Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
Winding Shaft and Method for Inserting a Winding Shaft into a Winding Device
Description
The invention relates to a winding shaft with a winding body and shaft
journals that are
situated at the ends of the winding body and are configured for insertion into
a winding
device.
The invention also relates to a method for inserting a winding shaft into a
winding de-
vice, in which the winding shaft has a winding body and shaft journals that
are situated
at the ends of the winding body, with which the winding shaft is inserted into
corre-
sponding recesses of the winding device.
Winding shafts for insertion into a winding device e.g. for winding web-like
material such
as webs of plastic film, fleece, and paper, are known and usually have a
winding body
equipped with winding journals at the ends of the winding body that are
configured for
insertion into the winding device and are held, for example, by corresponding
winding
arms of the device. In this connection, the winding shafts can be set into
rotation indi-
rectly through frictional contact with a contact roller or also directly by
means of a rotary
drive acting on the shaft journals and the web-like wound product.
- 1 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
Winding devices of this kind are known, for example, from DE 40 39 048 C2 and
EP
1184312 Al.
The winding is usually carried out with a sleeve that is slid onto the winding
body and
affixed to it in a rotationally secured, but detachable fashion by suitable
clamping
means, e.g. a sleeve made of cardboard as described in DE 86 04 891 U1. In so
doing,
it is also possible in the sense of a so-called multi-use winding, to place a
plurality of
sleeves onto the winding shaft that each extend only over a part of the axial
length of
the winding body and to already correspondingly divide the supplied wound
product in
advance by means of longitudinal cuts for the separate uses.
Known winding devices for winding material webs of particularly large widths,
however,
usually use laterally arranged mounts, e.g. clamping arbors, that fix winding
sleeves
extending continuously across the entire width and transmit the torque, as
described for
example in DE 1 574 438 Al. With large winding widths, winding sleeves of this
kind
have less of a tendency to flex as compared to a solid winding shaft with a
sleeve slid
onto it. Winding devices with laterally arranged mounts for continuous winding
sleeves,
however, usually cannot accommodate winding shafts, making them unsuitable for
a
multi-use winding. In addition, when winding a narrow material web onto a
winding
device that is suitable for winding wide material webs, an unnecessarily wide
winding
sleeve must be kept on hand, which protrudes far beyond the finished winding
and
causes handling difficulties.
The object of the invention, therefore, is to propose winding shafts of the
type men-
tioned at the beginning as well as a method for inserting a winding shaft into
winding
devices, which shafts and method overcome the disadvantages of the prior art
and offer
a greater degree of flexibility when winding material webs.
In order to attain the stated object, the invention proposes a winding shaft
that has the
features of claim 1.
A method according to the invention for inserting a winding shaft into the
winding device
is the subject of the independent method claim 6.
- 2 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
Advantageous embodiments and modifications of the invention are the subject of
the
dependent claims.
The invention proposes embodying a winding shaft so that the winding body is
com-
posed of a winding sleeve that is open at the ends and the shaft journals each
have an
insertion section with clamping means, with which they can be inserted into
the ends of
the winding sleeve and detachably clamped to the winding sleeve, and together
consti-
tute the winding shaft. A winding shaft that is composed in this way of a
winding sleeve
and shaft journals detachably fastened to the winding sleeve is equivalent in
its dimen-
sions to a known winding shaft, but on wide winding machines, also permits the
winding
of parent rolls on a continuous winding sleeve without the risk of excessive
deflection
and/or extreme weight of the winding shaft.
The corresponding winding device can be embodied according to the known design
principles of a winding device for winding shafts and with the use of the
winding shafts
according to the invention, permits the winding onto a continuous sleeve and
also,
through the use of a conventional winding shaft with winding sleeves mounted
on it, a
multi-use winding in accordance with the respective requirements.
According to one proposal of the invention, the winding sleeve is composed of
a tube
section that is dimensionally stable, particularly with regard to deflection,
whose compo-
sition is based on metal, cardboard, or a plastic such as a fiber-reinforced
plastic.
According to another proposal of the invention, the clamping means are
composed of
clamping jaws that are situated in the region of the insertion section, can be
radially
retracted and/or extended, and in the extended position, come into contact
with the
inside of the winding sleeve. The retraction and extension of the clamping
jaws here can
be carried out by means of compressed air, as is known in conventional winding
shafts,
so-called air shafts, in order to fix a winding sleeve made of cardboard or
the like that
has been slid on.
The winding shaft according to the invention can thus be preconfigured out of
a winding
sleeve and shaft journals, which are inserted with their insertion sections
into the ends
- 3 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
of the winding sleeve and locked in place, and can then then be inserted into
the wind-
ing device and maneuvered like a conventional winding shaft.
Between the shaft journal and the insertion section, a transition section is
advanta-
geously provided whose outer diameter essentially corresponds to the outer
diameter of
the winding sleeve and which constitutes a stop for the winding sleeve in the
insertion
process of the insertion section. This ensures an always definite, sufficient
insertion of
the insertion section into the end opening of the winding sleeve and on the
other hand,
makes it possible for the transition section to be produced in different
widths so that the
winding sleeve ¨ despite an existing large system width of the winding device
¨ can also
be adapted as needed to a narrow width of the winding product to be wound. In
this
case, the transition sections of the shaft journals are embodied as
significantly longer so
that once again, the total length of the winding shaft that is required for
the respective
winding device is on the whole achieved.
The method according to the invention for inserting a winding shaft into the
winding
device is based on the fact that the winding shaft has a winding body and
shaft journals
situated at the ends of the winding body, with which the winding shaft is
inserted into
corresponding recesses in the winding device. The invention proposes
performing the
following steps for inserting the winding shaft into the winding device:
a) Production of a winding sleeve that is open at the ends and comprises
the wind-
ing body
b) Production of shaft journals that have an insertion section and clamping
means
c) Insertion of the insertion section of each of the shaft journals into a
respective
end opening of the winding sleeve
d) Clamping of the inserted insertion sections of the shaft journals in the
winding
sleeve to form the winding shaft
e) Insertion of the winding shaft into the winding device
In this regard, according to the invention, a winding shaft is formed by
producing the
open winding sleeve according to the width of the material web to be wound,
inserting
- 4 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
and clamping the shaft journals in the respective end openings of the winding
sleeve,
and then inserting the thus produced winding shaft into the winding device.
The clamping of the insertion section in the winding sleeve can be produced by
radially
extending clamping jaws out from the insertion section to the inner surface of
the wind-
ing sleeve; preferably, this is carried out pneumatically.
Other embodiments and details of the winding shaft according to the invention
will be
explained in greater detail below in conjunction with the drawings that show
an exem-
plary embodiment. In the drawings:
Fig. 1 shows a partial sectional view of a winding shaft according to the
invention;
Fig. 2 shows the winding sleeve according to Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 shows a winding shaft according to the prior art.
Fig. 3 shows a winding shaft according to the prior art for insertion into a
corresponding-
ly embodied winding device.
Such a winding shaft 1 includes a winding body 2 and at both ends of the
winding body,
shaft journals 11 that are positioned on the longitudinal axis L and
configured for inser-
tion into the winding device. The winding body 2 is embodied as intrinsically
cylindrical
and before being placed into use, is completed with a winding sleeve, not
shown here,
made of cardboard or the like, which is slid in the direction of the
longitudinal axis L onto
the winding body 2 so as to encompass the latter and is affixed to the winding
shaft in a
rotationally secured fashion by means of compressed air-operated clamping jaws
111
that can be radially extended out from the circumference of the winding body
2.
The cardboard sleeve that is affixed in this way can be embodied of one piece
or of
multiple pieces in order to thus enable a so-called multi-use winding.
- 5 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
After completion of the winding process, the winding shaft together with the
winding that
has been produced on the at least one winding sleeve is removed from the
winding
device and the clamping jaws 111 are retracted into the circumference of the
winding
body 2 by a releasing of the introduced compressed air so that the winding
shaft 1 can
then be removed from the at least one winding sleeve and used for a new
winding.
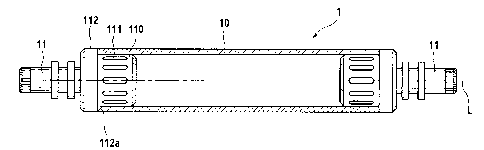
Figs. 1 and 2 show a winding shaft 1 according to the invention, whose outer
contour
largely coincides with that of the winding shaft from the prior art shown in
Fig. 3; in
particular, the shaft journals 11 are correspondingly embodied so that such a
winding
shaft 1 can also be used in a winding device that is configured for winding
shafts ac-
cording to Fig. 3.
The winding body of the winding shaft according to Figs. 1 and 2 is composed
of a
winding sleeve 10 that is open at the end and is composed, for example, of
metal, which
for the winding of a parent roll, is directly wound with the material web that
is to be
wound, i.e. no other sleeve made of cardboard or the like is slid onto it as a
core.
In order to use such a winding sleeve 10 with open ends 100 in a winding
device for
winding shafts according to the embodiment in Fig. 3, the shaft journals 11
provided at
the ends are each embodied with an insertion section 110, which can each be
inserted
into the respective open ends 100 of the winding sleeve 10 at the two ends
thereof. A
transition section 112 between the insertion section 110 and the shaft journal
11 in this
case forms a stop that is labeled with the reference numeral 112a, against
which the
end of the winding sleeve 10 rests. In this inserted position shown in Fig. 1,
the insertion
sections 110 are then affixed to the inner surface I of the winding sleeve 10
in a rota-
tionally secured fashion by means of a radial extension of clamping jaws 111
from the
circumference of the insertion section 10; this extension can be carried out
in an intrin-
sically known fashion by means of compressed air, which can be introduced, for
exam-
ple, via a corresponding valve and an internal compressed air line in the
shaft journal
11.
In this way, a temporary, detachable connection between the two shaft journals
11 and
the winding sleeve 10 is produced via the respective insertion sections 110;
in this state,
the winding sleeve 10 and the clamped shaft journals 11 jointly form a winding
shaft 1
- 6 -
CA 02912242 2015-11-17
whose configuration corresponds to that of the winding shaft according to Fig.
3 so that
they can be inserted into a correspondingly prepared winding device.
After completion of the winding procedure, the introduced compressed air is
released in
order to retract the clamping jaws back into the circumference of the
insertion sections
110 so that the rotationally secured connection between the winding sleeve 10
and the
insertion sections 110 of the shaft journals 11 is released and the latter can
be removed
from the end openings 100 of the winding sleeve 10. Consequently, the isolated
winding
sleeve 10 then remains along with the winding, not shown here, that has been
wound
onto it.
It is clear that through the embodiment of the winding shaft according to the
invention, a
winding of parent rolls with a continuous winding sleeve 10 can also be
carried out in
winding devices that are intrinsically embodied for accommodating conventional
winding
shafts 1 according to the exemplary embodiment in Fig. 3. The winding device
therefore
does not require any structural modification and it is possible to flexibly
react to each
winding task individually.
If in a winding device that is designed for large winding widths, a
significantly narrower
material web by contrast is to be wound onto a winding sleeve 10 of a
corresponding
width, then it is only necessary to correspondingly adapt the width of the
transition
region 112, in particular to enlarge it, so that an on the whole uniform
overall length of
the winding shaft 1 is achieved, allowing different winding sleeve lengths to
be used
without having to change the width of the winding device.
With the winding shaft according to the invention, it is possible to
alternatively use
winding shafts or winding sleeves in a single winding device. While the use of
winding
shafts according to Fig. 3 makes it possible in particular to produce a multi-
use winding,
it is alternatively possible, through the use of a winding shaft with a
continuous winding
sleeve according to Fig. 1, to also wind a parent roll with a large width.
- 7 -