Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
=
FLUID LEVEL VISUALIZATION SYSTEMS
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION
100011 The present application claims priority to U.S. Provisional
Application No.
62/255,053 filed on November 13, 2015, which is hereby incorporated herein by
reference.
FIELD
100021 The present disclosure relates to fluid level visualization systems,
specifically
fluid level visualization systems that include sight gauges.
BACKGROUND
100031 Objects, equipment, machines, and/or gearboxes often require that a
proper fluid
level or lubrication level be maintained and conditioned for safe and
effective operation.
Maintaining the proper fluid level can reduce friction, over-heating,
contamination, and wear of
the internal mechanical components, and failure to maintain the proper fluid
level can result in
failure of the object and/or costly repairs. Often, objects themselves are
opaque or are fully
enclosed with opaque housings or enclosures that make visually inspecting the
fluid level in the
object difficult. Accordingly, fluid level sight gauges are commonly used to
display the fluid
level in the object.
100041 The following U.S. Patents disclosed example fluid level
visualization systems
and example sight gauges.
100051 U.S. Patent No. 5,442,959 discloses a sight gauge placed between two
spaced
apart compression type fittings connected to a vessel to show the liquid level
in the vessel. The
sight gauge has an elongated tubular transparent tube shield and a slightly
longer elongated
transparent sight tube that is received within the sight tube shield. An upper
and a lower
connection plate are each telescopically received by the sight tube, the sight
tube shield being
captured between the connection plates. An upper and a lower nozzle member
each have an
opening to respectively capture the upper and lower ends of the sight tube. An
upper and lower
elastomeric 0-ring is received on the sight tube positioned between the
connection plates and the
-1-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
=
nozzle members. Bolts secure the nozzle member to the compression plates to
squeeze the 0-
rings against the sight tube so that the sight tube retains and supports the
tube shield. Each
nozzle member has an elongated tubular portion that can be received in a
compression fitting.
[0006] U.S. Patent No. 6,758,092 discloses a fluid level verification
apparatus for use on
liquid filled containers and configured to reduce inherent mechanical stresses
on the inspection
tube and resist leakage due to environmental, chemical, thermal or mechanical
expansion cycles
by using a protective shield member to encase the inspection sight member, and
also a method
for permanently sealing the fluid level detection apparatus.
100071 U.S. Patent No. 6,928,716 discloses a fluid level verification
apparatus for use on
liquid filled containers and configured to reduce inherent mechanical stresses
on the inspection
tube and resist leakage due to environmental, chemical, thermal or mechanical
expansion cycles
by using a protective shield member to encase the inspection sight member. and
also a method
for permanently sealing the fluid level detection apparatus.
SUMMARY
[0008] This summary is provided to introduce a selection of concepts that
are further
described herein below in the detailed description. This summary is not
intended to identify key
or central features of the claimed subject matter, nor is it intended to be
used as an aid in limiting
the scope of the claimed subject matter.
[0009] In certain examples. a sight gauge assembly for displaying a fluid
level of an
object includes a first connection member comprising a tap defining a bore
therethrough and
configured to extend through a housing of the object and a body comprising a
first
passageway and a second passageway wherein the first passageway fluidly
connects to the
second passageway and the bore through an interior of the body and the second
passageway
configured to fluidly communicate with the first bore and a first accessory; a
second
connection member comprising a tap defining a bore therethrough and configured
to extend
through the housing of the object and a body comprising a first passageway
fluidly connected
to the bore through an interior of the body of the second connection member;
and a sight tube
defining a hollow interior. The sight tube couples to the first connection
member and the
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
second connection member to define a first flow path through the hollow
interior of the sight
tube between the bore and first passageway of the first connection member and
the first
passageway and bore of the second connection member.
[0010] In certain examples, a fluid level visualization system includes a
first
connection member comprising a tap defining a bore therethrough and configured
to extend
through a housing and a body comprising a first passageway and a second
passageway, the
first passageway fluidly connected to the second passageway and the bore
through an interior
of the body and the second passageway configured to fluidly communicate with
the first bore
and a first accessory; a second connection member comprising a tap defining a
bore
therethrough and configured to extend through a housing, and a body comprising
a first
passageway -fluidly connected to the bore through an interior of the body of
the second
connection member; and a sight gauge assembly having a sight tube configured
to display a
fluid level and defining a hollow interior. The sight tube fluidly couples to
the first
passageway of the first connection member and the first passageway of the
second connection
member to define a first flow path through the hollow interior of the sight
tube between the
bore and first passageway of the first connection member and the first
passageway and the
bore of the second connection member. The fluid level visualization system
further includes a
first accessory coupled to the second passageway of the first connection
member such that the
first accessory fluidly communicates with the first flow path.
100111 In certain examples. a method of circulating the fluid through the
object
includes coupling a first connection member comprising a tap defining a bore
therethrough
and configured to extend through a housing of the object, coupling a second
connection
member comprising a tap defining a bore therethrough and configured to extend
through the
housing of the object, coupling a sight gauge assembly that has a sight tube
defining a hollow
interior to a first passageway of the first connection member and to a first
passageway of the
second connection member to define a first flow path through the hollow
interior of the sight
tube between the bore and first passageway of the first connection member and
the first
passageway and bore of the second connection member, coupling a first
accessory to the
second passageway of the first connection member such that the first accessory
is fluidly
-3-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
connected to the first flow path, coupling a second accessory to the second
passageway of the
second connection member such that the second accessory is fluidly connected
to the first
flow path, coupling a circulation system to the first accessory and the second
accessory to
define a second flow path parallel to the first flow path and between the
first connection
member and the second connection member, and circulating the fluid from the
object in a
second flow path with the circulation system, the fluid circulating in the
second flow path out
of the object through the second connection member and the second accessory
and back into
the object through the first accessory and the first connection member.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
100121 The present disclosure is described with reference to the following
Figures.
The same numbers are used throughout the Figures to reference like features
and like
components.
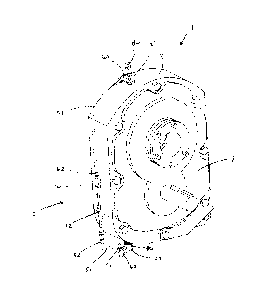
[0013] FIG. I is an example of a fluid level visualization system.
[0014] FIG. 2 is a front perspective view of a connection member.
[0015] FIG. 3 is a rear perspective view of the connection member of FIG.
2.
100161 FIG. 4 is a cross section view of the connection member of FIG. 2
taken on 4-4
shown in FIG. 3.
[0017] FIG. 5 is an exploded view of a sight gauge assembly.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0018] Referring to FIG. 1, a fluid level visualization system 1 includes a
sight gauge
assembly 10 that is coupled to an object 2 (e.g. a gearbox, oil drum). The
sight gauge assembly
is configured to display a fluid level of a fluid (e.g. oil, lubricant)
contained in the object 2.
The object 2 includes a housing 3 that defines an interior space (not shown)
that is configured to
hold the fluid. The housing 3 can define any number of holes or openings that
allow an operator
to fill the object 2 with fluid and/or drain fluid from the object 2. In one
non-limiting example,
the object 2 includes a fill opening (not shown) and a drain opening (not
shown). Any number of
openings can be defined in the housing 3. Other accessories or devices, such
as ventilators,
-4-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
desiccant breathers, fluid circulation systems, etc., can be coupled to the
object 2 such that
accessories or devices fluidly communicate with the openings. Furthermore, the
openings can be
used to extract a sample of the fluid from the object 2 for analysis (i.e.
chemical and/or visual
analysis). However, an object 2 with multiple openings defined in the housing
3 can increase the
risk of fluid leaks and/or debris (e.g. dust, drill shavings) entering the
interior space defined by
thc housing 3. Accordingly, the present inventor has endeavored to minimize
the number of
openings defined in the object 2 and/or use a single opening for multiple
purposes (e.g. multiple
accessories and/or devices fluidly communicate with the interior space defined
by the object 2
via a single opening, fill the object 2 with the fluid, drain fluid from the
object 2, extract a
sample of the fluid from the object 2). As such, the present inventor has
invented the fluid level
visualization system 1 that has a sight gauge assembly 10 which displays the
fluid level in the
object 2, reduces of the number of opening.s that must bc defined in the
housing 3 of the object
2, and increases number of accessories and/or devices that can fluidly
communicate with a single
opening.
[0019] The sight gauge assembly 10 includes a pair of connection members
21, 22 that
are configured to couple to the housing 3 of the object 2. When coupled to the
object 2, the first
connection member 21 is spaced apart from the second connection member 22.
Preferably, the
first connection member 21 is coupled to the housing 3 vertically above a
fluid level of a fluid
within the object and the second connection member 22 is coupled to the
housing 3 vertically
below the fluid level of the fluid within the object. The sight gauge assembly
10 includes a sight
tube 12 fluidly connected between the first connection member 21 and the
second connection
member 22. The sight tube 12 is exemplarily positioned to be vertically or
horizontally
oriented (depending upon the configuration of object 2) to be in positional
alignment with the
fluid level of the fluid contained in the interior space defined by the object
2. Due to the fluid
connection between the interior of the object 2 and the sight tube 12, the
sight tube 12
provides an indication representative of the fluid level of the fluid within
the object 2.
100201 In addition, preferably, the first connection member 21 and/or the
second
connection member 22 are coupled to the housing 3 at existing opening(s)
defined in the housini2,
3. Additional opening(s) (i.e. a new openings(s)) can be further defined in
the housing 3 (e.g. a
-5-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
new opening can be defined in the housing 3 by drilling) to accommodate the
first connection
member 21 and/or the second connection member 22, if needed. In certain
examples, the
connection member 21, 22 includes screw threads that engage with the object 2
to couple the
connection member 21, 22 to the object 2. In still further embodiments, the
connection members
21, 22 may be secured to the object 2, for example by =friction fit or
welding.
[0021] FIGS. 2-4 depict an exemplary embodiment of first connection member
21. It
will be recognized that second connection member 22 (FIG. 1) may exemplarily,'
be the same as
first connection member 21 and therefore the description herein of connection
member 21 may
similarly apply to embodiments of second connection member 22. The first
connection member
21 and/or the second connection member 22 can include any other components
and/or features
as depicted an/or described with reference to FIGS. 2-4. It will further be
recognized that in other
embodiments, the first connection member 21 and the second connection member
22 may differ
from each other while both remaining within the scope of the present
disclosure.
[0022] The connection member 21 exemplarily comprises a body 23 and a tap
40 that
extends away from the body 23. The body 23 is exemplarily a polyhedron in the
example
depicted, although it will be recognized that the connection member 21 and
body 23 may take
other shapes while remaining within the scope of the present disclosure. The
exemplary
polyhedron shape of the body 23 is provided by an end 33 opposite the tap 40.
Side 35 is
exemplarily opposite side 37, and both side 35 and side 37 are orthogonal to
the cnd 33. The
body 23 further includes a face 31, which is exemplarily orthogonal to the
sides 35, 37 and
angled relative to the end 33. In an exemplary.' embodiment, the face 31 and
the end 33 form an
obtuse angle B.
[0023] The tap 40 is configured to extend through the housing 3 of the
object 2, when
the connection member 21 is mounted to the object 2. The tap 40 is configured
with threads 42
for an exemplary threaded connection with the housing 3, although it will bc
recognized as noted
above that the tap 40 may be connected in a fluid-fiat manner through the
housing 3 in a variety
of ways as will be recognized by a person of ordinary skill in the art. The
tap 40 includes a bore
44 that creates a fluid connection between the inside of the housing 3 and the
interior 46 (Fig. 4)
of the connection member 21.
-6-.
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
=
[0024] The connection member 21 includes a plurality of ports as described
herein that
fluidly connect to the interior 46 of the connection member 21 by way of a
plurality of passages.
A face passageway 26 exemplarily extends into the connection member 21 from a
face port 32
in the face 31. Side passageways 24, 29 extend into the connection member 21
respectively from
side ports 36, 38 in the sides 35, 37. An end passageway 28 extends into the
connection member
21 from an end port 34 in the end 33. In an exemplary embodiment, the
passageway 26 extends
perpendicular to face 31, passageway 24 extends perpendicular to side 35,
passageway 29
extends perpendicular to side 37, and passageway 28 extends perpendicular to
cnd 33.
100251 As best depicted in FIG. 4, in an exemplary embodiments each of the
ports 32,
34, 36. 38 are positioned offset from a central axis 48 of the bore 44. In an
exemplary
embodiment, the centers of side ports 36, 38 and the end port 34 are all
offset from the central
axis 48 in a direction opposite from the face 31. The entire face 31 is
exemplarily offset from the
central axis 48 of the bore 44, therefore it logically follows that the center
of the face port 32
may similarly be offset from the central axis 48. In a still further exemplary
embodiment, the
center of the face port 32 is outside of the circumference of the tap 40, as
the face 31 extends in a
direction beyond the tap 40.
[0026] By way of the connection member 21, the fluid connection between the
inside of
the housing 3 is established through the bore 44 and the interior 46 to each
of the passageways
24, 26, 28, 29. The flow of fluid may be either into or out of the object 2
through the fluid
connection provided by the connection member 21, 22 as described in further
detail herein. This
provides a flexibility and an adaptability to the connection member 21, 22 to
simultaneously
support a sight gauge assembly 10 as described in further detail herein along
with a plurality of
accessories.
100271 Referring back to FIG. 1, the sight tube 12 defines a hollow
interior (not
shown), and the sight tube 12 is coupled to the connection members 21, 22 such
that the
hollow interior fluidly communicates with one of the passageways 24, 26, 28,
29 of the
connection members 21, 22. In an exemplary embodiment, the sight tube 12 is
fluidly
connected to one of the side passageways 24, 29. In an exemplary embodiment,
the selection
of one of the side passageways 24, 29 can position the sight tube 12 to least
obstruct access to
-7-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
==
the other passageways of the connection members 21, 22. The hollow interiors
46 of the
connection members 21, 22 in combination with the sight tube 12 of the sight
gauge assembly
define a flow path through which the fluid in the object 2 can flow such that
the fluid level
of the fluid in the object 2 is displayed. For example, when the first
connection member 21
and the second connection member 22 are positioned vertically above and below,
respectively,
the fluid level of the fluid in thc object 2 and the sight tube 14 is
vertically positioned between
the first connection member 21 and the second connection member 22, the fluid
flows into the
sight tube 12 such that the fluid level is displayed by the sight tube 12. The
sight tube 12 is
transparent and configured to display the fluid level. The sight gauge
assembly 10 includes a
guard 16 configured to partially surround the sight tube 12 and protect the
sight tube 12.
[0028] As will
be described in further detail herein with respect to FIG. 5, the
passageways 24, 26, 28, 29 are each configured to receive any of a plurality
of accessories which
may be described in further detail herein. In an exemplary embodiment, the
ports 32. 34, 36. 38
and passageways 24, 26, 28, 29 exemplarily comprise a plurality of different
diameters. In a non-
limiting exemplary embodiment, the side ports 36, 38 and the end port 34 are
exernplarily 1/4
inch in diameter, while the face port 32 is exemplarily 1/2 inch in diameter.
It will be recognized
that in other embodiments other diameters and/or other combinations of
diameters may be used.
The respective ports/passageways may exemplarily be threaded, such as to
threadingly receive
the accessories as described in further detail herein, in addition to the
sight gauge assembly 10.
The ports/passageways may exemplarily allow an operator to extract (or drain)
a sample of the
fluid from the object for analysis. In still
further exemplary embodiments, the
ports/passageways may be configured for other forms of fluid-tight
connections, for example
friction fit.
100291 In
exemplary embodiments, an adapter 80 accommodates connection of an
accessory (e.g. a desiccant breather) of an exemplary different diameter or
connection method to
an available port of the connection member 21, 22. By way of the interior 46
of the connection
members 21, 22 the bore and the passageways 24, 26, 28, 29 can fluidly
communicate with each
other such that fluid flow into and between the passageways 24, 26, 28, 29.
Therefore, in another
exemplary embodiment, one or more of the passageways 24, 26, 28, 29 may be
used as a drain.
-8-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
100301 Referring to FIG. 5, the sight gauge assembly 10 furthcr includes
tubes or
piping 51 and/or a plurality of fittings that couple the sight tube 12 and/or
the guard 16 to the
connection members 21, 22, as described above. The piping 51 and the fittings
allow the
operator to manipulate construction of the sight gauge assembly 10 such that
the sight gauge
assembly 10 can be used with any type of object 2. For exatnple, a large
length of piping 51
can be utilized to ensure that the sight tube 12 (see FIG. 1) is positioned in
an accessible and
operable position (i.e. the sight tube 12 can be accessed by the operator and
the level of the
fluid is indicated or displayed by the sight tube 12). The piping 51 can be
made of any suitable
material such as plastic, rubber, and/or the like, and the piping 51 is
malleable (i.e. the piping 51
can be bent, stretched, and/or compressed). In one example, the piping 51 is
made of brass and
has a 3/8 inch outside diameter. The type of fittings can vary, and the sight
gauge assembly 10
may include one type of fitting or a combination of several types of fittings.
The fittings can be
adhesive fittings, compressive fittings, welded connections, clamping devices,
and/or the like.
Preferably, the fittings are liquid tight and NTP or NPTF certified. In one
exemplary
embodiment, linear compressive fittings 52 couples first ends of the piping 51
to the sight tube
12 and/or the guard 16 and elbow compressive fittings 53 couple opposite
second ends of the
piping 51 to the connection members 21, 22. The elbow compressive fittings 53
enable the
operator to rotate and/or position the sight tube 12 and/or guard 16 relative
to the connection
members 21, 22. The elbow compressive fittings 53 also enable the operator to
manipulate
construction of the sight gauge assembly 10 to such that the sight tube 12
provides an indication
representative of the fluid level within the object 2, as described above.
100311 The connection members 21, 22 of the sight gauge assembly 10 are
configured
to received and/or couple with accessories such that the accessories fluidly
connect with the
interior space of the object 2, the passages of the connection members 21, 22
and/or the first
flow path (as described above) that extends through the sight tube 12. 'fhe
type and number of
accessories can vary, and the accessories are configured with threads for an
exemplary threaded
connection with the connection members 21, 22, although it will be recognized
that the
accessories may be connected in a fluid-tight manner in a variety of ways as
will be recognized
by a person of ordinary skill in the art. The types of accessories that can be
utilized include, but
-9-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
are not limited to, fluid piping, ventilation systems, fluid circulation
systems, air hoses, valves
(including ball valves, check valves, quick disconnect valves 61, 62, etc.),
adapters 80, close
nipples 84, socket plugs 86, and/or the like.
100321 In an exemplary embodiment, first quick disconnect valve 61 is
coupled to the
first connection member 21 and the second quick disconnect valve 62 is coupled
to the second
connection member 22 such that a fluid circulation system (not shown) can be
coupled to the
quick disconnect valves 61, 62. The fluid circulation system is configured to
draw the fluid
contained in the object 2 out through second connection member 22 and further
convey the fluid
to the first connection member 21 such that the fluid returns back to the
object 2 thereby
circulating the fluid through the object 2. As the fluid is conveyed between
quick disconnect
valves 61, 62 the fluid can be processed in any number of ways including
filtration, heating,
adding chemical additives, and/or adding supplemental or new fluid. The fluid
circulation
system defines a second flow path that is parallel to the first flow path. In
certain examples, the
fluid circulation system is a kidney loop filtration system that draws the
fluid from the object 2,
filters the fluid, and returns the fluid to the object 2. In certain examples,
the fluid circulation
system applies a sucks or draws the fluid out of the object via a quick
disconnect valve and/or a
connection member.
100331 In another exemplary embodiment, an adapter 80 is configured to
provide a
connection for devices that are not capable of directly coupling to the first
connection member
21 (e.g. the threads of the device are different than the treaded connection
of the first connection
member 21). The adapter 80 includes a first end that couples with the first
connection member
21 and a second end opposite the first end that couples with and/or receive
the device such as to
fluidly connect the device to the passages defined by the first connection
member 21. In another
exemplary embodiment, close nipples 84 having two male connection ends are
coupled to the
connection members 21, 22 to allow accessories having female connections to be
coupled to the
connection members 21, 22.
100341 In another exemplary embodiment, socket plugs 86 are configured
couple to the
connection members 21, 22 to block flow of the fluid through a passage.
Multiple socket plugs
can be coupled to connection members 21, 22 to block passages and ports when
the passages
-10-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
and/or ports are not in use (i.e. when an accessory is removed from the
connection member 21,
22). The socket plugs 86 can be utilized as drain plugs (i.e. the fluid may
drain from the object 2
when the socket plug 86 is removed) and/or sample taps (i.e. the socket plug
86 can be removed
so that sample of the fluid in the object 2 can be extracted or drained for
analysis)
[0035] The present disclosure includes methods for displaying the fluid
level of the
fluid in the object and methods of circulating the fluid through the object.
The methods can
include coupling a first connection member comprising a tap defining a bore
therethrough and
configured to extend through a housing of the object, coupling a second
connection member
comprising a tap defining a bore therethrough and configured to extend through
the housing of
the object, coupling a sight gauge assembly that has a sight tube defining a
hollow,' interior to a
first passageway of the first connection member and to a first passageway of
the second
connection member to define a first flow path through the hollow interior of
the sight tube
between the bore and first passageway of the first connection member and the
first
passageway and bore of the second connection member, coupling a first
accessory to the
second passageway of the first connection member such that the first accessory
is fluidly
connected to the first flow path, coupling a second accessory to the second
passageway of the
second connection member such that the second accessory is fluidly connected
to the first
flow path, coupling a circulation system to the first accessory and the second
accessory to
define a second flow path parallel to the first flow path and between the
first connection
member and the second connection member, and circulating the fluid from the
object in a
second flow path with the circulation system, the fluid circulating in the
second flow path out
of the object through the second connection member and the second accessory
and back into
the object through the first accessory and the first connection member.
[0036] In the above description, certain terms have been used for brevity,
clarity, and
understanding. No unnecessary limitations are to be inferred therefrom beyond
the
requirement of the prior art because such terms are used for descriptive
purposes and are
intended to be broadly construed. The different apparatuses, systems, and
method steps
described herein may be used alone or in combination with other apparatuses,
systems, and
-11-
CA 02948327 2016-11-14
methods. It is to be expected that various equivalents, alternatives and
modifications are
possible within the scope of the appended claims.
100371 This
written description uses examples to disclose the invention, including the
best mode, and also to enable any person skilled in the art to make and use
the invention. The
patentable scope of the invention is defined by the claims, and may include
other examples
that occur to those skilled in the art. Such other examples are intended to be
within the scope
of the claims if they have structural elements that do not differ from the
literal language of the
claims, or if they include equivalent structural elements with insubstantial
differences from
the literal languages of the claims.
-17-