Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2942712 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | CHUTE OR IMPACT WALL FOR USE IN OPENCAST MINING, COMPRISING A HEATING DEVICE |
| (54) French Title: | GOULOTTE OU PAROI DEFLECTRICE EQUIPEE D'UN DISPOSITIF CHAUFFANT POUR L'EXTRACTION A CIEL OUVERT |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | KIRBY EADES GALE BAKER |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 2015-03-06 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 2015-09-17 |
| Examination requested: | 2016-09-26 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/EP2015/054729 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO 2015135849 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2016-09-14 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
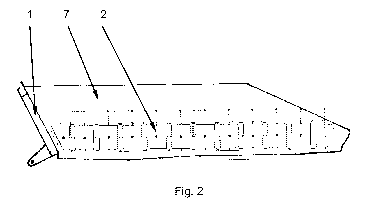
The invention relates to a heating device, wherein, according to the invention, flexible heating elements (2), which can be adapted in the size and shape thereof to the contour of the surface to be heated, are arranged on the side of the chute (1) or of the impact wall facing the conveyed material. The flexible heating elements are arranged between wall elements (7) and wear-protection elements, wherein the wear-protection elements lie on spacing plates and centrally on a support plate by means of edge surfaces of the wear-protection elements and the flexible heating elements (2) are thus protected against contact with the conveyed material. The sticking and freezing of conveyed material to chutes and impact walls are prevented by using the heating device.
Le dispositif chauffant selon l'invention comprend des éléments chauffants souples (2), de taille et de forme adaptables au contour de la surface à chauffer, qui sont disposés sur le côté de la goulotte (1) ou de la paroi déflectrice tourné vers le produit transporté. Les éléments chauffants souples sont disposés entre des éléments de paroi (7) et des éléments de protection contre l'usure. Ces éléments de protection contre l'usure reposent par leurs surfaces de bord sur des plaques d'écartement et au centre sur une plaque de soutien, protégeant ainsi les éléments chauffants souples (2) du contact avec le produit transporté. L'utilisation du dispositif chauffant permet d'empêcher le produit transporté de geler et de coller aux goulottes et aux parois déflectrices.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2019-02-28 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2019-02-28 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2018-03-06 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2018-02-28 |
| Change of Address or Method of Correspondence Request Received | 2018-01-09 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2017-08-28 |
| Inactive: Report - QC passed | 2017-08-10 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2016-10-27 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2016-10-05 |
| Letter Sent | 2016-10-04 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2016-10-03 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 2016-09-29 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2016-09-26 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2016-09-26 |
| Request for Examination Received | 2016-09-26 |
| Application Received - PCT | 2016-09-23 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2016-09-23 |
| National Entry Requirements Determined Compliant | 2016-09-14 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2015-09-17 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-03-06 |
The last payment was received on 2017-01-30
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Please refer to the CIPO Patent Fees web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 2016-09-14 | ||
| Request for examination - standard | 2016-09-26 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 2017-03-06 | 2017-01-30 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| TAKRAF GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| STEFFEN NOWAK |
| THOMAS STENZEL |