Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1
AGRICULTURAL HEADER WITH GROUND ENGAGING GAUGE MEMBERS FOR
ABOVE GROUND CUTTING
The present invention relates to an agricultural header for cutting a
standing crop where the header includes ground engaging gauge members in the
form
of skids or wheels for supporting the cutter bar at a position spaced from the
ground.
BACKGROUND
US 6,675,568 by Patterson et al discloses and US 8,245,489 by Talbot
discloses a height control arrangement using gauge wheels supported at
opposing
ends of a rigid header. The gauge wheels serve to minimize any substantial
deviations
from a central controlled height of the header at the outboard ends of the
header,
however the system is only effective when used on a rigid header or a flexible
header
which is kept rigid. Published Application 2016/0183461 published June 30 2016
by
Neudorf discloses a gauge wheel system for attachment to a harvesting header.
The
disclosures of the above documents may be referenced for more detail.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided a crop
harvesting header comprising:
a main frame structure extending across a width of the header;
a connection assembly carrying the main frame structure on a propulsion
vehicle in movement in a forward direction generally at right angles to the
width across
ground including a crop to be harvested;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
2
a crop receiving table carried on the main frame structure across the width
of the header;
a cutter bar across a front of the table which moves through the crop in a
cutting action and carrying a sickle knife which cuts the crop as the header
is moved
forwardly;
a skid element engaging the ground adjacent the cutter bar;
the skid element extending along the length of the cutter bar so that the
cutter bar is supported adjacent the ground as the skid element slides over
the ground;
a crop transport system on the table;
the harvesting header having a first position of the header in which the
skid element engages the ground and a second position of the header in which
the skid
element is raised away from the ground;
the main frame structure including a center frame portion, a first wing
frame portion and a second wing frame portion;
the first wing frame portion being connected to the center frame portion
by a first pivot coupling which provides pivotal movement of the first wing
frame portion
relative to the center frame portion about a first pivot axis extending in a
plane parallel
to the forward direction;
the first pivot coupling acting to support weight from the first wing frame
portion while outboard weight from the first wing frame portion outboard of
the first pivot
coupling rotates the first wing frame portion about the first pivot coupling
in a downward
direction;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
3
the second wing frame portion being connected to the center frame
portion by a second pivot coupling which provides pivotal movement of the
second wing
frame portion relative to the center frame portion about a second pivot axis
extending
in a plane parallel to the forward direction;
the second pivot coupling acting to support weight from the second wing
frame portion while outboard weight from the second wing frame portion
outboard of
the second pivot coupling rotates the second wing frame portion about the
second pivot
coupling in a downward direction;
the connection assembly including a float suspension system connected
to the center frame portion providing a variable lifting force from the
propulsion vehicle
acting to support the main frame structure relative to the propulsion vehicle;
a first interconnecting float linkage connected between the center frame
portion and the first wing frame portion which communicates a first variable
lifting force
from the center frame portion to the first wing frame portion against the
outboard weight
of the first wing frame portion;
a second interconnecting linkage connected between the center frame
portion and the second wing frame portion which communicates a second variable
lifting force from the center frame portion to the second wing frame portion
against the
outboard weight of the second wing frame portion;
in the first position of the header with the skid element engaging the
ground, the float suspension system and first and second interconnecting
linkages
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
4
provide a downforce from the skid element on the ground which is balanced
between
the center frame portion and the first and second wing frame portions;
and a gauging system used in the second position of the header
comprising:
a first ground engaging member supported on the first wing frame
portion at a location spaced outwardly from the center frame portion engaging
the
ground so as to receive lifting forces from the ground;
a second ground engaging member supported on the second wing
frame portion at a location spaced outwardly from the center frame portion
engaging
the ground so as to receive lifting forces from the ground; and
additional ground engaging members supported on the main frame
structure proximate the center frame portion engaging the ground so as to
receive lifting
forces from the ground;
each of the ground engaging members having a surface arrangement
engaging the ground at a position rearwardly of the cutter bar and forwardly
of a rear of
the table with the first, second and additional ground engaging members in the
second
position of the header collectively supporting the skid element spaced above
the ground
while the first and second wing frame portions pivot relative to the center
frame portion
in response to changes in ground height;
a mounting assembly of the surface arrangements comprising an
elongate support member connected at a forward end rearwardly of the cutter
bar and
forward of the rear of the table by a pivot coupling providing f Of pivotal
movement about
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
5
an axis parallel to the cutter, the elongate support member extending
rearwardly from
the pivot coupling at the forward end;
an adjustment device which raises and lowers each elongate support
member to raise and lower the surface arrangement between said first and
second
positions of the header;
wherein, in the first position of the header, each of the surface
arrangements is fully retracted by raising of the elongate support member to a
height
underneath the table in which the skid element engages the ground.
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided a crop
harvesting header comprising:
a main frame structure extending across a width of the header;
a connection assembly carrying the main frame structure on a propulsion
vehicle in movement in a forward direction generally at right angles to the
width across
ground including a crop to be harvested;
a crop receiving table carried on the main frame structure across the width
of the header:
a cutter bar across a front of the table which moves through the crop in a
cutting action and carrying a sickle knife which cuts the crop as the header
is moved
forwardly;
a skid element engaging the ground adjacent the cutter bar;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
6
the skid element extending along the length of the cutter bar so that the
cutter bar is supported adjacent the ground for cutting crop close to the
ground as the
skid element slides over the ground;
a crop transport system on the table;
the harvesting header having a first position of the header in which the
skid element engages the ground and a second position of the header in which
the skid
element is raised away from the ground;
and a gauging system used in the second position comprising a plurality
of ground engaging member each supported on the main frame structure engaging
the
ground so as to receive lifting forces from the ground;
each of the ground engaging members having a surface arrangement
engaging the ground at a position rearwardly of the cutter bar and forwardly
of a rear
edge of the table withi the ground engaging members in the second position of
the
header collectively supporting the skid element spaced above the ground;
a mounting assembly of the surface arrangements comprising an
elongate support member connected at a forward end rearwardly of the cutter
bar and
forward of the rear of the table by a pivot coupling providing fef pivotal
movement about
an axis parallel to the cutter, the elongate support member extending
rearwardly from
the pivot coupling at the forward end;
an adjustment device which raises and lowers the elongate support
member to raise and lower the surface arrangement between said first and
second
positions of the header;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
7
and wherein the connection assembly includes a tilt cylinder connected
to the main frame structure of the header which tilts the main frame structure
and the
cutter bar carried thereby forwardly and rearwardly about an axis parallel to
the cutter
bar;
and wherein in the second position of the header with the surface
arrangement lowered and the main frame structure tilted rearwardly is located
at a
cutting height from the ground of greater than 12 inches.
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided a crop
harvesting header comprising:
a main frame structure extending across a width of the header;
a connection assembly carrying the main frame structure on a propulsion
vehicle in movement in a forward direction generally at right angles to the
width across
ground including a crop to be harvested;
a crop receiving table carried on the main frame structure across the width
of the header;
a cutter bar across a front of the table which moves through the crop in a
cutting action and carrying a sickle knife which cuts the crop as the header
is moved
forwardly;
a skid element engaging the ground adjacent the cutter bar;
the skid element extending along the length of the cutter bar so that the
cutter bar is supported adjacent the ground for cutting crop close to the
ground as the
skid element slides over the ground;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
8
a crop transport system on the table;
the harvesting header having a first position of the header in which the
skid element engages the ground and a second position of the header in which
the skid
element is raised away from the ground;
and a gauging system used in the second position comprising a plurality
of ground engaging member each supported on the main frame structure engaging
the
ground so as to receive lifting forces from the ground;
each of the ground engaging members having a surface arrangement
engaging the ground at a position rearwardly of the cutter bar and forwardly
of a rear
edge of the table with the ground engaging members in the second position of
the
header collectively supporting the skid element spaced above the ground;
a mounting assembly of the surface arrangements comprising an
elongate support member connected at a forward end rearwardly of the cutter
bar and
forward of the rear of the table by a pivot coupling providing pivotal
movement about an
axis parallel to the cutter, the elongate support member extending rearwardly
from the
pivot coupling at the forward end;
an adjustment device which raises and lowers the elongate support
member to raise and lower the surface arrangement between said first and
second
positions of the header;
wherein, in the first position of the header, each of the surface
arrangements is fully retracted by raising of the elongate support member to a
height
underneath the table in which the skid element engages the ground.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
9
The arrangements defined above are preferably used in a header
construction wherein:
the main frame structure includes a center frame portion, a first wing
frame portion and a second wing frame portion;
the first wing frame portion is connected to the center frame portion by a
first pivot coupling which provides pivotal movement of the first wing frame
portion
relative to the center frame portion about a first pivot axis extending in a
plane parallel
to the forward direction;
the first pivot coupling acts to support weight from the first wing frame
portion while outboard weight from the first wing frame portion outboard of
the first pivot
coupling rotates the first wing frame portion about the first pivot coupling
in a downward
direction;
the second wing frame portion is connected to the center frame portion
by a second pivot coupling which provides pivotal movement of the second wing
frame
portion relative to the center frame portion about a second pivot axis
extending in a
plane parallel to the forward direction;
the second pivot coupling acts to support weight from the second wing
frame portion while outboard weight from the second wing frame portion
outboard of
the second pivot coupling rotates the second wing frame portion about the
second pivot
coupling in a downward direction;
the mounting assembly includes a float suspension system connected to
the center frame portion providing a variable lifting force from the
propulsion vehicle
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
10
acting to support the main frame structure for floating movement relative to
the
propulsion vehicle;
a first interconnecting float linkage is connected between the center frame
portion and the first wing frame portion which communicates a first variable
lifting force
from the center frame portion to the first wing frame portion against the
outboard weight
of the first wing frame portion;
a second interconnecting linkage is connected between the center frame
portion and the second wing frame portion which communicates a second variable
lifting force from the center frame portion to the second wing frame portion
against the
outboard weight of the second wing frame portion;
in the first mode of operation with the skid element engaging the ground,
the float suspension system and first and second interconnecting linkages
provide a
downforce from the skid element on the ground which is balanced between the
center
frame portion and the first and second wing frame portions.
However the header can also be of a structure which uses a rigid frame
or where the frame is fixed so as to be rigid when used in a particular mode.
It is more preferable that the cutting height in the second mode is greater
than 14 inches.
Preferably in this arrangement the first and second ground engaging
members are mounted at respective outer ends of the first and second wing
frame
portions additional ground engaging members are mounted on the first wing
frame
portion closely adjacent to the pivot axis and closely adjacent the pivot
axis, and the
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
11
center frame portion is supported only by said float suspension system and not
by any
additional ground engaging members.
Preferably each of the elongate support members extends rearwardly
under the table to a rear end rearward of the table and there is provided an
upstanding
extendible member connected at a lower end to the elongate support member and
to
the frame structure above the lower end and rearward of the table to raise and
lower
the cutter bar relative to the ground.
Preferably the extendible member comprises a pair of telescopic
members with an outer with an inner member slidable within an outer member,
wherein
the inner member has a plurality of longitudinally spaced holes for receiving
a pin of the
outer member to locate the inner and outer members at an extension position
defined
by the selected hole, wherein the holes are spaced transversely of the inner
member
and the pin is carried on a rotatable member which acts when rotated to move
the pin
transversely across the outer member so that the transverse position of the
pin when
rotated acts automatically to select one of the holes of the inner member.
Preferably the main frame structure includes a frame beam and a plurality
of frame members located at spaced positions across the main frame structure;
each frame member extending from the frame beam in a first portion
downwardly behind the table and in a second portion forwardly under the table
to
support the cutter bar;
the second portion forming a channel member with a downwardly facing
open face;
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
12
the elongate support members each being located in a second portion of
a respective one of said frame members and extending rearwardly under the
table.
Preferably each of the ground engaging surface arrangements is located
under the table.
Thus one key feature is that the system mounts a skid or skid and wheel
on a long arm which is attached to an upstanding actuator at the rear of the
frame. Another key feature relates to the location and arrangement of the skid
and
wheel in relation to the fact that it is pivoted at the front on a lug at the
frame and is
carried on a beam which is attached to an upstanding adjustable leg (cylinder
or
telescope) at the back of the frame.
Another key feature relates to the location and arrangement of the skid
and/or wheel so that the wheel can be fully retracted to allow the header to
operate in
the first mode with the cutter bar and skid element on the ground..
Another key feature relates to the long skid which extends from the pivot
just behind the cutter bar right back to the rear of the table or at the
upstanding
adjustment post.
One system uses four wheel assemblies (one at each end of the header
and one adjacent to or more particularly just outside or just inside of the
two hinge
locations near the center of the header. The wheel assemblies pivot near the
cutter bar
and have a short skid that is part of the structure that the header rides on
when cutting
directly on or close to the ground. The adjustment of all four wheel
assemblies is done
at the rear of the header.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
13
The long skid, like the wheel assembly, is located at each end of the
header and also near each hinge point for a total of four skids. These skids
also pivot
at the cutter bar with an adjustment mechanism at the rear of the header.
For the height adjustment of the wheel/skids, this can be effected by a
mechanical adjustment using a telescoping tube with a series of holes and a
pin that
can be used to position the wheels or skids to a predetermined height. A
second option
is the use of hydraulic cylinders that replace the mechanical adjuster and a
switch in
the combine cab that allows the operator to adjust the wheel height using the
combine's
hydraulics.
For both the wheels and the skids using either the mechanical or hydraulic
adjuster, a maximum cut height of approximately 14 to 18 inches can be
achieved. In
addition, with the wheels or skids being fully retracted while remaining in
place on the
header, the operator can cut with the cutter bar/skid element touching the
ground
without ever needing to remove the wheels/skids from the header.
The three section frame is designed to cut on the ground and such that
the cutter bar pressure is consistent or balanced across the full length of
the cutter bar
by means of a balance linkage that uses the weight of the header to balance
the weight
of the wings. This works very well for crops like soybeans, peas, lentils,
where it is
desirable to cut as close to the ground as possible. In these crops, the
cutter bar is
skidded along the ground and the flex balance linkage and header float system
allow
the header to follow contours with minimal pressure between the cutter bar and
the
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
14
ground. Current standard skid shoes provide some cutter bar height adjustment
in the
order of up to 5 inches.
In crops like cereals it is sometimes desirable to cut at a height of up to
14 to 18 inches while following the ground contour. Furthermore, it is
desirable to easily
go from cutting at this height, and back to cutting on the ground with minimal
effort. It is
thus desirable for the device that allows for cutting off the ground to stay
on the header
when cutting on the ground, and for the adjustment to be quick and easy.
The device includes contour wheels or long skid shoes. It consists of four
separate assemblies located such that the skid shoe or wheel assembly make
contact
with the ground and cause the header to flex and follow the contour of the
ground, much
like the header does when cutting on the ground. The locations of the wheels
or long
skid shoes is such that they provide enough of a moment about the virtual
balance
points of the flex header to overcome friction and cause the header to flex.
This virtual
balance point is located on the header wing, approximately one third the
distance from
the hinge point to the end of the header.
There are a total of four wheel assemblies across the width of the header.
Two are at each end of the header, and two are near the hinge points as
displayed in
Figure 2. These locations ensures enough moment about the virtual balance
point of
the header to overcome friction and cause the header to flex. This allows the
operator
to use the header while in flex mode in order to achieve better ground
following while
cutting as high as 18 inches off the ground. Ground following was previously
only
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
15
possible while cutting with the cutter bar resting on the ground or else on
the short skid
shoes for a maximum height of 5 inches.
The wheel assemblies can also be used on a header that does not have
a flexing frame in that the frame is rigid or the flexing action is locked
out. In this case,
there may be only two assemblies used and the wheels allow the operator to
maintain
consistent cut height from pass to pass, however cut height variation can
still occur due
to changing ground contours across the width of the header.
The wheel assembly contains an isolator or suspension system to aid in
eliminating header bounce and stress on components as the wheels travel over
bumps
and other incompressible objects. One embodiment of the isolator consists of a
torsional rubber isolator which is mounted to the elongate support member that
spans
from the cutter bar to the rear adjuster. In this case, the wheel assembly
contains two
links bolted to the torsional isolator. As the wheel strikes an object, the
links convert
the force into a moment which causes the isolator to rotate and absorb the
load. Other
means of providing shock absorption such as a rubber block, or spring and
shock
absorber or accumulator can be used.
The means of adjusting the height of the wheel assembly can be a manual
adjuster or a hydraulic wheel height adjustment system. With the manual
adjuster, the
operator sets all four adjusters to a height which is close to the desired cut
height and
fine adjustments can then be made to the cut height by changing the tilt of
the header
using the tilt cylinder that attaches the header to the adapter. With the
hydraulic
adjustment which contains four hydraulic cylinders in a series circuit in a
master slave
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
16
arrangement, and a switch in the combine cab, the operator can adjust the
height of
the wheels by actuating the cylinders using the in cab switch while harvesting
and can
adjust the tilt to obtain an increase in the height using the same switch.
One embodiment of the manual adjuster includes two telescoping tubes
with a pin adjustment system to lock the position. In one embodiment, the
outer tube
utilizes a series of holes in a circular pattern with each of the holes
aligning with one of
the holes on the inner tube. This arrangement allows the user to select the
height of the
adjuster by pulling the pin and rotating the pin holder to the desired setting
after which
the inner tube can either be extended or retracted until the pin engages in
the hole on
the inner tube.
Where the ground engaging member comprises a long skid shoe, this
comprises a skid member positioned such that the header rides on the shoes
when in
cutting position. The operator may choose to retract the shoes such that the
header
can cut on the ground, effectively removing the long skid shoes from
operation. This
enables the operator to adjust cut height such that a desired stubble length
can be
achieved. The embodiment shown allows for a stubble height ranging from 1.25
inch
up to 14 inches. This allows a flexible or rigid header to maintain a
consistent cutter
bar to ground spacing. In the case of a rigid header, cut height can still
vary due to
uneven ground across the full width of the header. The skid may use metal,
poly, or
other desirable material as the ground contacting surface. This surface may be
either
permanent or replaceable. The means of adjusting the cut height is the same as
described above with the contour wheels by means of a manual or automatic
method,
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
17
either using hydraulic or electric components. The long shoe may either be
integrated
into standard short skid shoes near the front of the header, or exist in
addition to short
standard skid shoes.
In another embodiment, the device can comprise the long skid shoe, with
the addition of a ground-contacting wheel or wheels mounted on each side of
the skid.
The wheels can be permanently attached to the skid shoe, removable, or
retractable
as desired. The wheels may be supported in a variety of ways, including but
not limited
to a rotational damping arm. The wheel may consist of a variety of materials,
including
a solid material or a pneumatic wheel. The wheel may be fixed position or
include an
adjustable member such that the wheel's position in proximity to the shoe may
be
altered. The wheel may be used to increase the stubble height beyond the range
of
the shoe. In this embodiment, 18 inches can be achieved using the wheels. The
wheel
offers all of the benefits of the skid shoe, while increasing the life of the
device in
abrasive conditions, as well as reducing friction and increasing cut height.
Various embodiments of the invention will now be described in
conjunction with the accompanying drawings in which:
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a rear elevational view of a prior art multi-section header.
Figure 2 is a top plan view of the prior art multi-section header according
to Figure 1.
Figure 3 is an end elevational view of the multi-section header according
to Figure 1.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
18
Figure 4 is a schematic representation of the balancing linkage of the
multi-section header according to Figure 1.
Figure 5 is a schematic elevational view of the balancing linkage in
relation to the suspension system supporting the header according to Figure 1
on the
feeder house of a combine harvester.
Figure 6 is a isometric view of one gauge wheel assembly for use in the
harvesting header of Figures 1 to 5 according to the invention.
Figure 7 is a side elevational view of the gauge wheel assembly of Figure
6 located on a cross-sectional view of the header of Figures 1 to 5 showing
the gauge
wheel in the retracted position with the cutter bar in the ground position of
the first mode.
Figure 8 is a side elevational view of the gauge wheel assembly of Figure
6 located on a cross-sectional view of the header of Figures 1 to 5 showing
the gauge
wheel in the extended position with the cutter bar in the maximum raised
position of the
second mode.
Figure 9 is an enlarged view of the wheels and suspension of the
embodiment of Figures 6 to 8.
Figure 10 is an enlarged view of the extendible post of the embodiment
of Figures 6 to 8.
Figure 11 is a further enlarged view of the extendible post of the
embodiment of Figures 6 to 8.
Figure 12 is a isometric view of a second embodiment of one gauge wheel
assembly for use in the harvesting header of Figures 1 to 5 according to the
invention
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
19
where the resilient suspension arrangement is located at the rear.
Figure 13 is a cross-sectional view along the lines 13-13 of the
embodiment of Figure 12.
Figure 14 is a cross-sectional view along the lines 14-14 of the
embodiment of Figure 12.
In the drawings like characters of reference indicate corresponding parts
in the different figures.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Referring to the accompanying figures, there is illustrated a gauge system
generally indicated by reference numeral 5. The gauge system is particularly
suited for
use with an agricultural header 10 manufactured by Macdon Industries Ltd.
under the
model number FD70/FD75/FD1/FD2. US patent 6,675,568 by Patterson et al, the
disclosure of which may be referenced for more detail discloses the general
operation
of the header. For convenience, Figures 1 through 3 from US 6,675,568 are
attached
herewith and some of the description with regard to operation of the header
from US
6,675,568 is reproduced in the following.
FIGS. 1 and 2 show in rear elevational view and in plan view respectively
the header 10 carried on an adapter 11 attached to the feeder house 12 of a
combine
harvester. In FIG. 1 the adapter is omitted for convenience of illustration.
The header 10 includes a frame 13 defined by a main rear beam 14 and
a plurality of forwardly extending arms 15 which extend downwardly from the
beam14
and then forwardly underneath a table 16 which extends across the header. At
the
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
20
forward end of the table 16 is provided a cutter bar 17. On top of the table
16 is provided
a draper transport system 18 which carries the crop from the cutter bar across
the
header to a discharge location at the feeder house 12. The draper thus include
two side
drapers extending from respective ends of the header inwardly toward the
feeder house
and a center adapter section 188 which acts to feed the crop from the side
drapers 18A
rearwardly to the feeder housing.
Reference is made to prior application Ser. No. 09/810,425 filed Mar. 19,
2001 and to application Ser. No. 09/965,119 filed Sep. 28, 2001 which disclose
details
of the adapter and its inter relation to the side drapers 18A, the disclosure
of which may
be referenced for more detail.
The header further includes a reel 19 including a beam 19A on which is
mounted a plurality of reel bats (not shown) which are carried on the beam 19A
for
rotation with the beam around the axis of the beam. The beam is carried on
reel support
arms 19B which extend from the beam rearvvardly and upwardly to a support
bracket
attached to the transverse main beam 14. The reel arms can be raised and
lowered by
hydraulic cylinders 19D connected between the respective arm and the beam 14.
In the embodiment shown the reel is mounted on three arms 19B
including two arms at the ends of the header and a single center arm. However
additional arms may be provided so that there are four such arms with two
center arms
being spaced apart either side of the adapter 11. It is well known to provide
an
arrangement of the beam 19A and the bats which accommodate flexing movement of
the reel so that one end can be higher than the other end without damaging the
bats or
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
21
the reel structure. Various different arrangements for accommodating such
flexing
movement are known and can be incorporated into the arrangement described
herein,
as is well known to one skilled in the art.
The adapter 11 provides a center support for the header at a center frame
portion 10A and comprises a frame 20 which attaches to the feeder house 12 and
carries at its lower end a pair of forwardly extending pivotal arms 21 which
extend
forwardly underneath respective ones of the frame members 15 of the header.
The
pivotal arms 21 can pivot upwardly and downwardly about a respective pivot
pins 23
each independently of the other arm. Each arm is supported by a respective
spring 24
carried on a respective stub arm 25 attached to the respective arm 21. Thus
the spring
24 provides tension on the stub arm 25 pulling it upwardly around the pin 23
which acts
to pull up the respective arm 21and provide a lifting force underneath the
header at a
lifting point partway along the respective frame member 15 and underneath the
draper
18 and the table 16.
At the center of the adapter is provided a link 26 which extends from the
frame 20 forwardly to the central bracket 19C of the beam arm support
brackets. The
link 26 is provided in the form of a hydraulic tilt cylinder which allows
adjustment of the
length of the cylinder thus pivoting the header forwardly and rearwardly about
the
support point of the arms 21 on the underside of the header. Thus the attitude
of the
header, that is the angle of the table 16 to the horizontal can be tilted by
operation of
the cylinder forming the link 26.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
22
In addition the attitude of the header about an axis extending forwardly of
the direction of movement that is at right angles to the transverse beam 14 is
effected
by the independent pivotal movement of the arms 21 provided by the springs 24
which
act as a floatation system. In addition the whole header can float upwardly
and
downwardly on the springs 24 with the link 26 pivoting to accommodate the
upward and
downward movement and the arms 21 pivoting about the respective pin 23.
The table 16 provides behind the cutter bar 17 a skid plate 16A typically
including a polymeric wear shield which is arranged to engage the ground. Thus
upward
force is provided from the ground which tends to lift the header taking weight
off the
.. support springs 24. In practice the springs are adjusted so that the
springs act to support
the majority of the weight of the header leaving a relatively small proportion
of the weight
to rest on the ground. Thus the header can float upwardly and downwardly as
the
ground provides areas of different height with one end of the header being
movable
upwardly independently of the other end by independent flexing of the springs
24. Thus
the header tends to follow the ground level.
The header is formed in a number of sections which are independently
pivotal each relative to the next and in which adjustment of the lifting force
provided by
the springs 24 is transferred to each of the sections proportionally so that
each section
can float upwardly and downwardly and each section applies a force to the
ground
.. which is proportional to the total force of the whole header.
Thus the beam 14 is divided into a number of separate pieces depending
upon the number of sections of the header. In the embodiment shown there are
three
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
23
sections including a center frame portion or section 10A carried on the
propulsion
vehicle by the adapter or center support 11, a first wing frame portion or
section 10B
and a second wing frame portion or section 10C. The center section 10A is
mounted at
the adapter so that the arms 21 extend into engagement with the center
section. The
wing sections are pivotally connected to the center section such that each can
pivot
upwardly and downwardly about a respective pivot axis generally parallel to
the
direction of movement.
Thus the beam 14 is split into three portions each co-operating with a
respective one of the sections 10A, 10B and 10C and defining a main beam
therefor.
Each section of the beam 14 includes respective ones of the frame members 15
which
support the respective portion of the table. Thus as best shown in FIG. 1,
there is a
break between the beam sections 14 of the center section 10A and one wing
section
10B. The end most frame member 15A of the wing section 10B is arranged at the
break.
The end frame member 158 of the center section 10A is spaced inwardly from the
break
leaving space for a pivot coupling 27 extending from the frame member 15A to
the
frame member 15B and defining a pivot pin 27A lying on the pivot axis between
the
wing section 10B and the center section 10A. In a rear elevational view, the
cutter bar
17 is also visible underneath the header at the forward end of the frame
members 15
and at the front of the table 16.
In the embodiment shown the cutter bar 17 is split at a junction lying along
the axis of a hinge pin so as to provide a pivot within the cutter bar
allowing the cutter
bar to bend at the junction.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
24
In an alternative arrangement (not shown) the cutter bar can be formed in
a manner which allows it to flex on the axis of the pin thus avoiding the
necessity for a
break in the cutter bar.
The cutter bar is of conventional shape including a U shaped member
with generally horizontal legs and a front curved nose to which is attached
the knife
support flange of a conventional nature. The knife support flange includes a
plurality of
holes for mounting conventional knife guards.
A bridging link is connected across the break so as to hold the sections
of the cutter bar 17 aligned while the pivotal movement occurs. The link
comprises a
plate welded to one part of the cutter bar with the link or plates spanning
the break and
extending to a pin which is welded to the other part of the cutter bar with
the link being
held in place by a nut.
Thus the two sections 10A and 10B are supported each relative to the
other for pivotal movement of the wing section 10B about an axis extending
through the
hinge pin and through the break in the cutter bar 17 so that the wing section
is supported
at its inner end on the center section but can pivot downwardly at its outer
end so that
the weight at the outboard end is unsupported by the center section and causes
downward or counter clockwise pivotal movement of the wing section 10B.
The wing section 10C is mounted in an identical or symmetrical manner
for pivotal movement about the other end of the center section 10A. The amount
of
pivotal movement allowed of the wing section relative to the center section
about the
axis of the pivot pin is maintained at a small angle generally less than 6
and preferably
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
25
less than 40 as controlled by suitable mechanical stop members which are
provided at
a suitable location with the required mechanical strength to support the wing
frame
section against upward or downward movement beyond the stop members. Suitable
stop members can be designed by a person skilled in the art and the details of
the stop
members are not described herein.
The outboard weight of the wing section 10B is supported on an
interconnecting linkage 30 which communicates that weight from the inner end
of the
beam 14 of the section 10B through to the support for the center section 10A
at the
springs 24. The linkage is shown particularly in FIGS. 4 and 5 as described in
further
detail below.
In general the linkage operates to transfer the outboard weight of the wing
section inwardly to the center section and at the same time to balance the
lifting force
provided by the springs 24 so that it is proportionally applied to the center
section and
to the wing section.
Thus in general the header is attached to the combine feeder house using
the float system described previously that supports the header so that it can
be moved
up when a vertical force about 1% to 15% of its weight is applied to the
cutter bar from
the ground. The reaction of the float linkage that typically supports 85% to
99% of the
header weight on the header is used to balance the weight of the wings.
The system is designed so that if the operator sets the float so that the
float system supports 99% of the header weight then the remaining 1% will be
evenly
distributed across the cutter bar. If the operator changes the float so that
85% is
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
26
supported by the combine harvester then the remaining 15% would also be evenly
distributed across the cutter bar without the operator making adjustments.
Thus, not
only is the total lifting force to each sections varied in proportion to the
total lifting force
but also that lifting force on each section is balanced across the width of
section. As the
sections are rigid between the ends, this requires that the lifting forces be
balance
between the ends to ensure the even distribution across the cutter bar of each
section
and thus of all the sections. This provides an arrangement in which the force
required
to lift the header is the same force at any location along the length of the
cutter bar,
whether that location is at the center section, at a junction between the
center section
and the wing section or at the wing section. This is achieved in this
embodiment by the
balancing system which transfers lifting force between the sections with the
forces
being balanced by a balance beam of the linkages 30.
The header frame sections and the reel sections are hinged and
supported so that the reel will stay in approximately the same position
relative to the
cutter bar. Thus the balance beam as described in more detail hereinafter
balances the
lifting force applied to the ends of the center section relative to the
lifting force which is
applied to the outboard weight of the wing section so that the lifting force
is even across
the width of the header. Thus if a lifting force is applied by the ground or
any other lifting
mechanism for example merely manually lifting the header at a particular
location
across its width, that would cause the header to rise at that point and to
fall at other
points. The amount of force necessary to lift the header at that point will be
the same
as it is at other points and this lifting force can be varied for the total
header and
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
27
proportioned across the width of the header automatically by the balance beams
as
described hereinafter.
It will be appreciated that the inboard weight of the wing section is
transferred through the pivot 27 to the outboard end of the center section and
that
weight is transferred directly to the balance beam. Also the outboard weight
of the wing
section is transferred through the linkages 30. Yet further a lifting force
from the arm 21
is applied to the balance beam.
The whole support assembly including the linkages 30, the lift arm 21 and
the springs 24 are arranged to provide a floating movement for each of the
first and
second frame portions that is the center and wing frame portions relative to
each other
and relative to the propulsion vehicle such that upward pressure from the
ground on
the skid element 16A which is greater in a downward force for a part of the
weight of
the header and supported by the lifting force tends to lift each of the center
and wing
frame portions relative to the propulsion vehicle.
The balance beam arrangement is arranged such that the first and second
lifting forces are varied proportionally as the total lifting force FT is
varied.
The height of the header is primarily controlled by controlling the height
of the feeder house 20 of the combine harvester relative to the ground using a
height
control mechanism 100. Typically the feeder house is pivotally supported on a
main
frame of the combine harvester and an actuator member is mounted between the
feeder house and the main frame to raise and lower the feeder house.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
28
The height of the main structure of the header is in turn supported for up
and down movement relative to the adapter 11 by supporting the main frame
structure
on the pivot arms 21 which are supported for floating movement by the springs
24 by
providing a total spring lifting force to the header. The linkages 30 in turn
distribute this
total spring force into a center lifting force Fc which provides lift to the
center frame
section and the inboard ends of the wing frame sections pivotally coupled
thereto as
well as a first lifting force and a second lifting force acting upon the first
and second
wing frame sections respectively in a direction intending to cause the
outboard ends of
the wing frames to be raised upwardly.
The linkages 30 supporting the main frame structure on the pivot arms 21
comprises two balance linkages associated with the two pivot arms
respectively. Each
balance linkage includes a balance beam 102 pivotally supported at an
intermediate
location between front and rear ends on the forward ends of the pivot arms 21.
The
forward ends of the two balance beams 102 are pivotally connected to
respective
locations on the center section of the main frame structure at transversely
spaced apart
locations. The forward ends of the balance beams 102 serve to provide the
center
lifting force Fc to the main frame structure. The opposing rear ends of the
two balance
beams 102 provide the first and second lifting forces to the first and second
wing frame
sections.
More particularly, the rear end of each balance beam 102 is pivotally
connected to an upright compression link 104 which extends upwardly from the
balance
beam 102 below the main frame structure to a top end in proximity to a top end
of the
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
29
main frame structure. Each balance linkage further includes a bell crank 106
pivotally
supported on the main frame structure adjacent the top end in which the bell
crank
includes a first lever 108 pivotally coupled to the top end of the respective
compression
link 104 and a second lever portion 110 extending upward to a pivot connection
with a
respective tension link 112.
Pivotal connection of the second lever 110 with the respective tension link
112 is located substantially directly above the pivotal connection of the bell
crank to the
main frame structure such that an upward force acting on the compression link
104
tends to rotate the bell crank in a direction corresponding to a laterally
inward tension
on the tension link 112 which is pivotally coupled at its outer end to a
respective one of
the wing frame sections which tends to pivot the wing frame section in a
direction about
its pivotal coupling to the center frame section in a direction corresponding
to the
outboard and of the wing frame section being raised upwardly.
The balance linkages 30 serve to balance the total lifting force provided
by the combine harvester through the pivot arms 21 to the center lifting force
at the
forward ends of the balance beams 102 and the first and second lifting forces
at the
rear ends of the balance beams so as to vary the lifting forces as the total
lifting force
varies and so as to balance the lifting forces from the ground applied along
the length
of the skid element.
The header further includes a stop member 114 which is arranged to limit
downward movement of the main frame structure of the header relative to the
adapter.
A distance sensor 116 is provided for sensing a distance of a point on the
header which
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
30
moves with the header in suspension movement relative to the bottom stop 114
which
is stationary relative to the combine harvester. The distance sensor therefore
generates a signal indicative of the sensed changes in the measured distance.
The
height control mechanism 100 which is arranged to raise and lower the feeder
house
of the combine harvester, receives the signal from the sensor 116 as an input
and is
automatically operated so as to attempt to maintain the sensed distance at a
required
set value. The set value is selected so that the header is free to float
between the bottom
stop and the upper limited movement both upwardly and downwardly to
accommodate
changes in ground height.
The gauge system 5 according to the present invention is particularly
suited for use with the above described header 10 to permit the header to
operate in a
balanced manner with the wing sections floating relative to the center section
when
operating at a raised cutting height with the cutter bar and skid member 16A
supported
well above the ground.
Thus as shown in Figures 1 to 5 there is provided a crop harvesting
header 10 with center and wing sections 10A, 10B and 10C. Each includes a main
frame structure so that together the combined frame structure extends across a
width
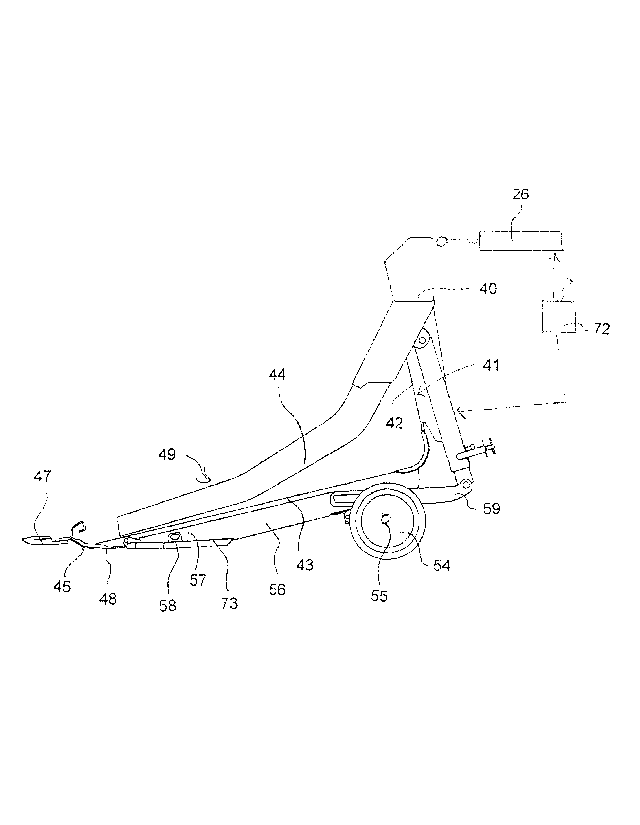
of the header. The main frame structure as best shown in Figures 7 and 8
includes a
main frame beam 40 across the rear at the top of the header and a plurality of
frame
members 41 located at spaced positions across the main frame structure. Each
frame
member 41 extends from the frame beam 40 in a first portion 42 downwardly
behind
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
31
the table 43 and in a second portion 44 forwardly under the table to support
the cutter
bar 45. The second portion 43 forms a channel member with a downwardly facing
open
face 46.
The frame structure is attached to a mounting assembly defined by the
adapter 11 of Figure 5 for carrying the main frame structure on the feeder
house 12 of
a propulsion vehicle such as a combine harvester by which the header is
transported
in movement in a forward direction generally at right angles to the width
across ground
including a crop to be harvested.
The crop cut by the sickle knife 47 of the cutter 45 falls onto the crop
receiving table 44 carried on the main frame structure across the width of the
header.
A skid element 48 on the main frame structure is located just behind the
sickle knife of the cutter bar for engaging the ground so as to receive
lifting forces from
the ground. The skid element 48 is located behind the cutter bar and extends
along
the length of the cutter bar so that the cutter bar is supported adjacent the
ground for
cutting crop close to the ground as the skid element 48 slides over the
ground.
A crop transport system 49 such as a draper system or auger is provided
on the table for moving the cut crop toward a discharge location of the
header. As
described above, the harvesting header is operable in a first mode of
operation shown
in Figure 7 with the skid element 48 engaging the ground and the cutter bar 45
adjacent
the ground and in a second mode of operation shown in Figure 8 with the skid
element
48 and the cutter bar raised away from the ground.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
32
As explained previously and shown in Figure 4, the first wing frame
portion 10B is connected to the center frame portion 10A by a first pivot
coupling 102
which provides pivotal movement of the first wing frame portion 108 relative
to the
center frame portion 10A about a first pivot axis extending in a plane
parallel to the
forward direction. Symmetrically the second wing frame portion 10C is mounted
on the
other side if the center section.
The first pivot coupling 102 is provided to support weight from the first
wing frame portion 10B while outboard weight from the first wing frame portion
10B
outboard of the first pivot coupling rotates the first wing frame portion 10B
about the
first pivot coupling in a downward direction. Symmetrically the second wing
frame
portion 10C is mounted on the other side if the center section and supported
by a
symmetrical coupling.
As explained previously, the mounting assembly including a float
suspension system 24 connected to the center frame portion providing a
variable lifting
force from the propulsion vehicle acting to support the main frame structure
for floating
movement relative to the propulsion vehicle. A first interconnecting float
linkage 108 is
connected between the center frame portion 10A and the first wing frame
portion 10B
which communicates a first variable lifting force from the center frame
portion to the first
wing frame portion against the outboard weight of the first wing frame
portion. A second
symmetrical interconnecting linkage communicates a second variable lifting
force from
the center frame portion to the second wing frame portion against the outboard
weight
of the second wing frame portion.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
33
In the first mode of operation with the skid element 48 engaging the
ground, the float suspension system 24 and first and second interconnecting
linkages
108 provide a downforce from the skid element 48 on the ground which is
balanced
between the center frame portion 10A and the first and second wing frame
portions
10B, 10C.
As set out hereinbefore, the above arrangements are conventional and
further details can be obtained from the referenced patents or from machines
well
known in the industry and manufactured by MacDon.
In accordance with the arrangement described herein, there is provided
a gauging system 50 used in the second mode of operation to hold the cutter
bar in the
raised position of Figure 8.
This includes four separate ground engaging members 51 located in the
positions shown in Figure 1. This includes a first ground engaging member 51
supported on the first wing frame portion 10B at a location spaced outwardly
from the
center frame portion and particularly at the outer end of the portion at the
crop divider
and end sheet of the header for engaging the ground so as to receive lifting
forces from
the ground, a second ground engaging member 51 supported on the second wing
frame
portion 10C also at the outer end and two additional ground engaging member 51
supported on the wing frame portions immediately proximate the center frame
portion
1OA for engaging the ground so as to receive lifting forces from the ground.
The two
additional members 51 can be located on the center section. The outer members
are
preferably located at the ends but also can be moved inboard.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
34
The location of the four ground engaging elements 51 at the locations
specified provides a proper balance of the header relative to the nominal
balance points
P on the wing frame portions 10B and 10C. The points P represent the locations
where
the three sections will be balanced if supported by members at the points. It
will be
noted that the actual ground engaging members are located at spaced positions
from
these points. Thus the outermost member 51 is located at the outer end of the
wing
and the innermost member 51 is located closely adjacent the pivot coupling.
These
locations are spaced sufficiently from the points P so that ground forces
transmitted to
the frame through the members 51 will allow the wings to flex around the pivot
points
and keep all three sections at a common spacing from the ground.
In the embodiment of Figures 6 to 9, each of the ground engaging
members 51 has a surface arrangement defined by the periphery 53 of a pair of
wheels
54 carried on an axle 55. The surface 53 engages the ground at a position
rearwardly
of the cutter bar and underneath the table such that, in the second mode of
operation,
the ground engaging members collectively support the skid element 48 spaced
above
the ground while the first and second wing frame portions are allowed to pivot
relative
to the center frame portion in response to changes in ground height.
The wheels 54 defining each of the surface arrangements are mounted
by the axle 55 on an elongate support member 56 connected at a forward end 57
adjacent to and rearwardly of the cutter bar 47 for pivotal movement about an
axis 58
parallel to the cutter bar 47. The elongate support member 56 forms a rigid
beam
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
35
arranged to be raised and lowered to raise and lower the wheels 54 and the
surface
arrangement 53 defined thereby;
As shown in Figure 8, each of the wheels is fully retractable, by raising of
the elongate support member or beam 56 to an uppermost raised position within
the
channel 43, to a height of the wheel underneath the table to cause the skid
element 48
or cutter bar polymer shield to engage and run across the ground in the first
mode of
operation cutting at ground level. In this mode the header will ride ieither
on the cutter
bar shield or on the skid shoe depending on the header angle.
Thus the first and second ground engaging members are mounted at
respective outer ends of the first and second wing frame portions and the two
inner
additional ground engaging members 51 are mounted on the first wing frame
portion
closely adjacent to the pivot axis and on the second wing frame portion
closely adjacent
the pivot axis. In the second mode of operation and in this arrangement where
the
ground engaging members are mounted only on the wing sections, the center
frame
portion is supported only by said float suspension system and not by any
additional
ground engaging members 51.
Each of the elongate support beams 56 extends rearwardly under the
table to a rear end 59 rearward of the table. At the rear end there is
provided an
upstanding telescopically extendible member 60 connected at a lower end 61 to
the
elongate support beam 56 and to a lug 63 of the frame structure at the upper
end 62
rearward of the table to raise and lower the beam relative to the frame and
thus the
cutter bar relative to the ground.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
36
As best shown in Figures 10 and lithe extendible member comprises a
pair of telescopic members 65 and 66 including an outer member 65 with an
inner
member 66 slidable within the outer member. The inner member 66 has a
plurality of
longitudinally spaced holes 67 for receiving a pin 68 of the outer member to
locate the
inner and outer members at an extension position defined by the selected hole.
The
holes 67 are spaced also transversely across the inner member and the pin is
carried
on a rotatable member 69 which acts when rotated to move the pin 68
transversely
across the outer member into a selected one of a plurality of holes 70 so that
the
transverse position of the pin is adjusted as the member 69 is rotated and
when rotated
acts automatically to select one of the holes of the inner member, thus
determining the
telescopic length of the member 60. The elongate support members are each
located
in a second channel portion 46 of a respective one of said frame members 41
and
extends rearwardly under the table to the rear member 60 for adjustment.
Each of the ground engaging surfaces 53 is located under the table so
that it is forward of the rear of the table. Thus when raised, the amount of
movement
allowed is relatively small. In order to achieve the required height of the
cutter bar of at
least 12 inches and preferably greater than 14 inches, the mounting assembly
includes
the tilt cylinder 26 connected to the frame structure of the header for tiling
the frame
structure and the cutter bar carried thereby forwardly and rearwardly. Thus
when
actuated by a switch 72 the tilt cylinder can be retracted to pull the front
of the header
upwardly to further increase the height of the cutter bar, although the
arrangement
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
37
described herein provides a required height of the cutter bar even without the
tiling
action of the cylinder 26.
In a case where the manual adjustment of the member 60 is replaced by
a hydraulic cylinder, common operation of the lowering of the elongate support
members 60 and the tilt cylinder causes the cutter bar to be raised such that
the cutter
bar is located at a cutting height from the ground of greater than 12 inches.
As shown in Figures 6, 7 and 8, the forward end 57 of the member 56 can
include a skid plate 73. The forward end is pivotally connected to a
transverse mounting
pin attached to the frame behind the skid element 48. Suitable lugs are
attached to the
frame member 41 at the forward end to receive the pin. As an alternative, the
skid plate
73 can form a part of the header and is mounted to the frame permanently by a
pin for
pivotal movement about the pin. In this arrangement the forward end of the
member
56 is attached by a coupling to the skid plate.
As shown in Figure 6 and 9, the axle 55 of the wheels 54 is mounted on
a suspension linkage 74 which allows the axle to move up and down on the
linkage
about a pivot pin 75 at the forward end with a resilient block or spring 76
resisting the
upward movement of the wheels toward the member 56. This provides a resilient
suspension arrangement between the elongate support member and the wheels
allowing up and down floating movement of the wheels.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
38
In Figures 12, 13 and 14 is shown an alternative arrangement where the
surface arrangement for engaging the ground comprises a skid surface 77 which
extends from a forward edge 78 effectively as a continuous slide surface
rearwardly to
a rear end 79 at the extendible member 60 just behind the rear edge of the
table. The
surface 77 thus forms a continuous surface which slides over the ground from a
front
edge at a position adjacent the cutter bar to a position at least adjacent to
the rear edge
of the table. As shown in the cross-sections of Figures 13 and 14, the skid
surface 77
is arched both longitudinally and transversely.
The skid surface is carried on the member 56 as a permanent attachment
thereto and can be used alone to run over the ground. Alternatively the skid
member
can be used in conjunction with a pair of ground wheels 54A mounted on the
member
56 by a suspension arrangement similar to that previously described. Thus when
the
wheels are used they can float upwardly relative to the skid surface so that
primarily
the wheels run on the ground and provide the support. The
wheels can be
removed in some conditions such as heavy mud where they may be ineffective or
may
collect mud. That is the wheel arrangement is removable to allow the skid
surface to
slide on the ground.
As can be seen in Figures 6 and 12, the wheel assemblies pivot near the
cutter bar and have a short skid 57 that is part of the structure that the
header would
only ride on when cutting directly on the ground. The device of Figure 6
comprises a
short skid shoe 57 on the leading edge near the cutting edge of the header
with a
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
39
member 56 extending rearward allowing the attachment of ground following
wheels 54
and an adjustment device 60 at the rear of the header.
The location of the four wheel assemblies where are at each end of the
header, and two are near the hinge points as displayed in Figure 1 ensures
enough
moment about the virtual balance point of the header to overcome friction and
cause
the header to flex. This allows the operator to use the header while in flex
mode in order
to achieve better ground following while cutting as high as 18" off the
ground.
The wheel assembly contains an isolator 74 to aid in eliminating header
bounce and stress on components as the wheels travel over bumps and other
incompressible objects. One embodiment of the isolator consists of a torsional
rubber
isolator which is mounted to the member 76 that spans from the cutter bar to
the rear
adjuster. In this case, the wheel assembly 54 and axle 55 which contains two
links is
bolted to the torsional isolator 76. As the wheel 54 strikes an object, the
links convert
the force into a moment which causes the isolator 74 to rotate and absorb the
load.
The means of adjusting the height of the wheel assembly can be a manual
adjuster such as is explained later or a hydraulic wheel height adjustment
system. With
the manual adjuster, the operator would set all four adjusters to a height
which is close
to the desired cut height and fine adjustments can then be made to the cut
height by
changing the tilt of the header using the cylinder 26. With the hydraulic
adjustment
which contains four hydraulic cylinders in a series circuit in a master slave
arrangement,
and a switch 72 in the combine cab, the operator can adjust the height of the
wheels
by actuating the cylinders using the in cab switch while harvesting.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
40
The long skid shoe embodiment of Figures 12, 13 and 14 consists of a
member positioned such that the header rides on the shoes when in cutting
position.
The operator may choose to retract the shoes such that the header can cut on
the
ground, effectively removing the long skid shoes from operation. This enables
the
operator to adjust cut height such that a desired stubble length can be
achieved. The
embodiment shown allows for a stubble height ranging from 1.25" up to 14".
The long shoe 77 may either be integrated into standard short skid shoes
57 near the front of the header, or exist in addition to short standard skid
shoes 57.
The wheels 54A can be permanently attached to the skid shoe or
removable as desired.
The wheels 54, 54A may consist of a variety of materials, including a solid
material as shown in this embodiment, or a pneumatic wheel.
The wheels 54 may be fixed position along the member 56 or include an
adjustable member (not shown) such that the distance of the wheel from the
cutter bar
may be altered.
The wheels 54A may be used to increase the stubble height beyond the
range of the shoe. In this embodiment, 18 inches may be achieved using the
wheels.
The wheels 54A offer all of the benefits of the skid shoe, while increasing
the life of the
device in abrasive conditions, as well as reducing friction.
The preferred method of providing shock absorption is to install a resilient
isolator 80 at the connection of the vertical post 60 and rear of the beam 56
carrying
the skid shoe member 77. The isolator provides a hinge with a resilient rubber
restrictor
CA 2974643 2019-10-29
41
at the hinge which provides flexibility between the rear of the skid and the
post 60 so
that the skid can ride up and down to accommodate changes in terrain. Various
arrangements for providing flexibility at this location are possible.
CA 2974643 2019-10-29