Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
METHOD AND DEVICE FOR RECEIVING
INFORMATION, AND COMPUTER-READABLE
MEDIUM
TECHNICAL FIELD
The embodiments of the disclosure relate to the field of wireless
communication technologies, and in particular to a method and a device for
receiving
information, and a computer readable medium.
BACKGROUND
With the development of a communication technology, the research on a 5th
Generation (5G) has been conducted. The radio access of the 5G is referred to
as New
Radio (NR). Since a frequency band adopted in the 5G NR is higher than a
frequency
band adopted in a Long Term Evolution (LTE) system, the path loss of radio
signal
transmission is increased and the coverage of a radio signal becomes small. In
a 5G
system, a beam is formed via a multi-antenna system of a base station by using
a
beamforming technology, thereby improving the gain of the radio signal and
compensating for the path loss.
In the 5G NR system, a common channel and a common signal cover the
whole cell in a multi-beam scanning manner, so that User Equipment (UE) in the
cell
can receive the common channel and the common signal. Moreover, the 5G NR
supports a wideband carrier, but due to limitation of UE capability, the UE
can
support a maximum bandwidth less than a bandwidth supported by a network
system.
Therefore, in the SG NR system, the wideband carrier of the network system is
further
configured to a plurality of Band WidthParts (BWPs).
For a paging process of the UE, under an environment of the multi-beam
scanning as well as the bandwidth of network system configured into a
plurality of
BWPs, how the UE can accurately receive a paging message is a problem that
needs
to be solved.
1
SUMMARY
In order to solve the above technical problem, the embodiments of the
disclosure
are intended to provide a method and a device for receiving information, and a
computer
readable medium, so that the success rate of receiving a paging message by the
UE can
be improved in a 5G NR system and thus the UE can accurately receive the
paging
message.
The technical solutions of the embodiments of the disclosure may be
implemented as follows.
In a first aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a method for
receiving information. The method is applied to a UE and may include the
following
operations.
Association relationships between paging bandwidths and synchronization or
reference signals are acquired, each association relationship comprising a
Quasi-Co-
Location (QCL) relationship, each paging bandwidth being located on a
respective one
of a plurality of Bandwidth Parts (BWPs), and the paging bandwidth being a
frequency
domain bandwidth or a frequency domain position, which is indicated by a
Control
Resource Set (CORESET).
A paging message is received in the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE,
according to a synchronization or reference signal having an association
relationship
with the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE in the association
relationships.
In a second aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a method for
receiving information. The method is applied to a network device and may
include the
following operations.
Indication information of a paging bandwidth corresponding to a UE and
indication information of a synchronization or reference signal having an
association
relationship with the paging bandwidth are carried in Remaining Minimum System
Information (RMSI) or Other System Information (OSI).
The RMSI or the OSI is sent to the UE.
In a third aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a UE. The UE may
include a first acquisition portion and a receiving portion.
The acquisition portion is configured to acquire association relationships
between paging bandwidths and synchronization or reference signals, each
association
2
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
relationship comprising a Quasi-Co-Location (QCL) relationship, each paging
bandwidth being located on a respective one of a plurality of Bandwidth Parts
(BWPs),
and the paging bandwidth being a frequency domain bandwidth or a frequency
domain
position, which is indicated by a Control Resource Set (CORESET).
The receiving portion is configured to receive, according to the
synchronization
or reference signal having an association relationship with a paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE in the association relationships, a paging message in
the paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE.
In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a network device.
The network device may include a carrying portion and a sending portion.
The carrying portion is configured to carry, in RMSI or OSI, indication
information of a paging bandwidth corresponding to a UE and indication
information
of a synchronization or reference signal having an association relationship
with the
paging bandwidth.
The sending portion is configured to send the RMSI or the OSI to the UE.
In a fifth aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a UE. The UE may
include a first network interface, a first memory and a first processor.
The first network interface is configured to receive and send signals in a
process
of receiving and sending information between the UE and other external network
elements.
The first memory is configured to store a computer program executed on the
first processor.
The first processor is configured to perform, when executing the computer
program, the operations of the method in the first aspect.
In a sixth aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a network device.
The network device may include a second network interface, a second memory and
a
second processor.
The second network interface is configured to receive and send signals in a
process of receiving and sending information the network device and other
external
network elements.
The second memory is configured to store a computer program capable of being
executed on the second processor.
3
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
The second processor is configured to perform, when executing the computer
program, the operations of the method in the second aspect.
3a
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
In a seventh aspect, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a computer
readable medium. The computer readable medium stores a program for receiving
information that, when executed by at least one processor, to implement the
operations of the method in the first aspect or second aspect.
According to the method and the device for receiving the information, and the
computer readable medium provided by the embodiments of the disclosure, the
UE,
after determining a paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE, acquires a
synchronization or reference signal associated with the paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE based on acquired association relationships between
paging
bandwidths and synchronization or reference signals. Thus, the UE can obtain a
synchronization and channel state according to the synchronization or
reference
signal, and receive a paging message from the paging bandwidth corresponding
to the
UE. In such manner, the UE can receive the paging message more accurately, and
the
success rate of receiving the paging message by the UE in paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE is improved.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
FIG. I is a flowchart of a method for receiving information according to an
embodiment of the disclosure.
FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of a Synchronization Signal (SS) block
according to an embodiment of the disclosure.
FIG. 3 is a diagram of system bandwidth division according to an embodiment
of the disclosure.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of another method for receiving information according to
an embodiment of the disclosure.
FIG. 5 is a diagram of composition of a UE according to an embodiment of the
disclosure.
FIG. 6 is a diagram of a specific hardware structure of a UE according to an
embodiment of the disclosure.
FIG. 7 is a diagram of composition of a network device according to an
embodiment of the disclosure.
4
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
FIG. 8 is a diagram of a specific hardware structure of a network device
according to an embodiment of the disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
In order to be able to understand the characteristics and technical contents
of
the embodiments of the disclosure in more detail, the implementation of the
embodiments of the disclosure will be described in detail below in combination
with
accompanying drawings. The appended accompanying drawings are merely for
reference, and are not intended to limit the embodiments of the disclosure.
First embodiment
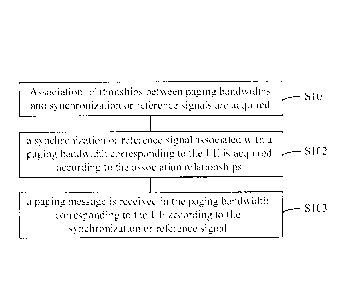
FIG. 1 illustrates a flowchart of a method for receiving information according
to an embodiment of the disclosure. The method may be applied to a UE and may
include the following operations.
At S101: association relationships between paging bandwidths and
synchronization or reference signals are acquired.
At S102: a synchronization or reference signal associated with a paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE is acquired according to the association
.. relationships.
At S103: a paging message is received in the paging bandwidth corresponding
to the UE, according to the synchronization or reference signal.
With the technical solutions illustrated in FIG. 1, after the UE determines a
paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE, the UE acquires, based on the
acquired
association relationships between the paging bandwidths and the
synchronization or
reference signals, a synchronization or reference signal associated with the
paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE. Thus, the UE can obtain a synchronization
and
channel state according to the synchronization or reference signal, and
receive a
paging message from the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE. In such a
manner, the UE can receive the paging message more accurately, and the success
rate
of receiving the paging message by the UE in the paging bandwidth
corresponding to
the UE is improved.
In the embodiment of the disclosure, each association relationship can be
used for indicating that the UE receives a paging message from a paging
5
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
bandwidth. Specifically, each association relationship preferably may be a
Quasi-
Co-Location (QCL) relationship.
Moreover, in the embodiment of the disclosure, the synchronization or
reference signal may include at least one of: a Synchronization Signal block
(SS
block), a Channel State Information Reference Signal (CSI-RS), or a Tracking
Reference Signal (TRS). Specifically, the synchronization or reference signal
may
be configured by a network device to the CE. Furthermore, the SS block and the
CSI-RS are used for Radio Resource Management (RRM) and mobility
measurement, and the TRS is used for time frequency tracking.
Specifically, in a 5G NR system, an SS and a broadcast channel need to
cover the whole cell in a multi-beam scanning manner so that a CE in the cell
receives the SS and the broadcast channel. The multi-beam transmission of the
SS
is implemented by defining an SS burst set. An SS burst set includes one or
more
SS bursts, and an SS burst includes one or more SS blocks. An SS block is used
for
.. bearing an SS and a broadcast channel of a beam. As a result, an SS burst
set may
include synchronization signals of beams, of which the number is the same as
the
SS block number, in a cell. An SS block includes a Primary Synchronization
Signal
(PSS) occupying one symbol, a Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS)
occupying one symbol and New Radio Access Technology-Physical broadcast
.. channels (NR-PBCHs) occupying two symbols. Specifically, the structural
diagram
of the SS block is illustrated in FIG. 2. In addition to the SS and the PBCH
on
which the multi-beam scanning needs to be performed, other some common
information such as Remaining Minimum System Information (RMSI) and a
paging message also needs to be sent in the multi-beam scanning manner.
For the technical solutions in FIG. 1, for the operation of acquiring the
association relationships in SI01, two exemplary implementation manners are
provided in the embodiment as follows.
In a first possible implementation manner, the operation that association
relationships between paging bandwidths and synchronization or reference
signals are
.. acquired may include the following operations.
RMSI or Other System Information (OSI) is received, where the RMSI or the
OSI is used for notifying indication information of each of the paging
bandwidths and
6
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
indication information of a synchronization or reference signal having an
association
relationship with the paging bandwidth.
It may be understood that the UE determines a paging bandwidth according to
an indication of indication information of the paging bandwidth, and acquires
the
synchronization or reference signal having the association relationship with
the
paging bandwidth according to the indication information of the
synchronization or
reference signal having the association relationship with the paging
bandwidth. In the
first possible implementation manner, for the RMSI, in the 5G NR system, a
common
search space needs to be defined for an initially accessed UE and is used for
receiving
common control information such as the RMSI. Therefore, a concept of a Control
Resource Set (CORESET) is introduced to define a resource set for carrying
control
information. The UE detects, in the resource set, a New Radio Access
Technology-
Physical Downlink Control channel (NR-PDCCH) to obtain scheduling information
of a New Radio Access Technology-Physical Downlink Shared channel (NR-PDSCH)
carrying the RMSI. Indication information of the CORESET is carried in the NR-
PBCH and is used by the UE to receive the RMSI. By the same reasoning, since
the
UE needs to receive the paging message, the UE also needs to determine CORESET
information for receiving paging indication information, i.e., CORESET for
paging.
The CORESET information is indicated to the UP via the RMSI, so that the UE
detects paging indication information according to the CORESET information to
receive the paging message.
In a second possible implementation manner, the operation that association
relationships between paging bandwidths and synchronization or reference
signals are
acquired may include the following operations.
Each association relationship is defined according to a preset association
relationship establishment strategy.
The preset association relationship establishment strategy comprises one of:
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship with a
synchronization or reference signal on a BWP on which the paging bandwidth is
located, where the paging bandwidth is a part of the BWP and the BWP is a part
of a
system bandwidth,
7
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship with a
synchronization or reference signal that is closest to the paging bandwidth in
a
frequency domain, or
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship with a
preset synchronization or reference signal.
For the second possible implementation manner, in the 5G NR, the system
bandwidth supports a wideband carrier and the system carrier bandwidth may be
up to
400 MHz. The network device has a high processing capacity and thus can
support
the wideband carrier. However, the UE is restricted by a cost, a power and the
like
and thus the wideband supported by the HE is restricted by the capability of
the UE.
As a result, one or more BWPs are configured for a wideband carrier, and each
BWP
includes a group of continuous Physical Resource Blocks (PRBs). For a UE, in a
serving cell, it is allowed that at most one active DL BWP and at most one
active UL
BWP coexist. Moreover, before a BWP is configured for the HE, there is an
initial
active Downlink/Uplink (DLIUL) BWP. The active DL/UL BWP is within a
minimum bandwidth range of the HE so as to be received by all capable UEs.
During
a RRC connection establishment process or after the RRC connection
establishment, a
special active DL/UL BWP may be configured for the HE.
For a UE in an idle state, due to the existence of the initial active DL/UL
BWP, the most direct manner is to carry the paging message on the initial
active
DL/UL BWP to send. Since the bandwidth of the initial active DL/UL BWP meets
the
minimum bandwidth capacity of the HE, all capable UEs may receive the paging
on
the initial active DL/UL BWP. However, generally, the minimum bandwidth
capacity
of the UE is 10 MI lz, which results in that the bandwidth of the initial
active DL/UL
BWP is limited. In addition to carrying the SS block, when the paging message,
the
data and the like are to be carried simultaneously, the congestion of paging
and data
transmission on the BWP is caused and thus the paging delay is increased. In
order to
avoid such a situation, the paging messages of the UE in the cell may be
dispersed to
a plurality of different BWPs, so that the paging messages are loaded on
different
BWPs for averaging. As illustrated in FIG. 3, a paging bandwidth for carrying
the
paging message is provided on each of a plurality of BWPs of the system
bandwidth,
and different UEs each may acquire a paging bandwidth for carrying a paging
message corresponding to the HE.
8
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
In the embodiment of the disclosure, the paging bandwidth may be a
frequency domain bandwidth or a frequency domain position, which is indicated
by
the CORESET; or may also be a frequency domain bandwidth carrying at least one
of
paging indication information or a paging message. In other words, the paging
bandwidth may be a frequency domain location at which the paging indication
information and the paging message are carried, or a frequency domain location
corresponding to the CORESET for transmission of the paging indication
information, or a frequency domain location at which the paging message is
sent.
It may be understood that the paging indication information specifically may
be carried in Downlink Control Information (DCI) sent by a Physical Downlink
Control Channel (PDCCH) that is scrambled with a Paging-Radio Network Ten-Tory
Identity (P-RNTI), and the UE receives, according to the paging indication
information, the paging message carried in a Physical Downlink Shared Channel
(PDSCH).
In the system bandwidth, there may be a plurality of SS blocks, e.g., a SS
block exists in each of different BWPs, and the UE in the idle state may
detect one or
more SS blocks in the system bandwidth. When the UE determines that a paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE has no association relationship (such as QCL
relationship) with the detected SS block(s), or that an SS detected by the UE
cannot
be used for synchronization reference when the UE receives the paging
bandwidth, it
is essential for the UE to acquire an SS or a reference signal that has an
association
relationship (such as QCL relationship) with the paging bandwidth
corresponding to
the UE. Therefore, the method illustrated in FIG. 1 may further include the
following
operation: responsive to that it is detected that the system bandwidth
includes more
than one synchronization or reference signal and the received paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE has no the QCL, association relationship with the
detected
synchronization or reference signal, a synchronization or reference signal
having the
QCL association relationship with the paging bandwidth correspondingly
received by
the UE is acquired. Specifically, the situation in which the paging bandwidth
corresponding to the .UE has no association relationship with the detected
synchronization or reference signal may include one of:
9
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
BWP on which the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE is located
different from a BWP on which the detected synchronization or reference signal
is
located, or
a distance between a frequency domain location of the paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE and a frequency domain location of the detected
synchronization or reference signal is greater than a set distance threshold,
so that the
frequency domain spacing distance is larger, or
a frequency domain location of the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE
and a frequency domain location of the detected synchronization or reference
signal
belong to different Radio-Frequency (RF) chains.
When the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE has no QCL relationship
with the detected synchronization or reference signal, the UE needs to obtain
an
appropriate synchronization or reference signal according to the technical
solutions
illustrated in FIG. 1 for synchronization, and thus the paging message sent on
the
.. paging bandwidth is further received.
Second embodiment
Based on the same inventive concept as the foregoing embodiments, FIG. 4
illustrates a flowchart of a method for receiving information according to an
embodiment of the disclosure. The method is applied to a network device and
may
include the following operations.
At S401: indication information of a paging bandwidth corresponding to a
UE and indication information of a synchronization or reference signal having
an
association relationship with the paging bandwidth are carried in RMSI or OSI.
At S402: the RMSI or the OSI is sent to the UE.
Specifically, the association relationship includes a QCL relationship.
It may be understood that after the UE receives the RMS or the OS!, a paging
bandwidth can be determined based on the indication information of the paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE, a synchronization or reference signal is
acquired
according to the indication information of the synchronization or reference
signal
having the association relationship with the paging bandwidth, and thereafter
a paging
message can be received according to the technical solutions in the first
embodiment,
the details are not repeated herein again.
Third embodiment
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
Based on the same inventive concept as the foregoing embodiments, FIG. 5
illustrates a UE 50 according to an embodiment of the disclosure. The UE 50
includes: a first acquisition portion 501, a second acquisition portion 502
and a
receiving portion 503.
The first acquisition portion 501 is configured to acquire association
relationships between paging bandwidths and synchronization or reference
signals.
The second acquisition portion 502 is configured to acquire, according to
the association relationships, a synchronization or reference signal
associated with
a paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE.
The receiving portion 503 is configured to receive, according to the
synchronization or reference signal, a paging message in the paging bandwidth
corresponding to the L1E.
In the above solutions, the first acquisition portion 501 is specifically
configured to receive RMSI or OS!, herein, the RMSI or the OSI is used for
notifying indication information of each of the paging bandwidths and
indication
information of a synchronization or reference signal having an association
relationship with the paging bandwidth.
In the above solutions, the first acquisition portion 501 is specifically
configured to define each association relationship according to a preset
association
relationship establishment strategy.
The preset association relationship establishment strategy comprises one of:
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship
with a synchronization or reference signal on a BWP on which the paging
bandwidth is located, herein, the paging bandwidth is a part of the BWP and
the
BWP is a part of a system bandwidth, or
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship
with a synchronization or reference signal that is closest to the paging
bandwidth in
a frequency domain, or
a paging message in a paging bandwidth has an association relationship
with a preset synchronization or reference signal.
In the above solutions, the synchronization or reference signal includes at
least one of: an SS block, a CSI-RS, or a TRS.
In the above solutions, the synchronization or reference signal is configured
1 I
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
by a network side to the UE. The SS block and the CSI-RS are used for RRM and
mobility measurement, and the TRS is used for time frequency tracking.
In the above solutions, the UE 50 further includes a determination portion
504, configured to: determine whether the paging bandwidth corresponding to
the
.. UE has an association relationship with a detected synchronization or
reference
signal, and trigger, responsive to that the paging bandwidth corresponding to
the
UE has no association relationship with the detected synchronization or
reference
signal, the first acquisition portion 501.
In the above solutions, the determination portion determines that the paging
bandwidth corresponding to the UE has no the association relationship with the
detected synchronization or reference signal includes:
a BWP on which the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE is located
is different from a BWP on which the detected synchronization or reference
signal
is located;
a distance between a frequency domain location of the paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE and a frequency domain location of the detected
synchronization or reference signal is greater than a set distance threshold;
or
a frequency domain location of the paging bandwidth corresponding to the
UE and a frequency domain location of the detected synchronization or
reference
signal belong to different RF chains.
In the above solutions, each association relationship includes a QCL
relationship.
It may be understood that in this embodiment, the "portion" may be a circuit,
a
processor, a program or software, and the like, and certainly may also be a
unit, may
further be modular and may also be non-modular.
In addition, each compositional portion in the embodiment may be integrated
into one processing unit, or each of the units may exist alone physically, or
two or
more units are integrated into one unit. The integrated unit may be
implemented in a
form of hardware, and may also be implemented in a form of a software
functional
module.
When the integrated units are implemented in the form of the software
functional unit and sold or used as an independent product, the units may be
stored in
a computer-readable storage medium. Based on such an understanding, the
technical
12
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
solutions of the disclosure essentially, or the part contributing to the prior
art, or some
of the technical solutions may be implemented in a form of a software product.
The
computer software product is stored in a storage medium and includes several
instructions to enable a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a
server,
or a network device) or processor to perform all or some of the operations of
the
methods described in the embodiments of the disclosure. The foregoing storage
medium includes any medium that can store a program code, such as a U disk, a
removable hard disk, a Read Only Memory (ROM), a Random Access Memoty
(RAM), a magnetic disk, or an optical disc.
Therefore, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a computer-readable
medium. The computer-readable medium stores a program for receiving
information
that, when executed by at least one processor, to implement the operations of
the
method in the first embodiment.
Based on the above UE 50 and the computer-readable medium, FIG. 6
illustrates a specific hardware structure of the UE 50 according to an
embodiment of
the disclosure, The specific hardware structure may include: a first network
interface
601, a first memory 602 and a first processor 603; and each component is
coupled
together via a bus system 604. It may be understood that the bus system 604 is
configured to implement connection and communication among these components.
In
addition to a data bus, the bus system 604 may further include a power bus, a
control
bus and a state signal bus. However, for the clarity, each bus is marked as
the bus
system 604 in FIG. 6. The first network interface 601 is configured to receive
and
send signals in a process of receiving and sending information between the UE
with
other external network elements.
The first memory 602 is configured to store a computer program which is
executed on the first processor 603.
The first processor 603 is configured to, when executing the computer
program, perform the following operations.
Association relationships between paging bandwidths and synchronization or
reference signals are acquired.
A synchronization or reference signal associated with a paging bandwidth
corresponding to the UE is acquired according to the association
relationships.
13
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
A paging message is received in the paging bandwidth corresponding to the
UE, according to the synchronization or reference signal.
It may be understood that the first memory 602 in the embodiment may be a
volatile memory or a non-volatile memory, or may include the volatile memory
and
the non-volatile memory. The non-volatile memory may be an ROM, a Programmable
ROM (PROM), an Erasable PROM (EPROM), an Electrically EPROM (EEPROM)
or a flash memory. The volatile memory may be an RAM and is used as an
external
high-speed cache. Through exemplary but not restrictive description, RAMs in
many
forms are available, such as a Static RAM (SRAM), a Dynamic RAM (DRAM), a
Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), a Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDR SDRAM), an
Enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), a Synchlink DRAM (SLDRAM) and a Direct
Rambus RAM (DR RAM). The first memory 602 of the system and the method
described herein is intended to include but not limited to these memories and
any
other suitable type of memory.
The first processor 603 may be an integrated circuit chip, and has a signal
processing capability. During an implementation process, each operation of the
method may be completed via an integrated logic circuit of hardware in the
first
processor 603 or an instruction in a software form. The first processor 603
may be a
universal processor, a Digital Signal Processor (DSP), an Application Specific
Integrated Circuit (ASIC), a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) or other
programmable logic devices, discrete gates or transistor logic devices,
discrete
hardware components. The processor may implement or execute each mcthod,
operation and logic block diagram disclosed in the embodiments of the
disclosure.
The universal processor may be a microprocessor or the processor may also be
any
conventional processor and the like. Operations of the methods disclosed in
combination with the embodiments of the disclosure may be directly executed
and
accomplished by means of a hardware decoding processor or may be executed and
accomplished using a combination of hardware and software modules in the
decoding
processor. The software module may be located in a mature storage medium in
the art,
such as an RAM, a flash memory, an ROM, a PROM, an [EPROM or a register. The
storage medium is located in the first memory 602; the first processor 603
reads
information in the first memory 602, and completes the operations of the above
method in combination with hardware thereof
14
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
It may be understood that these embodiments described herein may be
implemented by using hardware, software, firmware, middleware, a microcode or
a
combination thereof. For the implementation of the hardware, a processing unit
may
be implemented in one or more Application Specific Integrated Circuits
(ASICs), a
Digital Signal Processing (DSP), a DSP Device (DSPD), a Programmable Logic
Device (PLD), a Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), a universal processor, a
controller, a microcontroller, a microprocessor, and other electronic units
configured
to execute the functions of the disclosure or a combination thereof.
For the implementation of the software, technologies used herein may be
.. implemented via modules (such as a process and a function, etc.) for
executing the
functions of the disclosure. The software code may be stored in the memory and
is
executed by the processor. The memory may be implemented in the processor or
out
of the processor.
Specifically, the first processor 603 in the UE 50 is further configured to
perform, when executing the computer program, the operations of the method in
the
first embodiment, the details are not described herein again.
Fourth embodiment
Based on the same inventive concept as the foregoing embodiments, FIG. 7
illustrates a composition of a network device 70 according to an embodiment of
the
.. disclosure. The network device 70 may include: a carrying portion 701 and a
sending portion 702.
The carrying portion 701 is configured to carry, in RMSI or OSI, indication
information of a paging bandwidth corresponding to a UE and indication
information of a synchronization or reference signal having an association
relationship with the paging bandwidth.
The sending portion 702 is configured to send the RMSI or the OSI to the
UE.
In the above solutions, the association relationship includes a QCL
relationship.
In addition, an embodiment of the disclosure provides a computer-readable
medium. The computer-readable medium stores a program for receiving
information
that, when executed by at least one processor, to implement the operations of
the
method in the second embodiment. Detailed description on the computer-readable
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
medium refers to the description in the third embodiment, and will not be
repeated
here.
Based on the network device 70 and the computer-readable medium, FIG. 8
illustrates a specific hardware composition of a network device 70 according
to an
embodiment of the disclosure. The network device 70 may include: a second
network
interface 801, a second memory 802 and a second processor 803; and each
component
is coupled together via a bus system 804. It may be understood that the bus
system
804 is configured to implement connection and communication among these
components. In addition to a data bus, the bus system 804 may further include
a
power bus, a control bus and a state signal bus. However, for the clarity,
each bus is
marked as the bus system 804 in FIG. 8.
The second network interface 801 is configured to receive and send a signal in
a process of receiving and sending information between the network device and
other
external network elements.
The second memory 802 is configured to store a computer program which is
executed on the second processor 803.
The second processor 803 is configured to, when executing the computer
program, perform the following operations.
Indication information of a paging bandwidth corresponding to a UE and
indication information of a synchronization or reference signal having an
association relationship with the paging bandwidth are carried in Remaining
Minimum System Information (RMSI) or Other System Information (0S1).
The RMSI or the OSI is sent to the UE.
It may be understood that components in the specific hardware structure of the
network device 70 in the embodiment are similar to corresponding portions in
the
third embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
Specifically, the second processor 803 in the network device 70 is further
configured to perform, when executing the computer program, the operations of
the
method in the second embodiment, details are not described herein again.
It will be appreciated by one skilled in the art that the embodiments of the
disclosure may be embodied as a system, a method, or a computer program
product.
Accordingly, the disclosure may take the form of a hardware embodiment, a
software
embodiment or an embodiment combining software and hardware aspects.
16
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
Furthermore, the disclosure may take the form of a computer program product
implemented on one or more computer-readable storage media (including but not
limited to a magnetic disk memory and an optical memory) having a computer
available program code.
The disclosure is described herein with reference to flowcharts and/or block
diagrams of methods, devices (systems) and computer program products according
to
embodiments of the disclosure. It will be understood that each flow of the
flowcharts
and/or each block of the block diagrams, and combinations of flows of the
flowcharts
and/or blocks of block diagrams, can be implemented by computer program
instructions. These computer program instructions may be provided to a
processor of
a general purpose computer, a special purpose computer, an embedded processor
or
other programmable data processing apparatus to produce a machine, such that
the
instructions, which are executed by the processor of the computer or other
programmable instruction execution device, create means for implementing the
functions specified in one or more flows of the flowcharts and/or one or more
blocks
of the block diagrams.
These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer
readable storage medium that can direct a computer or other programmable data
processing device to operate in a particular manner, such that the
instructions stored in
the computer readable storage medium produce an article of manufacture
including an
instruction device, and the instruction device implements the functions
specified in
one or more flows of the flowcharts and/or one or more blocks of the block
diagrams.
The computer program instructions may also be loaded onto a computer or
other programmable data processing device, so that the computer or other
programmable data processing device executes a series of operations to produce
processing implemented by the computer and the instruction executed on the
computer or other programmable data processing device provides operations for
implementing the functions specified in one or more flows of the flowcharts
and/or
one or more blocks of the block diagrams.
The above are only preferred embodiments of the disclosure, and are not
intended to limit a scope of protection of the disclosure.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
17
CA 03052883 2019-08-07
In tlie embodiments of the disclosure, the UE acquires, after the UE
determines a paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE, a synchronization or
reference signal associated with the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE
based
.. on acquired association relationships between paging bandwidths and
synchronization
or reference signals, thus the UE can obtain a synchronization and channel
state
according to the synchronization or reference signal, and receive a paging
message
from the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE. In such a manner, the UE
can
receive the paging message more accurately, and the success rate of receiving
the
paging message by the UE from the paging bandwidth corresponding to the UE is
improved.
18