Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
1
Device Comprising a Pane and at Least One Lifting Rail, Method for
Its Production and Its Use
Description
The present invention relates to a device comprising a pane and at least one
lifting rail.
The present invention also relates to a method for producing the device.
Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of the device.
Devices comprising transparent panes and lifting rails as well as methods for
their
production are known. The lifting rails are flat molded parts that are ¨
viewed in vertical
section ¨ fork-shaped. The fork-shaped part with its ¨ viewed in the vertical
section ¨
tines thus forms a region that can bilaterally enclose the edges of
transparent panes. The
edges of the transparent panes are inserted into the interior of this region
and firmly
adhesively bonded on the bottom of the region as well as, optionally, areally
on both sides.
During this operation, it can happen that the uncured adhesive pressed out by
the edge of
the transparent pane from the two lower, still open regions of the enclosing
region of the
lifting rail, is caught, and is also cured.
Depending on the use of the device, it may be that no space is provided for
the pressed-out
mass of adhesive in the functional structure involved, such that it can,
undesirably, make
contact with other parts of the the structure. This can be the case in
particular if the
functional structure is used as a movable side window in automobile doors.
However, it can
also detach during the service life of the structure and cause undesirable
noise. Moreover, it
can, in particular, block openings through which water penetrating into the
structure can
drain. If the drains are plugged, this can, over time, result in corrosion
damage.
A further disadvantage of the formation of pressed-out adhesive masses is the
higher
consumption of adhesive.
In order to remedy the above described disadvantages after the fact, the
pressed-out mass
of adhesive can be removed mechanically before, during, or after the curing of
the adhesive.
This can be happen using suitable devices or manually. Meanwhile, the further
disadvantage
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
2 =
of an additional process step is encountered. Moreover, the adhesive residues
removed are
unusable waste that must be discarded.
Known from European patent application EP 1 936 088 Al is a frameless window
that
comprises a transparent pane, the lower edge of which is fixed in a slot of
one or a plurality
of holders with at least one layer of an adhesive, wherein the lower edge of
the pane is
joined to the walls of the slot of the holders by means of one or a plurality
of layers of a first
adhesive that is applied near the lateral end of the slot, wherein at least
one layer of a
second adhesive is applied in the slot between the layers of the first
adhesive. The method
is thus complicated and does not offer a full guarantee against the outflow of
adhesives.
Known from European patent application EP 1 936 087 Al is a frameless window
that
comprises a transparent pane, the lower edge of which is fixed in a slot of
one or a plurality
of holders with at least one layer of an adhesive, wherein the adhesive has a
modulus of
elasticity between 10 and 90 MPa at room temperature, and that the width of
the slot of at
least one holder is at least twice the thickness of the pane. It is, however,
necessary to
introduce one or a plurality of closing members to the mounting for the lower
edge of the
pane in the slit of a holder to prevent prevent leakage of the adhesive.
In contrast, the object of the present invention is to provide a method for
producing a device
comprising a transparent pane and at least one lifting rail firmly adhesively
bonded thereto,
that delivers, in a simple manner, devices that are free of pressed-out
adhesive.
These and other objects are accomplished according to the proposal of the
invention by the
device and the method with the features of the independent claims.
Advantageous
embodiments of the invention result from the features of the subclaims.
The lifting rail serves to connect a pane to a drive device, for example, a
traction device or a
lifting device, with which the transparent pane is moved horizontally or
vertically.
As is known, the lifting rail is a substantially flat component that is
preferably constructed
from a technical plastic, in particular a thermoplastic, such as polyethylene,
polypropylene,
polystyrene, polyoxymethylene, polycarbonate, polymethylmethacrylate,
polyamide,
polyester, in particular polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polyvinyl chloride,
polysulfone,
polyethersulfone, polyether ketone, and/or mixtures thereof.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
3
The lifting rail has a substantially or exactly square or rectangular outline,
wherein the region
that does not accommodate the transparent pane can also have, for example, a
concavely
or convexly rounded or trapezoidal outline.
The dimensions of the lifting rail can vary widely and are governed by the
respective
applicational purpose. Preferably, the lifting rail has a height of 3 to 15
cm, a length of 3 to
20 cm, and a thickness of 1 to 5 cm, wherein, in one embodiment, the total
thickness in the
region that spans the edge of the transparent pane is greater than in the
connection region,
which connects the lifting rail to a drive device, and, in another embodiment,
is the same
size.
The vertical section through the lifting rail, in other words, from the outer
edge of the
connection region to the outer edge of the region that spans the edge of the
transparent
pane, is fork-shaped, for example, tuning-fork-shaped. This means that the
lifting rail has a
stem surface, a region of bifurcation where the stem surface transitions into
the fork-shaped
region, which bilaterally encloses the edge of the transparent pane. However,
it is also
possible to use a fork shape in which the stem surface transitions smoothly
into the fork-
shaped region such that the stem surface and the outer surface of the region
that bilaterally
encloses the edge of the transparent pane form a flat surface.
It is advantageous for the contour in the interior of this region in the
region of bifurcation to
be adapted to the contour of the edge of the pane.
The stem surface of the lifting rail has at least one, in particular one,
through-hole, which is
preferably arranged centrally. The through-hole can have various outlines. It
can be circular,
rectangular, square, triangular, or hexagonal. Preferably, it is circular.
The through-hole is traversed by a bolt that is connected to the drive device,
preferably a
lifting device or traction device.
In another embodiment, the stem surface of the lifting rail has a cutout on
its outer edge, in
which the connection to a drive device, for example, a lifting device,
engages.
According to the invention, the lifting rail has a single-sided or double-
sided, preferably
single-sided bonding adhesive strip, which partially covers the stem surface,
with the through
hole or the cutout remaining exposed. If a double-sided adhesive strip is
used, the protective
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
4
covering on the outside is not removed after application of the adhesive strip
on the lifting
rail.
The adhesive strip can, in the tuning-fork-shaped configuration, at least
partially, preferably
completely, cover the region of the bifurcation.
According to the invention, the adhesive strip covers the region bilaterally
enclosing the edge
of the transparent pane and the mutually opposite open ends of the region. In
this
configuration, the adhesive strip is deformed by the edge of the pane during
the joining of
the pane and the lifting rail on the two opposite ends of the enclosing
region, in particular in
the direction of the stem surface.
In one embodiment of the device according to the invention, the adhesive strip
completely
encircles the stem surface, the bifurcation region, and the enclosing region.
In another embodiment, the adhesive strip covers the enclosing region such
that the regions
adjacent the upper edge of the lifting rail remain uncovered.
In another embodiment of the device according to the invention, the adhesive
strip is
transparent or opaque or transparent in at least one subregion transparent and
opaque in at
least one other subregion.
Conventional, known adhesive strips, for example, Tesa0 Transparent Tape 57405
(glossy)
or Scotch Magic Tape 810 (matte) are used as the adhesive strip to be used
according to
the invention. A suitable criterion for selecting particularly well-suited
adhesive strips is the
existence of the conventional, known cataplasma test test (7 days at 70 , 100%
relative
humidity), wherein there must be no disbonding of the adhesive strip from the
lifting rail. The
adhesive strip must also not tear and/or slide downward in the direction of
the stem surface.
Prior to the joining of the pane and the lifting rail, an adhesive is
introduced into the interior
of the enclosing region. A wide variety of adhesives can be used. Preferably,
a
polymerization adhesive, a polycondensation adhesive, or a polyaddition
adhesive it is used.
Preferably, a polyaddition adhesive, in particular a polyurethane adhesive, is
used.
During insertion of the pane, the adhesive distributes itself on the bonding
surface, with the
undesirable outflow of adhesive effectively prevented by the adhesive strip to
be used
according to the invention.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
Then, the adhesive is cured and a stable adhesive bond between the pane and
the lifting rail
develops.
5 The pane of the device according to the invention can be made of glass,
plastic, wood,
metal, or combinations of at least two of these materials.
Preferably, the pane is a transparent pane that is constructed in particular
from glass and/or
plastic.
In a preferred embodiment of the device according to the invention, the
transparent pane is a
safety glazing that has at least two transparent panes.
Suitable as the first and, optionally, the second pane are, in principle, all
substrates that are
thermally and chemically stable as well as dimensionally stable under the
conditions of
production and use of the transparent pane.
The first pane and/or the second pane preferably contain glass, particularly
preferably flat
glass, float glass, quartz glass, borosilicate glass, or soda lime glass, or
clear plastics,
preferably rigid clear plastics, in particular polyethylene, polypropylene,
polycarbonate,
polymethylmethacrylate, polystyrene, polyamide, polyester, polyvinyl chloride,
and/or
mixtures thereof. The first pane and/or the second pane are preferably
transparent, in
particular for the use of the pane as a movable side window of a vehicle or
other uses in
which high light transmittance is desired. In the context of the invention,
"transparent" means
a pane that has transmittance in the visible spectral range of >70%. For panes
that are not
positioned in the traffic-relevant field of vision of the driver, for example,
for roof panels, the
transmittance can, however, be much lower, for example, >5%.
The thickness of the transparent pane can vary widely and thus be ideally
adapted to the
requirements of the individual case. Preferably, panes with the standard
thicknesses from
1.0 mm to 25 mm, preferably from 1.4 mm to 5 mm are used for vehicle glazing,
and
preferably from 4 mm to 25 mm for furniture, appliances, and buildings, in
particular for
electric heaters. The size of the pane can vary widely and is governed by the
size of the
device according to the invention. The first pane and, optionally, the second
pane have, for
example, in the automotive industry and the architectural sector usual areas
from 200 cm2
up to 20 m2.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
.6
The transparent pane can have any three-dimensional shape. Preferably, the
three-
dimensional shape has no shadow zones such that it can be coated, for example,
by
cathodic sputtering. Preferably, the substrates are planar or slightly or
greatly bent in one or
a plurality of spatial directions. In particular, planar substrates are used.
The transparent
panes can be colorless or colored.
Multiple panes are bonded to one another by at least one intermediate layer.
The
intermediate layer preferably contains at least one thermostatic plastic,
preferably polyvinyl
butyral (PVB), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), and/or polyethylene terephthalate
(PET).
However, the thermoplastic intermediate layer can also contain, for example,
polyurethane
(PU), polypropylene (PP), polyacrylate, polyethylene (PE), polycarbonate (PC),
polymethylmethacrylate, polyvinyl chloride, polyacetate resin, casting resins,
poiyacrylates,
fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymers, polyvinyl fluoride, and/or ethylene
tetrafluoroethylene copolymers, copolymers or mixtures thereof. The
thermoplastic
intermediate layer can be formed by one or even by a plurality of
thermoplastic films
arranged one atop another, with the thickness of the thermoplastic films
preferably being
from 0.25 mm to 1 mm and typically 0.38 mm or 0.76 mm.
The device according to the invention can be produced using various methods.
It is,
however, preferably produced using the method according to the invention.
The method according to the invention is characterized by the following
process steps:
click save
(1) Providing at least one lifting rail, having
- a fork-shaped vertical section and
- a stem surface with a through-hole or a cutout on the outer edge
(2) Introducing an adhesive into the interior of the region in the region
of bifurcation in an
amount that reaches, after insertion of the pane, at most up to the upper edge
of the
enclosing region on both sides.
(3) Adhesively mounting an adhesive strip on the at least one lifting rail
such that it
partially covers the stem surface, with the through-hole remaining exposed,
and
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
7
covers the region bilaterally enclosing the edge of the pane and the mutually
opposite open ends of the enclosing region such that the adhesive strip is
deformed by the edge of the insertion pane upon insertion in these regions,
(4) Inserting the edge of the pane into the interior of the bilaterally
enclosing region,
wherein the two mutually opposite regions of the adhesive strip are deformed,
and
(5) Curing the adhesive.
Using the method according to the invention, the formation of pressed-out
plastic masses
can be prevented in a simple manner.
The method according to the invention can, however, also be used for producing
devices of
the prior art, in that the adhesive strip is peeled off. However, this
requires an additional
process step and there is the risk that parts of cured or uncured adhesive
will be torn off.
The device according to the invention, in particular the device according to
the invention
produced using the method according to the invention can ideally be used as a
functional
and/or decorative individual piece and/or as a built-in part in furniture,
appliances, and
buildings, as well as in means of transportation for transportation on land,
in the air, or on
water, but, in particular in motor vehicles, for example, as a movable rear
window and a side
window and/or a movable glass roof. Preferably, the device according to the
invention is
implemented as a vehicle side window or a glass roof.
Of course, the aforementioned features and those described in detail in the
following can be
used not only in the combinations and configurations indicated, but also in
other
combinations and configurations or alone without departing from the scope of
the present
invention.
Brief Description of the Figures
The invention is now explained in detail using exemplary embodiments, with
reference to the
accompanying figures. They depict, in simplified, not-to-scale representation:
Fig. 1 a side view of a lifting rail 1 with an associated pane 5 before
joining to form a
device according to the prior art;
Fig. la a vertical section through the arrangement of Fig. 1;
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
8
Fig. 2 a side view of the joined device 1,5 according to the prior art
with pressed-out
adhesive;
Fig. 2a a vertical section through the joined device 1,5 according to
the prior art;
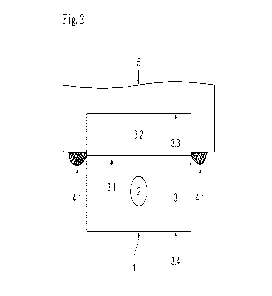
Fig. 3 a side view of a lifting rail 1 with an associated pane 5 prior
to joining to form a
device 1,5 according to the invention;
Fig. 3a plan view of the vertical edge of the lifting rail 1 and of the
vertical edge of the
associated pane 5;
Fig. 4 a side view of the joined device 1,5 according to the
invention;
Fig. 4a plan view of the vertical edge of the lifting rail 1 and of the
vertical edge of the
associated pane 5 of the device 1,5 according to the invention;
Fig. 5 a side view of the lifting rail 1 with a cutout 7;
Fig. 5a a vertical section through the lifting rail 1 along the section
line A-B;
Fig. 6 a side view of the lifting rail 1;
Fig. 6a a vertical section through the lifting rail 1.
In Fig. 1 through 4a the reference characters have the following meaning:
1 lifting rail with a fork-shaped vertical section
2 through-hole of the lifting rail 1 through the stem surface 3
3 stem surface of the lifting rail 1
3.1 region of bifurcation
3.2 region enclosing the edge of the pane 5
3.3 upper edge
3.4 outer edge
4 adhesive
4.1 pressed-out mass of adhesive
5 pane
6 adhesive strips surrounding the region of bifurcation 3.1
6.1 region of the adhesive strip 6 deformed by the pane 5
7 cutout on the outer edge 3.4
R direction of insertion
R1 direction of deformation
A-B section line
Detailed Description of the Figures
Fig. 1 and la
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
9
Fig. 1 depicts the side view of a detail of a transparent pane 5 and a lifting
rail 1 prior to
joining in the direction R to form the device 1,5 of the prior art.
Here, and in the following, the transparent pane 5 is a laminated safety glass
pane (VSG).
Here, and in the following, the lifting rail 1 is a component made of
polypropylene having the
length of 8 cm, the height of 6 cm, the thickness of 1 cm in the stem region
3, and the total
thickness of 1.5 cm in the region 3.2 (cf. Fig. la) surrounding the edge of
the transparent
pane. The lifting rail 1 further has a region of bifurcation 3.1, where the
region 3 transitions
into the region 3.2.
Centrally arranged in the stem region 3 is a circular through-hole with a
diameter of 1.5 cm,
which serves to accommodate a bolt for connection to a drive device, for
example, a lifting
device.
Fig. la depicts the vertical section through the lifting rail 1 and thus
illustrates its tuning-fork-
shaped configuration.
A polyurethane adhesive is filled into the interior of the region 3.2. Thus,
the lifting rail 1 and
the transparent pane 5 are ready for joining.
Fig. 2 and 2a
Fig. 2 depicts a side view of a joined device 1,5 of prior art comprising a
transparent
pane 5 and a lifting rail 1.
Fig. 2a depicts the vertical section through the device 1,5 of the prior art.
By means of the insertion of the transparent pane 5 into the interior of the
enclosing region
3.2, the uncured adhesive 4 is displaced and distributed on the bonding
surface. However, in
this process, the uncured adhesive 4 is also squeezed out laterally from the
region 3.2 and
thus forms the undesirable pressed-out adhesive masses 4.1.
Fig. 3 and 3a
Fig. 3 depicts a side view of the transparent pane 5 and of the lifting rail 1
prior to joining in
the direction R, R1 to form the device 1,5 according to the invention.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
Fig. 3a depicts the plan view of the lateral vertical end edge of the lifting
rail 1 to be used
according to the invention.
The lifting rail 1 to be used according to the invention has a
circumferentially adhesively
5 mounted adhesive strip 6 (Tesa Transparent Tape 57405 (glossy)). Here,
the stem region
3 is covered such that the through-hole 2 remains exposed. The region of
bifurcation 3.1 is
completely taped over, whereas, in contrast, the enclosing region 3.2 is
covered only to just
below the upper edge 3.3.
10 Fig. 3a depicts the manner in which the adhesive strip 6 bridges the
opening in the lateral
vertical end edge.
The adhesive 4 (not visible) is situated in the interior of the enclosing
region 3.2.
Thus, the transparent pane and the lifting rail 1 with the adhesive strip 6
are ready for
joining.
Fig. 4 and. 4a
Fig. 4 depicts the side view of the joined device 1,5 according to the
invention with the two
regions 6.1 of the adhesive strip 6 deformed by the edge of the transparent
pane 5. This
configuration is illustrated again by Fig. 4a, which offers a view of the
lateral vertical end
edges of the device 1, 5 according to the invention.
Fig. 5 and 5a
Fig. 5 depicts a side view of a lifting rail 1, as it can be used in the
method according to the
invention for producing the device 1,5 according to the invention.
Fig. 5 a depicts the vertical section through the lifting rail 1 of Fig. 5
along the section line A-
B.
The lifting rail 1 of Fig. 5 corresponded in its features to the lifting rail
1 of Fig. 1, with the
substantial difference that instead of the through-hole 2 in the stem surface
3, the outer edge
3.4 had the cutout 7. The connection to a drive device, for example, a lifting
device, was able
to engage in this cutout 7.
CA 03005485 2018-05-16
11
Fig. 6 and 6a
Fig. 6 depicts a side view of a lifting rail 1, as it can be used in the
method according to the
invention for producing the device 1,5 according to the invention.
Fig. 6 a depicts the vertical section through the lifting rail 1 of Fig. 6.
The lifting rail 1 of the Fig. 6 corresponded in its features to the lifting
rail 1 of Fig. 1, with the
substantial difference that its stem surface 3 and the enclosing region 3.2
formed a planar
surface. This is illustrated again by Fig. 6a, which shows that the vertical
section does not
have a tuning-fork-shaped configuration.