Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2902931 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | DUAL-MODE DUCTED FAN UNMANNED AIR VEHICLE |
| (54) French Title: | VEHICULE AERIEN SANS PILOTE A VENTILATEUR A CONDUIT DOUBLE MODE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (22) Filed Date: | 2015-09-03 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 2017-03-03 |
| Examination requested: | 2015-09-14 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | None |
|---|
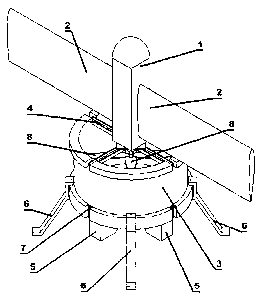
This invention of dual-mode ducted fan unmanned air vehicle has two flight
modes which
consist of hovering flight and horizontal flight. That means it could not only
hover in the air
as a helicopter but also fly horizontally in high speed mode as an airplane.
By using digital
signal system and electronic devices, this unmanned air vehicle can be
controlled remotely
or can autonomously complete variable missions, such as reconnaissance for
natural
disasters, suspect monitoring and aerial mapping. This innovative unmanned air
vehicle
consists of several components including duct, coaxial propellers, vanes,
fuselage, and
wings. The duct is the main part of ensuring the propeller slipstream to fully
pass through
vanes which are submerged in the propeller slipstream to achieve attitude
control of vehicle
even in low-speed flight and hovering. Two wings with fuselage attached to
duct is the
guarantee for providing sufficient lift during the horizontal flight.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2018-06-19 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2018-06-19 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2017-09-05 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2017-06-19 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2017-03-03 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2017-03-02 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2016-12-19 |
| Inactive: Report - No QC | 2016-12-09 |
| Letter Sent | 2015-11-10 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2015-11-06 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2015-11-06 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2015-11-06 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2015-09-14 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2015-09-14 |
| Request for Examination Received | 2015-09-14 |
| Application Received - Regular National | 2015-09-09 |
| Filing Requirements Determined Compliant | 2015-09-09 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - No RFE (bilingual) | 2015-09-09 |
| Inactive: QC images - Scanning | 2015-09-03 |
| Inactive: Pre-classification | 2015-09-03 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-09-05 |
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application fee - standard | 2015-09-03 | ||
| Request for examination - standard | 2015-09-14 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| HUIWEN HWZ ZHAO |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| HUIWEN ZHAO |