Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
1
INTELLIGENT EVACUATION ROUTE DEVICE
TECHNOLOGICAL FIELD
This invention relates to an intelligent evacuation route device that can be
customized
to the requirements of every structure (preferably buildings with 2 emergency
exits or more,
basements and parking lots among others). The intelligent device consists of a
processing unit
and a network of peripheral sensors, which may include sensors that detect
smoke, gas,
movement (speed-acceleration), temperature, water, human occupancy, structural
integrity
and explosive, toxic and volatile gases and an alarm system, and are
autonomously powered
as they have been designed based on alternative energies, such as
photovoltaics and/or with
rechargeable battery backup.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Some evacuation route systems are known to the prior state of the art, such as
the system
disclosed by Japanese patent number JP 8249556, which reports a device with a
fire voice
alarm that allows an easy guided evacuation. A number of sensors are installed
in a location
and they are activated when the presence of a fire is detected (when the fire
is generated). The
corresponding data related to the generation of the fire are transmitted to an
input port in a
control system by means of the operation of a switch. Such control system
identifies the
incoming fire generation data, determines that a fire was generated and
transmits the
information and the location to the sensors through an input/output control to
a DTMF
tone-emitting device.
The DTMF tone-emitting device converts the incoming data into a tone frequency
and
transmits it through a telephone line. The control system reads the sound data
relative to the
information received on the fire and converts it into a synthesized voice
signal as well as
analog signals and outputs that are transmitted through a loudspeaker so that
the personnel in
the location of the fire may hear the alarm.
On the other hand, document JP 8297794 refers to a disaster prevention system,
in order to
achieve an ideal evacuation based on the current dynamic state, where the
system is outfitted
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
2
with a disaster prevention sensor that detects its occurrence, a sensor that
determines the
number of people, a local terminal to display the information relative to the
evacuation route,
a monitoring device for the prevention of a disaster and a main computer that
controls the
local terminal.
The computer is outfitted with the means to calculate the level of safety,
which determines
how safe the corresponding evacuation route is in all the areas, using the
monitoring data of
the disaster prevention device, and a means to display the evacuation route,
which selects the
safest route in the area where the local terminal is installed.
The system also includes a sequential updating device, which directs to and
displays the
safest evacuation route, which uses new monitoring data for the calculations,
at a specific
interval after the sensor triggers an alarm at the local terminal.
On the other hand, document W00104853 refers to a device that projects an
escape pathway
to direct the evacuation in the event of a fire, which includes a variety of
laser diode lights
attached to the cover, the purpose of which is to emit beams or images
constantly along a
predetermined escape pathway. The images can range from indicating arrows to
images or
alphanumerical signs.
These laser diodes are activated by an alarm condition, such as the one
generated by a smoke
detector, an infrared detector or a similar device, or secondary action in
response to the
audible alarm of a main fire alarm, where these signals are controlled by a
microprocessor,
programmed to filter and process the signal digitally. Thus, the presence of a
main alarm is
established triggering the activation of the laser diodes showing the
evacuation pathway.
Document CN201441760 relates to a dynamic system for a guided evacuation, and
consists of
an intelligent system, which includes a smoke, fire and human detector to be
installed in an
area, with a display monitoring circuit and a dynamic display, which are also
mounted along
the evacuation route.
Based on the signal detected by the fire sensor, the human sensor and the
tridimensional
coordinate signals stored in the spatial database where the system is
installed, a central
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
3
processing unit can transmit an alarm signal after completing its calculations
and rendering a
decision. The instructions can be visualized on the dynamic display, so that
people can rely
on an efficient pathway leading to several directions with various numbers,
which may be
indicated dynamically, in order to avoid crowding and blocking certain
evacuation routes.
Finally, document TW201209763 refers to an intelligent system that assists in
the safe
evacuation of people in the event of a disaster and provides an efficient
maintenance
mechanism, also operating as an intelligent energy saving lighting device.
The system is comprised of a system server, intelligent devices that direct to
the exit, disaster
sensors, a message delivery server and a mobile telephone, with all the parts
communicating
with one another through wireless signals as well as the Internet.
These disaster sensors detect the location of the catastrophe when it occurs.
This information
is then transmitted to the server, which uses the data to send ideal
evacuation routes to all the
exit-directing devices.
Each exit-directing device also operates as an intelligent lighting device,
and uses a photo
sensor and infrared sensors to maintain a constant illumination level. The
system relies on an
audible signal to show the evacuation route to the personnel, that is, it does
not rely
exclusively on a visual or light signal.
Although the state of the art includes a variety of systems that allow the
assessment of
potential evacuation routes, clearly there is a need for an autonomous
intelligent device that
can detect not only fire, but also other potentially dangerous situations such
as gas leaks,
earthquakes, and the integrity and stability of the support structure, and
that is also capable of
analyzing in real time the conditions of the location at the time of
emergency, in order to
direct people to safe evacuation routes. Current evacuation systems determine
whether an
evacuation is required or not, warning about the emergency. The evacuation is
indicated with
lights coming on or turning off, which are also usually installed on the walls
of static
locations. However, none of these lights assess whether the evacuation is
being directed
through a route that is obstructed, has a fire, crowding or toxic gases, among
other things. In
general, these systems do not analyze dynamically the current emergency
conditions and
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
4
always direct to the same evacuation route. Therefore, there is a need to
develop an intelligent
system that can assess in real time as well as dynamically the current
emergency conditions
for each of the potential evacuation routes, so that following the assessment
people can be
directed to a route that will surely be clear.
Moreover, there is a need to create a device to decentralize the control
system, using a
computer or a mobile phone and develop an autonomous system, independent of
electrical
power or telecommunications networks, such as cell phones, which are more
prone to fail in
the event of a disaster.
An additional advantage of the device subject matter of this invention is the
fact that if one of
its parts is inoperative, the device will not necessarily stop working and be
unable to operate
in order to show the appropriate evacuation route, since said device uses
neuronal networks
making it an autonomous and intelligent instrument and is not affected by the
breakdown of
one of its parts.
Another technical advantage is that the sensing and indicating (1) module of
this invention,
the integration and processing circuit (1-D) is powered independently as they
have their own
power supply or battery and is not dependent on the power supplied to other
sensors that
measure environmental parameters. Thus, such circuit (1-D) is not vulnerable
in the event of
fault in one or more sensors. Additionally, the system allows for sensors to
be installed on
side walls of the signalling and sensing module.
Thus, the subject matter of this invention comprises the intelligent
evacuation route device
and the use of a structural integrity section within the sensing and
signalling module, which
consists of an accelerometer sensor and a microprocessor.
DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
The invention can be better understood by looking at the figures that show
each of the
components that comprise the intelligent system that we wish to protect. In
addition, the
figures include reference numbers for the components that comprise said
device.
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
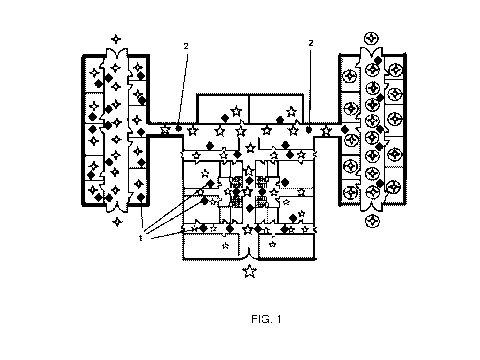
Figure 1 shows a diagram of the distribution of the intelligent evacuation
route device
invented, detailing a potential layout of the modules of the device, which
consist of the
following: one or more sensing and signalling (1) modules, depicted in the
illustration as
black diamonds, one or more intelligent route modules (2) depicted in the
illustration as black
circles, pursuant to the potential evacuation routes marked on Figure 1 as a
row of five-point
or four-point stars in a circle.
Figure 2 shows the front view of the sensing and signalling module (1), the
intelligent
evacuation route device, displaying the cover of the device (1-A), containing
the photovoltaic
cell (1-A), the indicating lights (1-A) and a horn (1-A). Figure 2-A displays
the internal view
of the sensing and signalling mode (1) of the intelligent evacuation route
device, showing the
communication system and the structural integrity sensor (1-B), the energy
regulating circuit
(1-C) and a integration and processing circuit (1-D). Figure 2B displays the
system sensors
(1-E).
Figure 3 shows the front view of the intelligent route module (2) of the
intelligent evacuation
route device, while Figure 3A shows the inside view of the intelligent route
module (2).
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The purpose of the invention is to supply an intelligent evacuation route
device, essentially
comprised of:
= One or more sensing and signalling modules (1), one or more intelligent
route
modules (2).
= The sensing and signalling module (1) comprises five sections: the front
cover (1-a),
the structural integrity sensor (1-B), the energy regulating circuit (1-C),
the integration
and processing circuit (1-D) and lastly the sensors (1-E).
The front cover (1-A) includes the speaker (1-A), the flow direction
indicating lights (1-A)
and the solar panel (1-A).
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
6
The structural integrity section (1-B) comprises an accelerometer sensor (14)
and a
microprocessor (13).
The energy regulating circuit (1-C) includes an energy regulating circuit
(110) and a battery
(19).
The integration and processing circuit (1-D), delivered by the sensors,
comprises the
microprocessor (12), the information transmission system (11) and the battery
(111).
The section of the sensors (I-E) which can be installed anywhere on the sides
of the sensing
and signalling module (1) comprises, for example, a smoke detector (15), a gas
detector (16),
a temperature detector (18) and a human occupancy and movement detector (17).
In this regard, the experts in the field will realize that the device invented
may support a high
number of sensors (in theory 216) and that the location will depend on the
space and
manufacturing design of the sensors as well as the dimensions of the
compartment containing
the sensing and signalling module (1).
= The intelligent route module (2) comprises three sections: the front
cover (2-A), the
energy regulating circuit (2-C) and the integration circuit that also
transmits the
signals generated by the sensors (2-D).
The section located across the front cover (2-A) of the intelligent route
module (2) includes
the compartment (2-a) and the solar panel (2-A).
The energy regulating circuit (2-C) component includes an energy regulating
circuit (23) and
a battery (24).
The intelligent processing circuit (2-D) component comprises a microprocessor
(21) and a
data transmitting system (22). The microprocessor (21) is responsible for
receiving the
information transmitted by the sensing and signalling module(s) (1),
processing it with the
support of a neuronal network, consisting of an input layer with potential
entries based on the
number of sensing and signalling modules (1), where the information is
received, a concealed
layer, and an output later that correspond to potential evacuation options.
CA 02900585 2015-08-04
7
After the microprocessor (21) has completed the intelligent process in real
time, the result or
the decision is then transmitted to an information transmitting system (22),
which in turn
relays the information to the sensing and signalling module (1), specifically
to the
information transmitting system (11), which translates the information
received from the
microprocessor (21) into measures, such as illuminating the exit arrow to the
right instead of
to the left, or broadcasting a warning on the speaker.
For example, if the invented device is installed in a laboratory, where acids
and other toxic
substances are handled, the toxic gas sensors in the device will instruct the
operators or the
personnel that masks must be worn upon exiting and what other measures must be
taken.