Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
1
DESCRIPTION
Method and apparatus for producing packets containing a food or
pharmaceutical product
Technical Field
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for producing
packets containing a food or pharmaceutical product. These packets
comprise a containment wrapper for the food or pharmaceutical product
and a dispensing spout.
State of the art
Production apparatuses of packets containing food or pharmaceutical
products of the known art comprise a plurality of turntables equipped with
grippers that grasp the packets. In these turntables the packets, during the
movement, undergo a plurality of treatments. For that purpose,
apparatuses of the known art comprise at least:
-one first turntable for welding the dispensing spout of the product to the
remaining parts of the product;
-a subsequent turntable for filling the packets with the pre-chosen product.
However, this embodiment entails a substantial system cost.
Oblect of the invention
In this context, the technical task on which the present invention is based
is to provide an apparatus and a production method of packets containing
a food or pharmaceutical product that resolve the above-mentioned
drawbacks of the known art.
In particular, an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus
and a production method of packets that allow the transport of the packets
to be made easy and cheap at the same time as ensuring maximum
hygiene.
The technical task set and the objects specified are substantially attained
by an apparatus and a method for producing packets, comprising the
technical characteristics as set out in one or more of the accompanying
claims.
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
2
Brief description of the drawings
Further characteristics and advantages of the present invention will more
fully emerge from the non-limiting description of a preferred but not
exclusive embodiment of an apparatus and a method for producing
packets, as illustrated in the accompanying drawings, in which:
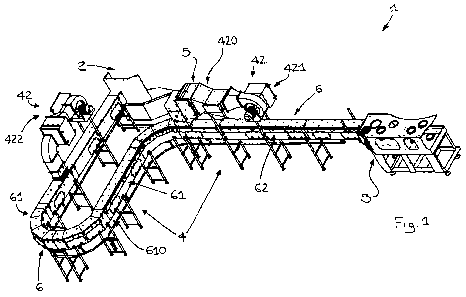
- Figure 1 shows a perspective view of a portion of a packaging apparatus
according to the present invention;
-Figures 2 and 3 show details of Figure 1;
-Figure 4 shows a section of the apparatus of Figure 1 with a packet
inserted.
Detailed description of preferred embodiments of the invention
In the accompanying drawings, reference number 1 indicates a production
apparatus of packets for a food or a pharmaceutical product.
Each packet 7 comprises a spout 70 and a product containment wrapper
71. The spout 70 and the product containment wrapper 71 are constrained
to each other, typically through welding. The wrapper 71 comprises
flexible sheets whereas the spout 70 is more rigid. The product contained
in the packets 7 is typically in liquid or in granular form.
The apparatus 1 comprises a connection station 2 of the spout 70 to
remaining parts of a packet 7 suitable to contain the product (in practice
there is a connection between the spout 70 and the corresponding
wrapper 71). Typically the connection station 2 is a welding station of the
spout 70 to the product containment wrapper 71.
Appropriately the apparatus 1 comprises a controlled atmosphere zone 3.
For example, in such controlled atmosphere zone 3, the filling of the
packets 7 with the product takes place. Therefore, in such zone 3
maximum hygiene must be guaranteed. The connection station 2, on the
other hand, is a zone in which (due to the specific processes performed)
dirt may be found, which is incompatible with the controlled atmosphere
zone 3. The connection station 2 is therefore far from the controlled
atmosphere zone 3.
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
3
The apparatus 1 comprises pneumatic transport means 4 of the packets.
The transport means 4 are operatively interposed between the connection
station 2 and the controlled atmosphere zone 3.
The pneumatic transport means 4 comprise support and guide means 41
of the packets that extend between the connection station 2 (the welding
station) and the controlled atmosphere zone 3.
In the absolutely non-limiting embodiment of the accompanying figures,
the support and guide means 41 extend along a longer trajectory than 10
metres, preferably about 18 metres long. This distance therefore allows
the controlled atmosphere zone 3 and the connection station 2 of the
spout 70 to be kept separate.
The transport means 4 further comprise generation means 42 of a
gaseous fluid current. This current is suitable to push the packets along
the support means 41. Advantageously such gaseous fluid is air.
Considering the reduced weight of the packets 7 (still empty in this step)
pneumatic transport is very efficient.
The apparatus 1 comprises heating means 5 of the gaseous fluid. The
heating means 5, in combination with at least a part of the generation
means 42 of a fluid current, define generation means 420 of a hot fluid
current for the advancement and simultaneous heating of the packets 7.
For example, but not necessarily, the heating means 5 comprise at least
one electrical element.
The controlled atmosphere zone 3 comprises an atmosphere containing
vaporised hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide performs an
important sanitisation/sterilisation function (but instead of hydrogen
peroxide a different sanitisation/sterilisation agent could be used). The hot
fluid current generated by the means 420 has a dual function: on the one
hand it hits the packets 7 enabling their movement along the support and
guide means 41, but on the other it ensures that the packets 7 that enter
the controlled atmosphere zone 3 are at a temperature such as to prevent
the condensation of the hydrogen peroxide on the packets 7 themselves.
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
4
The fact that the heating takes place using the fluid used for transport
allows important optimisation of the components.
In particular, the use of a turntable specifically equipped with heating
means for the packets 7 is avoided (equipment which has its own cost).
The pneumatic transport means 4 comprise a conveying channel 43 of
said fluid which extends parallel to said support and guide means 41 of the
packets.
The pneumatic transport means 4 also comprise at least one
advancement channel 45 of the packets 7; the advancement channel 45 of
the packets 7 houses said support and guide means 41. In particular, the
advancement channel 45 of the packets 7 houses the packets 7 during the
movement of the latter from the station 2 to the controlled atmosphere
zone 3. Appropriately the conveying channel 43 is operatively interposed
between the generation means 42 of a fluid current and the advancement
channel 45. The conveying channel 43 is in excess pressure with respect
to the advancement channel 45 of the packets, hence causing the
passage of the gaseous fluid from the conveying channel 43 to the
advancement channel 45. The transport means 4 also comprise deflector
means 44 interposed between the conveying channel 43 and the
advancement channel 45. Preferably the deflector means 44 identify an
imaginary boundary between the conveying channel 43 and the
advancement channel 45. The deflector means 44 direct the fluid, in
transit from the conveying channel 43 to the advancement channel 45, in
order to facilitate the advancement of the packets 7 along the support and
guide means 41.
Appropriately the conveying channel 43 of said fluid surmounts said
support and guide means 41. The deflector means 44 comprise a series of
fins alongside each other which extend along at least two thirds of the
length of the conveying channel 43 (preferably along the whole length).
Appropriately the pneumatic transport means 4 define an advancement
path of the packets from the connection station 2 of the spout to the
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
controlled atmosphere zone 3. Said path 6 comprises a first stretch 61
which acts as a storage unit 610 for the packets (in technical jargon the
expression "buffer" is used) and a second stretch 62 in which the packets
are hit by the current generated by the generation means 420 of a current
5 of hot fluid for heating the packets. The second stretch 62 is positioned
downstream from the first stretch 61 along an advancement direction of
the packets along the path 6.
The generation means 42 of a current of gaseous fluid comprise first
generation means 421 of a fluid current, for example a fan 421, typically of
the centrifugal type. Merely by way of example the heating means 5
mentioned above are placed downstream from the fan 423. The first
generation means 421 of a fluid current have a delivery that leads into the
beginning of the second stretch 62. The generation means 42 of a
gaseous fluid comprise second generation means 422 of a fluid current,
for example a fan 425, typically of the centrifugal type.
The second generation means 422 of a fluid current have a delivery that
leads into the length of the first stretch 61. Appropriately the channel 43
and the deflector means 44 extend both along the first and along the
second stretch 61, 62 of the advancement path 6.
The subject matter of the present invention is also a method for producing
packets for a food or pharmaceutical product. Appropriately the method is
implemented by an apparatus having one or more of the technical
characteristics described previously for the apparatus 1. The method
comprises the step of connecting a spout 70 to remaining parts of the
packet 7 intended to contain the food or pharmaceutical product. As
indicated previously such a connection typically envisages the welding of
the spout 70 to a containment wrapper 71 of the food or pharmaceutical
product. This takes place in a connection station 2. The connection of the
spout 70 to the wrapper 71 takes place when the wrapper 71 is still empty
(or however not containing the final product). The method further
comprises the step of transporting the packets 7 towards a controlled
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
6
atmosphere zone 3. Appropriately the step of transporting the packets 7
towards the controlled atmosphere zone 3 is preceded by the step of
hanging the spout 70 to which the remaining parts of the packets 7 are
connected onto the guide and support means 41.
The method finally envisages the step of filling the packets 7 in the
controlled atmosphere zone.
Appropriately the pneumatic transport of the packets 7 takes place from
the connection station 2 to the controlled atmosphere zone 3.
The step of transporting the packets 7 towards the controlled atmosphere
zone 3 comprises the step of directing a current of gaseous fluid towards
the packets 7 so as to make the packets 7 advance along support and
guide means 41 from which the packets 7 are hanging. In particular the
spout 70 comprises abutment means that rest on two edges 411, 412 of
the support and guide means 41. In particular the two edges 411, 412
extend parallel to each other defining a groove 413 interposed between
them, the spout 70 being able to slide within said groove 413. The two
edges 411, 412 are afforded on a replaceable plate 414 or on a set of
replaceable plates 414 so as to be able to adjust the width of the groove
413 orthogonally to the advancement direction of the packets 7.
Below the spout 70 the wrapper 71 extends being part of the packet 7.
The step of directing a current of gaseous fluid towards the packets 7 to
make the packets 7 advance envisages directing a current of hot fluid
towards the packets 7 to heat them. The wrapper 71 comprises two
overlapping flexible sheets connected so as to define a housing. During
the step of directing a current of a gaseous fluid towards the packets 7 the
two sheets extend substantially orthogonally to the advancement direction
of the packets 7. In this way the thrust action exerted by the gaseous fluid
is at its maximum.
The step of directing a current of hot fluid towards the packets 7 causes
both the advancement of the packets 7 along the support and guide
means 41 and the heating of the packets 7. Preferably such heating
CA 02889946 2015-04-29
WO 2014/072219
PCT/EP2013/072783
7
causes the packets 7 to reach a temperature of over 40 C,
advantageously over 50 C (appropriately such heathg determines a
temperature of the packets 7 comprised between 50 and 55 C). In
particular such temperatures affect the inside of the packets 7 in order to
prevent the condensation of the hydrogen peroxide in the packets 7. This
detail enables any condensation of vaporised hydrogen peroxide on the
packets to be avoided in the controlled atmosphere zone 3, said vaporised
hydrogen peroxide exerting a sanitisation and/or sterilisation action in the
controlled atmosphere zone 3.
The invention as it is conceived enables multiple advantages to be
attained.
An important advantage is connected with the fact that, due to the reduced
weight of the packets and the fact that the packets define a kind of veil,
pneumatic transport is very advantageous and effective in this type of
application. Furthermore, the use of a hot fluid as a transport fluid also
allows the packets to be heated at the same time as their movement
allowing system costs to be reduced (since the use of a specific heating
station for the packets upstream from the controlled atmosphere zone 3 is
avoided). Hence there is an optimisation of the components of the
apparatus 1. Furthermore the heating of the packets 7 which accompanies
a part of the transport enables hydrogen peroxide to be used in the
controlled atmosphere zone 3 since the condensation thereof within the
packets 7 is prevented.
The invention as conceived is susceptible to numerous modifications and
variants, all falling within the scope of the inventive concept characterised
thereby. Furthermore all the details can be replaced by other technically
equivalent elements. In practice, all the materials used, as well as the
dimensions, can be any according to requirements.