Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
BATTERY PACK FOR USE DOWNHOLE HAVING TORSION-LIMITING MEANS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to downhole measurement-while-drilling ("MWD")
apparatus, and more particularly to an elongate battery pack for use in MWD
drilling
apparatus having torsion damping or torsion-limiting means at one or both ends
thereof to
thereby eliminate or reduce "high g" rotational accelerations and
decelerations being
transmitted from the drill string to the battery pack within the MWD
apparatus. In one
embodiment the torsion damping means comprises an electrical slip ring which
allows
electrical communication between the battery pack and remaining components of
the MWD
apparatus, but allows relative rotational movement therebetween.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION AND DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
Drilling of wells, and in particular the directional drilling of wells
requires continuous
measuring of sensed information as to the location of the drill bit, such as
inclination of the
drill string and drill bit and the angular orientation (azimuth) thereof, so
that this critical
information may then be conveyed uphole in real time to the drill operator at
surface to allow
instantaneous adjustments to be made that will ensure the well is being
drilled as desired.
For such so-called "measurement while drilling" drilling applications,
particularly
where the drill bit is rotary steerable, sophisticated battery-powered
electronics located in
"subs" threadably inserted in the drill string proximate the drill bit sense
the desired
directional parameters in relation to the drill bit .
Devices such as mud pulsers situated downhole in the drill string and
operatively
electrically coupled to the downhole electronics, encode the sensed data into
a series of
pressure pulses. These pressure pulses travel uphole where they are sensed by
additional
electronic equipment and decoded into the relevant data for the operator to
view in real time.
US 9,638,025 entitled "Mud pulser with Poppet Valve, having Linear
determination
means" and CA 2,463,354 entitled "Intelligent Efficient Servo-Actuator with
Sensor for
Downhole Pulser" respectively describe two such mud-pulser units for use in
such mud-pulse
-1 -
CALLANA 281799013
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
telemetry which have an electric motor therein which regulates/moves a servo-
valve to create
the desired mud pulses by which the encoded data is sent uphole.
Due to downhole electronics and electrically-powered servo-motors of mud
pulsers all
requiring battery power, it is necessary that batteries situated downhole in a
drill string
continually supply high power and have long life to thereby avoid having to
frequently "trip
out" the drill string to replace batteries in the drill string. "Tripping
out"of a drill string is not
only expensive but also very time consuming, and it is thus desired that the
battery life be as
long as possible to reduce the frequency of having to 'trip out' the drill
string.
Disadvantageously the aforementioned high pressure pulses continually
generated
downhole for the purposes of mud pulse telemetry create large vibrational
forces which
detrimentally affect downhole electronics and batteries.
Some prior art "packaging" systems for MWD electronics have been created to
attempt to isolate downhole MWD electronics from vibration and shock forces
during drilling
which act on the housing within the drill string.
For example, US 4,547,833 entitled "High Density Electronics Packaging System
for
Hostile Environment" is one such packaging system which utilizes annular shoe
supports
provided on the chassis to isolate such electronics from axial vibrations and
axial forces.
However, during drilling operations, particularly at the greater and greater
depths and
lengths of deviated wells, drill-string "wind-up" can be extensive and
effectively cause the
drill string to act like a rotary spring. Once torque has been applied to the
drill string to allow
the drill to operate and drill, backing off the downhole pressure applied to
the bit ("weight on
bit") even momentarily can result in the drill string effectively becoming
unsprung and large
torsional acceleration forces being applied to MWD equipment, potentially
exceeding 100g,
as the drill string unwinds.
US 2016/0053557 entitled "Torsional Isolator" is a device which attempts to
reduce
(axial) vibration and shock during directional drilling inflicted on
electronics. Such device,
however, is not directed at reducing torsional acceleration forces per se.
Rather, the torsional
-2-
CALLAW\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
isolator of US 2016/0053557 allows the drill string electronics to oscillate
at a slower
rotational velocity than the data acquisition rate of the associated sensors
such that the sensor
records only an average value of azimuth heading and thereby purportedly
allows for a higher
accuracy measurement of the azimuth heading by the downhole sensor.
The above background information and description of prior publications is
provided
for the purpose of making known information believed by the applicant to be of
possible
relevance to the present invention. No admission is necessarily intended nor
should be
construed that any of the above below publications and information provided
below
constitutes prior art against the present invention.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Due to need for long battery life and high electrical power output in MWD
drilling
applications, modern downhole batteries in MWD applications are often,
although not always,
of the lithium ¨ion configuration, and are often "daisy chained" together in
series or in
parallel to achieve the desired voltages and amp-hours to run the required
electronic and
downhole MWD electronica and mud pulse telemetry devices.
These types of batteries usually require the lithium component of such
batteries to be
molten or in liquid state when operating in order to provide the maximum power
output. At
the elevated temperatures typically encountered downhole this is usually
achievable.
Disadvantageously, however, lithium ion batteries, in part due to the inherent
high
imparted vibratory stresses in downhole hostile environments, are
frequently prone to
failure, resulting in expensive and frequent "tripping out" of the drill
string to replace
structurally-compromised or failed batteries.
While axial vibrational forces imparted on such batteries, due to the rapid
pressure
pulsing by the mud pulser units, are no doubt a contributing cause of the
battery failures, the
inventors now believe that due to the high rotational acceleration forces as
described above
being inflicted on such batteries, which rotational acceleration forces
sometimes exceed
100g's, that such rotational forces alone or together with imparted axial
vibrations and
-3-
CAL LA\AA 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
accelerations, cause the higher incidences of failures of such batteries.
Accordingly a real need exists for providing high energy battery packs
downhole,
such as those of the lithium ion type, for use in MWD drilling but which have
means to
prevent high torsional forces being transmitted to and imparted on such
battery packs,.
Vibrational isolators for batteries are known, such as the example disclosed
in US
2016/0164056 entitled "Battery Holder and Isolator Assembly" for a vibrational
isolator for a
conventional automobile battery.
Automotive batteries, however, are not typically subjected to rotational
forces, and
moreover it is not in any way apparent how the battery isolator of US
2016/0164056 for a car
battery could be adapted to a downhole battery pack to resist rotational
forces of the
magnitude to which the batteries would be subjected to downhole.
To the inventors' knowledge, no rotational dampers or torque limiters have
been
applied to downhole battery packs, and in particular to battery packs used in
MWD
applications.
Problematically, if a battery pack is not directly rotationally
coupled/affixed to the
components of the drill string, twisting and disconnection of the voltage
leads of the battery
pack which are electrically coupled to the electronic sensors and mud pulsers
can result if
extensive relative rotation between these components is permitted.
The inventors have accordingly caused to be invented a battery pack and
battery pack
container for use downhole in a drilling environment, which is specially
adapted and
configured to reduce torsional acceleration forces which may otherwise be
applied to the
batteries contained therein, and, in embodiments where extensive relative
rotation is desired
to reduce torsional forces, means is provided to allow significant relative
rotational
movement between electrical leads from the battery, and electrical leads
emanating from
downhole MWD equipment which are electrically coupled to and powered by such
battery
pack.
Specifically, in a further refinement the invention such invention further
provides an
-4-
CAL_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
electrical coupling which allows for free relative rotation between the MWD
apparatus and
the battery pack, and which further overcomes the problem that voltage leads
therein may
become twisted. Reduced incidents of battery pack failure downhole are further
thereby
reduced.
In one broad embodiment of the present invention, the present invention
comprises a
battery pack container for use in a downhole MWD apparatus which battery pack
container is
configured to reduce torsional or twisting forces being imparted on one or
batteries contained
thereon, comprising:
(i) an elongate hollow container having an outer wall and a first and a second
mutually opposite end, adapted to contain therewithin at least one battery;
and
(ii) torsion damping means, situated at said first end of said elongate hollow
container, configured to damp angular rotation of said first end of said
hollow
container relative to a remaining portion of said elongate hollow container.
In a first refinement thereof the torsion damping means comprises a suitable
elastomeric material, of high temperature resistance to withstand downhole
temperatures
typically experienced in MWD applications. Such torsional damping material is
situated
proximate said first end of said elongate hollow container and is interposed
at a series of
locations between portions of said outer wall and portions of said remaining
portion of said
elongate hollow container. In a preferred embodiment the elastomeric material
is interposed at
a series of interdigitating locations between portions of said outer wall and
portions of said
remaining portion of said elongate hollow container.
One suitable elastomeric material for use in this application and which is
contemplated by the inventors is Viton01, capable of withstanding temperatures
up to
230C/440F, and other co-polymers of hexafluroproplylene and
vindlideneflouride.
Other elastomeric materials having similar capabilities with respect to
thermal
degradation resistance and similar modulus' of elasticities are likewise
imminently suitable
and will now occur to persons of skill in the art relating to MWD downhole
rubber compounds.
Trademark of E.I DuPont DeNemours & Company for synthetic rubber compositions
-5-
CAL_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
In an additional embodiment, the elastomeric material is situated in the
hollow
battery pack container so as to further provide not only torsional damping but
also axial
damping of axial forces exerted on said battery pack.
In such additional embodiment the elastomeric material may be the same as the
elastomeric material provided for the torsional damping. To provide axial
damping such
elastomeric material may be situated in the same, or in a different location,
as the elastomeric
material providing torsional damping.
In a second related embodiment of the present invention, the present invention
comprises a battery pack container for use in a downhole MWD apparatus, which
battery pack
container is configured to prevent torsional or twisting forces being imparted
on one or more
batteries contained therein, comprising:
(i) an elongate hollow battery container having an outer wall, a first end,
and
a mutually opposite second end, adapted to contain between said first end and
said
second end at least one battery and provide electrical power from said at
least one
battery to at least said first end of said elongate battery container; and
(ii) a torsion-limiting means, comprising:
(A) an electrical connector affixed to said first end of said elongate hollow
container, said electrical connector having:
(a) a first end, having electrical leads extending therefrom which are
electrically couplable to said at least one battery; and
(b) a second end, mutually opposite to said first end of said electrical
connector and in electrical communication with said first end, having
electrical leads extending therefrom coupleable to electrically power-
consumptive MWD apparatus, wherein said second end of said
electrical connector is adapted for rotational movement relative to said
-6-
CAL_LAV\A 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
first end of said electrical connector; and
wherein said rotatable electrical connector is configured to permit relative
rotational
movement between said electrical leads from said first end of said electrical
connector and
said electrical leads extending outwardly from said second end of said
electrical connector
and not transmit torsional forces from said MWD apparatus and said second end
of said
electrical connector to said first end of said electrical connector and said
at least one battery.
In a preferred embodiment thereof the electrical connector is an electrical
slip ring
connector, possessing a plurality of electrically conductive brushes
contacting a
corresponding plurality of electrically conductive annular rings.
One such electrical connector suitable for use with the battery pack to
provide
torsional limitation means is an electrical slip ring connector manufactured
by Green Tweed
Inc. (www.gtweed.com), model no GTC 3290.
The battery pack preferably comprises one or more batteries contained in said
elongated hollow container. If more than one battery is contained therein,
such more than one
battery is electrically coupled to each of the remaining batteries either in a
parallel circuit, or
in a series configuration, to thereby provide the required electrical voltage
and amp hour
power longevity for the required application.
Such second embodiment of the battery pack container of the present invention
may
likewise further comprise an elastomeric material situated in said elongate
hollow container to
further provide axial damping of axial forces on said battery pack.
Specifically, an elastomeric material may further be situated within the
elongate hollow
container and interposed between portions of said outer wall of said battery
to provide axial
damping.
Finally, in a further related embodiment of the present invention, the
invention
comprises a MWD power supply system for use in a downhole MWD apparatus,
configured
to prevent torsional or twisting forces from the MWD apparatus being imparted
on one or
more batteries therein, comprising:
-7-
CALLAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
(i) an elongate hollow battery container having a first end, and a mutually
opposite second end, adapted to between said first end and said second end
contain at
least one battery and provide electrical power from said at least one battery
to at
least said first end of said elongate battery container;
(ii) at least one battery, contained in said battery container;
(iii) torsion limiting means, comprising:
(A) a female or male electrical connector half, affixed to said first
end of said battery container, having electrical leads extending
therefrom which are electrically coupled to said at least one battery;
and
(B) a mating male or female electrical connector half, opposite in
gender to that in sub-paragraph (A) above, fixedly coupled to said
MWD apparatus and having electrical leads extending therefrom
coupleable to electrically power-consumptive MWD apparatus;
wherein said female or male electrical connector half in subparagraph
(A) above is freely rotatable within said male or female electrical
connecter half of subparagraph (B) above while simultaneously
providing electrical communication therebetween and permitting
relative rotational movement between said electrical leads from said
electrical connector half of subparagraph (A) and said electrical leads
extending from said second electrical connector half of subparagraph
(B) and does not transmit torsional forces from said MWD apparatus
to said at least one battery in said battery pack.
In one embodiment of the MWD power supply system, one of said electrical
connectors of paragraph (A) or (B) possesses a plurality of electrically
conductive brushes and
the remaining mating electrical connector of subparagraph (A) or (B) comprises
a
-8-
CAL LA 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
corresponding plurality of electrically conductive annular rings, which when
one electrical
connector is inserted in the other said electrically conductive brushes
respectively contact said
annular rings.
Again, the MWD power supply system as disclosed above may further comprise an
elastomeric material situated proximate said first end of said elongate hollow
container to
further and additionally provide axial damping of axial forces which are
exerted on said battery
pack.
Specifically, in a further embodiment wherein the torsion limiting means
comprises a
rotatable electrical conductor, an elastomeric material may further be
situated proximate said
first end of said elongate hollow container and interposed between portions of
an outer wall of
said battery container wall and a remaining portion of said battery container,
to further provide
axial damping of axial forces on said battery pack.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further advantages and permutations and combinations of the invention will now
appear from the above and from the following detailed description of the
various particular
embodiments of the invention, taken together with the accompanying drawings
each of which
are intended to be non-limiting, in which:
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of one embodiment of the battery pack/battery
pack
system of the present invention:
Fig. 1A is an enlarged view of region "A" of Fig. 1;
Fig. 2 is an enlarged semi-transparent view of region "A" of Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a perspective view of another embodiment of the battery pack/battery
pack system of the present invention, having electrical sockets at both ends
thereof providing
the ability to be electrically coupled in series or in parallel with another
similar battery pack;
-9-
CA L_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
Fig. 3A is an enlarged view of region "A" as shown in each of Fig. 3 and Fig.
6:
Fig. 3B is an enlarged view of region "B" of Fig. 3;
Fig. 4 is a semi-transparent view of the battery pack of Fig. 3;
Fig. 5 is a side perspective view of the embodiment of the battery
pack/battery pack
system shown in Fig. 3, wherein two such battery packs are electrically
coupled together, in
either a "series" or "parallel" electrical coupling;
Fig. 6 is an enlarged, exploded, semi-transparent view of the electrically
coupled
battery packs of Fig. 5;
Fig. 7 is a side perspective view of another battery pack system of the
present
invention, having torsion-limiting means in the form electrical connectors at
each of opposite
ends of the battery pack;
Fig. 8 is an enlarged, exploded, semi-transparent view of the battery pack
shown in
Fig. 7;
Fig. 9 is a side perspective view of two battery packs as shown in Fig. 7
coupled in
"daisy chained" (i.e.end-to-end) configuration;
Fig. 10 is an exploded view showing an alternative battery pack system of the
present
invention, utilizing a battery pack torsion-limiting means wherein gender-
opposite male and
female rotatable connectors are electrically coupled to mutually opposite ends
of the battery
pack;
Fig. 11 is a side view of the battery pack assembly of Fig. 10, in assembled
condition;
Fig. 12 is a cross-sectional view taken along plane 4-4 of Fig. 11;
Fig. 13 is a partially exploded view showing the manner of locating and
inserting the
battery pack of Fig. 10 within a sealed assembly for insertion downhole;
-1 0-
CAL_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
Fig. 14 is a cross sectional view of the battery pack system of Fig. 10,
showing the
manner of electrically coupling the battery pack system to uphole and downhole
electrical
MWD components while providing torsional isolation for the batteries within
the battery pack
system;
Fig. 15 is a further modification of the battery pack system shown in Fig. 10,
further
having additional (alternative) torsion reduction means on an electrical
connector mounted to
an MWD device, which connects electrically to the battery pack' ;
Fig. 16 is a side perspective view of the elements shown in Fig. 15, showing
the
manner of inter-connecting the electrical connector of the MWD apparatus with
the one end
of the battery pack;
Fig. 17 is a side perspective view semi-transparent view of a further
embodiment of
the battery pack/battery pack system of the present invention having an
elastomeric material
situated proximate the first end of the elongate hollow battery container and
interposed in an
interdigitating manner between portions of the outer wall of said battery
container and
remaining portions of the battery container to provide not only torsional
damping of
rotational forces but also axial damping of axial forces; and
Fig. 18 side perspective view of an embodiment of the battery pack/battery
pack
system of the present invention having an elastomeric material situated
proximate mutually
opposite ends of the hollow battery container, interposed in an
interdigitating manner between
portions of the outer wall of said battery container and remaining portions of
the battery
container to thereby provide not only torsional damping of rotational forces
but also axial
damping of axial forces which would otherwise be directly transmitted to
batteries within the
battery container.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF SOME PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
-1 1 -
CALLAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
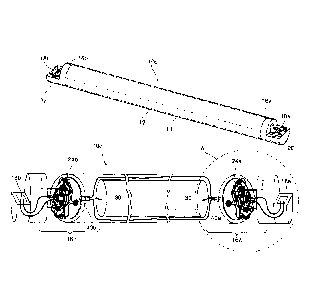
Fig. 1 shows a first embodiment of the battery pack/battery pack system 10 of
the
present invention for use in a downhole MWD apparatus, with Fig. 1A showing an
enlarged
view of a first end 20 in region "A" thereof.
An elongate hollow container 12 is provided, having an outer wall 14 , a first
end
20 and a mutually opposite second end 22, adapted to contain therewithin at
least one battery
(item 30, Fig 2,4).
An electrical socket 18 is preferably provided at first end 20 for allowing
electrical
coupling of battery pack 10 to electrically power-consumptive MWD sensors and
mud pulsers
(not shown).
Torsion damping means 16 are situated at said first end 20 of elongate hollow
container 12. Torsion damping means 16 damps angular rotation of first end 20
of hollow
battery container 12 relative to a remaining portion thereof including said
second end 22 of
elongate battery container 12.
As may be seen in the form of the invention depicted in Fig. 2 [Fig. 2 being
an
enlarged semi-transparent view of region "A" of Fig. 1], torsion damping means
16 in a first
embodiment thereof comprises an electrical connector 24 affixed to a portion
26 of the
hollow container 12 proximate the first end 20 of the elongate hollow
container 12. The
electrical connector 24 in such embodiment comprises a first end 40 having
electrical leads
41a, 41b extending therefrom which are electrically couplable to the at least
one battery 30.
At second end 50 of electrical connector 24 ( mutually opposite first end 40
and in electrical
communication with said first end 40) are provided another pair of electrical
leads 51a, 51b
which extend from second end 50 to electrical socket 18, where they may be
electrically
coupled to provide electrical current to power MWD apparatus (not shown)
downhole.
Importantly, in this embodiment of the torsion limiting means 16 permits
relative
angular rotational movement of second end 50 of electrical connector 24
relative to the first
end 40 of electrical connector 24. Specifically, electrical connector 24 is
configured to
permit relative rotational movement between electrical leads 41a, 41b from
first end 40 and
electrical leads 51a, 51b extending outwardly from second end 50 of electrical
connector
-12-
CAL_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
24. In such manner, MWD apparatus such as sensors and mud pulsers physically
and
electrically connected to first end 40 of battery pack container/system 10 are
torsionally
isolated from acceleration and deceleration forces which may be imposed
thereon via the
MWD components which are physically affixed, either directly or indirectly, to
the drill
string.
To maintain electrical communication while allowing relative angular rotation
between MWD components situated proximate the first end of the battery pack 10
and the
battery pack itself, electrical connector 24 comprises, in the embodiment
thereof shown in
Fig. 2, electrical leads 51a, 51b in electrical communication with
respectively two annular
slip rings 52a, 52b, situated on second end 50 of electrical connector 24,
each of which are
respectively in contact with and thus in electrical communication with
electrically-conductive
brushes 54a, 54b. Electrically-conductive brushes 54a, 54b are in turn in
electrical
communication with electrical leads 51a, 51b extending from first end 40 of
electrical
connector 24.
Electrically conductive brushes 54a, 54b connected to leads 51a, 51b are
preferably
spring-biased into contact with corresponding annular ring members 52a, 52b
via respective
springs 55a, 55b to ensure continuous contact and thus continuous electrical
communication
between annular ring members 52a, 52b and conductive brushes 54a, 54b, while
nevertheless
permitting relative rotation therebetween and eliminating otherwise certain
twisting and thus
forcible parting of one or more electrical leads 51a, 51b and conductive
brushes 54a, 54b and
the resultant loss of supply of electrical power from battery pack 10.
The novel battery pack 10 described above thus prevents downhole MWD mud
pulser
sensor equipment and mud pulsers which are directly or indirectly coupled to a
drill string
(not shown) and which would otherwise transmit rotational forces from such
drill string to
first end 20 of battery container 10 coupled thereto, from being unable to do
so due to the
provision and configuration of electrical connector 24 provided on battery
pack 10, which
prevents transmittal of any rotational accelerational or decelerational forces
applied to a first
end 20 of battery container 12 to one or more batteries 30 contained in
battery container 12.
- 13 -
CALLAW \ 3528720\2
CA 2991220 2019-12-19
Fig. 3 shows a preferred modification of the battery pack/battery pack system
10 of
the present invention, whereby advantageously a pair of electrical sockets
18a, 18b, are
provided at first end 20 and second end 22 respectively of battery pack 10,
which are in
electrical communication with one or more batteries 30 contained in battery
pack system 10.
The resultant advantage of such preferred modification being further described
in more detail
below and in reference to Fig. 5.
Fig. 4 is a semi-transparent view of the battery pack of Fig. 3.
Advantageously, and as seen from Fig. 5, batteries packs of this
configuration, such as
battery packs 10a and 10b, may be "daisy chained" (i.e. coupled in end-to end
manner) as
shown in Fig. 5 where respective second ends 22 thereof are electrically and
physically
coupled together to thereby provide torsional isolation at both ends of the
battery pack with
respect to any MWD equipment which may be physically and/or electrically
coupled to such
ends thereof.
Fig 6 depicts a semi-transparent partially exploded view of the resulting
coupled
battery pack of Fig.5, comprising coupled battery packs 10a and 10b physically
and
electrically coupled together at their respective second ends 22.
Fig. 7 shows another embodiment of the battery pack of the present invention,
namely
a single battery pack 10c having electrical socket connectors 18a, 18b at
respective first and
second ends 20, 22 thereof for electrically and physically coupling to MWD
electrical
equipment and mud pulsers. Such battery pack 10c further has torsion limiting
means 16a,
16b as described below at opposite ends 20, 22 thereof.
Fig. 8 shows an enlarged, exploded, semi-transparent view of the battery pack
10c
shown in Fig. 7.
Advantageously, however, as may be seen from Figs. 7 & 8, torsional limiting
means
16a, 16b in the form of electrical connectors 24a, 24b connected to battery
pack ends 40a,
40b, as described above, are provided in battery container 12 proximate each
of respective
first and second mutually opposite ends 20, 22, to prevent torsional forces
from being
transmitted from either or both ends 20, 22 to batteries 30 situated therein.
- 14 -
CALLAW1352872012
CA 2991220 2019-12-19
Further advantageously, the configuration of the battery pack system of Fig's
7 and 8
likewise allow for battery packs 10a, 10b of such design to be "daisy chained"
together in
end-to-end relation in either "parallel" or "series" electrical coupling to
form a single battery
pack 10, as shown in Fig. 9, allowing more flexibility in providing battery
power from
combined battery pack 10 most suited to the electrical demands and desired
longevity for
powering downhole electrical equipment which is directly or indirectly also or
physically
coupled thereto.
Importantly, the invention is not to be understood as being limited to the
type of
electrical slip ring connectors 24 as described above for providing torsion
limiting means, and
many alternative configurations for electrical connectors which allow relative
rotational
movement between electrical leads coupled to a downhole MWD apparatus, and
electrical
leads 41a, 41b coupled to one or more batteries 30, are contemplated.
One alternative electrical conductor configuration for the battery pack system
of the
present invention which is equally workable as the slip ring connector 24 is
male¨female
electrical connector half members 71, 72, comprising a male cylindrical half
member 71
with a plurality of electrically conductive annular rings 75 thereon which is
situated at a first
end 20 of battery container 12 and electrically coupled to batteries 30
contained therein, as
shown for example in Fig's 10-14 herein.
For example, a male electrical connector half member 71 forming part of
battery pack
system 10d, may be releasibly lockingly inserted with a mating female
connector half
member 72 having a corresponding plurality of resiliently flexible
electrically conductive
elements 76 peripherally surrounding an inner cylindrical surface 80 thereof
adapted to
contact the annular rings 75 in any and all angular rotations of the male
electrical connector
71 when inserted in female connector 72.
Many other equally suitable forms of electrical connectors which allow
relative
rotation therebetween but continuously allow electrical connection will now
occur to persons
of skill in the art. All are equally contemplated as being utilizable for
providing the torsion
limiting capability of the present invention.
-15-
CAL_LA\N\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
Torsional limiting means 16a, 16b of the present invention, such as employed
in the
battery pack system 10 shown in Fig. 9, advantageously allows electrical MWD
equipment
(not shown) to be electrically and physically coupled to both first and second
ends 20, 22 of
battery pack 10c each to be torsionally isolated from batteries 30 within
battery container 12.
Thus all batteries 30 contained therein are torsionally isolated from
rotational accelerative and
decelerative forces being applied to battery (ies) 30 from either or both ends
20, 22 of battery
container 12.
In this regard, Figs. 10-14 show a battery pack system/assembly 10d of the
present
invention, wherein the torsion-limiting means 16 comprises respective mating
male 71 and
female 72 rotatable electrical connectors, one of which is situated on at
least one end 20 of
battery pack system 10d, and the other of which is electrically and physically
coupled,
directly or indirectly, to MWD electrical apparatus (not shown) for which
battery power is
required to operate.
With reference to Fig. 10 and 11, Fig. 10 shows such an alternative battery
pack
system 10d as immediately described, utilizing a battery pack having torsion-
limiting means
16 wherein gender-opposite male and female rotatable electrical connectors
half members 71,
72 are disposed at mutually opposite ends of battery pack 10d and which are
respectively
electrically coupled to mutually opposite ends 20, 22 of the battery pack 10d.
Fig. 11 is a side view of the battery pack assembly 10d of Fig. 10, in
assembled
condition.
Fig. 12 is a cross-sectional view taken along plane 4-4 of Fig. 11, showing
the
configuration of the female electrical connector half member 72 coupled to end
22 of battery
container 12;
Fig. 13 is a partially exploded view showing the manner of locating and
inserting the
battery pack 10d of Fig. 10 within a sealed assembly 90 for insertion within
drill pipe (not
shown).
Fig. 14 is a cross sectional view of the battery pack system 10d of Fig. 10,
showing
-16-
CALLAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
the manner of electrically coupling the battery pack system 10d to uphole and
downhole
electrical MWD components while providing torsional isolation for the
batteries 30 within the
battery pack system 10d;
Other torsional limiting means 16a, 16b other than electrical connectors 24 or
male ¨
female electrical connectors 71, 72 of the type described above may be
employed to allow for
relative angular rotation.
Specifically, the torsion limiting means 16 of the present invention is not to
be
understood as being limited to electrical slip ring connectors 24 or mating
rotatable electrical
connector male-female half-members 71,72 as described above for providing
torsion limiting
means, and many alternative torsional limiting means are contemplated.
For example, in substitution of any of the electrical connectors 24, 24a, or
24b or
mating rotatable electrical connector male-female half-members 71,72
contemplated for use
in the present invention as torsion limiting means 16, instead (or in
addition) an elastomeric
material 60 may be interposed in hollow battery container 12 in the outer wall
14 thereof, as
shown for example in Figs. 17 & 18 further described below, to resiliently
absorb and
frictionally damp high acceleration and deceleration forces exerted on battery
pack 10, 10b,
or 10c. The amount of allowed relative angular rotation . where the
elastomeric material is
comprised of a material such as Viton , while not as large as in the case of
electrical slip
ring connectors 24, is sufficient to damp to a degree torsional forces and
allow a degree of
relative angular rotation to absorb sudden transitional accelerative forces,
but nevertheless not
being so significant to thereby over-twist electrical leads 41a, 41b, and 51a,
51b which are
physically coupled together and in electrical communication.
By way of example , Figs 17-18 show a battery pack system/assembly 10e, where
the
torsion-limiting means 16 comprises an elastomeric material 60 situated
proximate said first
end 20 of said elongate hollow container 12 and interposed in an
interdigitating manner
between portions of said outer wall 14 and a remaining portions of battery
container 12
which provides torsional damping of rotational forces applied to said first
end 20 of battery
container 12 (which is physically and electrically coupled, directly or
indirectly to MWD
-17-
CAL_LAVV\ 2817990\3
CA 2991220 2018-01-08
equipment which is in turn physically coupled to an MWD sub located in the
drill string)
relative to a remaining portion and said second end 22 of battery container 12
to thereby
torsionally isolate batteries 30 in such battery container 12.
Fig. 17 shows a side perspective view of a further embodiment of the battery
pack/battery pack system of the present invention 10e having an elastomeric
material situated
proximate the first end 20 of the elongate hollow battery container 12 and
interposed in an
interdigitating manner between portions of the outer wall 14 of battery
container 12 and
remaining portions of the battery container 12 to thereby provide not only
torsional damping
of rotational forces but also axial damping of axial forces; and
Fig. 18 is side perspective view of the battery pack/battery pack system 10e
of the
present invention depicted in Fig. 17, having torsional limiting means 16 in
the form of an
interposed elastomeric material 60 disposed proximate each of opposite ends
20, 22 of battery
container 12, to thereby isolate batteries 30 therein from torsional
accelerative and
decelearative forces which may be applied to either or both ends 20, 22 of
battery container 12.
Fig. 15 is a further modification of the battery pack system 10d shown in Fig.
10,
further having additional further torsion reduction means 16 in addition to
the rotatable male
and female electrical connectors 71, 72, further having additional torsional
damping feature
16 in the form of an elastomeric material 60 mounted in a cavity 92 on female
connector half
72õ in which protruding prongs 94 of the battery container 12 proximate male
half
member 71 may be inserted into apertures 97 centrally located in elastomeric
material 60
on female connector half member 72. In such manner relative angular rotation
in either
direction between half members 71, 72 is damped.
Fig. 16 is a side perspective view of the elements shown in Fig. 15, and shows
the
manner of inter-connecting the electrical connector 100 of the MWD apparatus
with a first
end 20 of the battery pack 10 having a male rotatable electrical connector
half member 71
thereon. Fig. 16 shows how the protruding prongs 94 on the first end 20 of the
battery
container 12 are inserted into apertures 97 within elastomeric material 60
situated on female
rotatable connector half member 72, to thereby provide relative angular damped
- 18 -
CAL_LAW\ 3528720\2
CA 2991220 2019-12-19
rotation between half member 72 and battery container 12.
Many other torsional damping configurations using elastomeric materials 60 or
resiliently-biased members such as and including but not limited to torsional
springs
interposed in the battery container 12 of the battery pack system 10, may be
used and will
now occur to persons of skill in the art.
Such alternative torsion-limiting means 16 may be used in association with
battery
container 12 and forming part of the battery pack system 10 of the present
invention. All are
equally contemplated as being within the scope of the invention herein.
For a complete definition of the invention and its intended scope, reference
is to be
made to the summary of the invention and the appended claims read together
with and
considered with the disclosure and drawings herein.
- 19 -
CALLAW\ 3528720\2
CA 2991220 2019-12-19