Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
1
CONFIGURABLE INPUT/OUTPUT UNIT
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] The present disclosure relates to the field of configurable
electronic components. More specifically, the present disclosure relates to a
configurable input/output unit, and a configurable modular card provided
therewith.
BACKGROUND
[0002] An input/output (I/O) unit is a component of an electronic card
allowing the electronic card to communicate with external entities, such as
computing devices. For instance, a processing unit of the electronic card
generates data, which are transmitted to a computing device via the I/O unit.
Data
can also be received from a computing device by the electronic card via the
I/O
unit, to be further processed by its processing unit. The I/O unit supports
one or
several communication protocols (e.g. Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc.) to communicate
with
the external entities.
[0003] The I/O unit generally operates in pre-defined manner, according
to pre-defined operating parameters which can be stored in a memory of the
electronic card. However, in various types of applications, such as for
example
flight simulators, it may be convenient to use generic electronic cards which
can
be configured to operate in a particular manner to implement specific
functionalities. Thus, the same generic electronic card is capable of behaving
differently, based on its specific configuration. The specific configuration
generally
consists in executing a specific software to implement a specific
functionality.
However, to provide more flexibility in the way the generic electronic card
can
operate, it may be practical to also have an I/O unit which can be configured.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
2
[0004] Therefore, there is a need for a configurable input/output unit,
and
a configurable modular cad provided therewith.
SUMMARY
[0005] According to a first aspect, the present disclosure provides a
configurable input/output unit comprising a plurality of configurable inputs
and
outputs. The plurality of configurable inputs and outputs comprises a
predefined
output for sending a broadcast message, and a predefined input for receiving a
broadcast response message.
[0006] According to a second aspect, the present disclosure provides a
configurable modular card. The card comprises a board, at least one processor
mounted on the board, and at ieast one memory mounted on the board and in
electronic communication with the processor. The card comprises the
aforementioned configurable input/output unit. The card comprises a bus
electronically connected with the configurable input/output unit, the at least
one
processor and the at least one memory for providing electronic data exchange
there between. The card comprises input/output configuration code stored in
the
memory. The input/output configuration code, when executed by the at least one
processor, configures the plurality of inputs and outputs of the configurable
input/output unit based on the broadcast response message.
[0007] In a particular aspect, the aforementioned configurable modular
card is adapted for being used in a simulator, and further comprises a power
supply. The power supply receives an entry power of a predetermined voltage
and
comprises a plurality of configurable power supply circuits. The card
comprises
power supply configuration code stored in the memory. The power supply
configuration code, when executed by the at least one processor, configures
the
plurality of power circuits of the power supply based on the broadcast
response
message.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
3
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0008] Embodiments of the disclosure will be described by way of
example only with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
[0009] Figure 1A is a block diagram of a configurable input/output unit;
[0010] Figure 1B is a block diagram of a configurable modular card
including the configurable input/output unit of Figure 1A;
[0011] Figure 1C is a block diagram of the configurable modular card of
Figure 1B adapted for being used in a simulator;
[0012] Figure 2 is a block diagram of a configurable simulator including
several of the configurable modular cards of Figure 1C, according
to a first aspect;
[0013] Figure 3 is a block diagram of a configurable simulator including
several of the configurable modular cards of Figure 1C, according
to another aspect;
[0014] Figure 4 is a bloc diagram of the configurable modular card of
Figure 1C, according to still another aspect;
[0015] Figure 5 illustrates a method for operating a configurable
simulator including a plurality of the configurable modular cards of
Figure 1C, according to yet another aspect; and
[0016] Figure 6 illustrates an exemplary flight simulator including
several
of the configurable modular cards of Figure 1C.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0017] The foregoing and other features will become more apparent
upon reading of the following non-restrictive description of illustrative
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
4
embodiments thereof, given by way of example only with reference to the
accompanying drawings. Like numerals represent like features on the various
drawings.
[0018] Various aspects of the present disclosure generally address one
or more of the problems of input/output units having configuration
capabilities.
CONFIGURABLE INPUT/OUTPUT UNIT
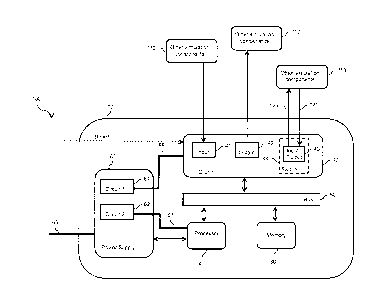
[0019] Referring now to Figure 1A, a configurable input/output (I/O)
unit
40 is represented.
[0020] The configurable I/O unit 40 comprises a plurality of
configurable
inputs and outputs. For illustration purposes, the configurable I/O unit 40
represented in Figure 1A comprises a configurable input 41, a configurable
output
42 and a configurable input/output 43. The configurable input 41 is capable of
receiving data from one or several computing devices. The configurable output
42
is capable of transmitting data to one or several computing devices. The
configurable input/output 43 is capable of exchanging (transmitting and
receiving)
data with one or several computing devices 110.
[0021] The configurable I/O unit 40 may also comprise one or several
switches. For example, an optional switch 44 is represented in Figure 1A. The
switch 44 is capable of at least one of the following: switching, multiplexing
and
de-multiplexing signals exchanged between the configurable input/output 43 and
the one or several computing devices 110.
[0022] The configurable I/O unit 40 may comprise any number of
configurable inputs and outputs. Each configurable input and output of the
configurable I/O unit 40 is capable of communicating with a single or with a
plurality of computing devices 110.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
[0023] The configurable inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit
40 provide communication capabilities in accordance with one or several types
of
communication protocols. For instance, the configurable I/O unit 40 may
include
at least one Ethernet board for receiving / transmitting data via the Ethernet
protocol. Alternatively or concurrently, the configurable I/O unit 40 may
include an
analog or digital input/output, a serial input/output, a USB board, a Wireless
Fidelity (Wi-Fi) board for receiving / transmitting data via the Wi-Fi
protocol, a
cellular board for receiving / transmitting data via a cellular communication
protocol (e.g. UMTS, LTE, etc.), a Control Area Network bus, an 12
input/output.
The configurable I/O unit 40 may also include a High-Definition Multimedia
Interface (HDMI) board, for transmitting video (and audio) data to a screen.
Other
types of inputs and outputs may be implemented by the configurable I/O unit
40,
based on the various types of computing devices 110 with which the
configurable
=
I/O unit 40 is exchanging data.
[0024] The configurable I/O unit 40 further sends a broadcast message
and receives a broadcast response message. The broadcast message may be
sent by different outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 and the broadcast
response message may be received by different inputs of the configurable I/O
unit
40. Also, different communication protocols may be used for sending the
broadcast message and receiving the broadcast response message. In a
particular aspect, the configurable I/O unit 40 has a predefined output for
sending
the broadcast massage and a predefined input for receiving the broadcast
response message. In the embodiment illustrated in Figure 1A, the broadcast
message 120 is sent and the broadcast response message 121 is received via
input/output 43. Alternatively, the broadcast message 120 may be sent via
output
42 and the broadcast response message 121 received via input 41. In another
embodiment, the broadcast message 120 may be sent via an Ethernet board of
the configurable I/O unit 40, and the broadcast response message 121 may be
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
6
received via a Wi-Fi board of the configurable I/O unit 40. Alternatively, the
broadcast message 120 may be sent via a Wi-Fi board of the configurable I/O
unit
40, and the broadcast response message 121 may be received via an Ethernet
board of the configurable I/O unit 40.
[0025] In a particular embodiment, the broadcast message 120
comprises a configuration request, and the configuration request comprises an
identifier. The broadcast message 120 is received by a configuration component
of a computing device 110. The configuration component determines
configuration parameters based on the identifier of the configuration request.
Then, the configuration component transmits the configuration parameters to
the
configurable I/O unit 40, via the broadcast response message 121 sent to the
predefined input. The configuration request may include an identification of
the
predefined input for receiving the broadcast response message 121.
Alternatively,
the predefined input is determined by the configuration component (e.g. among
a
plurality of inputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 memorized by the
configuration
component).
[0026] A broadcast message 120 is used since the configuration
component is not necessarily known in advance. By sending the message 120 in
a broadcast mode, the configurable I/O unit 40 ensures that the message 120 is
received by the configuration component (as well as by other entities). The
configuration component receives the broadcast message 120, determines that it
is the intended recipient, processes the broadcast message 120, and sends back
the broadcast response message 121.
CONFIGURABLE MODULAR CARD
[0027] Referring now to Figure 1B, a configurable modular card 100
comprising the configurable I/O unit 40 of Figure 1A is represented.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
7
[0028] The card 100 comprises a board 10 and a processor 20 mounted
on the board. Although a single processor 20 is represented in Figure 1B, the
card
100 may comprise several processors operating in parallel, as is well known in
the
art. Additionally, each processor may be a single core or a multicore
processor.
The at least one processor executes software code stored in a memory 30.
[0029] The card 100 also comprises the memory 30 mounted on the
board 10 and in electronic communication with the processor 20. Although a
single memory 30 is represented in Figure 1B, the card 100 may comprise
several
memories or banks of memories. Each memory present on the card 100 may be
dedicated to a single processor of the card 100, or may be shared between
several processors of the card 100. The memory 30 also stores data generated
by
the execution of the software code by each processor 20, data received via the
configurable I/O unit 40, etc.
[0030] The card 100 further comprises the configurable I/O unit 40,
which has been previously described in relation to Figure 1A. The software
code
executed by the processor 20 may be received through the configurable I/O unit
40.
[0031] The configurable I/O unit 40 may comprise any number of
configurable inputs and outputs, as long as it is compatible with the size and
shape of the board 10, and with the space left by the other electronic
components
on the board 10.
[0032] When the processor 20 executes software code to implement a
functionality of the card 100, the processor 20 may process data received by
the
configurable I/O unit 40 from other computing devices 110, and generate data
sent by the configurable I/O unit 40 to other computing devices 110.
[0033] The predefined output (for sending the broadcast message) and
the predefined input (for receiving the broadcast response message) of the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
8
configurable I/O unit 40 may be permanently stored in the memory 30, when the
card 100 is manufactured! pre-configured before usage. Upon startup of the
card
100, the processor 20 may execute a bootstrap program permanently stored in
the memory 30. The bootstrap program includes the sending of the broadcast
massage 120 over the memorized predefined output and the receiving of the
broadcast response message 121 over the memorized predefined input.
[0034] In a particular embodiment, the identifier included in the
configuration request comprised in the broadcast message 120 consists of an
identification of the card 100 (e.g. a serial number). The identifier may
further
include an identification of the predefined input (e.g. an Ethernet or an
Internet
Protocol (IP) address). The broadcast message 120 is received by a
configuration
component of a computing device 110. The configuration component determines
configuration parameters based on the identification of the card 100. Then,
the
configuration component transmits the configuration parameters to the card
100,
via the broadcast response message 121 sent to the predefined input. The
predefined input may be identified via the identifier included in the
configuration
request, if the identifier includes the identification of the predefined
input. The
configuration component may determine the configuration parameters based on
many possible variants (e.g. replacement card needed, processing capability
required, software code executed by the processor 20, physical I/0 capacity,
etc.).
The configuration parameters may also include a list of other configurable
modular cards with which the card 100 needs to communicate to implement a
particular functionality of the software code executed by the processor 20.
[0035] The card 100 also comprises a bus 50, electronically connected
with the configurable I/O unit 40, with the at least one processor 20 of the
board
10, and with the at least one memory 30 of the board 10. The bus 50 provides
electronic data exchange there between. For example, the processor 20 reads
data in the memory 30 via the bus 50, processes the data, and transmits the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
9
processed data via the bus 50 to the configurable I/O unit 40 (for further
transmission by an output of the configurable I/O unit 40 to a computing
device
110). Similarly, the processor 20 receives data from the configurable I/O unit
40
(the data was received by an input of the configurable I/O unit 40 from a
computing device 110) via the bus 50, processes the data, and transmits the
processed data via the bus 50 to the memory 30 for memorization therein.
[0036] Input/output (I/O) configuration code (not represented in Figure
1B) is stored in the memory 30. The I/O configuration code is executed by the
processor 20, to configure the plurality of inputs and outputs (e.g. 41, 42
and 43)
of the configurable I/O unit 40 based on the received broadcast response
message 121.
[0037] The configuration of the configurable I/O unit 40 may include a
network configuration of its inputs and outputs. Network configuration is well
known in the art, and depends on the specific types of inputs and outputs, and
on
the specific types of communication protocols they support. For instance, the
configuration of an Ethernet input/output may include the configuration of its
IP
address. The configuration of a Wi-Fi input/output may include the
configuration of
a Service Set Identifier (SSID) and a wireless key, as well as its IP address.
In
these examples, the IP address, SSID and wireless keys are network
configuration parameters transmitted to the card 100 via the broadcast
response
message 121.
[0038] The configuration of the configurable I/O unit 40 may include a
functional configuration of its inputs and outputs. For instance, a first sub-
functionality of the card 100 is associated with a first input/output. All
data
exchanged with specific computing device(s) 110 when executing the first sub-
functionality are transmitted and received with the first input/output.
Another sub-
functionality of the card 100 is associated with a second input/output. All
data
exchanged with other specific computing device(s) 110 when executing the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
second sub-functionality are transmitted and received with the second
input/output. For example, the configurable I/O unit 40 may have two video
outputs. A first video output is connected to a video screen of a first user
and the
second video output is connected to a video screen of a second user. The
processor 20 runs software code, which generates specific video data for the
first
user (first sub-functionality) and specific video data for the second user
(second
sub-functionality). The received broadcast response message 121 provides the
following configuration: specific video data for the first user shall be
transmitted
via the first video output and specific video data for the second user shall
be
transmitted via the second video output.
[0039] The I/O configuration code may be permanently stored in the
memory 30, when the card 100 is manufactured / pre-configured before usage.
Upon startup of the card 100, the processor 30 may execute the I/O
configuration
code, after reception of the broadcast response message 121. The I/O
configuration code may also be executed at other moments: after a reset of the
tard 100, after a failure (software or hardware) of the card 100 requiring a
complete reconfiguration, etc. The configuration parameters of the
configurable
I/O unit 40, received via the broadcast response message 121, can be
permanently stored in the memory 30, to be available to the I/O configuration
code at any time.
[0040] Alternatively, the I/O configuration code may not be initially
present in the memory 30, but downloaded from an external entity (e.g. one of
the
computing devices 110) and stored in the memory 30 for further use. The
predefined output and the predefined input (e.g. 43) of the configurable I/O
unit 40
can be used for performing the download of the I/O configuration code.
Broadcast
message 120/ broadcast response message 121 can be used for this purpose; or
additional broadcast message / broadcast response message dedicated to the
download of the I/O configuration code can be used.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
11
[0041] I/O testing code (not represented in Figure 1B) may also be
stored in the memory 30. The I/O testing code is executed by the processor 20
to
generate testing signals to the plurality of inputs and outputs of the
configurable
I/O unit 40 configured based on the broadcast response message 121.
[0042] The testing signals generated to the plurality of inputs and
outputs
of the configurable I/O unit 40 allow a verification that the inputs and
outputs are
operating in conformance with the configuration parameters received via the
broadcast response message 121. The verification may include a verification of
the network configuration of the inputs and outputs. For instance, the testing
signals may permit a determination that a specific input or a specific output
are
respectively capable of receiving and transmitting data, at a specified
throughput,
with a specified delay, with a specified packet loss rate, etc. The
verification may
also include a verification of the network connectivity of the inputs and
outputs
with specific computing devices 110.
[0043] Similarly to the I/O configuration code, the I/O testing code may
be permanently stored in the memory 30, when the card 100 is manufactured /
pre-configured before usage. Alternatively, the I/O testing code may not be
initially
present in the memory 30, but downloaded from an external entity (e.g. one of
the
other simulation components 110) and stored in the memory 30 for further use.
[0044] If several processors are mounted on the board 10, the I/O
configuration code and the I/O testing code may be executed by the same
processor 20 or by different processors 20. Additionally, the I/O testing code
may
be divided in multiple functional modules executed by different processors 20
operating in parallel.
CONFIGURABLE MODULAR CARD ADAPTED FOR USE IN A SIMULATOR
[0045] The simulators mentioned in the present disclosure may be used
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
12
for different simulation purposes. For example, a first type of simulator may
consist of a vehicular simulator, such as an aircraft simulator, a terrestrial
vehicle
simulator, a boat simulator, an underground simulator, a mining simulator or a
nuclear plant simulator.
[0046] A simulator is a complex system generally comprising a plurality
of components. A first type of component consists of a computing component,
comprising a processor for executing specific simulation software (simulation
software and simulation code are used interchangeably in the present
disclosure).
A computing component generally receives data, processes the received data by
means of the specific simulation software to generate new data, and transmits
the
new data. A computing component may also be capable of interacting with one or
several dedicated hardware components, such as sensors, mechanical actuators,
pneumatic actuators, hydraulic actuators, displays, switches, lights, electric
components, etc. The computing component may receive data from a dedicated
hardware component and / or send commands to the dedicated hardware
component (e.g. receive data from a sensor and send actuating commands to an
actuator). The computing components also exchange data with each other, to
execute and synchronize the simulation.
[0047] The simulator is generally implemented as a plurality of sub-
systems for implementing a plurality of functionalities of the simulator. Each
sub-
system comprises a plurality of computing components and a plurality of
dedicated hardware components. The computing components are centrally
controlled by one or several dedicated entities having a processor executing
control software. The computing components are usually implemented by
dedicated cards, each dedicated card having specific electronic components
designed to implement a specific functionality or sub-functionality of the
simulator.
Additionally, each dedicated card may only be capable of executing dedicated
software stored in a memory of the dedicated card. Thus, when such a dedicated
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
13
card is not operating properly, the only alternative is to repair the
dedicated card
(possibly interrupting the simulation) or to replace the dedicated card with
the
exact same type of dedicated card (which may not be available immediately or
may be very expensive).
[0048] The present disclosure introduces a configurable modular card,
which can be configured to play the role of several of the aforementioned
computing components. Thus, the simulator is no longer dependent on multiple
dedicated cards, which are replaced by instances of the configurable modular
card. The configurable modular card comprises several configurable electronic
components (such as a configurable input/output unit, a configurable power
supply). The simulation software executed by a particular configurable modular
card is also configurable. The configurable modular cards are configured and
controlled by one or several dedicated entities having a processor executing
configuration and control software. Thus, when a specific configurable modular
card implementing a critical functionality of the simulator is not operating
properly,
another configurable modular configurable card of the simulator can be
reconfigured to implement the critical functionality in place of the defective
card.
[0049] Figure 6 illustrates an exemplary flight simulator 600 including
a
simulation controller 610 and several configurable modular cards (631, 632,
641,
642, 652, 661 and 671). The configurable modular cards hierarchically
implement
two exemplary sub-systems (engines 620 and landing gear 650) of the flight
simulator 600. Figure 6 will be described with more details later in the
description.
[0050] Referring now to Figure 10, a configurable modular card 100
similar to the card of Figure 1B, and adapted for use in a simulator, is
represented.
[0051] The card 100 comprises all the components described in relation
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
14
to Figure 1B (board 10, configurable I/O unit 40, processor(s) 20, memory 30,
and
bus 50). In addition, the card 100 comprises a power supply 60.
[0052] The at least one processor 20 executes a simulation code, or a
portion of the simulation code, to implement a functionality of the simulator.
Examples of functionalities of the simulator include without limitation:
simulating
information displayed on a display, simulating a motion of an aircraft,
simulating
electric circuits of an aircraft, simulating hydraulic circuits of an
aircraft, simulating
a heartbeat, simulating a bodily function, and/or any other type of simulation
code
known. The simulation code executed by the processor 20 may be received
through the configurable I/O unit 40.
[0053] The plurality of configurable inputs and outputs of the
configurable I/O unit 40 are capable of exchanging data (transmitting and / or
receiving) with one or several other simulation components 110. Each
configurable input and output' of the configurable I/O unit 40 is capable of
communicating with a single or with a plurality of other simulation components
110, such as for example: panel, electronics, sensors, motors and actuators
and/or guidance of any type of aircraft or vehicle, aircraft avionics, etc.
[0054] When the processor 20 executes a simulation code to implement
a functionality of the simulator, the processor 20 may process data received
by
the configurable I/O unit 40 from other simulation components 110, and
generate
data sent by the configurable I/O unit 40 to other simulation components 110.
[0055] The previously mentioned configuration parameters of the
broadcast response message 121 may include a list of the other configurable
modular cards with which the card 100 must communicate to perform the
simulation. For example, the configuration parameters may include a list of
cards
and their corresponding sub-functionalities, so that the card 100 may
communicate directly with the other cards upon execution of the simulation, by
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
identifying that a specific sub-functionality is performed by a specific card
from the
list. The configuration parameters may also include a list of dedicated
hardware
components with which the card 100 must communicate to perform the
simulation. One of the other simulation components 110 represented in Figure
1C
may implement the configuration component.
[0056] As mentioned previously, the configuration of the plurality of
inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 may comprise determining
which inputs and outputs are used to receive and / or send data related to a
specific sub-functionality of the simulator.
[0057] The card 100 also comprises the power supply 60. The power
supply 60 receives an entry power 65 of a predetermined voltage, and comprises
a plurality of configurable power supply circuits. For illustration purposes,
the
power supply 60 represented in Figure 1C comprises two configurable power
supply circuits 61 and 62. The power supply 60 may comprise any number of
configurable power supply circuits, as long as it is compatible with the size
and
shape of the board 10, and with the space left by the other electronic
components
on the board 10.
[0058] A configurable power supply circuit provides power to one or
several electronic components of the card 100. Additionally, some of the
configurable power supply circuits may provide power to electronic components
of
one or several other simulation components 110. For illustration purposes, the
configurable power supply circuit 61 represented in Figure 10 provides power
66
to the configurable I/O unit 40 and the configurable power supply circuit 62
provides power 67 to the processor 20. Depending on implementation
preferences or the capabilities of the power supply 60 or of the power needs
of
the other components powered by the card 100, components which use power
with the same voltage and current as the entry power 65, may directly receive
power from the entry power 65 instead of going through the power supply 60 as
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
16
exemplified by the dotted line between the entry power 65 and the I/O unit 40.
Although not represented in Figure 1C for simplification purposes, the
configurable power supply circuits 61 and 62 may also provide power to the bus
50, the memory 30, and to other simulation component(s) 110. Alternatively,
additional configurable power supply circuit(s) may be used to provide power
to
the bus 50, the memory 30, and to other simulation component(s) 110. For
example, the other simulation component(s) 110 may consist of one or several
screens for displaying data, the screens receiving power from at least one of
the
configurable power supply circuit(s) of the power supply unit 60.
[0059] Power supply configuration code (not represented in Figure 1C) is
stored in the memory 30. The power supply configuration code is executed by
the
processor 20, to configure the plurality of power circuits (e.g. 61 and 62) of
the
power supply 60 based on the received broadcast response message 121.
[0060] The configuration of each specific power circuit may consist of a
specific amperage (the voltage is similar to the entry power 65), a specific
voltage
(the amperage is similar to the entry power 65), pulse-width modulated power,
or
a specific combination of amperage and voltage, for the power delivered by the
specific power circuit. If a power circuit has several outputs for delivering
power to
several entities, each power output may be configured individually.
[0061] The broadcast response message 121 comprises power
configuration parameters (e.g. amperage and / or voltage) for each
configurable
power circuit of the power supply 60. In the embodiment illustrated in Figure
1C,
the same broadcast message 120 / broadcast response message 121 is / are
used for configuring the configurable I/O unit 40 and the power supply 60.
Alternatively, a dedicated broadcast message / broadcast response message may
be used for respectively configuring the configurable I/O unit 40 and the
power
supply 60.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
17
[0062] One or several power circuits of the power supply 60 may have a
default configuration, to allow proper operations of the card 100 until the
broadcast response message 121 comprising the power configuration parameters
is received. The default configuration of some of the power circuits may be
overridden by the received power configuration parameters, while the default
configuration of some of the power circuits may be maintained.
[0063] The power supply configuration code may be permanently stored
in the memory 30, when the card 100 is manufactured / pre-configured before
usage. Upon startup of the card 100, the processor 30 may execute the power
supply configuration code, after reception of the broadcast response message
121. The power supply configuration code may also be executed at other
moments: after a reset of the card 100, after a failure (software or hardware)
of
the card 100 requiring a complete reconfiguration, etc. The configuration
parameters of the power supply 60, received via the broadcast response message
121, can be permanently stored in the memory 30, to be available to the power
supply configuration code at any time.
[0064] Alternatively, the power supply configuration code may not be
initially present in the memory 30, but downloaded from an external entity
(e.g.
one of the other simulation components 110) and stored in the memory 30 for
further use. The predefined output and the predefined input (e.g. 43) of the
configurable I/O unit 40 can be used for performing the download of the power
supply configuration code. Broadcast message 120 / broadcast response
message 121 can be used for this purpose; or additional broadcast message /
broadcast response message dedicated to the download of the power supply
configuration code can be used.
[0065] Power supply testing code (not represented in Figure 1C) is
stored in the memory 30. The power supply testing code is executed by the
processor 20 to generate testing signals to the plurality of power circuits of
the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
18
power supply 60 configured based on the broadcast response message 121.
[0066] The testing may include a continuous verification of voltage
condition and current condition. For this purpose, the testing signals
generated to
the plurality of power circuits of the power supply 60 allow a verification
that the
power circuits are operating in conformance with the configuration parameters
received via the broadcast response message 121. For instance, the testing
signals may permit a determination that a specific power circuit is operating
at a
specified voltage and / or amperage.
[0067] Similarly to the power supply configuration code, the power
supply testing code may be permanently stored in the memory 30, when the card
100 is manufactured / pre-configured before usage. Alternatively, the power
supply testing code may not be initially present in the memory 30, but
downloaded
from an external entity (e.g. one of the other simulation components 110) and
stored in the memory 30 for further use.
[0068] If several processors are mounted on the board 10, the power
supply configuration configurations code and the power supply testing code may
be executed by the same processor or by different processors. Additionally,
the
power supply testing code may be divided in multiple functional modules
executed
by different processors operating in parallel.
CONFIGURABLE SIMULATOR WITH A PLURALITY OF CONFIGURABLE
MODULAR CARDS
[0069] Referring now concurrently to Figures 1C and 2, a configurable
simulator 200 with a plurality of configurable modular cards is represented.
[0070] The simulator 200 comprises a configuration component 210 and
a plurality of configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104. The plurality
of
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
19
configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104 are instances of the
configurable modular card 100, which has been previously described with
reference to Figures 1A, 1B and 1C. Although four instances of the
configurable
modular card 100 have been represented in Figure 2, the simulator 200 may
comprise any number of these cards.
[0071] The configuration component 210 includes an input/output (I/O)
unit 211 and a processor 212. The configuration component 210 may include
additional electronic components, such as additional processors, at least one
memory, a bus, a power unit; not represented in Figure 2 for simplification
purposes.
[0072] The configuration component 210 configures the plurality of
configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104. The configuration of
instances
of the configurable modular card 100 has been previously described with
reference to Figures 1A, 1B and 1C. Each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
sends a broadcast message (on a predefined output of its configurable I/O unit
40), to the configuration component 210. The broadcast message is received by
the I/O unit 211 of the configuration component 210 and transmitted to the
processor 212. Although Figure 2 shows physical connections between the
various I/O units, the connections there between could be logical connections,
and/or wireless connections. The processor 212 determines configuration
parameters for the configurable modular card (e.g. 101) and transmits the
configuration parameters to the I/O unit 211. The I/O unit 211 sends a
broadcast
response message with the configuration parameters to the configurable modular
card (e.g. 101). The broadcast response message is received on a predefined
input of the configurable I/O unit 40 of the configurable modular card (e.g.
101).
[0073] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
executes its I/O configuration ccde to configure the plurality of inputs and
outputs
of its configurable input/output unit 40 based on the received broadcast
response
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
message.
[0074] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
executes its power supply configuration code to configure the plurality of
power
circuits of its power supply 60 based on the received broadcast response
message.
[0075] The simulator 200 may comprise more than one configuration
component 210. For instance, the configuration component 210 may be
responsible for configuring the configurable modular cards 101 and 102, and
another configuration component (not represented in Figure 2) may be
responsible for configuring tie configurable modular cards 103 and 104.
Furthermore, a configuration component may be implemented by a configurable
modular card 100. For example, the configurable modular card 103 may be
configured by the configuration component 210, and implement the functionality
of
a configuration component for the configurable modular card 104.
[0076] When a configurable modular card (e.g. 101) of the simulator 200
is configured, its processor 20 is capable of executing a simulation code to
implement a functionality of the simulator 200. Its configurable I/O unit 40
is
capable of exchanging (receiving and sending) data with at least one other
simulation component. Executing the simulation code to implement the
functionality of the simulator 200 comprises processing the data received by
the
configurable I/O unit 40 and generating the data sent by the configurable I/O
unit
40. The specific inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 used for
exchanging a specific type of communication data or for communicating with a
specific other simulation component are determined by the I/O configuration
code
executed by the processor 20.
[0077] The other simulation component may consist of another
configurable modular card 100 or of a dedicated hardware component 220 (e.g. a
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
21
display, a light, a mechanical actuator, etc.) different from the configurable
module
card 100. For example, as illustrated in Figure 2, the configurable modular
card
101 exchanges data with the configurable modular card 102. The configurable
modular card 102 exchanges data with the configurable modular cards 101 and
104. The configurable modular card 103 exchanges data with the configurable
modular cards 104 and the dedicated hardware component 220. The configurable
modular card 104 exchanges data with the configurable modular cards 102 and
103.
[0078] A dedicated hardware component (e.g. 220) such as a display, a
light, a mechanical actuator, is under the control of one or several
configurable
modular cards (e.g. 103). In this, case, the data exchanged there between
consist
of commands generated by the simulation software executed by the processor 20
of the configurable modular cards (e.g. 103). The commands are sent to the
dedicated hardware component (e.g. 220) to trigger an event representative of
the
current state of the simulation. Such events may comprise: displaying data on
a
display, switching on or off a light, activating a mechanical actuator (e.g.
to move
a seat in which a trainee is sitting), controlling analog gauge (to actuate a
gauge
for equipment such as for example an altimeter, a pump gauge, a compressor
gauge, etc.). Alternatively, a dedicated hardware component (e.g. 220) may
consist of a sensor, and the data exchanged between the sensor and one or
several configurable modular cards (e.g. 103) consist in data collected by the
sensor and sent to the configurable modular card(s).
[0079] The power supply configuration code executed by the processor
20 of a configurable modular card (e.g. 103) configures the power supply
circuits
of its power unit 60 to deliver power to electronic components (e.g. processor
20,
configurable I/O unit 40) of the configurable modular card (e.g. 103). More
specifically, the configuration comprises determining at least one of specific
amperage or a specific voltage of the power delivered to a specific electronic
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
22
component. Additionally, some of the power supply circuits of the power unit
60
may be configured to deliver power to electronic components of another entity.
For instance, some of the power supply circuits of the power unit 60 of the
configurable modular card 103 may be configured to deliver power to electronic
components of the configurable modular card 104 or to electronic components of
the dedicated hardware component 220.
CONFIGURABLE SIMULATOR WITH DISTRIBUTED SIMULATION
CAPABILITIES
[0080] Referring now concurrently to Figures 1C and 3, a configurable
simulator 300 comprising a plurality of configurable modular cards for
performing
a distributed simulation is represented.
[0081] The simulator 300 comprises a simulation controller 310 and a
plurality of configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104. The plurality
of
configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104 are instances of the
configurable modular card. 100, which has been previously described with
reference to Figures 1A, 1B and 10. Although four instances of the
configurable
modular card 100 have been represented in Figure 3, the simulator 300 may
comprise any number of these cards.
[0082] The simulation controller 310 corresponds to the configuration
component 210 represented in Figure 2, but with additional capabilities for
managing a distributed simulation and for reconfiguring the configurable
modular
cards when appropriate.
[0083] The simulation controller 310 includes an input/output (I/O) unit
311 and a processor 312. The simulation controller 310 may include additional
electronic components, such as additional processors, at least one memory, a
bus, a power unit; not represented in Figure 3 for simplification purposes.
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
23
[0084] The simulation controller 310 configures the plurality of
configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104. The configuration of
instances
of the configurable modular card 100 has been previously described with
reference to Figures 1A, 1B and 1C. Each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
sends a broadcast message to the simulation controller 310. The broadcast
message is received by the I/O unit 311 of the simulation controller 310 and
transmitted to the processor 312. The processor 312 determines configuration
parameters for the configurable modular card (e.g. 101) and transmits the
configuration parameters to the I/O unit 311. The I/O unit 311 sends a
broadcast
response message with the configuration parameters to the configurable modular
card (e.g. 101). The broadcast response message is received by the
configurable
I/O unit 40 of the configurable modular card (e.g. 101).
[0085] The configuration parameters are determined based on a pre-
defined configuration of the simulator. For instance, as illustrated in Figure
3, the
simulator 300 may comprise two sub-systems 350 and 360. The first sub-system
350 implements a first functionality of the simulator, for example simulating
a
motion of an aircraft. The second sub-system 360 implements a second
functionality of the simulator, for example simulating information displayed
on a
display. Functionalities may be divided in sub-functionalities and the pre-
defined
configuration of the simulator determines which configurable modular cards
implement which functionalities or sub-functionalities. Examples of systems
include: flight control, autopilot system, navigation system, power management
system, etc.
[0086] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
generates the broadcast message sent by its configurable I/O unit 40 to the
simulation controller 310.
[0087] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
executes its I/O configuration code to configure the plurality of inputs and
outputs
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
24
of its configurable input/output unit 40, based on the broadcast response
message
(comprising the configuration parameters) received by its configurable I/O
unit 40.
[0088] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
executes its power supply configuration code to configure the plurality of
power
circuits of its power supply 60, based on the broadcast response message
(comprising the configuration parameters) received by its configurable I/O
unit 40.
[0089] The processor 20 of each configurable modular card (e.g. 101)
executes a simulation code to implement a functionality of the simulator, the
executed simulation code being determined based on the broadcast response
message (comprising the configuration parameters) received by its configurable
I/O unit 40. The simulation code may decouple the hardware from the software
by
including tags referring to each hardware component and hardware sub-
component which is involved in the simulation. For example, the input/output
of
the I/O unit 40 to be used is tagged and reference is made to the tag in the
simulation code rather than to the input/output themselves. By tagging the
hardware components and hardware sub-components involved in the simulation,
and referring to the tags in the simulation code, it becomes possible to
modify the
modular card 100 and the interactions between the modular cards and the other
components, by simply re-assigning the tags to other hardware components and
hardware sub-components, as needed, and even on the fly or dynamically.
[0090] When a specific functionality of the simulator is divided in
several
sub-functionalities, the processors 20 of several configurable modular cards
(e.g.
101 and 102, or alternatively 103 and 104) execute simulation codes
implementing the several distributed sub-functionalities of the specific
functionality
of the simulator.
[0091] In the example illustrated in Figure 3, the first functionality
of the
simulator implemented by the first sub-system 350 may consist of two
distributed
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
sub-functionalities, implemented respectively by the simulation code executed
by
the processors 20 of the two configurable modular cards 101 and 102. The
second functionality of the simulator implemented by the second sub-system 360
may consist of two distributed sub-functionalities, implemented respectively
by the
simulation code executed by the processors 20 of the two configurable modular
cards 103 and 104.
[0092] The simulator 300 may comprise more than one simulation
controller. For instance, the simulation controller 310 is responsible for
controlling
the configurable modular cards 101, 102, 103 and 104 of the sub-systems 350
and 360; and another simulation controller (not represented in Figure 3) may
be
responsible for controlling the configurable modular cards of at least one
other
sub-system (not represented in Figure 3). Furthermore, a simulation controller
may be implemented by a configurable modular card 100.
[0093] The simulator 300 may also comprise a hierarchy of systems and
sub-systems controlled by a hierarchy of simulation controllers. For example,
the
second sub-system 360 may include at least one lower level sub-system 365. The
configurable modular card 103 may implement simulation controller
functionality
similar to the simulation controller 310. Thus, the configurable modular card
103 is
controlled by the simulation controller 310, and controls configurable modular
cards (not represented in Figure 3) of the lower level sub-system 365.
[0094] The simulation code executed by the processor 20 of the
configurable modular card (e.g. 101) may be initially stored in the memory 30
of
the configurable modular card. The simulation code may be divided in software
modules implementing the various functionalities and sub-functionalities of
the
simulator. Thus, the processor 20 may select to execute a particular software
module, corresponding to the functionality or sub-functionality specified by
the
configuration parameters of the received broadcast response message.
Alternatively, the particular software module may not be initially stored in
the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
26
memory 30, and the configurable modular card (e.g. 101) may need to download
it, for example from a pre-defined software server or from the simulation
controller
310.
[0095] As mentioned earlier in reference to Figures 1A, 1B, 1C and 2,
the configurable I/O unit 40 of a configurable modular card (e.g. 101) is
capable of
exchanging (receiving and sending) data with at least one other simulation
component.
[0096] The other simulation component may consist of another
configurable modular card 100. For example, the configurable modular cards 101
and 102 exchange data generated by the simulation code executed by the
processors 20 of the configurable modular cards 101 and 102. Each modular card
101 and 102 implements a distributed sub-functionality of the global
functionality
implemented by the sub-system 350. The exchange of data enables a
synchronization of the sub-functionalities implemented respectively by the
configurable modular cards 101 and 102. Similarly, an exchange of data enables
a synchronization of the sub-functionalities implemented respectively by the
configurable modular cards 103 and 104. Each modular card 103 and 104
implements a distributed sub-functionality of the global functionality
implemented
by the sub-system 360. Although not represented in Figure 3, configurable
modular cards of different sub-systems (e.g. 102 and 103) may also exchange
data.
[0097] The other simulation component may also consist of a dedicated
hardware component 320, 321 and 322. A dedicated hardware component such
as a display, a light, a mechanical actuator, is under the control of one or
several
configurable modular cards 100. In this case, the data exchanged there between
consist of commands generated by the simulation software executed by the
processor 20 of the configurable modular cards 100. The commands are sent to
the dedicated hardware component to trigger an event representative of the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
27
current state of the simulation. Alternatively, a dedicated hardware component
may consist of a sensor, and the data exchanged between the sensor and one or
several configurable modular cards 100 consist in data collected by the sensor
and sent to the configurable modular card(s).
[0098] In the example illustrated in Figure 3, the functionality
implemented by the first sub-system 350 simulates a motion of an aircraft and
the
functionality implemented by the second sub-system 360 simulates information
displayed on a display. The dedicated hardware component 321 is a mechanical
actuator for moving a seat in which a trainee is sitting, controlled by the
configurable modular card 101. The dedicated hardware component 322 is a light
or a set of lights representative of various events occurring during the
motion of
the aircraft, controlled by the configurable modular card 102. The dedicated
hardware component 320 is a display for displaying data, controlled
simultaneously by the configurable modular cards 103 and 104. Those skilled in
the art will understand that the functionality is not limited to the example
of Figure
3, and other functionalities and sub-systems such as the following could be
implemented by the present modular card: vehicle components, aircraft
components, avionics equipment, cockpit panels, vehicle panels, etc.
[0099] In a particular aspect, the I/O unit 311 of the simulation
controller
310 receives a test notification with test results from one (e.g. 101) of the
plurality
of configurable modular cards. The processor 312 of the simulation controller
310
analyses the test results, determines an operational status of the
configurable
modular card (e.g. 101), and determines reconfiguration parameters based on
the
test results and the previously determined configuration parameters. For
example,
if the configurable modular card 101 in charge of controlling the mechanical
actuator 321 is not operating properly, the configurable modular card 102 may
be
reconfigured to control the actuator 321. The configurable modular card 102
may
be reconfigured to only control the actuator 321, or may be reconfigured to
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
28
simultaneously control the actuator 321 and the light(s) 322. Alternatively, a
configurable modular card (e.g. 104) of the other sub-system 360 may be
reconfigured to control the actuator 321. Thus, the reconfiguration parameters
may affect one or several configurable modular cards (e.g. 102 or 104) of one
or
several sub-systems (e.g. 350 or 360).
[00100] The I/O unit 311 of the simulation controller 310 sends a
reconfiguration request with the reconfiguration parameters to the
configurable
modular card(s) (e.g. 102) which need to be reconfigured.
[00101] Upon reception of the reconfiguration request by the configurable
I/O unit 40 of a configurable modular card (e.g. 102), its processor 20
executes
the input/output configuration code to reconfigure the plurality of inputs and
outputs of its configurable I/O unit 40 based on the reconfiguration request.
The
processor 20 also executes the power supply configuration code to reconfigure
the plurality of power circuits of the power supply 60 based on the
reconfiguration
request. The processor 20 further executes a simulation code to implement a
functionality or sub-functionality of the simulator, the executed simulation
code
being determined based on the reconfiguration request. For example, the
processor 20 of the configurable modular card 102 executes simulation code to
control the actuator 321 instead of the previously executed simulation code
for
controlling the light(s) 322.
[00102] Referring now to Figure 6, an example of a simulator comprising
a plurality of configurable modular cards for performing a distributed
simulation is
represented. Figure 6 illustrates a flight simulator 600 including a
simulation
controller 610 and a hierarchy of configurable modular cards (631, 632, 641,
642,
652, 661 and 671).
[00103] The flight simulator 600 comprises a first sub-system 620 for
simulating a first functionality of an aircraft: the engines. The sub-system
620
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
29
comprises two lower level sub-systems 630 and 640 for respectively simulating
a
left engine and a right engine of the aircraft.
[00104] The configurable modular cards 631 and 632 are in charge of the
simulation of the left engine. The cards 631 and 632 are directly configured
and
controlled by the simulation controller 610. The cards 631 and 632 control
several
dedicated hardware components: displays 635, lights 636 (dedicated to the left
engine simulation); and cabin actuators 635 (shared between the left and right
engine simulation).
[00105] The configurable modular cards 641 and 642 are in charge of the
simulation of the right engine. The cards 641 and 642 are directly configured
and
controlled by the simulation controller 610. The cards 641 and 642 control
several
dedicated hardware components: displays 645, lights 646 (dedicated to the
right
engine simulation); and cabin actuators 635 (shared between the left and right
engine simulation).
[00106] The flight simulator 600 comprises a second sub-system 650 for
simulating a second functionality of the aircraft: the landing gear. The sub-
system
650 comprises two lower level sub-systems 660 and 670 for respectively
simulating left wheels and right wheels of the aircraft.
[00107] The configurable modular card 652 is in charge of the simulation
of the common functionalities of the landing gear sub-system 650. The card 652
is
directly configured and controlled by the simulation controller 610. The card
652
control several dedicated hardware components: hydraulic circuits 655 and
electric circuits 656.
[00108] The simulation sub-controller 651 is in charge of the control of
the
lower level sub-systems 660 and 670 of the sub-system 650. The simulation sub-
controller 651 is directly configured and controlled by the simulation
controller
610. The simulation sub-controller 651 may interact with the card 652 to
control
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
the lower level sub-systems 660 and 670. The simulation sub-controller
functionality 651 may be integrated in the card 652.
[00109] The configurable modular card 661 is in charge of the simulation
of specific functionalities of the left wheels. The card 661 is configured and
controlled by the simulation sub-controller 651. The card 661 controls several
dedicated hardware components: lights 665 (dedicated to the left wheels
simulation); and cabin actuators 657 (shared between the left and right wheels
simulation).
[00110] The configurable modular card 671 is in charge of the simulation
of specific functionalities of the right wheels. The card 671 is configured
and
controlled by the simulation sub-controller 651. The card 671 controls several
dedicated hardware components: lights 675 (dedicated to the right wheels
simulation); and cabin actuators 657 (shared between the left and right wheels
simulation).
CONFIGURABLE SIMILUTOR WITH INTEGRATED TESTING CAPABILITIES
[00111] Now referring back concurrently to Figures 1C and 3, in another
aspect, the simulator 300 comprises integrated testing capabilities. The
simulation
controller 310 manages a series of tests executed by the plurality of
configurable
modular cards (101, 102, 103 and 104) under its control, and centralizes the
results of the tests.
[00112] In one embodiment, the configurable modular cards (e.g. 101)
have auto-testing capabilities. They autonomously perform a series of tests,
and
report the test results to the simulation controller 310. The tests are
performed by
the processor 20 (execution of a testing code) of the configurable modular
card
(e.g. 101) and the test results are transmitted to the simulation controller
310 via a
test notification. The test notification is generated by the processor 20 by
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
31
aggregating the test results, and is transmitted by the configurable I/O unit
40 of
the configurable modular card (e.g. 101).
[00113] The I/O unit 311 of the simulation controller 310 receives the
test
notification, and its processor 312 processes the test results present in the
test
notification. Processing the specific test results corresponding to a specific
configurable modular card (e.g. 101) allows a determination of an operational
status of the specific configurable modular card (e.g. 101). Based on the test
results received from the plurality of configurable modular cards (101, 102,
103
and 104) under its control, the simulation controller 310 maintains a global
operational status of all the configurable modular cards under its control.
[00114] As previously described, the simulation controller 310 may
trigger
a reconfiguration of some of the configurable modular cards (101, 102, 103 and
104) under its control, based on their global operational status. For
instance, the
configurable modular card 102 may be reconfigured to implement a functionality
previously implemented by the configurable modular card 101, due to a failure
of
the configurable modular card 101 detected by the series of tests performed on
this card.
[00115] As previously described with reference to Figures 1A, 1B and 1C,
the testing code executed by the processor 20 of a configurable modular card
(e.g. 101) comprises generating testing signals to the plurality of inputs and
outputs of its configurable I/O unit 40 configured based on the broadcast
response
message received by the configurable I/O unit 40. The testing code executed by
the processor 20 of a configurable modular card (e.g. 101) also comprises
generating testing signals to the plurality of power circuits of the power
supply 60
configured based on the broadcast response message received by the
configurable I/O unit 40.
[00116] Additionally, the testing code executed by the processor 20 of a
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
32
configurable modular card (e.g. 101) further comprises monitoring the
execution
of the simulation code executed by the processor 20.
[00117] The simulation code executed by the processor 20 implements a
functionality of the simulator 300. Functionalities may be divided in several
distributed sub-functionalities, each specific sub-functionality being
implemented
by a specific configurable modular card 100. Thus, monitoring the execution of
the
simulation code may consist in monitoring the code corresponding to a specific
sub-functionality. If a configurable modular card 100 implements several sub-
functionalities, the testing code may only monitor a subset of these sub-
functionalities.
[00118] As previously described, the simulation code executed by the
processor 20 of the configurable modular card (e.g. 101) may comprise code for
controlling a dedicated hardware component (e.g. 321) by means of control
commands sent to this dedicated hardware component (e.g. 321). For example,
the dedicated hardware component 321 is a mechanical actuator for moving a
seat in which a trainee is sitting. In this case, executing the testing code
further
comprises generating testing signals to the dedicated hardware component (e.g.
321) to verify that this dedicated hardware component is operating according
to
the control commands it has received from its controlling configurable modular
card (e.g. 101).
[00119] In another embodiment, the configurable modular cards (e.g. 101)
execute a series of tests determined by the configuration controller 310. The
execution of the testing code by the processor 20 of a specific configurable
modular card (e.g. 101) is triggered by the reception of a test request
received
from the simulation controller 310. The test request specifies at least one
specific
test to be performed via the execution of the testing code by the processor
20.
The at least one specific test includes one of: testing the inputs and outputs
of the
configurable I/O unit 40, testing the plurality of power circuits of the power
supply
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
33
60, monitoring the execution of the simulation code by the processor 20, and
generating testing signals to another simulation component (e.g. 321).
[00120] Referring now to Figure 4, a simplified version of the
configurable
modular card 100 of Figure 1C is represented, illustrating the configuration
parameters and software codes of the card 100. The memory 30 of the card 100
stores configuration parameters, a configuration code, a simulation code and a
testing code.
[00121] The configuration parameters of the card 100 are initially stored
in
a memory (not represented in Figure 4) of a configuration component 410; and
transmitted to the memory 30 through the configurable I/O unit 40 of the card
100,
via the aforementioned broadcast message 120 / broadcast response message
121. The configuration component 410 corresponds to one of: the configuration
component 210 represented in Figure 2 or the simulation controller 310 (having
configuration capabilities) represented in Figure 3.
[00122] The simulation code executed by the card 100 is also initially
stored in the memory of the configuration component 410, and transmitted to
the
memory 30 through the configurable I/O unit 40. The aforementioned broadcast
message 120 / broadcast response message 121 may be used for this purpose.
Another transmission mechanism may also be used for this purpose.
Alternatively,
the simulation code may be initially stored in the memory 30, or transmitted
by a
software server (not represented in Figure 4).
[00123] The memory 30 stores the configuration code, which is executed
by the processor 20 of the card. For instance, the configuration code stored
in the
memory 30 includes a power supply configuration code, which when executed by
the processor 20 configures the power supply 60 of the card 100, based on
specific configuration parameters related to the power supply 60 and stored in
the
memory 30. The configuration code stored in the memory 30 also includes an I/O
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
34
unit configuration code, which when executed by the processor 20 configures
the
configurable I/O unit 40, based on specific configuration parameters related
to the
configurable I/O unit 40 and stored in the memory 30.
[00124] The processor 20 executes the simulation code stored in the
memory 30. The simulation code may include a plurality of software modules,
corresponding to several simulation functionalities and sub-functionalities.
The
execution of specific software modules, and the order in which they are
executed,
may be determined by specific configuration parameters related to the
simulation
flow and stored in the memory 30.
[00125] The memory 30 stores the testing code, which is executed by the
processor 20. The testing code may be initially stored in the memory 20, or
transmitted by the configuration component 410, or by a software server, (not
represented in Figure 4). For instance, the testing code stored in the memory
30
includes a power supply testing code, which when executed by the processor 20
tests the power supply 60. The testing code stored in the memory 30 also
includes an I/O unit testing code, which when executed by the processor 20
tests
the configurable I/O unit 40. The testing code stored in the memory 30 further
includes simulation testing code, which when executed by the processor 20
monitors the execution of the simulation code.
METHOD FOR OPERATING A CONFIGURABLE SIMULATOR COMPRISING A
PLURALITY OF CONFIGURABLE MODULAR CARDS
[00126] Referring now concurrently to Figures 4 and 5, a method 500 for
operating a configurable simulator comprising a plurality of configurable
modular
cards is represented.
[00127] The configurable simulator operated by the method 500 may
correspond to the simulator 200 previously described in relation to Figure 2
and /
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
or to the simulator 300 previously described in relation to Figure 3. The
configurable simulator comprises a plurality of configurable modular cards
corresponding to the cards 100 previously described in relation to Figures 1A,
1B,
1C and 4. For simplification purposes, only two configurable modular cards 504
and 506 are represented in Figure 5, but the simulator may include any number
of
configurable modular cards. A simulation controller 502 is represented in
Figure 5,
corresponding to the configuration components 210 and 410 previously described
in relation to Figures 2 and 4, and / or to the simulation controller 310
previously
described in relation to Figure 3. The simulation controller 502 may be
integrated
to the configurable simulator, or may be an external component in
communication
with the configurable simulator by means of a communication protocol such as
the
Ethernet protocol or the Wi-Fi protocol.
[00128] The method 500 comprises storing 510 configuration parameters
for the plurality of configurable modular cards (504 and 506) in a memory (not
represented) of the simulation controller 502.
[00129] The method 500 comprises storing 520 a configuration code, a
simulation code and a testing code in a memory 30 of the plurality of
configurable
modular cards (504 or 506). In a particular aspect, at least one of the
configuration code, the simulation code and the testing code may be stored in
a
memory of the simulation controller 502 and transmitted from the simulation
controller 502 to the card (504 or 506). Alternatively, the codes are
initially present
in the memory 30 of the card (504 or 506).
[00130] The method 500 comprises transmitting specific configuration
parameters for a specific card (504 or 506) from the simulation controller 502
to
the card (504 or 506). Thus, each card (504 or 506) may have its own specific
configuration parameters, generated and stored at the simulation controller
502.
In a particular aspect, transmitting the specific configuration parameters
comprises sending 525 a broadcast message from the card (504 or 506) to the
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
36
simulation controller 502, and receiving 526 a broadcast response message with
the specific configuration parameters from the simulation controller 502 at
the
card (504 or 506).
[00131] The method 500 comprises storing 530 the received specific
configuration parameters in the memory 30 of the card (502 or 504).
[00132] The method 500 comprises executing 540 the configuration code
by a processor 20 of the card (504 or 506) based on the specific configuration
parameters of the card.
[00133] Executing the configuration code includes configuring a plurality
of inputs and outputs of a configurable input/output (I/O) unit 40 of the card
(504
or 506) based on the specific configuration parameters of the card.
[00134] In a particular aspect, configuring the plurality of inputs and
outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 comprises performing a network
configuration of the inputs and outputs.
[00135] In another particular aspect, the configurable I/O unit 40
exchanges data with at least one other simulation component. Configuring the
plurality of inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 may comprise
determining which inputs and outputs exchange the data with the at least one
other simulation component. The at least one other simulation component may be
another configurable modular card. For instance, the cards 504 and 506 may
exchange data via their respective I/O units 40. Alternatively, the at least
one
other simulation component may be a dedicated hardware component (not
represented in Figure 5) controlled by the card (502 or 504). The dedicated
hardware component may be ocie of the following: a sensor, a display, a light,
a
switch, a mechanical actuator, a pneumatic actuator, a hydraulic actuator, an
electric component, etc.
[00136] Executing the configuration code also includes configuring a
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
37
plurality of power circuits of a power supply 60 of the card (504 or 506)
based on
the specific configuration parameters of the card.
[00137] In a particular aspect, configuring the plurality of power
circuits of
the power supply 60 comprises determining at least one of: a specific amperage
and a specific voltage of the power delivered by the specific power circuit to
an
electronic component. The electronic component may be located on the card (504
or 506) or on a dedicated hardware component controlled by the card.
[00138] The method 500 comprises executing 550 the simulation code by
the processor 20 of the card (504 or 506) to implement a functionality of the
simulator. Executing the simulation code to implement a functionality of the
simulator may comprise at least one of: simulating information shown on a
display, simulating a motion of an aircraft, simulating electric circuits of
an aircraft,
simulating hydraulic circuits of an aircraft. The simulation code executed by
the
processor 20 may also comprise code for controlling the aforementioned
dedicated hardware component(s).
[00139] In a particular aspect, several configurable modular cards (e.g.
504 and 506) receive specific configuration parameters from the simulation
controller 502 for configuring their respective processors 20 to execute
simulation
codes implementing several distributed sub-functionalities of a particular
functionality of the simulator.
[00140] The memory 30 of the card (504 or 506) may store a plurality of
simulation codes corresponding to several functionalities of the simulator.
Executing the configuration code may further comprise determining the
simulation
code executed by the processor 20 among the plurality of simulation codes
stored
in the memory 30 based on the specific configuration parameters of the card.
[00141] The method 500 comprises executing 560 the testing code by the
processor 20 of the card (504 or 506).
CA 02882009 2015-02-13
38
[00142] Executing the testing code includes generating testing signals to
the plurality of inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 configured
based
on the specific configuration parameters of the card (504 or 506).
[00143] In a particular aspect, the testing signals generated to the
plurality
of inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 allow a verification of
the
network configuration of the inputs and outputs.
[00144] In another aspect, the testing signals generated to the plurality
of
inputs and outputs of the configurable I/O unit 40 allow a verification of the
network connectivity of the inputs and outputs with another simulation
component
(e.g. another configurable modular card or a dedicated hardware component).
[00145] Executing the testing code also includes generating testing
signals to the plurality of power circuits of the power supply 60 configured
based
on the specific configuration parameters of the card (504 or 506).
[00146] In a particular aspect, the testing signals generated to the
plurality
of power circuits of the power supply 60 allow a verification that the power
circuits
are operating at a specified voltage or amperage.
[00147] Executing the testing code further includes monitoring the
execution of the simulation code by the processor 20 of the card (504 or 506).
[00148] The method 500 may comprise generating by the processor 20 of
the card (504 or 506) a test notification sent 565 by the configurable I/O
unit 40 of
the card to the simulation controller 502 with test results of the testing
code
executed by the processor 20 of the card.
[00149] The method 500 may also comprise determining 570 at the
simulation controller 502 new configuration parameters for at least one of the
plurality of configurable modul,ar cards (e.g. 504) based on the received test
results. The new configuration parameters are sent 575 to each of the impacted
CA 02882009 2015-07-23
39
cards (e.g. 504). Then, each impacted card (e.g. 504) executes 580 its
configuration code based on the received new configuration parameters and
reconfigures itself.
[00150] The method
500 may further comprise triggering 555 the execution
of the testing code at a card (e.g. 504) by the reception of a test request
from the
simulation controller 502.
[00151] The
present disclosure has introduced a configurable simulator
comprising a plurality of configurable modular cards. The usage of these cards
introduces a great deal of flexibility in the operations of the simulator.
Each card
being individually configurable (and reconfigurable), the simulator can be
easily
(re)-configured to accommodate an addition of card(s), a removal of card(s), a
replacement of card(s). The simulator can also be reconfigured to adapt to one
or
several of its cards being out of order. Configuring or reconfiguring the
simulator
consists in configuring or reconfiguring one or several of its cards. Thus, a
complete simulator, or a sub-system of a complete simulator, may be designed
based on a set of configurable modular cards. The set of configurable modular
cards is delivered as a set of generic cards having a common hardware and no
initial specific hardware and software configuration. The set of configurable
modular cards is then configured as illustrated in the present disclosure, to
implement the multiple functionalities of a complete simulator, or
alternatively to
implement a particular functionality of a sub-system of a complete simulator.
REPLACEMENT SHEET