Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
An Engineering Geological Drilling Construction Method Based on Wire
Line Coring Drilling Tool
Technical field
The invention relates to the technical field of engineering geological
drilling, and
particularly relates to an engineering geological drilling construction method
based on
a wire line coring drilling tool.
Background Art
Engineering geological drilling, according to certain objectives and
requirements,
utilizes drilling machines and tools to drill into stratums, to take out rock
cores and soil
samples to ascertain geological conditions and foundation bearing capability.
This
requires to drill into topsoil and has special sampling requirements, and also
requires
doing special testing operation in the drilling hole. One of the objectives of
engineering
drilling is to extract undisturbed soil sample to measure the soil physico-
mechanical
properties such as natural structure capacity, density, temperature, shearing
strength,
compressibility coefficient, etc., to conduct rock-soil characteristics
description and
determine the soil layer bearing capacity and stability, and to provide
reliable design
basis for various engineering constructions.
At present, the most widely applied engineering geological drilling is
utilizing a
spindle-type drilling rig, for example, XY-1 type or XY-2 type, and a single
barrel
drilling tool, and using hard alloy drilling bit mechanical rotation method to
drill, dry
drilling with no water supplied, the big drill lifted once for every drill
footage of 0.5 m
- 1 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
to 2 m. When taking rock core and conducting standard penetration test, the
whole set
of drilling rod and drilling tool has to be lifted out from the hole. The
biggest
advantages of this method are that the cost is low and the operation is
simple. But the
limitations and disadvantages of the drilling rig and drilling tool are also
very obvious.
Because single barrel drilling is adopted, the disturbance to soil layer is
large, and it's
hard to extract undisturbed soil sample in complex stratums, which lead to the
poor
rock core quality; during coring and standard penetration test, the whole
drilling rod
and drilling tool also have to be lifted or put down repeatedly, which would
damage the
hole wall easily, and phenomena such as chip off-falling, hole collapse and
the like
often occur, which lead to drill jamming accidents. In addition, during
standard
penetration test, the drilling rod would hit the hole wall easily because of
its elastic
deformation caused by the hammering, which affects the stability of the hole
wall, and
meanwhile the friction between the drilling rod and the hole wall affects the
test
accuracy.
Technical problem
In order to overcome the disadvantages in the prior art mentioned above, this
invention provides an engineering geological drilling construction method
based on a
wire line coring drilling tool, which adopts a single-action double-barrel
drilling tool
for full-hole barrel-following drilling, and during coring and standard
penetration tests,
the drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly remain still all the time in
the drilling
- 2 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
hole, so that the disturbance to the soil layer is small, and the hole wall is
protected
from damage.
Technical solution
To solve the technical problem, the invention provides an engineering
geological
drilling construction method based on a wire line coring drilling tool, and
the method
comprises the following steps:
step 1, selecting a drilling tool, wherein a single-action double-barrel wire
line
coring drilling tool is adopted as the drilling tool, the drilling tool
comprises an outer
barrel assembly and an inner barrel assembly, the outer barrel assembly
comprises an
outer barrel and a coring bit installed at the lower end of the outer barrel,
the inner
barrel assembly comprises a core barrel and a spring clamp which is clampable
inside
the outer barrel assembly;
step 2, installing the coring bit at the lower end of the outer barrel, and
installing
the core barrel at the lower end of the spring clamp, wherein the spring clamp
is
suspended inside the outer barrel assembly, and the upper end of the outer
barrel
assembly is connected with the power head of a drilling rig through a drilling
rod;
step 3, driving, by the power head of the drilling rig, the drilling rod to
drive the
coring bit on the outer barrel assembly to rotate for cutting rock and soil,
wherein as an
oil cylinder feeds under increased pressure, the core barrel keeps a non-
rotation state
and sleeves rock cores which enter the core barrel continually;
- 3 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
step 4, lifting, by the oil cylinder, after the drilling depth reaches the
length of the
core barrel, the whole drilling tool from the hole bottom for a short distance
to pull off
the rock cores, and clamping and fixing the drilling rod by a gripper of the
drilling rig;
step 5, putting down a wire line coring fisher to fish out the inner barrel
assembly
filled with rock cores, while keeping the drilling rod and the outer barrel
assembly still,
and using another set of inner barrel assembly for replacement to be put into
the outer
barrel assembly again for the next round of drilling;
step 6, repeating the steps from step 3 to step 5 until the drilling reaches
the
expected drilling depth, lifting, by the oil cylinder, the whole drilling tool
from the hole
bottom for a short distance to pull off the rock cores, putting down the wire
line coring
fisher to fish out the inner barrel assembly filled with rock cores, while
keeping the
drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly still in the drilling hole;
step 7, connecting a standard penetrometer by a test bar and passing through
the
drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly to be sent to a bottom of the
drilling hole;
step 8, connecting a top end of the test bar with a standard penetration
hammer
base, and carrying out a standard penetration test by utilizing the standard
penetration
hammer above the test bar to hit the standard penetration hammer base in a
manner of
free falling, wherein during the test, the drilling rod and the outer barrel
assembly
remain still in the drilling hole;
step 9, utilizing a main winch to lift out the standard penetrometer quickly
after
the standard penetration test is finished.
- 4 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
As an improvement for the above technical solution, in step 4 and step 6, the
whole drilling tool is lifted by the oil cylinder by 100 mm from the hole
bottom to pull
off the rock cores.
As an improvement for the above technical solution, the minimum inner diameter
of the outer barrel assembly is no less than 56 mm, and the maximum outer
diameter of
the standard penetrometer is no greater than 50 mm.
As an improvement for the above technical solution, the outer diameter of the
coring bit is 75.7 mm, and the inner diameter of the coring bit is 56 mm.
As an improvement for the above technical solution, in step 2, the length of
the
inner barrel assembly is adjusted and checked to guarantee that the inner
barrel
assembly and the step part of the inner wall of the drilling bit are not in
contact with
each other, and the water-passing gap is no greater than 1 mm.
Advantageous effects
In the drilling construction method, the single-action double-barrel drilling
tool is
adopted for full-hole barrel-following drilling, it drills as it is pressed in
during rotating,
the drilling speed is very fast, the mud consume is less, the core barrel
keeps a
non-rotation state, the disturbance to soil layer is small, the coring quality
is high, and
undisturbed soil sample can be extracted. During coring and standard
penetration test,
the drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly remain still in the drilling
hole all the
time, the hole wall is protected, the damage of the hole wall from repeatedly
lifting the
- 5 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
drill is avoided. Meanwhile the friction between the test bar and the hole
wall is
reduced, and uncertain factors are reduced, which make the test results more
accurate.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The invention is described further in combination with the accompanying
drawings and specific embodiments as follows, wherein:
Figure 1 is a structural schematic view of an embodiment of the invention when
drilling and coring;
Figure 2 is a structural schematic view of an embodiment of the invention
during
a standard penetration test.
Detailed description of the invention
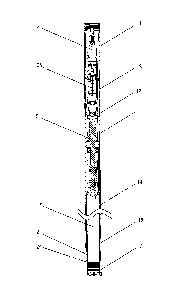
As shown in Figure 1, an adopted drilling tool in a drilling method of this
invention is a single-action double-barrel wire line coring drilling tool,
comprising an
outer barrel assembly 1 and an inner barrel assembly 2 which is inserted in
the outer
barrel assembly 1. The outer barrel assembly 1 comprises a spring clamp
stopper 11, a
spring clamp chamber 12, a socket ring 13, an outer barrel 14, a reamer 16 and
a coring
bit 15, which are connected from up to down successively. The minimum inner
diameter of the outer barrel assembly 1 is no less than 56 mm. The coring bit
15 is
made of hard alloy, or polycrystalline diamond compact drilling bit or
impregnated
diamond drilling bit can also be adopted, with the outer diameter of 75.7 mm
and the
inner diameter of 56 mm. The inner barrel assembly 2 comprises a drilling tool
head
assembly 21, a core barrel 22, a snap spring base 23 and a snap spring 24,
which are
- 6 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
connected from up to down successively. The socket ring 13 can limit and
support the
drilling tool head assembly 21, and a spring clamp 25, which is matchable with
the
spring clamp stopper 11 for fastening, is arranged on the drilling tool head
assembly
21.
As shown in figure 2, a test bar 3 is arranged through the outer barrel
assembly 1,
a standard penetration hammer base 4 is connected at the top end of the test
bar 3, a
standard penetrometer 5 is connected at the lowered end, and the standard
penetrometer
5 has a maximum outer diameter no greater than 50 mm in order to be inserted
into the
outer barrel assembly 1.
The engineering geological drilling construction method based on a wire line
coring drilling tool of this invention, comprising the following steps:
step 1, selecting a drilling tool, wherein a single-action double-barrel wire
line
coring drilling tool is adopted as the selected drilling tool.
step 2, installing the coring bit 15 at the lower end of the outer barrel 14,
and
installing the core barrel 22 at the lower end of the spring clamp 25, wherein
the spring
clamp 25 is suspended inside the spring clamp chamber 12. Adjusting and
checking the
length of the inner barrel assembly 2 to guarantee that the snap spring base
23 and the
step part of the inner wall of the drilling bit are not in contact with each
other, and the
water-passing gap is no greater than 1 mm. The upper end of the spring clamp
stopper
.. 11 is connected with the power head of a drilling rig through a drilling
rod.
- 7 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
step 3, driving, by the power head of the drilling rig, the drilling rod to
drive the
coring bit 15 on the outer barrel assembly 1 to rotate for cutting rock and
soil, as the oil
cylinder feeds under increased pressure, the core barrel 22 keeps a non-
rotation state
and sleeves rock cores which enter the core barrel 22 continually.
step 4, after the drilling depth reaches the length of the core barrel 22,
lifting, by
an oil cylinder, the whole drilling tool for 100 mm from the hole bottom to
pull off the
rock cores, and clamping and fixing the drilling rod by a gripper of the
drilling rig.
step 5, putting down a wire line coring fisher to fish out the inner barrel
assembly
2 filled with rock cores, while the drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly
1 remain
still, and changing for another set of inner barrel assembly 2 to be put into
the outer
barrel assembly 1 again for the next round of drilling.
step 6, repeating the steps from step 3 to step 5 until the drilling reaches
the
expected drilling depth, lifting, by the oil cylinder, the whole drilling tool
for 100 mm
from the hole bottom to pull off the rock cores, and putting down a wire line
coring
fisher to fish out the inner barrel assembly 2 filled with rock cores, while
the drilling
rod and the outer barrel assembly 1 remain still in the drilling hole.
step 7, connecting a standard penetrometer 5 by a test bar 3 and passing
through
the drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly 1 to be sent to a bottom of the
drilling
hole.
step 8, connecting a standard penetration hammer base 4 to the top end of the
test
bar 3, carrying out a standard penetration test by utilizing the standard
penetration
- 8 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
hammer above the test bar 3 to hit the standard penetration hammer base 4 in a
manner
of free falling, and during the testing period, the drilling rod and the outer
barrel
assembly 1 remain still in the drilling hole.
step 9, utilizing a main winch to lift out the standard penetrometer 5 quickly
after
the standard penetration test is finished.
In step 2 of the method of this invention, the snap spring base 23 and the
step part
of the inner wall of the drilling bit 16 are not in contact with each other,
which is
convenient for supplying water during drilling, and the water-passing gap is
no greater
than 1 mm, which can avoid soil entering into the gap between the core barrel
22 and
the outer barrel 14 during drilling process and prevent causing jamming of the
core
barrel 22.
The drilling tool is pressed in and drills during rotating, the full-hole
barrel-following drilling speed is very fast, about 25 meters can be drilled
within 8
hours in sandstone stratum and cobblestone stratum, and the mud consume is
less.
Because the core barrel 22 keeps a non-rotation state, the disturbance to soil
layer is
small, the coring quality is high, and undisturbed soil sample can be
extracted. During
standard penetration test, the drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly 1
remain still in
the drilling hole all the time, the hole wall is protected, the damage of the
hole wall
from lifting the drill repeatedly is avoided, and meanwhile the friction
between the test
bar 3 and the hole wall is reduced, it's avoided that the test bar 3 would hit
the hole
- 9 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10
wall when deformed from bending, and uncertain factors are reduced which make
the
test results more accurate.
Industrial Applicability
The engineering geological drilling method based on a wire line coring
drilling
tool of this invention, since a single-action double-barrel drilling tool is
adopted, it is
pressed in and drills during rotating, the full-hole barrel-following drilling
speed is
very fast, the mud consume is less, the core barrel keeps a non-rotation
state, and the
disturbance to soil layer is small. After the drilling depth reaches the
length of the core
barrel, the oil cylinder lifts the whole drilling tool for a distance from the
hole bottom
to pull off the rock cores, the coring quality is high, and undisturbed soil
sample can be
extracted.
And, according to the invention, during coring and standard penetration test,
the
drilling rod and the outer barrel assembly remain still all the time in the
drilling hole,
the hole wall is protected, the damage of the hole wall from lifting the drill
repeatedly
is avoided, and meanwhile the friction between the test bar and the hole wall
is reduced,
and uncertain factors are reduced, so that the test results are more accurate,
which is
more beneficial for carrying out the construction.
- 10 -
CA 3004688 2018-05-10