Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-1-
TITLE: INDUSTRIAL LIGHTING SUPPORT SYSTEM
FIELD
[0001] The present disclosure relates generally to a telescoping light pole
with an internal
passage for electrical wiring and configured for a telescoping function
facilitating worker
access to a remote fixture.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Lighting systems are used in many applications, with different
constructions provided
for different environments. Lighting is particularly important in industrial
applications, which
often requires work in low light conditions (e.g., at night). However, due to
environmental
conditions, accessing pole-mounted lights can be difficult and often
dangerous. Adjustable
lighting systems have been developed for industrial applications. As a result
of the perils of
ladder use in industrial settings, systems have been developed to safely lower
the remote end
(top end) of a light pole.
SUMMARY
[0003] Aspects of the present disclosure relate to systems, methods, and
devices for lighting
fixture pole support. General embodiments may include a pole support system
including a
tubular lower support; a guide member interior to the lower support, the guide
member
extending substantially along a length of the lower support; a telescoping
upper support
inside the lower support and axially movable between an extended position and
a retracted
position, the upper support being at least partially received in an annular
space between the
lower support and the guide member; a biasing member biasing the upper support
to the
extended position; and a locking assembly partially surrounding the lower
support at one end
of the lower support. The locking assembly may include a body having a passage
in which
the upper support slides therethrough, the body attached to the lower support
to enclose the
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-2-
passage at a first end while maintaining the passage in fluid communication
with the interior
of the lower support; and a lock configured to selectably engage the upper
support to
constrain axial motion of the upper support.
[0004] The biasing member may include a spring in the annular space between
the lower
support and the housing. The body may be attached to the lower support by at
least one
selectably sealingly engageable fastener. The guide member may include fluid-
tight tubular.
The system may include a base configured for coupling with the fluid-tight
tubular and the
lower support at corresponding ends opposite the locking assembly and
configured to isolate
an interior of the fluid-tight electrical conduit from the annular space
between the lower
support and the housing. The base may include a channel between the first end
of the base
and a second end of the base in fluid-tight communication with the fluid-tight
tubular. The
passage may be an axial passage. The lock comprises a translational member
configured to
translate into the passage against the upper support through an opening
transverse to the axial
passage. The locking assembly may include a raised surface in the passage
opposite the
translational member. The raised surface may be a ledge. The system may
include electrical
wiring, wherein a portion of the electrical wiring within the upper support is
configured to
conform to a length of a portion of the upper support above the locking
mechanism. The
system may include a wiring seal. The guide member may be coaxial with a
longitudinal axis
of the lower support.
[0005] Other general embodiments may include a pole support system including a
tubular
lower support; a fluid-tight wiring chamber interior to the lower support, the
wiring chamber
extending substantially along a length of the lower support; a telescoping
upper support
inside the lower support and axially movable between an extended position and
a retracted
position, the upper support being at least partially received in an annular
space between the
lower support and the wiring chamber; a biasing member biasing the upper
support to the
extended position; and a locking assembly partially surrounding the lower
support at one end
of the lower support. The locking assembly may include a body having a passage
in which
the upper support slides therethrough, the body attached to the lower support
to enclose the
passage at a first end while maintaining the passage in fluid communication
with the interior
of the lower support; and a lock configured to selectably engage the upper
support to
constrain axial motion of the upper support. The tubular lower support may
have an interior,
an upper end, and a base end, with the base end having a connector configured
to connect
with a pre-existing feature. The fluid-tight wiring chamber may be disposed
within the
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-3-
biasing member and may block fluid flow from the interior of the lower support
to a location
exterior to the lower support. The pre-existing feature may be an electrical
enclosure, such as
a junction box or electrical fitting for industrial electrical conduit. The
pole support system
may include a wiring assembly having a first portion disposed in the upper
support and a
second portion disposed in the lower support, wherein the tubular wiring
chamber seals
around the second portion at an opening in the lower support to prevent fluid
flowing via the
opening into the electrical enclosure. The pole support system may include an
adaptor
coupled to the tubular wiring chamber, and a wiring seal coupled to the
adaptor, where the
wiring seal and adaptor cooperate to block fluid flow to the interior of the
fluid-tight tubular
wiring chamber.
[0006] Other general embodiments may include a locking assembly for use in a
pole support
system, as described herein. For example, the locking assembly may include a
body having a
passage configured for sliding transmission of an upper support therethrough,
the body
configured for selectable sealing engagement to a tubular lower support to
enclose the
passage at a first end while maintaining the passage in fluid communication
with the interior
of the lower support; and a lock configured to selectably engage the upper
support to
constrain axial motion of the upper support.
[0007] The foregoing and other objects, features and advantages of the
disclosure will be
apparent from the following more particular descriptions of exemplary
embodiments of the
disclosure as illustrated in the accompanying drawings wherein like reference
numbers
generally represent like parts of exemplary embodiments of the disclosure.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0008] The following figures are part of the present specification, included
to demonstrate
certain aspects of embodiments of the present disclosure and referenced in the
detailed
description herein. Unless otherwise noted, figures are not drawn to scale.
[0009] FIGS. 1-3 illustrate a pole support system for industrial lighting in
accordance with
embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0010] FIGS. 4A & 4B illustrate locking assemblies in accordance with
embodiments of the
present disclosure.
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-4-
[0011] FIGS. 5A-5D illustrate a base in accordance with embodiments of the
present
disclosure.
[0012] FIG. 6 illustrates a pole support system having a wiring chamber in
accordance with
embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0013] FIGS. 7A-7L illustrate embodiments configured for various modes of use
in
accordance with embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0014] FIG. 8 illustrates a further pole support system for industrial
lighting in accordance
with embodiments of the present disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0015] Exposed wiring for lighting systems is susceptible to environmental
hazards, such as
moisture. Some known systems have a passage interior to the pole running to
the remote end,
and wiring (wires, cables, etc.) running through the passage to the light
fixture. Known
systems are inefficient in protecting the installed wiring. Normal movement of
the
components often damages internal wiring (e.g., "pinching").
[0016] Further, traditional industrial fixtures (particularly those with
ballast hinges) are
configured for use on a pole with a particular operational axis (e.g., the
axis while in use).
Because most industrial fixtures are not designed for use with a lowerable
pole, changing the
operational axis introduces instability in the fixture. One reason for the
instability is the
introduction when lowering the fixture of additional forces that are not
present during normal
operation. Forces having a component normal to the operational axis may be
particularly
problematic. Thus, traditional lowered poles using joints or the like for
lowering may result
in instability of the fixture, particularly while the pole is deviated from
its operational axis.
This instability may result in fixtures detaching prematurely, and possibly
falling from height,
which is a safety hazard.
[0017] It would be desirable to increase protection for wiring in light poles
in industrial
settings while still facilitating repair or maintenance of light fixtures atop
the light pole by
bringing the fixture to ground level. It would also be desirable to enable a
single worker to
perform the action of raising and/or lowering the fixture, thereby reducing
the costs of labor
relating to maintenance, while maintaining the pole in its operational axis.
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-5-
[0018] Generally, embodiments of the present disclosure may relate to spring
assisted
telescoping industrial light poles. As part of the telescoping nature of the
present disclosure,
the upper support (or upper pole) is slidably engaged with the lower support
(or lower pole).
The telescoping supports, along with the spring assist, allow the top mounted
light fixture to
be moved up and down. Thus the light fixture can be raised or lowered to the
position of a
user in the identical operational axis. Thus safety is increased, as there is
less risk of accident
when moving the light fixture in relation to a user. Aspects of the present
disclosure also
relate to safeguards for the wiring providing power to the fixture. Further
aspects relate to
general robustness and longevity of the pole support system in environmental
conditions
likely to be experienced upon installation in an outdoor or marine industrial
setting (e.g.,
mines, offshore oil rigs). For example, depending on the particular materials
used, a 10-foot
pole support system of the present design may be rated for winds of over 300
miles per hour.
[0019] The principles of the disclosure are explained by describing in detail,
specific
example embodiments of devices, systems, and methods for facilitating access
to industrial
lighting. Aspects of the present disclosure resist deleterious conditions,
such as, for example,
rain, high winds, impact, conditions associated with industrial environments,
and so on.
[0020] General embodiments of the disclosure include pole support systems and
devices for
incorporation within a pole support system. The pole support system may be
configured for
use with traditional light fixtures and enable height adjustment of a fixture
via a telescoping
upper pole. More specific example embodiments are described below. Embodiments
relate to
wired support systems (e.g., 'wired poles'). A wired pole may include wiring
or cabling
operatively coupled with the lighting or other mounted item. Some aspects of
the present
disclosure may allow toggling between optimal orientations for maintenance and
operation
more easily, safely and/or rapidly.
[0021] Example embodiments were chosen and described in order to best explain
the
principles of the disclosure and their practical application, and to enable
others of ordinary
skill in the art to understand the disclosure for various embodiments with
various
modifications as are suited to the particular use contemplated. Those skilled
in the art will
understand, however, that the invention may be embodied as many other devices,
systems,
and methods. For example, various aspects of the methods and devices may be
combined in
various ways or with various products, including existing products. Many
modifications and
variations will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art. The scope
of the invention is
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-6-
not intended to be limited by the details of example embodiments described
herein. The
scope of the disclosure should be determined through study of the appended
claims.
[0022] Specific design details have been provided for illustration, but should
not be
considered limiting. Readers of skill in the art will recognize that many
variations of
telescoping pole support systems may be implemented consistent with the scope
of the
disclosure as described by the appended claims.
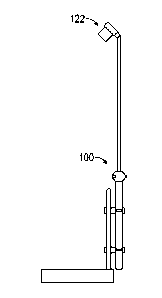
[0023] FIGS. 1-3 illustrate a pole support system for industrial lighting in
accordance with
embodiments of the present disclosure. Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the pole
support system
100 comprises a lower support 106, a telescoping upper support 102, and a
locking assembly
104 attached to the locking assembly 104. The lower support 106 may be
tubular. Tubular
as used herein may include tubular with cylindrical, rectangular, elliptical,
or irregular cross-
sections. The pole support system supports at least one light fixture 122.
Light fixture 122
may be a traditional light fixture. Upper support 102 and lower support 106
may be
implemented as 2-inch tubular comprising aluminum, galvanized or stainless
steel, or the
like, or any other material as would occur to one of skill in the art.
[0024] FIG. 3 shows a cross section of pole support system 100. Referring to
FIG. 3, pole
support system 100 further includes a guide member 108 interior to the lower
support 106.
The guide member 108 may extend substantially along the length of the lower
support 106.
"Substantially along the length of the lower support 106," as described
herein, may be
defined as a range spanning (at either end) from 18 inches longer to 6 inches
shorter than the
lower support. Other embodiments may include guide member 108 extending
greater than 18
inches farther than the lower support 106.
[0025] Upper support 102 lies inside the lower support 106 and is axially
movable between
an extended position and a retracted position. Locking assembly 104 at least
partially
surrounds the lower support 106 at one end of the lower support 106. The upper
support 102
may be at least partially received in an annular space 109 between the lower
support 106 and
the guide member 108. The guide member 108 may be concentric with the lower
support
106 and/or upper support 102. A biasing member 110 in the annular space 109
biases the
upper support 102 to the extended position. The biasing member 110 may be
implemented as
a spring (as shown), an elastomeric member, a pneumatic or hydraulic system,
and so on.
[0026] In operation, an attached light fixture 122 is accessible by adjusting
the pole support
system height via the upper support 102 retracting into the lower support 106.
The
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-7-
telescoping connection between the upper support 102 and the lower support 106
is aided by
the "spring assist" from the biasing member 110. The spring assist reduces the
amount of
strength needed to raise or lower the upper support to a desired height. The
light fixture 122
is secured at a desired height by the lock assembly 104.
[0027] Locking assembly 104 includes a chamfer away from the upper support on
the upper
surface to resist standing water while maintaining structural strength. Other
embodiments
may include an arched upper surface, a level upper surface, or other designs.
The lower
surface may be the same or different than the upper surface. It is to be
understood that
varying designs may have associated advantages and disadvantages that
recommend their
use, and that all such variations are within the scope of the present
disclosure.
[0028] FIGS. 4A & 4B illustrate locking assemblies in accordance with
embodiments of the
present disclosure. Locking assembly 104 includes a body 114 having a passage
115 in
which the upper support 102 (FIG.3) slides therethrough. The passage 115 may
be tailored to
the upper support 102 to allow sliding translation of upper support 102 while
discouraging
ingress of moisture and particulates. The body 114 is attached to the lower
support 106 to
enclose the passage 115 at a first end while maintaining the passage 115 in
fluid
communication with the interior of the lower support 106. The body 114 may be
attached to
the lower support 106 by at least one selectably sealingly engageable fastener
(e.g., via
threaded connection or mechanical seal), by use of adhesives, epoxies, or
resins, or using
other fasteners.
[0029] Lock 116 is configured to selectably engage the upper support 102 to
constrain axial
motion of the upper support 102. The locking assembly 104 further includes a
raised surface
124 in the passage. Lock 116 may be implemented using various fasteners or
biasing
mechanisms.
[0030] Referring to FIG. 4B, in example embodiments, the lock 116' may be a
translational
member 117 configured to translate into the passage 115 against the upper
support 102 in
response to tightening of threaded bolts 120 into corresponding threaded
channels (not
shown) in the body 114'. The locking assembly 104' further includes a raised
surface 126 in
the passage 115 opposite the translational member 117, implemented as a ledge
(i.e., a flat
surface against which the upper support 102 is held upon engaging the lock
116'. Other
embodiments of lock 116, 116' may employ corresponding nuts or the like, use
clasps or
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-8-
other fasteners, or operate using rotational versus translational motion. Any
type of fastener
may be used to engage the lock 116, 116'.
[0031] Referring to FIGS. 1 & 3, the electrical system is routed through the
lower and upper
supports and provides power to the attached light fixture 122. Embodiments of
the present
disclosure may also include wiring 112 interior to the upper and lower support
members and
the guide member. Guide member 108 may be implemented as fluid-tight
electrical conduit
or similar fluid-tight tubular. Additionally or alternatively to guide member
108, wiring
chamber 160 may be interior to the lower support 106, as described below with
reference to
FIG. 6.
[0032] FIGS. 5A-5D illustrate a base in accordance with embodiments of the
present
disclosure. Base 130 includes a channel 140 between the first end of the base
132 and a
second end of the base 134. Base 130 is configured for coupling with fluid-
tight tubular (e.g.,
electrical conduit) and the lower support 106 at their corresponding ends
opposite the locking
assembly 104. Upon being coupled with the tubular and channel in fluid-tight
communication with the fluid-tight electrical conduit. Threaded connections
144 and 146
enable sealing engagement with the conduit and the lower support 106,
respectively. Upon
connection, base 130 is configured to isolate the interior of the fluid-tight
electrical conduit
from the annular space 109 between the lower support 106 and the guide member
108.
Threaded connection 142 at the second end 134 enables sealing engagement with
interior of
junction box 150. Weep holes 136 allow condensation or other moisture to drain
from the
annular space 109.
[0033] Referring to FIG. 6, wiring chamber 160 may comprise electrical conduit
or the like,
but may not be necessary for guiding biasing member 110 or upper support 102.
Wiring
chamber may include an adaptor 162. In some embodiments, the adaptor 162 and
the wiring
chamber 160 (or guide member 108) may be coupled through threaded engagement.
Wiring
seal 164 may be used to prevent ingress of moisture into wiring chamber 160
(or guide
member 108). Wire 112 includes an elastically coiled portion 166, which is
configured to
conform to a length of a portion of the upper support above the locking
mechanism. The
elastically coiled portion 166 is configured such that, when the upper support
102 is lowered,
the portion 166 will re-coil, thus preventing wiring 112 from bunching along
the interior
surface of the wiring chamber 160 (or guide member 108).
CA 02931712 2016-05-25
WO 2015/077732
PCT/US2014/067194
-9-
[0034] The light fixture 122 is connected to the upper support 102. The
illumination source
of the light fixture 122 is powered through a connection to the electrical
system, comprising a
power source and wiring 112. The power source can be externally supplied or
provided in a
base, which may act as a support for the first pole. The wire is protected
within the supports.
More specifically, the wire is housed in the guide member or wiring chamber of
the lower
support and the interior chamber of the upper support. This positioning
separates the wire
from the spring assist system (e.g., biasing member 110). The provision of a
separate
housing for the wiring 112 is prevents the wire from interacting with or
becoming damaged
by the spring assist. In addition, the sealed conduit of the guide member or
wiring chamber
protects the wire from moisture, which can also be problematic.
[0035] FIGS. 7A-7L illustrate various modes of use including wall mounting and
spring
mounting. As will be apparent, various means of mounting the pole support
system described
above will occur to those of skill in the art.
[0036] Features of the present disclosure have been referred to herein using
modifiers such as
"upper" and "lower." These terms are used purely for convenience of
description. As would
be apparent to those of skill in the art, elements of the present disclosure
may be installed and
operate at various angles. Further, the elements described above as upper,
lower, on top of,
below, and the like may be reversed. FIG. 8 illustrates a pole support system
for industrial
lighting in accordance with embodiments of the present disclosure. Pole
support system 800
comprises an upper support 806, a telescoping lower support 802 which retracts
into the
upper support 806 via the locking assembly. It is readily apparent that this
configuration will
have different associated advantages and disadvantages than the configurations
above, but
will operate in a similar manner by the telescoping support in conjunction
with the spring
assist.
[0037] The discussion above has focused primarily on embodiments of the
disclosure for use
with industrial light poles. Other embodiments may be used with other types of
elongate
objects, or in other environments. It should be understood that the inventive
concepts
disclosed herein are capable of many modifications. To the extent such
modifications fall
within the scope of the appended claims and their equivalents, they are
intended to be
covered by this patent.