCT/EP2013/065164 - 40. - ,
2012P11623W0US
floor plate and the reinforcement element to form a hollow-
chamber profile having a rectangular cross-section.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
,PCT/EP2013/065164 - -
2012P11623W0US
The reinforcement element is preferably connected to the floor
plate in a materially engaging manner. To this end, there may
be provision for the floor plate and the reinforcement element
to be provided as separate components which are then joined
together by means of suitable joining methods, such as, for
example, welding, before the floor plate is inserted into the
shell of the rail vehicle.
There may also be provision for the reinforcement element to be
joined directly to the floor plate or a part-segment of the
floor plate, for example, by the floor plate profile being
provided as an extruded profile.
In an embodiment of the invention, the floor plate profile may
comprise at least two segments which are connected to each
other in a materially engaging manner or positive-locking
manner. For positive-locking connection, there may be provision
for the individual segments to have in the joining region, for
example, tongue and groove profiles, by means of which the
segments can be connected to each other.
According to an embodiment of the floor profile according to
the invention, there is provision for the reinforcement element
to have a fixing element for directly or indirectly assembling
units and/or system components of the rail vehicle under the
floor.
The term "directly assembling" is intended to be understood in
the context of the invention to mean that the unit or the
system component is not fixed directly to the fixing element
but instead retention and/or carrier elements are fixed to the
fixing element, to which elements the units or system
components can in turn be fixed.
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
.PCT/EP2013/065164 - 5@ -
2012P11623W0US
The term "units" is intended to be understood in the context of
the invention to be operationally technical devices of the rail
system, such as, for example, components of the compressed air
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164
2012P11623WOUS
system, heating system, drive system and/or braking system, and
components of the sanitary supply and disposal systems. The
term "system components" is intended to be understood in the
context of the invention to be, for example, control lines,
signal lines, compressed air lines and supply/disposal lines.
According to another embodiment of the invention, there is
provision for the floor plate to have a fixing element in the
direction of the track bed. That fixing element may also be
used for directly or indirectly assembling units and/or system
components of the rail vehicle under the floor.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention, there is provision
for a cable duct to be able to be fixed under the floor plate
by means of a fixing element of a reinforcement element and a
fixing element of the floor plate, by means of which cable duct
control lines, signal lines, compressed air lines and/or
supply/disposal lines can readily be laid along the
longitudinal axis of the rail vehicle.
In another embodiment of the invention, there is provision for
the floor profile to have at least two reinforcement elements.
In this instance, the reinforcement elements may in particular
be arranged so as to be symmetrically spaced apart from the
longitudinal center axis of the rail vehicle body. This has the
advantage that, in the region of the highest action of force,
sufficient capacity is provided to absorb the tensile and
pressure forces which occur and the forces can be redirected
into the remaining shell structure.
In another embodiment of the invention, there is provision for
the floor profile to be positioned on longitudinal carriers of
the rail vehicle shell and to be able to be connected thereto
in a materially engaging or non-positive-locking/positive-
locking manner. In this instance, a releasable non-positive-
locking/positive-locking connection of the profile to the
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
.PCT/EP2013/065164 - 6 - .
2012P11623WOUS
longitudinal carriers is particularly preferred since improved
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
.PCT/EP2013/065164 -
2012P11623W0US
accessibility to the underfloor region, in particular to the
bogies, can thus be achieved in the event of maintenance.
According to another embodiment of the invention, there is
provision for the floor plate to have reinforcement ribs. The
reinforcement ribs may extend both in the longitudinal
direction and in the transverse direction of the rail vehicle
body and increase the torsional rigidity of the floor profile
in the direction of extent thereof, respectively. The
reinforcement ribs may be joined to the floor plate by means
of, for example, welding, or already be produced as a shaped
element in the case of extruded floor plates during production
of a floor plate segment.
In another embodiment of a floor profile according to the
invention, there is provision for a closure plate to be
arranged between at least two reinforcement elements in such a
manner that there is formed between the reinforcement elements
a space which is suitable for guiding air. That air-guiding
space can advantageously be used to supply cooling air to the
drive motors which are mounted in the bogies. In this instance,
there may be provision for the closure plate to have a support
element, with which it can be supported with respect to the
floor plate in the region between the reinforcement elements in
order to reduce or eliminate the occurrence of vibrations of
the closure plate during running operation.
Furthermore, the invention proposes a rail vehicle which has a
floor profile according to the invention as described above at
least in the region of a bogie.
The invention is explained in greater detail below with
reference to Figures, in which:
Figure 1 shows the embodiment of a vehicle floor according to
the prior art;
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
.PCT/EP2013/065164 - 8.- .
2012P11623W0US
Figure 2 shows an embodiment of a floor profile according to
the invention for a rail vehicle; and
Figure 3 shows another embodiment of a floor profile according
to the invention for a rail vehicle.
Figure 1 shows the embodiment of a vehicle floor 800 above a
bogie according to the current prior art. The floor is
constructed as a hollow-chamber profile 801. The hollow
chambers 802 have to be endoscopically examined prior to the
introduction of the lines in order to identify and where
applicable to remove from within the hollow chambers 802 any
occurrences of contamination which could during operation of
the rail vehicle lead to damage to lines guided inside the
hollow-chamber profile 801. Alternatively, any control and
supply lines are guided through cable ducts 803, which have to
be assembled below the hollow-chamber profile 801. This
significantly limits the free structural space in particular in
the region of the bogies.
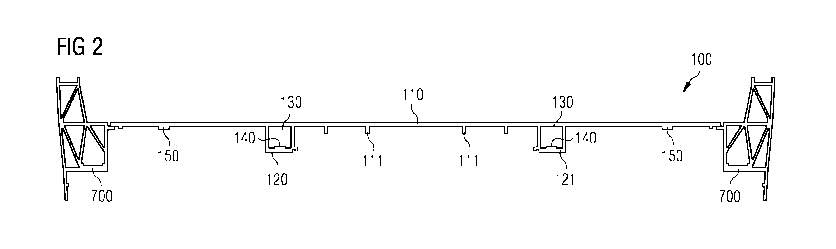
Figure 2 shows an embodiment according to the invention of a
floor profile 100 for a rail vehicle. The single-shell floor
profile 100 for a rail vehicle has a floor plate 110 and at
least one reinforcement element 120. The reinforcement element
120 extends parallel with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle
and forms with the floor plate 120 a hollow-chamber profile
130. In the embodiment shown, the floor plate 110 has
reinforcement ribs 111. The reinforcement ribs 111 may extend
both in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the vehicle
and transversely relative to the longitudinal axis of the
vehicle. The floor profile preferably has at least two
reinforcement elements 120, 121, the reinforcement ribs 111
being arranged at least in the region between the at least two
reinforcement elements 120, 121. The reinforcement element 120
has a fixing element 140 for directly or indirectly assembling
units and/or system components of the rail vehicle under the
floor. The floor plate 110 also has in the direction of the
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
PCT/EP2013/065164 - 8a 7, .
2012P11623WOUS
track bed a fixing element 150
CA 02881331 2015-02-06
'PCT/EP2013/065164 - 9,
2012P11623W0US
which may be used for directly or indirectly assembling units
and/or system components of the rail vehicle under the floor.
The floor profile 100 is positioned on longitudinal carriers
700 of the vehicle shell and is connected thereto in such a
manner that the longitudinal forces produced can be dissipated
adequately into the longitudinal carriers 700.
Figure 3 shows another embodiment of a floor profile 100
according to the invention for a rail vehicle. Curved retention
members 201, 202 are fixed to the fixing elements 140, 150 by
means of suitable securing screws/bolts 151, 151. The curved
retention members 201, 202 retain a cable duct 200, through
which system components, such as, for example, control lines,
signal lines, compressed air lines or supply/disposal lines can
be directed. A closure plate 220 is arranged between the two
reinforcement elements 120, 121 in such a manner that a space
210 suitable for guiding air is formed between the
reinforcement elements. The closure plate 220 has a support
element 221, via which the closure plate 220 is supported with
respect to the floor plate 110 in order to damp oscillations
and vibrations of the closure plate 220 during running
operation.