Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
1
FASTENING DEVICE
The present invention relates to a fastening device for the military sector.
In armored vehicles, it may be necessary to fasten retrofit kit items such as
per-
sonal equipment or the like to a wall of a cabin or a hull of the armored
vehicle.
For this purpose, fastening points in the form of welded-on bent sheet metal
parts or welded-on threaded bosses may be provided. Any number of fastening
points may be provided, depending on the equipment in the armored vehicle.
Against this background, it is an object of the present invention to provide
an im-
proved fastening device for the military sector.
Accordingly, a fastening device for the military sector for fastening to a
surface is
suggested. The fastening device comprises a fastening element which comprises
a
receiving portion for a fastening means, a first adhesive surface which is
provided
on the fastening element and comprises a first adhesive, and a second adhesive
surface which is separated from the first adhesive surface and provided on the
fastening element, which second adhesive surface comprises a second adhesive,
wherein the first adhesive has a greater stretchability than the second
adhesive.
As the fastening device is not welded to the surface but is adhesively bonded
to it,
a weld spot induced weakening of the wall associated with the surface is
prevent-
ed. Thus, crack formation in the wall due to welds may be prevented. Further-
more, providing the fastening device retrospectively is possible with less
effort as
compared to a welding solution. Thus, the fastening device is particularly
suita-
ble for retrofitting. However, the fastening device may also be used as
original
equipment.
By providing two different adhesives, the one adhesive, in particular the
second
adhesive, is operable to transfer quasi-static and dynamic loads, and the
other
adhesive, in particular the first adhesive, is operable to absorb a highly
dynamic
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
2
load, in particular a non-recurring highly dynamic load such as with a
blasting
impact on a vehicle having such a fastening device or in the event of a crash
of
the vehicle. The second adhesive preferably fails during the highly dynamic
load,
so that after the highly dynamic load the fixation of the fastening device to
the
surface is only ensured by means of the first adhesive. The first adhesive,
which
is resilient compared to the second adhesive, is greatly stretched during the
high-
ly dynamic load; however, it does not fail. This means that the two adhesives
ful-
fill their function independently of each other. After the highly dynamic
load, the
fastening device is preferably replaced or rebonded.
The term "stretchability" here means the characteristic of the adhesives to
change their shape under force. Stretchability indicates how much the
respective
adhesive may be stretched relative to a respective adhesive layer thickness
asso-
ciated with the respective adhesive without falling, i. e. rupturing or
tearing. A
fastening arrangement may comprise the fastening device and the surface. The
surface is preferably the surface of a wall of a vehicle cabin of an armored
vehicle
or a vehicle hull. Die fastening device may also be referred to as military
fas-
tening device.
The first adhesive surface being separated from the second adhesive surface
means that the first adhesive preferably does not come into contact with the
sec-
ond adhesive. For this purpose, a web portion or an air gap, for example, may
be
provided between the first adhesive surface and the second adhesive surface.
The fastening element may, for example, be made from an aluminum alloy or
from a steel alloy, for example stainless steel. The fastening element is
preferably
cylindrical with a circular cross-sectional geometry. However, the fastening
ele-
ment may also be oval, triangular, rectangular, square, polygonal, L-shaped or
the like in cross section. This means that the fastening element may have any
geometry in the cross-section. This allows the fastening device to be adapted
to
any application.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
3
Compared to the first adhesive and the second adhesive, the fastening element
is
very stiff, so that when a force is applied to the fastening element, the two
adhe-
sives are not subjected to a linear or punctiform load, but to a surface load.
This
prevents a local overload of the adhesives, which can be a starting point of
cracks.
This may be achieved by the fastening element having a large thickness as com-
pared to the adhesive layer thicknesses of the adhesives.
The fastening element may also comprise a third adhesive differing from the
first
adhesive and the second adhesive, which is adapted to secure the fastening de-
li) ment to the surface until the first adhesive and/or the second adhesive
are cured
or have set. The third adhesive may be a fast-setting adhesive such as a pres-
sure-sensitive adhesive or cyanoacrylate. A third adhesive surface for the
third
adhesive may be provided on the fastening element. The third adhesive may also
be provided on a fixing frame that is separable from the fastening element.
The
fixing frame may, for example, be of a circular configuration, and may be
opera-
ble to be pushed over the fastening element for assembly.
The receiving portion may be a threaded boring provided in the fastening ele-
ment into which the fastening means may be screwed. The fastening means may
be a threaded bolt or a screw. Alternatively, the receiving portion may be a
bolt,
for example with threading, protruding from the fastening element. The fas-
tening means may then be a nut, for example.
According to one embodiment, the first adhesive comprises a first adhesive
layer
thickness and the second adhesive comprises a second adhesive layer thickness
which is smaller than, larger than or equal to the first adhesive layer
thickness.
The first adhesive layer thickness is preferably larger than the second
adhesive
layer thickness. The adhesive layer thicknesses may, for example, each be 1 to
3
millimeters. The adhesive layer thicknesses may, for example, be adjusted by
wa-
fers adapted to be placed on and adhered to the first adhesive surface and the
second adhesive surface. The differing stretchability of the two adhesives may
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RNIV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
4
also be adjusted by different adhesive layer thicknesses. This means that the
first
adhesive may be chemically identical to the second adhesive. The different
stretchability is then adjusted via the different adhesive layer thicknesses.
Pref-
erably, however, the first adhesive and the second adhesive are chemically
differ-
ent from each other.
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive is stretchable by up to
50%,
preferably by up to 60%, more preferably by up to 70%, more preferably by up
to
80%, more preferably by up to 90%, more preferably by up to 100% of the first
adhesive layer thickness.
This means that the first adhesive only fails after it is stretched by up to
50% to
100% of the first adhesive layer thickness. Furthermore, the first adhesive
may
also only fail when stretched by more than 100% of the first adhesive layer
thick-
ness, for example, by 150%, 200% or 300% of the first adhesive layer
thickness.
Thus, particularly high strain rates of 103s-1 are achievable without the
first ad-
hesive failing.
According to another embodiment, the second adhesive is stretchable by up to
10%, preferably by up to 8%, more preferably by up to 6%, more preferably by
up
to 4%, more preferably by up to 2% of the second adhesive layer thickness.
The second adhesive may also be stretchable by more than 10% or by less than
2% of the second adhesive layer thickness. However, it is important here that
the
two adhesives have differing stretchability. In particular, the first adhesive
may
have a higher stretchability than the second adhesive. Conversely, it is also
pos-
sible for the second adhesive to have a higher stretchability than the first
adhe-
sive.
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive is a polyurethane and the
second adhesive is an epoxy resin.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
' RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
Preferably, both the first adhesive and the second adhesive are multi-
component
adhesives which are mixed prior to application to the fastening element. The
dif-
fering stretchability of the first adhesive and the second adhesive may also
be
achieved, for example, by using a multi-component system to produce adhesives
5 with differing stretchability by means of different mixing ratios.
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive surface and/or the second
adhesive surface are constructed mirror-symmetrically to a first plane of sym-
metry and/or to a second plane of symmetry of the fastening element.
The first plane of symmetry is preferably arranged perpendicular to the second
plane of symmetry. An intersection of the first plane of symmetry and the
second
plane of symmetry forms a center axis or axis of symmetry of the fastening ele-
ment. In particular, the first adhesive surface and/or the second adhesive
surface
are constructed point-symmetrically.
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive surface is at least
sectional-
ly arranged within the second adhesive surface.
The second adhesive surface preferably completely extends around the first ad-
hesive surface such that the first adhesive surface is disposed completely
within
the second adhesive surface. Alternatively, the first adhesive surface may
also at
least partially not be enclosed by the second adhesive surface such that the
first
adhesive surface passes through the second adhesive surface.
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive surface and the second ad-
hesive surface are spirally intertwined.
A spirally wound web portion of the fastening element or a spirally wound air
gap may be provided between the first adhesive surface and the second adhesive
surface.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
' RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
6
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive surface is separated from
the second adhesive surface by means of a web portion.
The web portion may be materially integrally formed with the fastening
element.
The web portion may alternatively also be a component that is separate from
the
fastening element, which may in particular also be formed from a different
mate-
rial then the fastening element. The web portion may, for example, be formed
from a resiliently deformable material. This allows for a particularly good
seal to
be achieved between the first adhesive surface and the second adhesive
surface.
The web portion may, for example, be adhesively bonded to the fastening
element
or otherwise releasably or non-releasably connected to the fastening element.
According to another embodiment, the web portion comprises an end face contact-
ing the surface for adjusting a first adhesive layer thickness of the first
adhesive
and/or a second adhesive layer thickness of the second adhesive.
The first adhesive layer thickness is in particular defined as a distance from
the
end face of the web portion to the first adhesive surface. The second adhesive
lay-
er thickness is in particular defined as a distance from the end face of the
web
portion to the second adhesive surface. The first adhesive layer thickness and
the
second adhesive layer thickness may be adjusted by the height of the web por-
tion, or the depth of the first adhesive surface with respect to the end face
of the
web portion and the depth of the second adhesive surface relative to the end
face
of the web portion. Furthermore, an optional sealing device, for example an 0-
ring, may be provided at the end face of the web portion for sealing the first
ad-
hesive surface from the second adhesive surface. Also, the previously
mentioned
third adhesive may be provided at the end face, by means of which the
fastening
element is operable to be secured to the surface until the first adhesive
and/or the
second adhesive are cured. The third adhesive may, for example, be a pressure-
sensitive adhesive protected by a protective film or a cyanoacrylate.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
7
According to another embodiment, at least one channel passing from the first
ad-
hesive surface through the second adhesive surface or passing by it is
provided.
The channel allows the first adhesive to emerge when placing the fastening de
-
vice on the surface. This allows for carrying out a visual quality control,
because,
when the first adhesive emerges from the channel, it is ensured that the first
ad-
hesive surface and a corresponding part of the surface of the wall are fully
wetted
by the first adhesive. Any number of channels may be provided. Preferably, the
channels are arranged mirror-symmetrical to the first plane of symmetry and/or
the second plane of symmetry.
According to another embodiment, the at least one channel comprises side walls
arranged such that the at least one channel narrows toward an axis of symmetry
of the fastening element.
Conversely, the at least one channel widens from the axis of symmetry to the
outside. The side walls may be part of the web portion. The side walls may
also
be arranged parallel to each other or may be arcuately curved.
According to another embodiment, the at least one channel joins a boring of
the
receiving portion.
In particular, the at least one channel joins an runout of the boring. Thereby
ex-
tending the channel through the second adhesive surface may be dispensed with.
Thus, both the first adhesive surface and the second adhesive surface may be
constructed mirror-symmetrically to both the first plane of symmetry and to
the
second plane of symmetry. This allows for a particularly good force
distribution to
be achieved when operating the fastening device. The at least one channel may
also comprise a first boring extending in the direction of the boring of the
receiv-
ing portion and a second boring arranged perpendicular to the first boring and
passing by the second adhesive surface. Thereby the contamination of the
receiv-
ing portion with the first adhesive may be prevented.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
' RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
8
According to another embodiment, the first adhesive surface is divided into a
plu-
rality of separated first surface portions and the second adhesive surface is
divid-
ed into a plurality of separated second surface portions, wherein the first
surface
portions and the second surface portions are arranged in a row or matrix
pattern.
The first surface portions and the second surface portions are each separated
by
web portions or air gaps. The first surface portions and the second surface
por-
tions being arranged in a row pattern means that always a second surface p0r-
tion is arranged between two first surface portions and vice versa. The first
sur-
face portions and the second surface portions being arranged in a matrix
pattern
means that the first surface portions and the second surface portions are not
only
arranged in a row pattern, but also in a column pattern. This results in a
check-
ered distribution of the first surface portions and the second surface
portions.
According to another embodiment, the fastening element comprises a first fas-
tening portion, which comprises the first adhesive surface comprising the
first
adhesive, and a second fastening portion separated from the first fastening
por-
tion, which comprises the second adhesive surface comprising the second adhe-
sive.
The first fastening portion and the second fastening portion are preferably em-
bodied as separate components. The first fastening portion and the second fas-
tening portion may have a common receiving portion for the fastening means.
Other possible implementations of the fastening device also comprise combina-
tions of features or embodiments that are not explicitly mentioned above or de-
scribed below in the context of the exemplary embodiments. The person skilled
in
the art will also add individual aspects as improvements or additions to the
re-
spective basic form of the fastening device.
85187990
9
Some embodiments disclosed herein provide a fastening device for the military
sector for
fastening to a surface, comprising: a fastening element which comprises a
receiving portion
for a fastening means, a first adhesive surface which is provided on the
fastening element
and comprises a first adhesive, and a second adhesive surface which is
separated from the
.. first adhesive surface and provided on the fastening element, which second
adhesive surface
comprises a second adhesive, wherein the first adhesive and the second
adhesive are
chemically different from each other, wherein the first adhesive has a greater
stretchability
than the second adhesive, wherein the second adhesive is operable to transfer
quasi-static
and dynamic loads, wherein the first adhesive is operable to absorb a highly
dynamic load,
and wherein the second adhesive fails during the highly dynamic load, so that
after the
highly dynamic load, the fixation of the fastening device is only ensured by
means of the
first adhesive.
Furthermore, the fastening device is explained in more detail on the basis of
preferred
embodiments with reference to the enclosed figures.
Fig. 1 shows a schematic side view of an armored vehicle;
Fig. 2 shows a schematic sectional view of an embodiment of a fastening device
for the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 shows a schematic view of the fastening device of Fig. 2;
Fig. 4 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 5 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 6 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-10-05
85187990
9a
Fig. 7 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 8 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 9 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Fig. 10 shows a schematic view of another embodiment of a fastening device for
the
armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-10-05
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
Fig. 11 shows a schematic sectional view of another embodiment of a fastening
device for the armored vehicle of Fig. 1;
5 Fig. 12 shows a schematic view of the fastening device of Fig. 11;
Fig. 13 shows a schematic sectional view of another embodiment of a fastening
device;
10 Fig. 14 shows a schematic sectional view of another embodiment of a
fastening
device; and
Fig. 15 shows a schematic view of the fastening device of Fig. 11.
In the figures, identical or functionally identical elements have been
provided
with the same reference numbers, unless otherwise indicated.
Fig. 1 shows a schematic side view of an embodiment of an armored vehicle 1.
The vehicle 1 may be a military vehicle. The vehicle 1 may be a land vehicle,
in
particular a wheeled vehicle or a tracked vehicle. The vehicle I may further
be a
rolling stock, a watercraft or an aircraft. The vehicle 1 comprises a cabin 2,
which
encloses an internal volume I of the vehicle 1 and separates said internal
volume
I from the surrounding area U of the vehicle 1.
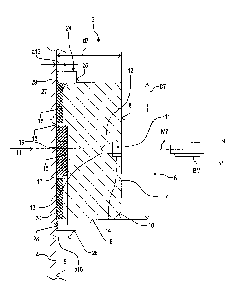
Fig. 2 shows a schematic sectional view of an embodiment of a fastening ar-
rangement 3 for the vehicle 1. By using the fastening arrangement 3 retrofit
kit
items, for example, or the like are operable to be fastened in the internal
volume
I of the cabin 2 to a wall 4 of the vehicle 1. The fastening arrangement 3 may
comprise the wall 4. The wall 4 may, for example, be part of the cabin 2 or
part of
a hull of the vehicle 1. The wall 4 has a surface 5 facing the internal volume
I.
However, the surface 5 may also face away from the internal volume I and face
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
= RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
11
the surrounding area U of the vehicle 1. This means that the fastening arrange-
ment 3 may also be provided on the outside of the vehicle 1.
The fastening arrangement 3 further comprises a fastening device 6. The fas-
tening device 6 may be referred to as boss, in particular as threaded boss.
The
fastening device 6 has a fastening element 7. The fastening element 7 is
prefera-
bly embodied rotationally symmetrical to a center axis or axis of symmetry M7.
The fastening element 7 may have a cylindrical geometry with a circular cross
section. The fastening element 7 has back side 8 facing away from the surface
5
and a circumferential cylindrical outer surface 9. The outer surface 9
transitions
via a circumferential bevel 10 into the back side 8.
The fastening element 7 is, for example, made from an aluminum or a steel
alloy,
in particular from stainless steel. Alternatively, the fastening element 7 may
also
be made from a plastic material. The fastening element 7 has, for example, a
thickness d7 and a diameter D7. The thickness d7 is, for example, one-third of
the diameter D7.
The fastening element 7 further comprises a receiving portion 11 for a
fastening
means BM. The fastening means BM may, for example, be a threaded bolt or a
screw. The receiving portion 11 comprises a boring 12 having a conical runout
13,
said boring 12 preferably being arranged rotationally symmetrical to the axis
of
symmetry M7. A thread 14 is provided in the boring 12, in particular an
internal
thread. Alternatively, the receiving portion 11 may also be embodied as a bolt
projecting from of the fastening element 7.
Facing the surface 5, the fastening element 7 comprises a first adhesive
surface
15 and also a second adhesive surface 16 separated from the first adhesive sur-
face 15. The first adhesive surface 15 is preferably smaller than the second
adhe-
sive surface 16. Conversely, the second adhesive surface 16 may be smaller
than
the first adhesive surface 15 or the two adhesive surfaces 15, 16 are of the
same
size. The adhesive surfaces 15, 16 may be separated by means of an air gap.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
12
Alternatively, the first adhesive surface 15 and the second adhesive surface
16
may be separated by means of a web portion 17, as shown in Fig. 2. The web por-
tion 17 is preferably materially integrally formed with the fastening element
7.
This means that the fastening element 7 and the web portion 17 form one com-
ponent. Alternatively, the receiving portion 17 may also be a component that
is
separate from the fastening element 7. The web portion 17 may then, for exam-
ple, be made of a different material then the fastening element 7. In this
case, the
web portion 17 may in particular be formed from a resiliently deformable
materi-
al. The web portion 17 is then operable to fulfill a sealing function.
An end face 18 of the web portion 17 is arranged spaced apart from the first
ad-
hesive surface 15 by an adhesive layer thickness a15. Furthermore, the second
adhesive surface 16 is arranged spaced apart from the end face 18 by an
adhesive
layer thickness a16. The web portion 17 thus may be operable to define the
adhe-
sive layer thicknesses a15, a16. The adhesive layer thicknesses a15, al6 may
be
of the same size or of different sizes, as shown in Fig. 2. For example, the
first
adhesive layer thickness al5 is larger than the second adhesive layer
thickness
a16. Conversely, the second adhesive layer thickness a16 may as well be larger
than the first adhesive layer thickness a15. The adhesive layer thicknesses
a15,
a16 may, for example, be adjusted by wafers placed on the adhesive surfaces
15,
16. Alternatively, the adhesive layer thicknesses a15, a16 may be adjusted by
machining the fastening element 7.
A first adhesive 19 is provided at the first adhesive surface 15 for
connecting the
fastening element 7 to the surface 5. The second adhesive surface 16 is
associated
with a second adhesive 20. Conversely, the first adhesive 19 may as well be
asso-
ciated with the second adhesive surface 16 and the second adhesive 20 with the
first adhesive surface 15. The adhesives 19, 20 may be chemically different
from
each other or chemically identical and only differ in their adhesive layer
thick-
nesses a15, a16. Preferably, however, the two adhesives 19, 20 are chemically
different from each other. In particular, the first adhesive 19 has a higher
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
13
stretchability than the second adhesive 20. Conversely, it is also possible
for the
second adhesive 20 to have a higher stretchability than the first adhesive 19.
For
example, the first adhesive 19 is a polyurethane (PU) and the second adhesive
20
is an epoxy. In particular, both adhesives 19, 20 are multi-component
adhesives.
The term "stretchability" means the characteristic of the adhesives 19, 20 to
change their shape under force. Stretchability indicates how much the
respective
adhesive 19, 20 may be elongated relative to its respective adhesive layer
thick-
ness a15, a16 without falling, i. e. rupturing or tearing. The first adhesive
19 is
stretchable by up to 50%, preferably by up to 60%, more preferably by up to
70%,
more preferably by up to 80%, more preferably by up to 90%, more preferably by
up to 100% of the first adhesive layer thickness a15, before it fails, i. e.,
until the
first adhesive 19 ruptures or tears. Furthermore, the first adhesive 19 may
also
only fail when stretched by more than 100% of the first adhesive layer
thickness
a15, for example, by 150%, 200% or 300% of the first adhesive layer thickness
a15. Thus, particularly high strain rates of 103s-1 may be achieved.
In comparison, the second adhesive 20 is only stretchable by up to 10%,
prefera-
bly by up to 8%, more preferably by up to 6%, more preferably by up to 4%,
more
preferably by up to 2% of the second adhesive layer thickness a16. However,
the
second adhesive 20 may also be stretchable by more than 10% or by less than 2%
of the second adhesive layer thickness al6 before it fails.
Fig. 3 shows a view of the fastening device 6 in the viewing direction III of
Fig. 2.
The adhesives 19, 20 are not shown in Fig. 3. In Fig. 3, the first adhesive
surface
15 is represented hatched and the second adhesive surface 16 is represented
not
hatched. As shown by Fig. 3, the first adhesive surface 15 is at least
sectionally
enclosed by the second adhesive surface 16. The web portion 17 is preferably
cir-
cularly shaped and comprises a channel 21 passing through the second adhesive
surface 16. The channel 21 has two side walls 22, 23, which are preferably in-
clined such that the channel 21 narrows toward an axis of symmetry M7. The
side walls 22, 23 are part of the web portion 17. The side walls 22, 23 may
also
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
=
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
14
extent parallel to each other. The channel 21 may arbitrarily oriented to a
direc-
tion of gravity g. This means that in the orientation of Fig. 3, the channel
21 may
point upward, downward or sideways.
Preferably, both the first adhesive surface 15 and the second adhesive surface
16
are formed symmetrically, in particular mirror-symmetrically, to a first plane
of
symmetry El. Deviating from the illustration in Fig. 3, the first adhesive
surface
and the second adhesive surface 16 may also be formed symmetrically, in par-
ticular mirror-symmetrically, to a second plane of symmetry E2. The second
10 plane of symmetry E2 is arranged perpendicular to the first plane of
symmetry
El. The axis of symmetry M7 forms an intersection of the two planes of sym-
metry El, E2.
The functionality of the fastening device 6 is explained below. To fasten the
fas-
15 tening device 6 to the surface 5, firstly the first adhesive 19 is
applied to the first
adhesive surface 15. Subsequently, the second adhesive 20 is applied to the
sec-
ond adhesive surface 16. The application of the adhesives 19, 20 may also be
ac-
complished in reverse order or simultaneously.
The fastening device 6 is then placed in the desired position on the surface 5
and
is preferably secured until at least one of the adhesives is 19, 20 is cured.
An op-
tional fixing frame 24 may be provided for this purpose. The fixing frame 24
is,
for example, embodied as a ring extending around the fastening element 7, in
which the fastening element 7 may be received. However, the fixing frame 24
may also have any other geometry. As shown in Fig. 2, the fixing frame 24 com-
prises a back side 25 oriented away from the surface 5, a cylindrical outer
surface
26 and a cylindrical inner surface 27 to which the outer surface 9 of the
fastening
element 7 abuts.
The fixing frame 24 further comprises an end face 28 facing the surface 5. A
third
adhesive 29 is preferably provided on the end face 28 for securing the fixing
frame 24 to the surface 5. The third adhesive 29 may, for example, be a
pressure-
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
=
R1V1V16004PW0 Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
sensitive adhesive protected by a protective film or a fast-curing adhesive
such as
a cyanoacrylate. The fixing frame 24 may be secured to the surface 5 ahead of
the
fastening element 7 or the fixing frame 24 is operable to be slid over the fas-
tening element 7 after placing said fastening element 7 on the surface 5.
Alterna-
5 tively, the third adhesive 29 may also be provided directly on the
fastening ele-
ment 7. For example, the third adhesive 29 may be provided on the end face 18
of
the web portion 17 or on an additionally provided adhesive surface on the fas-
tening element 7.
10 When pressing the fastening element 7 against the surface 5, the first
adhesive
19 is pressed out through the channel 21 so that by looking at the channel 21,
it
is possible to ascertain that the first adhesive 19 is applied to the entire
first ad-
hesive surface 15 and is in contact with the surface 5. Thus, channel 21 is
opera-
ble for monitoring the result of the bonding process. By using the web portion
17,
15 it is possible to prevent the first adhesive 19 from coming into contact
or becom-
ing mixed with the second adhesive 20. Thereby an undesired negative effect on
the result of the bonding process due to mixing of the adhesives 19, 20 is
avoided.
When the fastening device 6 is in use, i.e., after both the first adhesive 19
and the
second adhesive 20 have completely set or cured, the less stretchable second
ad-
hesive 20 receives quasi-static and dynamic loads, in particular loads acting
in
the direction of gravity g, which are acting on said fastening device when the
ve-
hicle 1 is in use, for example, during an off-road ride or due to the net
weight of
the retrofit kit items fasten to the fastening device 6.
In the event of a highly dynamic load, such as with a blasting impact on the
vehi-
cle 1 or a crash, the second adhesive 20 is operable to fail and rupture or
tear,
due to its lower stretchability compared to the first adhesive 19. The failure
of
the second adhesive 20 is intentional. However, detaching of the fastening
device
.. 6 from the surface 5 is prevent by the first adhesive 19, which has a high
stretch-
ability compared to the second adhesive 20. Subsequently to the highly dynamic
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
=
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
16
load, during which the second adhesive 20 failed, the fastening device 6 may
be
replaced or re-bonded.
In deviation from the circular geometry shown is Fig. 3, the fastening element
7
may also have an oval geometry, so that static and dynamic loads acting in the
direction of gravity g may be better absorbed. Alternatively, the fastening
ele-
ment 7 may also have a polygonal geometry, for example, a triangular, a square
or a rectangular geometry. Furthermore, the fastening element 7 may also have
an L-shaped geometry.
Fig. 4 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. The
fastening
device 6 according to Fig. 4 differs from the fastening device 6 according to
Figs. 2
and 3 only in that not only one channel 21 but two channels 21, 30 passing
from
the first adhesive surface 15 through the second adhesive surface 16 are
provid-
ed. In particular, a first channel 21 and a second channel 30 are provided.
Like
the first channel 21, the second channel 30 has two side walls 31, 32 that are
in-
clined such that the second channel 30 narrows toward the axis of symmetry M7.
In this embodiment of the fastening device 6 according to Fig. 4, the two
adhesive
surfaces 15, 16 are not only arranged symmetrically to the first plane of sym-
metry El but also symmetrically to the second plane of symmetry E2. This
allows
for a particularly even force distribution to be achieved. The channels 21, 30
may
be arbitrarily oriented to the direction of gravity g.
Fig. 5 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. The
fastening
device 6 according to Fig. 5 differs from the fastening device 6 according to
Figs. 2
and 3 only in that not only one channel 21 but three channels 21, 30, 33
passing
from the first adhesive surface 15 through the second adhesive surface 16 are
provided. The channels 21, 30, 33 are preferably arranged evenly distributed
over
a circumference of the fastening element 7. In particular, a first channel 21,
a
.. second channel 30 and a third channel 33 are provided. Like the first
channel 21
and the second channel 30, the third channel 33 has two side walls 34, 35 that
are inclined such that the third channel 33 also narrows toward the axis of
sym-
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PW0 Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
17
metry M7. The fastening element 7 may also comprise more than three channels
21, 30, 33. For example, four or more channels 21, 30, 33 may be provided. The
channels 21, 30, 33 are preferably always arranged symmetrically, in
particular
mirror-symmetrically, to the planes of symmetry El, E2. The channels 21, 30,
33
may be arbitrarily oriented to the direction of gravity g.
Fig. 6 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. The
fastening
device 6 according to Fig. 6 differs from the fastening device according to
Figs. 2
and 3 only in that the web portion 17 is not essentially circularly shaped but
spi-
rally shaped. This means that the first adhesive surface 15 and the second
adhe-
sive surface 16 are spirally intertwined. This allows for a particularly even
force
distribution to be achieved.
Fig. 7 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. The
fastening
device 6 according to Fig. 7 differs from the fastening device 6 according to
Figs. 2
and 3 in that the first adhesive surface 15 is divided into a plurality, for
example
four, of separated first surface portions 36 to 39. Each of the first surface
portions
36 to 39 is separated from the second adhesive surface 16 by means of a
dedicat-
ed web portion 17, of which in Fig. 7 only one is provided with a reference
num-
ber.
Each first surface portion 36 to 39 further comprises a channel 21, as
discussed
above, which narrows toward the axis of symmetry M7 and through which the
first adhesive 19 may be pressed out when applying the fastening device 6 to
the
surface 5. The first surface portions 36 to 39 are preferably arranged
symmetri-
cally to the first plane of symmetry El and symmetrically to the second plane
of
symmetry E2. The number of first surface portions 36 to 39 is arbitrary. For
ex-
ample, two, three, four, five six or even more first surface portions 36 to 39
may
be provided, preferably being distributed symmetrically within the second adhe-
sive surface 16.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
18
Fig. 8 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. The
fastening
device 6 according to Fig. 8 differs from the fastening device 6 according to
Figs. 2
and 3 in that the first adhesive surface 15 is not arranged within the second
ad-
hesive surface 16. In particular, the first adhesive surface 15 and the second
ad
-
hesive surface 16 are arranged next to each other. To this end, the web
portion 17
may be arranged centered between the first adhesive surface 15 and the second
adhesive surface 16, i. e., symmetrically to the first plane of symmetry El.
How-
ever, the web portion 17 may also be positioned asymmetrically so that the
adhe-
sive surfaces 15, 16 differ in size.
In this case, the first adhesive surface 15 and the second adhesive surface 16
are
preferably arranged symmetrically to the second plane of symmetry E2 and
asymmetrically to the first plane of symmetry El. Conversely, the first
adhesive
surface 15 and the second adhesive surface 16 may also be arranged asymmetri-
cally to the second plane of symmetry E2 and symmetrically to the first plane
of
symmetry El. Instead of the web portion 17 an air gap separating the first
adhe-
sive surface 15 from the second adhesive surface 16 may be provided. The fas-
tening device 6 according to Fig. 8 can be manufactured particularly easily
and
cost-effectively. The web portion 17 may be arbitrarily oriented to the
direction of
gravity g. This means that in the orientation of Fig. 8 the web portion 17 may
be
arranged upward, downward or obliquely.
Fig. 9 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. Contrary to
the embodiment of the fastening device 6 according to Figs. 2 and 3, in this
em-
bodiment of the fastening device 6, the first adhesive surface 15 is divided
into a
plurality of first surface portions 36 to 39. The second adhesive surface 16
is
analogous to the first adhesive surface 15 also divided into a plurality of
second
surface portions 40 to 44. The number of first surface portions 36 to 39 and
the
number of second surface portions 40 to 44 is arbitrary. For example, four
first
surface portions 36 to 39 and five second surface portions 40 to 44 may be
provid-
ed, which are arranged alternately, so that a structure in a row pattern
results.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
=
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
19
In particular, there is always a second surface portion 40 to 44 arranged
between
two first surface portions 36 to 39 and vice versa.
Between the first surface portions 36 to 39 and the second surface portions 40
to
44 a respective web portion 17 is preferably provided, of which, however, only
one
is assigned a reference number in Fig. 9. Instead of the web portions 17, air
gaps
may be provided between the first surface portions 36 to 39 and the second sur-
face portions 40 to 44 such that the first adhesive surface 15 is separated
from
the second adhesive surface 16. The first surface portions 36 to 39 and the
second
surface portions 40 to 44 may be arranged symmetrically to the planes of sym-
metry El, E2 or at least symmetrically to one of the planes of symmetry El,
E2.
The first surface portions 36 to 39 and the second surface portions 40 to 44
may
also be positioned obliquely to the planes of symmetry El, E2. The surface por-
tions 36 to 44 may be arbitrarily oriented to the direction of gravity g. This
means that in the orientation of Fig. 9 the surface portions 36 to 44 may be
ar-
ranged horizontally, vertically or obliquely.
Fig. 10 shows a view of another embodiment of a fastening device 6. Compared
to
the embodiment of the fastening device 6 according to Figs. 2 and 3, in this
em-
bodiment of the fastening device 6, the first adhesive surface 15 is divided
into a
plurality of first surface portions 36 to 39, of which only four are provided
with a
reference number in Fig. 10. The first surface portions 36 to 39 are shown as
cir-
cles in Fig. 10. The second adhesive surface 16 is analogous to the first
adhesive
surface 15 also divided into a plurality of second surface portions 40 to 44,
of
which, however, only five are provided with a reference number in Fig. 10. The
second surface portions 40 to 44 are shown as squares in Fig. 10. The number
of
first surface portions 36 to 39 and the number of second surface portions 40
to 44
is arbitrary. For example, an equal number of first surface portions 36 to 39
and
second surface portions 40 to 44 are provided.
Alternatively, a different number of first surface portions 36 to 39 and
second
surface portions 40 to 44 may be provided. The first surface portions 36 to 39
and
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
the second surface portions 40 to 44 are arranged in a matrix pattern such
that
each first surface portion 36 to 39 is arranged adjacent to a second surface
por-
tion 40 to 44 and vice versa. The first surface portions 36 to 39 and the
second
surface portions 40 to 44 are both preferably arranged symmetrically to the
first
5 plane of symmetry El and symmetrically to the second plane of symmetry
E2. As
described above, web portions 17, which are not shown in Fig. 10, may be
provid-
ed between the first surface portions 36 to 39 and the second surface portions
40
to 44. Alternatively, air gaps may be provided between the first surface
portions
36 to 39 and the second surface portions 40 to 44 for separating the first
adhesive
10 surface 15 from the second adhesive surface 16.
Fig. 11 shows a schematic sectional view of a further embodiment of a
fastening
arrangement 3 comprising a fastening device 6. The fastening device 6
according
to Fig. 11 differs from the fastening device 6 according to Figs. 2 and 3 in
that the
15 first adhesive surface 15 is completely enclosed by the second adhesive
surface
16, as shown in Fig. 12, which shows the view XII of Fig. 11. This means that
the
first adhesive surface 15 and the second adhesive surface 16 are constructed
symmetrically to both the first plane of symmetry El and the second plane of
symmetry E2. The web portion 17 is in this case embodied as a closed, circular
20 geometry.
Starting at the first adhesive surface 15, a channel 45 in the form of a
boring
which is embodied rotationally symmetrical to the plane of symmetry M7 extends
into the runout 13 of the boring 12 of the receiving portion 11. The
symmetrical
structure of the adhesive surfaces 15, 16, allows for a particularly even
force dis-
tribution to be achieved. Verification, whether the first adhesive 19 fully
wets the
first adhesive surface 15 and the surface 5 can take place by the first
adhesive 19
being pressed through the channel 45 into the runout 13.
Fig. 13 shows a schematic sectional view of a further embodiment of a
fastening
arrangement 3 comprising a fastening device 6. The fastening device 6
according
to Fig. 13 differs from the fastening device 6 according to Figs. 11 and 12
only in
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
21
that the channel 45 does not enter into the runout 13 of the boring 12 of the
re-
ceiving portion 11, rather the channel 45 comprises a first boring 46
extending
towards the runout 13 but terminating ahead of said runout 13 and a second bor-
ing 47 perpendicular to boring 46 and entering into said boring 46. Thereby it
is
possible to prevent the first adhesive 19 from running into the receiving
portion
11 and contaminating the thread 14 with adhesive. The boring 47 may be arbi-
trarily oriented to the direction of gravity g. This means that in the
orientation of
Fig. 13, the boring 47 may point upward, downward or sideways.
Fig. 14 shows a schematic sectional view of a further embodiment of a
fastening
arrangement 3 comprising a fastening device 6. Fig. 15 shows the view XV of
Fig.
14, wherein the adhesive surfaces 15, 16 are not shown in Fig. 15. In this
embod-
iment of the fastening device 6, the fastening element 7 is divided into a
first fas-
tening element portion 48 and a second fastening element portion 49 which is
separated from the first fastening element portion 48. The first fastening
element
portion 48 may be embodied rotationally symmetrical to a center axis or axis
of
symmetry M7-1 and the second fastening element portion 49 may be embodied
rotationally symmetrical to a center axis or axis of symmetry M7-2. The axes
of
symmetry M7-1, M7-2 are preferably positioned parallel to each other.
The fastening element portions 48, 49 may be embodied cylindrically and may
have any cross section, for example a circular cross section. The fastening
ele-
ment portions 48, 49 may be connected to each other spaced apart from the sur-
face 5 and have a common receiving portion 11. In this embodiment of the fas-
tening device 6, the first adhesive surface 15 and the second adhesive surface
16
are separated by an air gap 50. This means that the web portion 17 is expenda-
ble. The fastening element portions 48, 49 may be constructed symmetrically to
the plane of symmetry El. Each fastening element portion 48, 49 may be con-
structed symmetrically to a respective plane of symmetry E2-1, E2-2. The fas-
telling elements 48, 49 may be arbitrarily oriented to the direction of
gravity g.
This means that in the orientation of Figs. 14 and 15 the fastening element
por-
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
RIVIV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
22
tions 48, 49 may be positioned one above the other, next to each other or
offset to
one another.
By using the fastening device 6 a weakening of the homogeneous base material
of
the wall 4 is preventable due to using the adhesives 19, 20 as compared to a
weld.
The elimination of welds, which can be the starting point for crack formation
un-
der load, leads to higher operational reliability of the fastening device 6 as
com-
pared to welded threaded bosses. Due to the adhesive connection between the
fastening device 6 and the surface 5, different materials may be used for the
fas-
tening element 7 and the wall 4. This may, for example, prevent contact
erosion.
The fastening device 6 is suitable both for original equipment and as a
retrofit
solution. Compared to welded-on threaded bosses, less costs and effort are re-
quired for retrofit solutions, since no heat coupling into the wall 4 is
required.
Deinstalling heat-sensitive components, as required for welded solutions, is
not
necessary. Deinstalling or shutting-down electronic components is also not
neces-
sary, as no current is introduced into the wall 4 when the fastening device 6
is
installed.
The quasi-static and dynamic loads may be transferred by means of the second
adhesive 20 during operation of the fastening device 6. In the event of a one-
time
highly dynamic load, such as with a blasting impact on the vehicle 1 or a
crash,
the fastening device 6 does not fail, because, although the second adhesive 20
may rupture or tear due to its lower stretchability, but the first adhesive 19
does
not fail due to its high stretchability. Thus, the two adhesives 19, 20
fulfill their
function independently of each other. By means of the web portion 17, the adhe-
sive layer thickness a15 of the first adhesive 19 and the second adhesive
layer
thickness a16 of the second adhesive 20 are easily and reproducibly
adjustable.
Alternatively, the adhesive layer thicknesses a15, a16 may also be adjusted by
mixing glass beads into one of the adhesives 19, 20.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
µ R11V16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
23
Although the present invention has been described using examples, it can be
modified in many ways.
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
=
RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
24
LIST OF REFERENCE NUMBERS
1 Vehicle
2 Cabin
3 Fastening assembly
4 Wall
5 Surface
6 Fastening device
7 Fastening element
8 Rear side
9 Outer surface
10 Bevel
11 Receiving portion
12 Boring
13 Runout
14 Thread
15 Adhesive surface
16 Adhesive surface
17 Web portion
18 End face
19 Adhesive
20 Adhesive
21 Channel
22 Side wall
23 Side wall
24 Fixing frame
25 Rear side
26 Outer surface
27 Inner surface
28 End face
29 Adhesive
30 Channel
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
' RMV16004PWO
Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
31 Side wall
32 Side wall
33 Channel
34 Side wall
5 35 Side wall
36 Surface portion
37 Surface portion
38 Surface portion
39 Surface portion
10 40 Surface portion
41 Surface portion
42 Surface portion
43 Surface portion
44 Surface portion
15 45 Channel
46 Boring
47 Boring
48 Fastening element portion
49 Fastening element portion
20 50 Air gap
a15 Adhesive layer thickness
a16 Adhesive layer thickness
BM Fastening means
25 d7 Thickness
D7 Diameter
El Plane of symmetry
E2 Plane of symmetry
E2-1 Plane of symmetry
E2-2 Plane of symmetry
Direction of gravity
Internal volume
CA 03045212 2019-05-28
. RMV16004PWO Q0147 WO
Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles GmbH
26
M7 Axis of symmetry
M7-1 Axis of symmetry
M7-2 Axis of symmetry
U Surrounding area