Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
STRENGTHENING METHOD FOR FILLET PART OF CRANKSHAFT AND
STRENGTHENING DEVICE THEREFOR
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Technical Field
[0001] The present invention relates to a strengthening method for a fillet
part
of a crankshaft and a strengthening device therefor, and in particular relates
to a
technique for strengthening the fillet part not only in a radial direction,
but also
in an axial direction.
Background Art
[0002] For example, a crankshaft includes a crank pin and a journal pin, and
the crank pin rotatably supports a large end part of a connecting rod, whereas
the journal pin is rotatably supported by a journal bearing of an engine
block.
Each of the crank pin and the journal pin has a corner part, at which a groove
(fillet part) is formed so as to have a cross section of a semicircular shape
in
order to avoid interference with a mating member. The fillet part is a part
having low strength, but receives great bending moment when an explosion
occurs in an internal combustion engine. Therefore, it is desired to
strengthen
top portions of the pin of the fillet part (at phases of 0 degrees and 180
degrees
in the case of an in-line four cylinder engine).
[0003] A forging device including a punch with slope surfaces is disclosed in
Japanese Patent No. 3899246. The slope surface is formed at each side of an
end of the punch so as to have a circular arc shape in a side view, and a
convex
die is slidably arranged thereto. In this forging device, when the convex die
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
presses the fillet part, it protrudes outwardly along the slope surface and
also
axially presses the fillet part so as to obtain a strengthened portion in a
wide
area.
[0004] However, in the technique disclosed in Japanese Patent No. 3899246,
the above effect cannot be obtained. This is because the slope surface used as
a cam surface for making the convex die protrude outwardly is a conical
surface
(in [0011]), and a space is formed between the convex die and the conical
surface when the convex die protrudes outwardly even at a small degree,
whereby the convex die tilts against the punch.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0005] Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a
strengthening method for a fillet part of a crankshaft not only in a radial
direction, but also in an axial direction and to provide a strengthening
device
therefor.
[0006] The present invention provides a strengthening method for a fillet part
of each of a pin part and a journal part of a crankshaft, and the method
includes
pressing a pressing member from a direction perpendicular to an axis of the
pin
part or the journal part, against a portion configured to receive at least one
of
bending load and torsional stress at the maximum degree in a circumferential
direction of the fillet part when the crankshaft is practically used, so as to
apply
compressive residual stress to the portion. In this method, the pressing
member is slidably supported in a direction tilted with respect to the axial
direction against the pressing direction and is slidingly moved in a direction
2
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
tilted with respect to the axial direction when pressing the fillet part.
[0007] In the present invention, the pressing member is slidingly moved in the
axial direction when pressing the fillet part, whereby the fillet part is
pressed in
the axial direction by the pressing member. Therefore, the fillet part can be
strengthened not only in the radial direction, but also in the axial
direction.
[0008] In the present invention, the pressing member desirably includes a
guide member that is provided at a trailing end side thereof. The guide
member desirably has a convex slope surface, which faces the pressing member.
The pressing member is desirably constructed of a pair of pressing pieces,
which are configured to come into contact with or separate from each other,
and
desirably has a concave slope surface, which faces the convex slope surface
and
has the same shape as the convex slope surface. In this case, the convex slope
surface desirably presses the concave slope surface so that the pressing
member
slides while pressing the fillet part.
[0009] In addition, the present invention also provides a strengthening device
for a fillet part of each of a pin part and a journal part of a crankshaft,
and the
device is configured to press a pressing member from a direction perpendicular
to an axis of the pin part or the journal part, against a portion configured
to
receive at least one of bending load and torsional stress at the maximum
degree
in a circumferential direction of the fillet part when the crankshaft is
practically
used, so as to apply compressive residual stress to the portion. The device
includes a guide member, which has a slope surface at an end thereof, and a
pressing member, which has a sliding surface slidable along the slope surface
and has a pressing surface with a configuration along the fillet part. The
slope
3
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
surface is uniformly tilted relative to a pressing direction of the pressing
member so as to face the fillet part.
[0010] In the present invention, when the pressing surface of the pressing
member presses the fillet part, the pressing member slides along the slope
surface of the guide member and moves in the axial direction. Therefore, the
pressing surface presses the fillet part in the axial direction, whereby the
fillet
part is strengthened not only in the radial direction, but also in the axial
direction.
[0011] In the present invention, the slope surface of the guide member
preferably has a convex shape so as to face the pressing member. The pressing
member is preferably constructed of a pair of pressing pieces, which are
configured to come into contact with or separate from each other, and
preferably
has a concave slope surface, which faces the convex slope surface and has the
same shape as the convex slope surface. In this case, the convex slope surface
preferably presses the concave slope surface so that the pressing member
slides
while pressing the fillet part.
[0012] In the present invention, the pressing member desirably includes a
pressing surface for pressing the fillet part at a predetermined pressing
amount,
and the pressing surface desirably includes a forming area in a range within
45
degrees from a normal direction to each side in a circumferential direction
and
desirably includes a gradually changing area in a range within 90 degrees from
the normal direction to each side in the circumferential direction beyond the
forming area. The forming area is formed of an approximately cylindrical
curved surface having a curvature radius that is obtained by subtracting the
4
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
predetermined pressing amount from a curvature radius of a cross section of
the
fillet part. The gradually changing area has a curvature radius that gradually
increases to a relief radius that is obtained by adding a relief amount to the
curvature radius of the fillet part.
[0001] In the above case, the curvature radius of the forming area is smaller
than that of the shaft member, whereby strengthening can be performed in a
wider area (in an area of 45 degrees of one side at the maximum). In addition,
the pressing member includes the gradually changing area having the radius
that
gradually increases until the relief radius in which the relief amount is
added to
the curvature radius of the shaft member. Therefore, the compressive residual
stress applied to the shaft member is gradually decreased in accordance with
the
gradually changing area, and the strengthened portion reaches a portion
without
the compressive residual stress, whereby tensile residual stress is decreased
at
the portion adjacent to the portion to which the compressive residual stress
is
applied. The forming area is preferably formed within a range of 30 to 45
degrees from the normal direction to each side in the circumferential
direction.
The gradually changing area is preferably formed in a range of 60 to 75
degrees
from the normal direction to each side in the circumferential direction beyond
the forming area.
[0002] In this case, an imaginary straight line that is perpendicular to the
slope
surface in a cross section including the axis line desirably passes a working
part
of the pressing surface for pressing the fillet part. This is because if the
working part of the pressing surface for pressing the fillet part is separated
from
the imaginary straight line, the pressing member is difficult to slide along
the
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
slope surface of the guide member when the pressing surface presses the fillet
part in a direction perpendicular to the axis line.
[0015] In addition, the slope surface is preferably a cylindrical curved
surface,
for example. In this case, the guide member may be tilted and be secured on a
milling machine or the like, and the slope surface can be processed by milling
the guide member with a milling tool. On the other hand, the pressing member
has an approximately semi-ring shape, for example, and has a sliding surface
with a columnar curved surface so as to slide in the axial direction of the
columnar curved surface relative to the slope surface. Moreover, the pressing
surface may be provided at a side edge of an inner circumferential surface of
the
pressing member. The pressing surface may be formed into a protrusion that
protrudes toward the fillet part and that also protrudes in the axial
direction of
the fillet part.
[0016] According to the present invention, the fillet part of the crankshaft
is
strengthened not only in the radial direction, but also in the axial
direction.
Moreover, the strengthening can be performed in a wider area of the fillet
part,
and tensile residual stress is decreased at the portion adjacent to the
portion to
which the compressive residual stress is applied.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[0017] Fig. 1 is a side view showing a crankshaft to be strengthened in an
embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a side view showing a condition in which a crank pin is
strengthened in an embodiment of the present invention.
6
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
Fig. 3 is a side view showing a condition in which a journal pin is
strengthened in an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 4A is a front view showing an upper punch in an embodiment of
the present invention, and Fig. 4B is a sectional side view of the upper
punch.
Fig. 5A is a front view showing a holder of an embodiment of the
present invention, and Fig. 5B is a sectional side view of the holder.
Fig. 6 is an enlarged side view showing a condition in which a crank
pin is strengthened in an embodiment of the present invention.
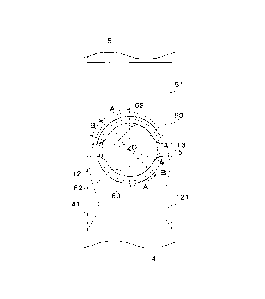
Fig. 7 is a cross sectional view taken along the line of the arrows VII ¨
VII in Fig. 2 for showing a strengthening method for a shaft member of an
embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 8 is an enlarged view showing details of a machined part.
PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION
[0018] An embodiment of the present invention will be described with
reference to the figures hereinafter. Fig. 1 is a side view showing a
crankshaft
1 to be strengthened in this embodiment. The crankshaft 1 is formed by hot
forging, and it is made by forming radially protruding crank arms 12 at
journal
pins 11, which function as a rotating shaft, arranging a crank pin 13 between
sides of each of a pair of the crank arms 12, and forming a balance weight 14
at
an end of one of the pair of the crank arms 12. Each of the journal pins 11
and
the crank pins 13 has a fillet part 15 that is formed on each side thereof,
and the
fillet part 15 is a groove having a cross section with an approximately
semicircular shape.
7
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
[0019] Fig. 2 shows a condition in which the fillet parts 15 of the crank pins
13 are subjected to plastic working by a lower die 2 and an upper die 3, and
the
crankshaft 1 is placed on the lower die 2 so that the crank pins 13 are
directed in
the vertical direction. The lower die 2 includes a first lower punch 21, which
is provided at one side thereof and extends upwardly at a longer length, and
includes a second lower punch 22, which is provided at the other side thereof
and extends upwardly at a shorter length. Similarly, the upper die 3 includes
a
first upper punch 31, which is provided at one side thereof and extends
downwardly at a longer length, and includes a second upper punch 32, which is
provided at the other side thereof and extends downwardly at a shorter length.
[0020] Fig. 3 shows a condition in which the fillet parts 15 of the journal
pin
11 are subjected to plastic working by a lower die 4 and an upper die 5. The
lower die 4 is provided with a lower punch 41 that extends upwardly. The
upper die 5 is provided with an upper punch 51 that extends downwardly.
[0021] Fig. 4A is a front view showing the upper punch 51, and Fig. 4B is a
cross sectional view of the upper punch 51. In these figures, the reference
symbol 52 represents a holder (guide member). The holder 52 is made by
forming a semicircular hole 54 at one side of a rectangular plate 53, as shown
in
Fig. 5A. The hole 54 has a center as shown by the alternate long and short
dashed line in Fig. 5B and is formed into a circular shape when viewed from a
direction tilted with respect to one of the front and the back sides of the
plate 53
in the thickness direction. The hole 54 has an edge part, at which a slope
surface 55 having a V-shaped cross section is formed. The slope surface 55 is
made to have a sloped angle 0 of 60 to 150 degrees in the cross section
passing
8
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
through the center of the plate 53. The holder 52 having such a structure is
mounted with a pair of pressing pieces (pressing members) 60.
[0022] The pressing piece 60 has an approximately semi-circular ring shape
and has a sliding surface 61, which is formed at the outer circumference
thereof
and has the same shape as the slope surface 55. The pressing piece 60 also has
a protrusion (pressing surface) 62, which is formed at an edge of the inner
circumference thereof at a side opposite to the other pressing piece 60 and
protrudes to the inner circumference and outwardly in the thickness direction
thereof. The pair of the pressing pieces 60 have a symmetrical shape in the
cross section shown in Fig. 4B and have the sliding surfaces 61 that form a
concave part, and the slope surface 55 of the plate 53 fits to the concave
part in
a wedge-shaped manner. The pressing piece 60 is formed with a hole 63 that
penetrates in the thickness direction, and a bolt 64 and nuts 65 are attached
to
the hole 63. The bolt 64 and the nuts 65 prevent the pair of the pressing
pieces
60 from being separated from each other more than a predetermined distance.
In addition, the holder 52 has a stopper 66 that is attached at a lower
surface
thereof so as to prevent falling off of the pair of the pressing pieces 60
therefrom.
[0023] Fig. 6 is a cross sectional view showing the details of the pressing
piece 60. As shown in Fig. 6, the protrusion 62 of the pressing piece 60 has a
cross section with an approximately semicircular shape and has a curvature
radius that is smaller than that of the fillet part 15. In addition, the
protrusion
62 protrudes to the crank arm 12, thereby forming a space between the
protrusion 62 and the crank arm 12 over the protrusion 62. Moreover, an
9
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
imaginary straight line "L" (refer to Fig. 6) that is perpendicular to the
slope
surface 55 passes a working part "F" of the protrusion 62 for pressing the
fillet
part 15. It should be noted that the first upper punch 31, the first lower
punch
21, the second lower punch 22, the lower punch 41, and the second upper punch
32, are also formed as in the case of the upper punch 51 described above.
[0024] Fig. 7 shows shapes of the lower punch 41 and the upper punch 51,
which are viewed from a side. The protrusion 62 of the upper punch 51 has a
forming area "A" in a range within 45 degrees from a normal line "1" direction
(direction from the curvature center "0" to the center line of the upper punch
51) to each side in the circumferential direction. The forming area "A" is
formed of an approximately cylindrical curved surface with a curvature radius
that is obtained by subtracting a pressing amount from the curvature radius of
the cross section of the fillet part 15. Here, the "pressing amount" is a
thickness to be worked on the fillet part 15 along the normal line "1" by the
protrusion 62. The protrusion 62 approximately uniformly works in the
forming area "A".
[0025] As shown in Fig. 8, a gradually changing area "B" is provided in a
range within 90 degrees from the normal line "1" direction to each side in the
circumferential direction, beyond the forming area "A". In this area, the
curvature radius is gradually increased to a relief radius "N" that is
obtained by
adding a relief amount to the curvature radius of the fillet part 15. In Fig.
8,
the solid line represents a circle of a radius "R" of the fillet part 15, the
broken
line represents a circle of a target radius "S" after forming (the radius of
the
fillet part 15 ¨ the pressing amount), and the alternate long and two short
dashed
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
line represents a circle of the relief radius "N" (the radius of the fillet
part 15 +
the relief amount). In the gradually changing area "B", the shape of the
protrusion 62 is set by measuring a cam profile around the curvature center
"0"
and by setting the distance from the curvature center "0" at each angle point.
[0026] Specifically, first, the angle ranges of the forming area "A" and the
gradually changing area "B" are set, and then angle points are determined by
setting a radius every 10 degrees from an end point of the forming area "A".
In this case, the angle range of the gradually changing area "B" is divided by
10
degrees so that the angle point number is calculated, and a difference between
the relief radius "N" and the target radius "S" is calculated. Next, the
curvature radius of the protrusion 62 is enlarged every 10 degrees by a
calculated value that is obtained by dividing the calculated difference by the
angle point number. Thus, the distance from the curvature center "0" is
gradually increased as the angle increases from the normal line "1" direction
to
each side in the circumferential direction beyond the forming area "A", and it
agrees with the radius "R" of the fillet part 15 at the point "P". Moreover,
when the angle further increases in the circumferential direction, the
protrusion
62 is protruded in a direction reverse to the forming area "A", and the
distance
from the curvature center "0" reaches the relief radius "N".
[0027] The lower punch 41 is constructed in a manner similar to that of the
upper punch 51. That is, the protrusion 62 of the lower punch 41 has a
forming area "A" in a range within 45 degrees from the normal line "1"
direction
to each side in the circumferential direction. The forming area "A" is formed
of an approximately cylindrical curved surface with a curvature radius that is
11
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
obtained by subtracting a pressing amount from the curvature radius of the
cross
section of the fillet part 15. In addition, a gradually changing area "B" is
provided in a range within 90 degrees from the normal line "1" direction to
each
side in the circumferential direction, beyond the forming area "A". In this
area,
the curvature radius is gradually increased to a curvature radius that is
obtained
by adding a relief amount to the curvature radius of the fillet part 15.
[0028] Next, a method of strengthening the fillet part 15 by using the lower
punch 41 and the upper punch 51 having the above structures will be described.
In this embodiment, the fillet part 15 is strengthened by plastic working at
ordinary temperature. When the upper die 5 is lowered, the forming area "A"
of the protrusion 62 of the upper punch 51 contacts the fillet part 15 of the
crank
pin 13 and presses the fillet part 15 in conjunction with the forming area "A"
of
the protrusion 62 of a first lower punch 121. At this time, as shown in Fig.
6,
the slope surface 55 of the holder 52 comes between the pair of the pressing
pieces 60 in a wedge-shaped manner, thereby separating the pair of the
pressing
pieces 60 from each other. Then, the protrusion 62 presses a portion of the
fillet part 15 in the axial direction side. By performing this processing,
compressive residual stress is applied to portions of the fillet part 15 in
the
radial direction side and in the axial direction side. In the forming area
"A",
since approximately the entirety of the portion of the fillet part 15 is
formed in
the vertical direction by the pressing amount, the compressive residual stress
is
approximately uniform. The compressive residual stress offsets tensile stress,
which may occur when a bending moment is applied to the fillet part 15.
[0029] On the other hand, in the gradually changing area "B", the pressing
12
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
amount is gradually decreased from the normal line "1" direction in the
circumferential direction, and the pressed portion of the fillet part 15
reaches a
portion that is not pressed. Therefore, the compressive residual stress that
is
applied to the fillet part 15 is gradually decreased in the gradually changing
area
"B" and becomes zero at the portion that is not pressed. Accordingly, tensile
residual stress, which occurs at a portion in the vicinity of the portion
provided
with the compressive residual stress, is decreased.
[0030] Here, the crankshaft 1 is designed for an in-line four cylinder engine,
and in such a case, portions at the phase angles of 0 degrees and 180 degrees,
that is, the top point and the bottom point of the fillet part 15 as shown in
Fig. 7
receive at least one of the bending load and the torsional stress at the
maximum
degree when explosive combustion occurs in the internal combustion engine.
For example, in the case of the crank pin 13, the bottom point of the fillet
part
15 is located at a position in a direction reverse to the direction of the
balance
weight 14 by 180 degrees. In another example, in the case of the journal pin
11, the bottom point of the fillet part 15 is located at a position in the
direction
of the balance weight 14.
[0031] In this embodiment, the portions of the fillet part 15, to which at
least
one of the bending load and the torsional stress at the maximum degree is to
be
applied, are pressed by the upper punch 51 and the lower punch 41, whereby
compressive residual stress is applied to the portions of the fillet part 15
in the
radial direction side and in the axial direction side. In addition, the
compressive residual stress is applied only to the portions that need to be
strengthened, and therefore, the processing is efficiently performed.
Moreover,
13
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
,
the fillet part 15 is partially plastic worked, whereby elongation in the
axial
direction due to the plastic working is reduced.
[0032] In particular, in the above embodiment, since the forming area "A" and
the gradually changing area "B" are provided to the upper punch 51 and the
lower punch 41, a wide area of the fillet part 15 is strengthened while the
tensile
residual stress, which occurs at portions in the vicinity of the portions
provided
with the compressive residual stress, is decreased. In addition, since the
imaginary straight line "L" that is perpendicular to the slope surface 55 of
the
holder 52 passes the working part "F" of the protrusion 62 for pressing the
fillet
part 15, the pressing pieces 60 are reliably slid and are moved in the axial
direction.
[0033] Next, the crankshaft 1 is turned upside down and is placed on the lower
die 2 so that a left end crank pin 13 and a crank pin 13 on the right side of
the
left end crank pin 13 face the vertical direction, and the fillet parts 15 are
subjected to the plastic working in the same manner as described above. In
addition, the fillet parts 15 of the journal pin 11 are subjected to the
plastic
working by the lower die 4 and the upper die 5 shown in Fig. 3. In these
cases,
the same effects can also be obtained as in the case described above.
[0034] Although two crank pins 13 are strengthened by using the upper
punches 31 and 32 and the lower punches 21 and 22 as shown in Fig. 2 in the
above embodiment, the crank pins 13 may be strengthened one by one by a pair
of the upper and lower punches. Alternatively, all of the crank pins 13 and
all
of the journal pins 11 may be strengthened at one time by using a die assembly
for the entire shape.
14
CA 02923468 2016-03-10
[0035] The present invention can be utilized for strengthening the fillet
parts
of a crankshaft.