Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
SEALING BELT CONVEYORS AGAINST PRODUCT LEAKAGE
This disclosure relates to the field of conveying equipment and in particular
a seeding
apparatus for one pass seeding and fertilizing.
BACKGROUND
Typically belt conveyors for granular material such as grain, oilseeds,
fertilizer, and like
agricultural products typically comprise an upper run of the belt passing
through a tube
that supports the belt in a troughed configuration. The tube is mounted on a
mobile
framework in an inclined orientation. The belt passes over a top roller at the
upper
discharge end of the conveyor, and the return run of the belt runs under the
tube in a flat
orientation supported by idler rollers, plate sections or the like spaced at
suitable intervals
under the conveyor.
The return run typically passes through an S-drive mounted under the conveyor
tube. In
the S-drive, idler rollers cause the belt to wrap around the drive roller,
increasing the
frictional force between the belt and drive roller and allowing significant
power to be
transferred from the drive roller to the belt.
A typical portable conveyor for agricultural products will be mounted in a
frame
supported on wheels and include an actuator operative to raise and lower an
upper
discharge end of a conveyor tube while the lower intake end stays near the
ground to
receive agricultural products to be carried up the conveyor and discharged
into the top of
a grain bin. The lower receiving end typically includes a metal hoppered
intake section
where the belt runs flat before passing into the tube and moving to the
troughed
orientation inside the tube. In this flat portion the edges of the belt may be
curved up
somewhat, and there will be a seal strip, typically a stiff rubber strip,
fastened along a top
=
2107613v1 1
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
edge thereof to the walls of the hopper such that the lower edge thereof bears
against.the
belt to prevent granular material from moving off the side edges of the belt.
In belt conveyors for agricultural products, there is also often a hoppered
intake portion
attached to the bottom end of the conveyor and extending outward generally
horizontally
at an angle to the tube so that the intake portion can be positioned under the
center
discharge of a belly dump grain trailer for example. The top run of the belt
then runs
horizontal to the bottom end of the tube then must make an angle upward. The
belt is
under tension and in response to that tension tends to rise as it turns upward
from the
horizontal to enter the inclined tube. In order to hold the belt down, it is
common to
provide an S-roller assembly whereby the belt passes from the front end of the
hopper
rearward over a first roller at the bottom of the tube and under a second
roller that is
under the first roller then up the inclined tube.
Problems commonly arise when conveying small particles such as grains, and in
particular very small oily particles such as canola or flax. The seeds tend to
move over
the side edges of the belt, for example at the S-roller assembly and under the
seal strips.
The seeds gather under various portions of the belt and under the seal strip
where they are
crushed. The crushed oilseeds release oil which causes the belt to slip on the
drive rollers,
and the crushed seeds are very sticky and gummy and build up on the belt and
rollers,
under the seal strip, and in various other areas under and around the belt,
fouling the
mechanisms.
United States Patent Number 8,727,108 to Dekoning addresses this problem by
providing
a seal over raised edges of the belt in the intake area, and a trap opening
configured to
allow seeds moving up the tube under the belt to fall out of the tube.
2107613v1 2
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present disclosure provides a belt conveyor apparatus that overcomes
problems in the
prior art.
In a first embodiment the present disclosure provides a belt conveyor
apparatus
comprising a tube mounted on a frame supported on wheels for travel on a
ground
surface, the tube sloping upward from a lower intake end to an upper discharge
end and a
hopper extending outward along the ground surface from the lower intake end of
the
tube. A belt has an upper run passing along a hopper floor of the hopper then
over a top
S-roller of an S-roller assembly and under a bottom S-roller of the S-roller
assembly, and
up through the tube to the discharge end of the tube, and with a return run
extending
under the tube and hopper. Right and left sidewalls of the hopper extend
upward and
outward from side edges of the hopper floor. Resilient right and left bottom
seal strips
each extend from a front end of the hopper to a rear portion of the hopper
over the top S-
roller and are fastened along an upper edge thereof to a corresponding
sidewall such that
a lower edge of each bottom seal strip bears against a top surface of the belt
adjacent to a
side edge of the belt. Resilient right and left top seal strips each extend
from the front
end of the hopper to the rear portion of the hopper over the top S-roller and
are fastened
along an upper edge thereof to a corresponding sidewall on top of the
corresponding
bottom seal strip such that a lower edge of each top seal strip bears against
a top surface
of the belt beside the lower edge of the corresponding bottom seal strip.
In a second embodiment the present disclosure provides a belt conveyor
apparatus
comprising a tube mounted on a frame supported on wheels for travel on a
ground
surface, the tube sloping upward from a lower intake end to an upper discharge
end and a
hopper extending outward along the ground surface from the lower intake end of
the
tube. A belt has an upper run passing along a hopper floor of the hopper then
over a top
S-roller of an S-roller assembly and under a bottom S-roller of the S-roller
assembly, and
2107613v1 3
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
up through the tube to the discharge end of the tube, and with a return run
extending
under the tube and hopper. The S-rollers are each mounted on a roller shaft
extending
through right and left frame walls, and the roller shafts extend through
resilient right and
left roller seal plates attached to the corresponding right and left frame
walls. Right and
left side edges of the belt bear against outer surfaces of the corresponding
right and left
roller seal plates as the belt passes through the S-roller assembly, and outer
ends of the S-
rollers extend into the right and left roller seal plates to seal the right
and left seal plates
against outer surfaces of the S-rollers.
In a third embodiment the present disclosure provides a belt conveyor
apparatus
comprising a tube mounted on a frame supported on wheels for travel on a
ground
surface, the tube sloping upward from a lower intake end to an upper discharge
end and a
hopper extending outward along the ground surface from the lower intake end of
the
tube. A belt has an upper run passing along a hopper floor of the hopper then
over a top
S-roller of an S-roller assembly and under a bottom S-roller of the S-roller
assembly, and
up through the tube to the discharge end of the tube, and with a return run
extending
under the tube and hopper. A support surface is positioned under the upper run
of the
belt between the lower S-roller and the lower intake end of the tube such that
the belt
slides over the support surface.
The present disclosure provides a belt conveyor apparatus where leakage of
granular
material off the belt is reduced. Leakage areas are provided with improved
seals, with
two separate seals along the top of the generally horizontal section of the
belt running
through the hopper, and roller seals sealing ends of the S-rollers and
providing a tightly
fitting groove where the belt edges run preventing migration of material off
the belt.
Supporting the bottom of the belt with the support surface and transition
plates prevents
the belt from deforming under the weight of granular material propelled onto
the inclined
portion of the belt adjacent to the bottom S-roller.
2107613v1 4
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
While the invention is claimed in the concluding portions hereof, preferred
embodiments
are provided in the accompanying detailed description which may be best
understood in
conjunction with the accompanying diagrams where like parts in each of the
several
diagrams are labeled with like numbers, and where:
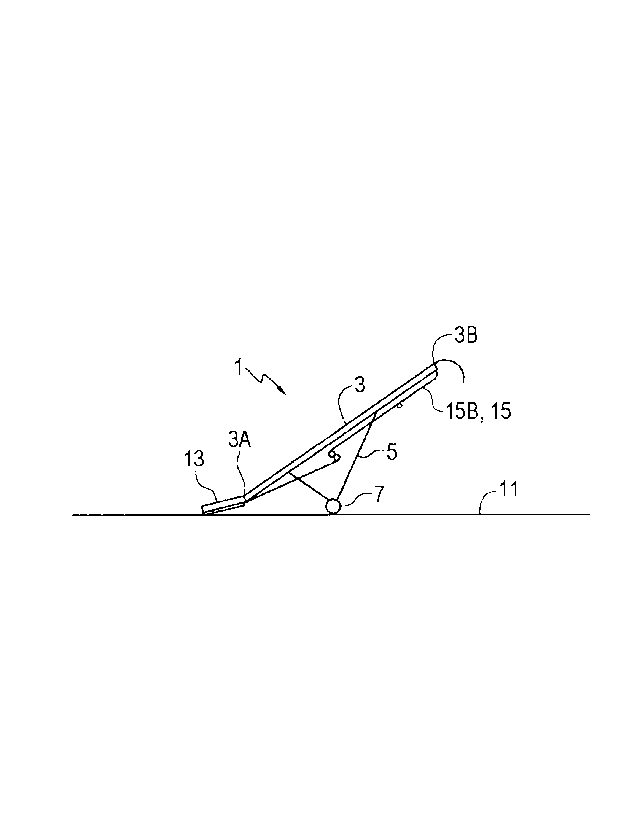
Fig. 1 is a schematic side view of an embodiment of a belt conveyor apparatus
of the
present disclosure;
Fig. 2 is a top view of the hopper and intake end of the tube of the
embodiment of Fig.
1 with the belt removed for illustration purposes;
Fig. 3 is a schematic sectional side view along line 3-3 in Fig. 2 with the
belt installed;
Fig. 4 is a schematic sectional end view of the hopper and top and bottom seal
strips of
= the embodiment of Fig. 1;
Fig. 5 is a schematic sectional end view of the S-roller assembly of the
embodiment of
Fig. 1 with the belt removed for illustration purposes;
Fig. 6 is a schematic sectional side view of the S-roller assembly and right
roller seal
plate with the belt installed;
Fig. 7 is a schematic sectional side view showing the movement of granular
material
from the generally horizontal portion of the belt passing along the hopper
floor to the
inclined portion of the belt between the bottom S-roller and the intake end of
the tube
of the embodiment of Fig. 1;
2107613v1 5
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
Fig. 8 is a schematic top view of the bottom S-roller, the support surface,
and the
transition plates of the embodiment of Fig. 1 with the belt removed for
illustration
purposes;
Fig. 9 is a schematic side view of the bottom S-roller, the support surface,
and the
transition plates shown in Fig. 8, again with the belt removed for
illustration purposes.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENTS
Figs. 1 ¨ 3 schematically illustrate an embodiment of a belt conveyor
apparatus 1 of the
present disclosure. The apparatus 1 comprises a tube 3 mounted on a frame 5
supported
on wheels 7 for travel on a ground surface 11. The tube 3 slopes upward from a
lower
intake end 3A thereof to an upper discharge end 3B, and a hopper 13 extends
outward
along the ground surface 11 from the lower intake end 3A of the tube 3. The
hopper 13 is
configured as is known in the art to reach under a bottom discharge of a
trailer to receive
granular material such as grain and the like.
A belt 15 has an upper run 15A passing along a hopper floor 17 of the hopper
13 then
over a top S-roller 19A of an S-roller assembly 19, and under a bottom S-
roller 19B of
the S-roller assembly 19, and then up through the tube 3 to the discharge end
3B of the
tube 3, and has a return run 15B extending under the tube 3 and hopper 13 as
can be seen
if Fig. 3. Fig. 3 is a schematic sectional view along line 3-3 in the top view
of Fig. 2., In
Fig. 2 the belt has been removed to allow for illustration of the apparatus 1,
and the belt
15 is shown in Fig. 3.
Right and left sidewalls 21R, 21L of the hopper 13 extend upward and outward
from side
edges of the hopper floor 17. Resilient right and left bottom seal strips 23R,
23L each
extend from a front end 13F of the hopper 13 to a rear portion 13R of the
hopper 13 over
the top S-roller 19A and is fastened along an upper edge thereof to a
corresponding
2107613v1 6
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
sidewall 21 such that a lower edge 25 of each bottom seal strip 23 bears
against atop
surface of the belt 15 adjacent to a side edge of the belt 15, as
schematically illustrated in
Fig. 4.
Resilient right and left top seal strips 27R, 27L each extend from a front end
13F of the
hopper 13 to a rear portion 13R of the hopper over the top S-roller 19 and
fastened along
an upper edge thereof to a corresponding sidewall 21 on top of the
corresponding bottom
seal strip 23 such that a lower edge 29 of each top seal strip 27 bears
against a top surface
of the belt 15 beside the lower edge 25 of the corresponding bottom seal strip
23.
The top seal strips 27 are slightly wider than the bottom seal strips 23, and
the top and
bottom seal strips 23, 27 are conveniently attached to the corresponding
sidewalls 21 by
fasteners 31 through common holes 33 in the seal strips 23, 27 and sidewalls
21.
The two seals 23, 27 provide a double lip seal system to prevent granular
material from
reaching the edge of the belt 15. The two bottom edges 25, 29 are close
together but
distinct and material leaking under the bottom edge 29 of the top seal strip
23 is blocked
from migrating to the edge of the belt 15 by the bottom edge 25 of the bottom
seal strip
23. When a single seal strip is used the weight of the material on the strip
deforms the
strip and forces particles under the seal strip. When the top seal strip 27 is
placed Over
the bottom seal strip 23, the additional seal strip provides relief from the
weight of the
material and allows the bottom seal strip to maintain an effective seal.
As schematically illustrated in Figs. 5 and 6 the S-rollers 19A, 19B are each
mounted on
a roller shalt 35 extending through right and left frame walls 37R, 37L. The
roller shafts
extend through resilient right and left roller seal plates 39R, 39L attached
to the
corresponding right and left frame walls 37R, 37L. The distance D between the
outer
surfaces of the right and left roller seal plates 39R, 39L is less than a
width of the belt 15,
such that right and left side edges of the belt 15 bear against outer surfaces
41 of the
2107613v1 7
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
corresponding right and left roller seal plates 39R, 39L as the belt 15 passes
through the
S-roller assembly 19 and the moving belt wears a groove 43 in the outer
surface 41 of
each roller seal plate 39 and the side edges of the belt 15 move in the
grooves 43,
effectively sealing the side edges of the belt 15 to prevent particles from
moving off the
belt 15.
In Fig. 5 the belt 15 has been removed to allow for illustration of the
apparatus 1, and the
belt 15 is shown in Fig. 6. As seen in Fig. 5 the outer ends of the S-rollers
19 extend into
the right and left roller seal plates 39 to seal the right and left seal
plates 39 against outer
surfaces 45 of the S-rollers 19. Fig. 6 schematically illustrates the roller
seal plate 39R
and the belt 15 passing through the S-rollers 19A, 19B.
As seen in Figs. 2 and 3 a support surface 47 is positioned under the upper
run 15A of the
belt 15 between the lower S-roller 19B and the lower intake end 3A of the tube
3 such
that the belt 15 slides over the support surface 47. During operation,
granular material 49
is propelled at significant speed from the from the rear end of the belt 15
running
generally horizontally along the floor 17 of the hopper onto the inclined
portion of the
belt between the bottom S-roller 19B and the intake end 3A of the tube,
exerting
considerable forces F tending to distort the belt 15 such that granular
material moves off
the side edges thereof. The support surface 47 prevents downward movement and
distortion of the belt 15. The support surface will typically be provided by a
pan or plate
but could be provided by a plurality of rods or bars spaced close enough
together to
prevent downward movement of the belt 15.
Right and left transition plates 51R, 51L extend from front ends 53 thereof
adjacent to the
bottom S-roller 19B to rear ends 55 thereof at the lower intake end 3A of the
tube 3. The
transition plates 51 are configured to force the belt 15 from a flat
orientation at the
bottom S-roller 19B to a troughed orientation at the lower intake end 3A of
the tube. The
transition plates 51 each comprise a substantially flat portion 57 extending
under
2107613v1 8
CA 2987360 2017-12-01
=
corresponding right and left side portions of the belt 15, and forming
portions 59 tapering
upward and inward from the front end of the transition plate to the rear end
of the
transition plate. Conveniently the support surface 47 is attached to the flat
portions 57 of
the right and left transition plates 51R, 51L.
The support surface 47 and transition plates 51 support the bottom surface of
the belt
through the transition from a flat orientation leaving the bottom S-roller 19B
to the
troughed orientation entering the intake end 3A of the tube 3. With the belt
15 supported
the tendency for the side edges thereof to pull away from the supporting walls
and allow
leakage is reduced.
The present disclosure provides a belt conveyor apparatus 1 where leakage of
granular
material off the belt 15 is reduced by sealing vulnerable areas and supporting
the bottom
of the belt so that the weight of granular material 49 on the belt 15 does not
deform the
belt.
The foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the
invention.
Further, since numerous changes and modifications will readily occur to those
skilled in
the art, it is not desired to limit the invention to the exact construction
and operation
shown and described, and accordingly, all such suitable changes or
modifications in
structure or operation which may be resorted to are intended to fall within
the scope of
the claimed invention.
=
2107613v1 9
CA 2987360 2017-12-01