Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
LOW PROFILE MOWER BLADES
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application claims priority to U.S. Provisional Patent
Application Serial No. 62/397,177, filed September 20, 2016 titled LOW PROFILE
MOWER BLADES and U.S. Design Patent Application Serial No. 29/578,374, filed
September 21, 2016, and titled CUTTING BLADE which are herein incorporated by
reference in their entireties.
BACKGROUND
1. Field of the Disclosure
[0002] The present disclosure relates to lawn and garden equipment, and
more particularly, to a low-profile cutting blade for a mower.
2. Description of Related Art
[0003] Currently available lawn mowers such as walk-behind mowers,
riding mowers, garden tractors, and the like include a cutting deck having at
least one
cutting blade configured to cut grass and other vegetation. When using a
cutting
blade with a bagging attachment, the blade often includes an inclined surface
to create
lift under the deck to stand the grass upright and provide an airstream to
move grass
clippings into the bagging attachment such as the cutting blade shown in U.S.
Pat. No.
6,301,868. However, usage of this type of cutting blade in situations
involving soils
containing a relatively high sand content can erode the inclined surface
portion of the
cutting blade. After time, the inclined surface may be entirely removed,
thereby
eliminating the lift functionality of the blade. This can require relatively
frequent
blade replacement.
[0004] Therefore, a need exists for a mower blade having a low-lift air
flow
such that some airstream is provided while reducing the wear of sand
impingement
upon the blade.
BRIEF SUMMARY
[0005] According to one aspect of the present disclosure, a mower blade
for a lawn maintenance device includes an elongate blade having opposed end
edges
1
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
and opposed side edges. The elongate blade is adapted for mounting onto a
rotary
mower for rotation about a center axis extended transverse to the elongate
blade and
separating the elongate blade into opposed elongate end portions extended from
said
center axis. The elongate blade has a blade major axis. The elongate blade
defines a
curved portion such that the curved portion is opposite a cutting edge. The
curved
portion extends from the elongate blade in an upward direction where the two
meet
and curves toward a lower face of the elongate blade.
[0006] According to another aspect of the present disclosure, a mower
blade for a lawn maintenance device includes an elongate blade having opposed
end
edges and opposed side edges. The elongate blade is adapted for mounting onto
a
rotary mower for rotation about a center axis extended transverse to the
elongate
blade and separating the elongate blade into opposed elongate end portions
extended
from the center axis. The elongate blade has a blade major axis. The elongate
blade
defines a curved portion such that the curved portion is opposite a cutting
edge. The
curved portion extends from the elongate blade in an upward direction where
the two
meet and curves toward a lower face of the elongate blade. A distal portion of
the
curved portion is offset vertically from a cutting edge to develop lift during
rotation.
[0007] According to still another aspect of the present disclosure, a mower
blade for a lawn maintenance device includes an elongate blade having opposed
end
edges and opposed side edges. The elongate blade is adapted for mounting onto
a
rotary mower for rotation about a center axis extended transverse to the
elongate
blade and separating the elongate blade into opposed elongate end portions
extended
from the center axis. The elongate blade has a blade major axis. The elongate
blade
defines a curved portion such that the curved portion is opposite a cutting
edge. The
curved portion extends from the elongate blade in an upward direction where
the two
meet and curves toward a lower face of the elongate blade. The curved portion
has a
constant cross-section over most of the blade major axis.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0008] The foregoing and other aspects of the present disclosure will
become apparent to those skilled in the art to which the present disclosure
relates
upon reading the following description with reference to the accompanying
drawings,
in which:
2
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
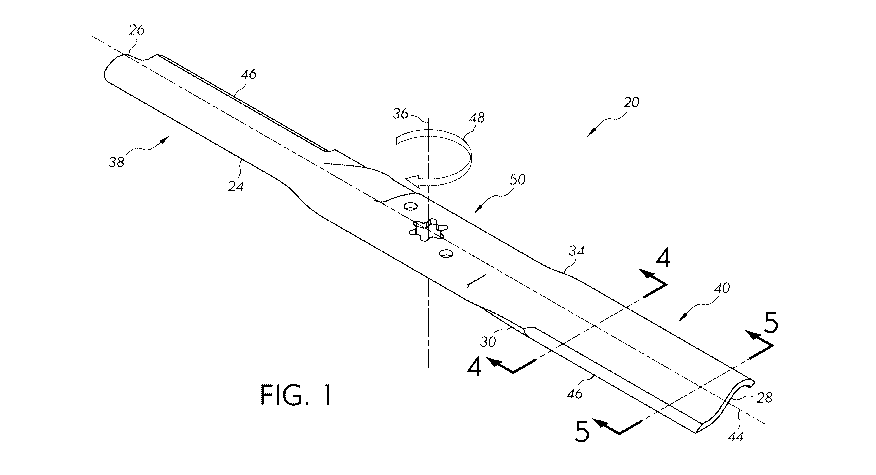
[0009] FIG. 1 is an isometric view of an exemplary low profile mower
blade according to at least one embodiment of the present disclosure;
[0010] FIG. 2 is an elevation view of the low profile mower blade of FIG.
1;
[0011] FIG. 3 is a top view of the low profile mower blade of FIG. 1;
[0012] FIG. 4 is a cross-section view taken along line 4-4 of FIG.1;
[0013] FIG. 5 is a cross-section view taken along line 5-5 of FIG. 1; and
[0014] FIG. 6 is an isometric view of a low profile mower blade showing
an alternative mounting arrangement.
[0015] It should be noted that all the drawings are diagrammatic and not
drawn to scale. Relative dimensions and proportions of parts of these figures
have
been shown exaggerated or reduced in size for the sake of clarity and
convenience in
the drawings. The same reference numbers are generally used to refer to
corresponding or similar features in the different embodiments. Accordingly,
the
drawing(s) and description are to be regarded as illustrative in nature and
not as
restrictive.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0016] Example embodiments that incorporate one or more aspects of the
present disclosure are described and illustrated in the drawings. These
illustrated
examples are not intended to be a limitation on the present disclosure. For
example,
one or more aspects of the present disclosure can be utilized in other
embodiments
and even other types of devices. Moreover, certain terminology is used herein
for
convenience only and is not to be taken as a limitation on the present
disclosure. Still
further, in the drawings, the same reference numerals are employed for
designating
the same elements.
[0017] Turning to FIG. 1, an isometric view of an exemplary low profile
mower blade 20 is shown. The low profile mower blade 20 includes an elongate
blade 24 having a first end edge 26 and a second end edge 28 that are opposed
to one
another. A first side edge 30 and a second side edge 34 are also opposed to
one
another, and together, the first end edge 26, the second end edge 28, the
first side edge
30, and the second side edge 34 generally form the four sides of the low
profile
mower blade 20.
3
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
[0018] The low profile mower blade 20 is adapted for mounting onto a
lawn maintenance device (e.g., a rotary mower) (not shown) for rotation about
a
center axis 36 extended transverse to the elongate blade 24. The center axis
36
separates the elongate blade 24 into opposed elongate end portions 38, 40
extending
from the center axis 36. The elongate blade 24 also includes a blade major
axis 44.
[0019] In one example, the elongate blade 24 can be configured with a pair
of sharpened cutting edges 46. The sharpened cutting edges 46 are located on
the first
and second side edges 30, 34 such that when the low profile mower blade 20
rotates
in the direction shown by arrow 48, the sharpened cutting edges 46 are each on
a
leading edge of the elongate blade 24 to cut grass and/or vegetation. In one
example,
the sharpened cutting edges 46 can be two inches to six inches in length.
[0020] .. The central portion 50 of the low profile mower blade 20 can
include structure for mounting the low profile mower blade 20 to a rotating
shaft,
such as a spindle, engine shaft, etc. such that the low profile mower blade 20
can be
rotated by a power source on a rotary mower (not shown). The power source can
be
any suitable power source including, but not limited to, a gasoline powered
engine, a
corded electric motor, a battery-powered electric motor, etc. Similarly, the
low
profile mower blade 20 can define one or more apertures to cooperate with
physical
features located on the rotary mower to attach the low profile mower blade 20
to
structure on the rotary mower. Any suitable attachment structure or definition
is
contemplated with the present disclosure.
[0021] .. Turning to FIG. 2, the exemplary low profile mower blade 20 is
shown in an elevation view. As seen in the figure, one sharpened cutting edge
46 is
shown on the lower right side of the low profile mower blade 20.
[0022] Many cutting blades and mower blades incorporate a ramped
surface or sail opposite the sharpened cutting edge 46 in order to produce
lower air
pressure above and higher air pressure below the rotating cutting blade so as
to
effectively create lift of the grass, other vegetation, and subsequent
clippings. This
lift can be used to straighten the grass and vegetation prior to cutting and
provide a
force to move the clippings to a collection bag or out a discharge chute (not
shown).
However, in particular situations such as cutting grass and/or vegetation in a
location
that contains a relatively high percentage of sand within the soil, the ramped
surface
or sail is constantly experiencing an impingement of sand particles along the
length of
4
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
the ramped surface. This, in turn, effectively sandblasts or wears away the
ramped
surface within a relatively short time.
[0023] Turning to FIG. 3, a top view of the low profile mower blade 20 is
shown. As previously described, the low profile mower blade includes the
elongate
blade 24 having end portions 38, 40 extending from the center axis
(represented by a
dot at 36). The elongate blade 24 also includes a blade major axis 44 and is
configured with a pair of sharpened cutting edges 46. The sharpened cutting
edges 46
are located on the first and second side edges 30, 34 such that when the low
profile
mower blade 20 rotates in the direction shown by arrow 48, the sharpened
cutting
edges 46 are each on a leading edge of the elongate blade 24 to cut grass
and/or
vegetation.
[0024] Turning to FIG. 4, a cross-section view of the elongate blade 24 is
shown. Rather than including a sail or ramped surface opposite the cutting
edge, the
elongate blade 24 defines a curved portion 54 such that the curved portion 54
is
opposite the sharpened cutting edge 46. As shown, the curved portion 54
extends
from the elongate blade 24 in an upward direction from where the sharpened
cutting
edge 46 and the curved portion 54. In this example, the term "upward
direction" is
used to define the direction that is perpendicular to a driven surface (e.g.,
the turf) that
is generally considered "up," as the lawn maintenance device is normally
operated.
The curved portion 54 then curves to point downward toward a lower face 56 of
the
elongate blade 24. The curved portion 54 provides significantly less air
turbulence as
the low profile mower blade 20 revolves around the center axis 36. This
reduction in
air turbulence encourages objects (e.g., grains of sand) to flow over and
behind the
rotating low profile mower blade 20 rather than striking a portion of the low
profile
mower blade 20 such as a sail or ramped portion and subsequently destroying
the sail
or ramped portion. The airflow pattern is generally represented by arrow 58 in
FIG.
4.
[0025] .. The curved portion 54 defines a concave space 60 on the lower face
56 of the elongate blade 24. The concave space 60 also encourages the
development
of a lower air pressure above the grass and/or vegetation in order to urge the
grass
and/or vegetation to an upright position for cutting by the rotating low
profile mower
blade 20.
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
[0026] In at least one example of the low profile mower blade 20, the
curved portion 54 of the elongate blade 24 includes a distal portion 64 is
offset
vertically from the sharpened cutting edge 46. As shown in FIG. 3, the distal
portion
64 offset from the sharpened cutting edge 46 is measured along a line that is
generally
parallel to the center axis 36. In a specific example, the distal portion 64
of the
curved portion 54 is higher in elevation from the driven surface (e.g., the
turf) than the
sharpened cutting edge 46. This offset distance is represented by dimension
66.
Similar to the geometry of the curved portion 54, the offset distance 66 helps
develop
lift during rotation of the low profile mower blade 20. In one example, the
offset
distance 66 is less than about one-half inch (1.2 cm). In another example, the
offset
distance 66 is greater than about one-quarter inch (0.6 cm).
[0027] Turning to FIG. 5, another cross-section view of the elongate blade
24 is shown. FIGS. 4 and 5 are identical apart from the reference numerals.
The
comparison is useful to show that over most of the blade major axis 44, the
elongate
blade 24 has a constant cross-section. This can be of particular use when
scaling the
low profile mower blade 20 to different mower applications. For example, if a
walk-
behind mower requires a 30-inch long blade, and there is a 28-inch long blade
already
designed, the designer can merely add another inch to each of the end portions
38, 40
to create the 30-inch long blade. Similarly, to design a low profile mower
blade 20
with a shorter length, a designer merely removes a desired length from each of
the end
portions 38, 40. This can save design and engineering time, and thus cost.
[0028] It is also worthy of note that the curved portion 54 develops
flexion
stability between the central portion 50 and the end portions 38, 40 of the
low profile
mower blade. In many relatively flat mower blades, a flat piece of metal stock
is
sharpened on either side to function as a mower blade. However, these known
flat
blades often lack a flexion stability and can flex according to arrows 68 in
FIG. 2. As
can be appreciated, this type of flexion can create undesired variability in
grass
cutting height and results in a rough grass cut that is often undesirable. As
such, the
added stiffness provided by the curved portion 54 to the elongate blade 24 can
be
beneficial.
[0029] Turning to FIG. 6, an alternate mounting structure is shown. As
previously mentioned, any suitable mounting structure or definition can be
used with
the low profile mower blade 20 of the present disclosure. As an example, FIG.
6
6
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552 PCT/US2017/052384
shows apertures 70 and embossed areas 74 suitable for use with a quick-change
attachment scheme as described in U.S. Patent Application No. 14/847,909 and
its
family members.
[0030] The apparatus of the present disclosure can have several benefits.
The low profile mower blade can increase the lifespan of the mower blade when
used
over soils or surfaces having a relatively high sand content. In some
examples, the
low profile mower blade can last as much as four times as long as a typical
lawn
mower blade having a sail or ramped surface to develop lift. In other
examples, the
blade can last three times as long as a typical lawn mower blade.
Additionally, the
low profile mower blade can present a greater surface area upon which to
deflect
objects such as grains of sand in comparison to typical sail-employing mower
blades.
The greater surface area not withstanding, the low profile mower blade also
can
eliminate a significant amount of blade wear caused by object impingement
simply by
having the low profile. This lower profile can also significantly reduce the
drag
forces operating on the low profile mower blade. In some cases, the drag can
be
reduced by as much as 12.5% in comparison to a standard mower blade.
[0031] Other benefits can include a constant cross-section profile that is
easily scalable to other mower applications (e.g., longer or shorter blade
lengths).
The described low profile mower blade can also provide flexion stability or
stiffness
along the blade major axis to reduce and/or eliminate rough cuts due to the
mower
blade ends moving up and down relative to the center portion during operation.
[0032] While this disclosure has been written in conjunction with the
specific embodiments described above, it is evident that many alternatives,
combinations, modifications and variations are apparent to those skilled in
the art.
Accordingly, the described embodiments of this disclosure, as set forth above
are
intended to be illustrative only, and not in a limiting sense. Various changes
can be
made without departing from the spirit and scope of this disclosure.
Combinations of
the above embodiments and other embodiments will be apparent to those of skill
in
the art upon studying the above description and are intended to be embraced
therein.
Therefore, the scope of the present disclosure is defined by the appended
claims, and
all devices, processes, and methods that come within the meaning of the
claims, either
literally or by equivalence, are intended to be embraced therein. Furthermore,
to the
extent that the term "includes" is used in either the detailed description or
the claims,
7
CA 03041627 2019-04-24
WO 2018/057552
PCT/US2017/052384
such term is intended to be inclusive in a manner similar to the term
"comprising" as
"comprising" is interpreted when employed as a transitional word in a claim.
8