Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
NEW METHOD FOR VISUAL QUANTITATIVE DETECTION OF DUAL HEAVY
METAL IONS
FIELD
[0001] The present disclosure relates to the technical field of biological
detection, specifically
to a method and biosensor for detecting dual heavy metal ions.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Mercury in nature exists mainly in three forms, including elemental
mercury (Hg),
organic mercury (alkyl mercury, phenyl mercury), and inorganic mercury (Hg +
and Hg2+ salts and
their complexes), and mercury can perform biological and chemical conversion
between various
forms. It is the only metal present in liquid form at room temperature. The
physical shape of
mercury is silver-white, and it has a melting point of -38.87 C, a boiling
point of 356.6 C, a
density of 13.59 g/cm 3, and the element symbol is Hg. Silver has an elemental
state but generally
exists in a silver ore in a combined state. It has a white shiny form with a
melting point of
961.78 C, a boiling point of 2212 C, a density of 10.49 g/cm 3, and the
element symbol is Ag.
[0003] Traditional detection methods for Hg2+ and Ag+ mainly include atomic
absorption
spectroscopy (AAS), atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS), inductively
coupled plasma mass
spectrometry, electrochemical analysis, atomic absorption spectrophotometry,
etc. These methods
have high sensitivity, wide detection range, and are suitable for multiple
sample analysis.
However, the use of large equipment needs higher maintenance cost and
professional operations
which increase the cost of detections. At the same time, the pre-treated
process of samples is
- -
13826439.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
complicated, and a part of the samples need to be treated with corrosive
reagent; and the detecting
period is long. Due to the above disadvantages, the conventional methods are
not suitable for the
on-site analysis lack of precision instruments, etc., which is difficult to
meet the requirements of
actual analysis.
SUMMARY
[0004] The detection method and the biosensor established by the present
disclosure overcome
the deficiencies of the existing detection techniques and realize accurate,
rapid, simple and
efficient detection and analysis of heavy metals, and it is a novel method for
detecting two heavy
metals, which is cheap, fast, sensitive and specific.
[0005] The present disclosure aims to provide a method for detecting a metal
comprising
nucleic acid amplification in vitro, wherein the reaction system of nucleic
acid amplification in
vitro comprises a downstream primer, a template, and at least two upstream
primers; each of the
respective nucleotide sequences of the at least two upstream primers has at
least one nucleotide
different from the other; each upstream primer of the at least two upstream
primers comprises a
complementary sequence A, a linking arm, a complementary sequence B, a
nucleotide sequence
capable of specifically amplifying the template, and a nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to
the metal to be detected; the linking arm is provided between the
complementary sequence A and
the complementary sequence B, and the nucleotide sequence capable of
specifically amplifying
the template and the nucleotide sequence capable of binding to the metal to be
detected are
provided at 5' terminal or 3' terminal of the upstream primer; the nucleotide
sequences of the
complementary sequence A and the complementary sequence B are complementary
and/or
reverse complementary to each other; the linking arm comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting
polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension
during in vitro
nucleic acid amplification; the downstream primer comprises the nucleotide
sequence capable of
specifically amplifying the template; and the downstream primer comprises the
nucleotide
sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template.
[0006] The template at least comprises a complementary sequence G, a
complementary
-2-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
sequence H and a sequence I, wherein the complementary sequence G and the
complementary
sequence H are respectively complementary and/or reverse complementary to the
nucleotide
sequence of the at least two upstream primers capable of specifically
amplifying the template;
and the nucleotide sequence of the sequence I is the same as the nucleotide
sequence of the
downstream primer capable of specifically amplifying the template.
[0007] The complementation includes complementation or reverse complementation
as defined
by the conventional art or common general knowledge, and/or performing
complementation or
reverse complementation according to complementary principles as defined by
the conventional
art or common general knowledge.
[0008] The polymerase includes a polymerase that can be used for in vitro
nucleic acid
amplification.
[0009] The nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template
includes a
primer designed according to a characteristic sequence of the template; the
characteristic
sequence includes the characteristic sequence defined by the conventional art
or common general
knowledge; and the design methods are recorded by the conventional art or
common general
knowledge.
[0010] The A, B, G, H, and I are only used to distinguish different
complementary sequences or
sequences, and are not used for sorting.
[0011] Specifically, the method further comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 3):
[0012] 1) the nucleic acid amplification in vitro includes ultra-rapid PCR,
wherein the reaction
process of the ultra-rapid PCR comprises: 90-98 C for 2-6s and 50-60 C for 2-
8s, for 20-40
cycles in total;
[0013] specifically, the reaction process of the ultra-rapid PCR comprises: 95
C for 2s and
58 C for 3s for 30 cycles in total;
[0014] more specifically, the concentration of the upstream primer and the
downstream primer
in the reaction system of the ultra-rapid PCR is more than 10 times of the
concentration of the
normal PCR, even more specifically, 20 times; the reaction system of the ultra-
rapid PCR further
comprises a DNA polymerase, and the concentration of the DNA polymerase is
more than 10
-3-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
times of the concentration of the normal PCR, specifically, 60 times;
[0015] 2) the linking arm comprises a compound having a long-chain structure;
and
[0016] 3) the nucleotide sequence capable of binding to the metal to be
detected includes a
nucleotide sequence containing thymine or cytosine.
[0017] Specifically, the method further comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 8):
[0018] 1) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 via the
linking arm;
[0019] 2) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking, via
the linking arm, nucleotide sequences which are modified from the nucleotide
sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 1 and/or SEQ ID NO: 2 by substituting, adding and/or deleting
one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 1
and/or SEQ ID NO: 2;
[0020] 3) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the
linking arm;
[0021] 4) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking, via
the linking arm, nucleotide sequences which are modified from the nucleotide
sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or deleting
one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5;
[0022] 5) the downstream primer includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0023] 6) the downstream primer includes a nucleotide sequence which is
modified from the
nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or
deleting one or
more nucleotides and has the same function as the nucleotide sequence set
forth in SEQ ID NO:
3;
.. [0024] 7) the template includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 6; and
[0025] 8) the template includes a nucleotide sequence which is modified from
the nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one
or more
-4-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
nucleotides and has the same function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 6.
[0026] The same function refers to enabling the amplification of the template.
[0027] Specifically, the linking arm is oxyethyleneglycol bridge, and the
chemical structure of
oxyethyleneglycol is:
o-
I
0=--P-0-
1
I .
[0028] More specifically, one of the at least two upstream primers comprises:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -CTCTC TCTTT
CCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTTTT or TGAGGTAGTAGG
TTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -AACTATACAACCTACTACCTCATTTTT
TTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC .
[0029] Even more specifically, the at least two upstream primers comprise:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -CTCTCTCTTTC
CCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTTTT and TGAGGTAGTAGG
TTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -AACTATA CAACCTACTACCTCATT1T1
TTTTTTGC AC ATAACACCC.
[0030] Specifically, the downstream primer is a primer labeled with immune
marker, wherein
the immune marker comprises biotin, and the biotin is labeled on the first
nucleotide at the 5'
terminal of the downstream primer; and the labeling method belongs to a
conventional art; and
more specifically, the downstream primer is Biotin-TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC.
[0031] Specifically, the method further comprises a color reaction based on
nucleic acid
self-assembly, wherein the reaction system of the color reaction based on
nucleic acid
self-assembly comprises a hairpin sequence, wherein the hairpin sequence
comprises hairpin
sequence 1 and/or hairpin sequence 2; the hairpin sequence 1 comprises a
complementary
sequence C, a complementary sequence D and 3 or more arbitrary nucleotides,
wherein the 3 or
-5-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
more arbitrary nucleotides are provided at the 5' terminal and/or the 3'
terminal of the hairpin
sequence; the hairpin sequence 2 comprises a complementary sequence E and a
complementary
sequence F; and the complementary sequence D and the complementary sequence F
are
complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other; the complementary
sequence C is
complementary and/or reverse complementary to the complementary sequence A
and/or
complementary sequence B, and the complementary sequence C and the
complementary
sequence E are complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other.
[0032] The numbering of the sequences is used to distinguish different hairpin
sequences, not
for sorting; the C, D, E, and F are only used to distinguish different
complementary sequences,
not for sorting.
[0033] Specifically, the hairpin sequence comprises one of the following 1) to
4):
[0034] 1) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 7
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 7 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7;
[0035] 2) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 8
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 8 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 8;
[0036] 3) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 9
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 9 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0037] 4) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 10
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 10 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0038] The same function refers to: the upstream primer can open the hairpin
structure of the
-6-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
hairpin sequence 1 by base complementation, and the hairpin sequence 1 can
realize a
self-extension of the nucleotide chain under the action of TDT enzyme; the
hairpin sequence 2
can open the hairpin structure of the hairpin sequence 1 by base
complementation; the hairpin
sequence 1 and the hairpin sequence 2 can mutually cyclically open each
other's hairpin structure
and connect to each other; the hairpin sequence 1 can realize the self-
extension of the nucleotide
chain under the action of TDT enzyme at the same time in a linking body formed
by the hairpin
sequence 1 and the hairpin sequence 2.
[0039] Specifically, the color reaction based on nucleic acid self-assembly
further comprises at
least one of the following 1) to 2):
[0040] 1) mixing at least one reaction system prepared by the method according
to the present
disclosure with at least one hairpin sequence of the method according to the
present disclosure,
and incubating at 37 C for 20 min; adding TdT enzymatic reaction system to
react at 37 C for
min, and heating at 75 C for 10 min; adding hemin and G-quadruplex inducing
buffer and
incubating at 37 C for 20min; and adding ABTS2- and hydrogen peroxide for
color reaction;
15 [0041] specifically, before adding TdT enzyme to the reaction system,
the purification step is
further comprised; specifically, the purification step comprises attaching
biotin to the downstream
primer and then purifying target product with biotin through the binding of
biotin and streptavidin;
and
[0042] 2) in the reaction system of the color reaction based on nucleic acid
self-assembly, the
20 .. final concentration of each of the hairpin sequence 1 and the hairpin
sequence 2 is 21.iM.
[0043] Specifically, the method further comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 4):
[0044] 1) determining whether a target to be detected is in an object to be
detected by color
change of the final reaction system; specifically, when the color of the
reaction system changes,
the object to be detected contains the target to be detected; more
specifically, when the color of
the reaction system changes to blue-green, the object to be detected contains
the target to be
detected;
[0045] 2) calculating the concentration of the target to be detected in the
object to be detected
by a method of preparing a standard curve according to the color of the final
reaction system;
-7-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0046] 3) detecting two or multiple ions by increasing the types of the
upstream primer, hairpin
sequence 1, and hairpin sequence 2;
[0047] specifically, for two or multiple detection, the microarray method can
be used to
determine whether the object to be detected contains the target to be detected
or contains several
targets to be detected; the microarray method comprises separately applying
the different kinds of
hairpin sequences in different wells to perform reaction, and then determining
whether the target
to be detected or several targets to be detected is contained according to the
reaction result: when
the color of the reaction solution changes or turns blue-green, it is
determined that the target to be
detected is presented; the total number of wells in which the color change or
the blue-green color
is generated is the total number of types of the target to be detected
contained in the sample to be
detected;
[0048] the types of the hairpin sequence 1 comprises: the complementary
sequence C in the
hairpin sequence 1 is the same type of hairpin sequence as the hairpin
sequence complementary
or reverse complementary to the complementary sequence A and/or B in the
upstream primer,
otherwise, the sequences are different types of hairpin sequence 1; and the
upstream primers
having identical nucleotide sequences are the same upstream primer;
[0049] 4) purifying the in vitro nucleic acid amplification product before the
color reaction
based on nucleic acid self-assembly; and
[0050] specifically, the purification is carried out by a kit purification or
magnetic bead
purification; the purification comprises removing other impurities other than
the in vitro nucleic
acid amplification products and hairpin sequence linking products in the
reaction system.
[0051] The other object of the present disclosure is to provide a kit and/or a
biosensor for
detecting a metal, the kit and/or the biosensor comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 6):
[0052] 1) at least two upstream primers, wherein each of the respective
nucleotide sequences of
the at least two upstream primers has at least one nucleotide different from
the other; each
upstream primer of the at least two upstream primers comprises a complementary
sequence A, a
linking arm, a complementary sequence B, a nucleotide sequence capable of
specifically
amplifying the template, and a nucleotide sequence capable of binding to the
metal to be detected;
-8-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
the linking arm is provided between the complementary sequence A and the
complementary
sequence B, and the nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the
template and the
nucleotide sequence capable of binding to the metal to be detected are
provided at 5' terminal or
3' terminal of the upstream primer; the nucleotide sequences of the
complementary sequence A
and the complementary sequence B are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the linking arm comprises a moeity capable of inhibiting polymerase
binding and/or a
moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension during in vitro nucleic acid
amplification; and
the downstream primer comprises the nucleotide sequence capable of
specifically amplifying the
template;
[0053] 2) a template, wherein the template at least comprises a complementary
sequence G, a
complementary sequence H and a sequence I, wherein the complementary sequence
G and the
complementary sequence H are respectively complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
nucleotide sequence of the at least two upstream primers capable of
specifically amplifying the
template; and the nucleotide sequence of the sequence I is the same as the
nucleotide sequence of
the downstream primer capable of specifically amplifying the template;
[0054] 3) a downstream primer, a template and at least two upstream primers,
wherein each of
the respective nucleotide sequences of the at least two upstream primers has
at least one
nucleotide different from the other; each upstream primer of the at least two
upstream primers
comprises a complementary sequence A, a linking arm, a complementary sequence
B, a
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template, and a
nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to the metal to be detected; the linking arm is provided
between the
complementary sequence A and the complementary sequence B, and the nucleotide
sequence
capable of specifically amplifying the template and the nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to
the metal to be detected are provided at 5' terminal or 3' terminal of the
upstream primer; the
nucleotide sequences of the complementary sequence A and the complementary
sequence B are
complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other; the linking arm
comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting
new strand
extension during in vitro nucleic acid amplification; the downstream primer
comprises the
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template; and the
downstream primer
-9-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
comprises the nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the
template;
[0055] 4) at least two upstream primers and a hairpin sequence, wherein
[0056] each of the respective nucleotide sequences of the at least two
upstream primers has at
least one nucleotide different from the other; each upstream primer of the at
least two upstream
primers comprises a complementary sequence A, a linking arm, a complementary
sequence B, a
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template, and a
nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to the metal to be detected; the linking arm is provided
between the
complementary sequence A and the complementary sequence B, and the nucleotide
sequence
capable of specifically amplifying the template and the nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to
the metal to be detected are provided at 5' terminal or 3' terminal of the
upstream primer; the
nucleotide sequences of the complementary sequence A and the complementary
sequence B are
complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other; the linking arm
comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting
new strand
extension during in vitro nucleic acid amplification; and the downstream
primer comprises the
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template; and
[0057] the hairpin sequence comprises hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the
hairpin sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary
sequence D and 3
or more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the 3 or more arbitrary nucleotides are
provided at the 5'
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B, and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other;
[0058] 5) at least two upstream primers, a template and a hairpin sequence,
wherein
[0059] each of the respective nucleotide sequences of the at least two
upstream primers has at
least one nucleotide different from the other; each upstream primer of the at
least two upstream
-10-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
primers comprises a complementary sequence A, a linking arm, a complementary
sequence B, a
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template, and a
nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to the metal to be detected; the linking arm is provided
between the
complementary sequence A and the complementary sequence B, and the nucleotide
sequence
capable of specifically amplifying the template and the nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to
the metal to be detected are provided at 5' terminal or 3' terminal of the
upstream primer; the
nucleotide sequences of the complementary sequence A and the complementary
sequence B are
complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other; the linking arm
comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting
new strand
extension during in vitro nucleic acid amplification; and the downstream
primer comprises the
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template;
[0060] the template at least comprises a complementary sequence G, a
complementary
sequence H and a sequence I, wherein the complementary sequence G and the
complementary
sequence H are respectively complementary and/or reverse complementary to the
nucleotide
sequence of at least two upstream primers capable of specifically amplifying
the template; and
the nucleotide sequence of the sequence I is the same as the nucleotide
sequence of the
downstream primer capable of specifically amplifying the template; and
[0061] the hairpin sequence comprises hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the
hairpin sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary
sequence D and 3
or more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the 3 or more arbitrary nucleotides are
provided at the 5'
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B, and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other;
6) a downstream primer, a template, at least two upstream primers and a
hairpin sequence,
wherein
- II -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0062] each of the respective nucleotide sequences of the at least two
upstream primers has at
least one nucleotide different from the other; each upstream primer of the at
least two upstream
primers comprises a complementary sequence A, a linking arm, a complementary
sequence B, a
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template, and a
nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to the metal to be detected; the linking arm is provided
between the
complementary sequence A and the complementary sequence B, and the nucleotide
sequence
capable of specifically amplifying the template and the nucleotide sequence
capable of binding to
the metal to be detected are provided at 5' terminal or 3' terminal of the
upstream primer; the
nucleotide sequences of the complementary sequence A and the complementary
sequence B are
complementary and/or reverse complementary to each other; the linking arm
comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting
new strand
extension during in vitro nucleic acid amplification; and the downstream
primer comprises the
nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template;
[0063] the downstream primer comprises the nucleotide sequence capable of
specifically
amplifying the template;
[0064] the hairpin sequence comprises hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the
hairpin sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary
sequence D and 3
or more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the 3 or more arbitrary nucleotides are
provided at the 5'
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B, and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other;
[0065] specifically, the nucleotide sequence capable of binding to the metal
to be detected
includes a nucleotide sequence containing thymine or cytosine;
[0066] specifically, one of the at least two upstream primers comprises at
least one of the
following 1) to 4):
-12-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0067] 1) a primer obtained by linking the nucleotide sequences set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 1 and
SEQ ID NO: 2 via the linking arm;
[0068] 2) a primer obtained by linking, via the linking arm, nucleotide
sequences which are
modified from the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 and/or SEQ ID
NO: 2 by
substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and have the same
function as the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 and/or SEQ ID NO: 2;
[0069] 3) a primer obtained by linking the nucleotide sequences set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 4 and
SEQ ID NO: 5 via the linking arm;
[0070] 4) a primer obtained by linking, via the linking arm, nucleotide
sequences which are
modified from the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID
NO: 5 by
substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and have the same
function as the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5;
[0071] specifically, the downstream primer includes the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 3 and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide
sequence set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more
nucleotides and has
the same function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0072] specifically, the template includes the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 6,
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 6 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6;
[0073] specifically, the linking arm comprises the compound having a long-
chain structure;
[0074] specifically, the linking arm is oxyethyleneglycol bridge, and the
chemical formula of
oxyethyleneglycol is:
- 13 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
0=P-0-
I .
[0075] Specifically, one of the at least two upstream primers comprises:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-CTCT
CTCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTTTT
or
TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -
AACTATA
CAACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0076] Specifically, the at least two upstream primers comprise:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-CTCTC
TCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGC
CACGTTCGGTTTT and
TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge- AACTATACA
ACCTACTACCTCAITI ______ TTTTIFTTTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0077] Specifically, the downstream primer is a primer labeled with immune
marker, wherein
the immune marker comprises biotin, and the biotin is labeled on the first
nucleotide at the 5'
terminal of the downstream primer; and the labeling method belongs to a
conventional art; more
specifically, the downstream primer is Biotin-TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC.
[0078] Specifically, the hairpin sequence comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 4):
[0079] 1) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 7
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 7 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7;
[0080] 2) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 8
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 8 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 8;
-14-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0081] 3) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 9
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 9 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0082] 4) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 10
and/or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 10 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0083] The complementation includes complementation or reverse complementation
as defined
by the conventional art or common general knowledge, and/or performing
complementation or
reverse complementation according to complementary principles as defined by
the conventional
art or common general knowledge.
[0084] The polymerase includes a polymerase that can be used for in vitro
nucleic acid
amplification.
[0085] The nucleotide sequence capable of specifically amplifying the template
specifically
includes a primer sequence designed according to a characteristic sequence of
the template; the
characteristic sequence includes the characteristic sequence defined by the
conventional art or
common general knowledge; and the design includes the design method recorded
by the
conventional art or common general knowledge.
[0086] A, B, G, H, and I are only used to distinguish different complementary
sequences or
sequences, not for sorting.
[0087] Specifically, the kit and /or the biosensor comprise at least two
upstream primers, and at
least one of the following 1) to 8):
[0088] 1) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 via the
linking arm;
[0089] 2) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking, via
the linking arm, nucleotide sequences which are modified from the nucleotide
sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 1 and/or SEQ ID NO: 2 by substituting, adding and/or deleting
one or more
- 15 -
13790822. 1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 1
and/or SEQ ID NO: 2;
[0090] 3) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking the
nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the
linking arm;
[0091] 4) one of the at least two upstream primers includes a primer obtained
by linking, via
the linking arm, nucleotide sequences which are modified from the nucleotide
sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or deleting
one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5;
[0092] 5) the downstream primer includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0093] 6) the downstream primer includes a nucleotide sequence which is
modified from the
nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or
deleting one or
more nucleotides and has the same function as the nucleotide sequence set
forth in SEQ ID NO:
3;
[0094] 7) the template includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 6; and
[0095] 8) the template includes a nucleotide sequence which is modified from
the nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one
or more
nucleotides and has the same function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 6.
[0096] The same function refers to enabling the amplification of the template.
[0097] Specifically, the linking arm comprises a compound having a long-chain
structure.
[0098] Specifically, the linking arm is oxyethyleneglycol bridge, and the
chemical structure of
oxyethyleneglycol is:
_o
0=P-0"
-16-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[00991 More specifically, one of the at least two upstream primers comprises:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-CTCTC
TCT'TTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTTTT
or
TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -AACTATAC
AACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0100] Specifically, the at least two upstream primers comprise:
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-CTCTC
TCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTITT
and
TGAGGTA GTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-AACTATAC
AACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0101] Specifically, the downstream primer is a primer labeled with immune
marker, wherein
the immune marker comprises biotin, and the biotin is labeled on the first
nucleotide at the 5'
terminal of the downstream primer; and the labeling method belongs to a
conventional art; and
more specifically, the downstream primer is Biotin-TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC.
[0102] Specifically, the kit and/or the biosensor further comprise a hairpin
sequence, wherein
the hairpin sequence comprises hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin sequence 2;
the hairpin
sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary sequence D
and three or
more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the three or more arbitrary nucleotides
are provided at the 5'
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B , and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other.
[0103] The hairpin sequence comprises one of the following 1) to 4):
[0104] 1) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 7
and/or a nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
-17-
13790822,1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
NO: 7 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7;
[0105] 2) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 8
and/or a nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 8 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 8;
[0106] 3) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 9
and/or a nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 9 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0107] 4) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 10
and/or a nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 10 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0108] Specifically, the kit and/or the biosensor further include at least one
of TDT reaction
buffer, dATP, dGTP, TdT enzyme, hemin, G-quadruplex inducing buffer, ABTS2-,
hydrogen
peroxide, home-made XP beads, and magnetic beads modified with streptavidin on
the surface.
[0109] Specifically, the kit and/or the biosensor comprise the following 1) to
5):
1) TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -AAC
TATACAACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTITTGCACATAACACCCC;
2) AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -
CTCTCTCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTT'FT ;
3) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6;
4) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3; and
5) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7; the nucleotide sequence
set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 8; the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; the
nucleotide sequence set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
- 18 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0110] The chemical structure of oxyethyleneglycol is:
[0111] The present disclosure aims to provide a method for detecting Ag+, the
method
comprises amplifying nucleic acid in vitro, wherein the reaction system of
nucleic acid
amplification in vitro comprises a upstream primer, a downstream primer and a
template; the
upstream primer comprises: a primer obtained by linking the nucleotide
sequences set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the linking arm, or a primer obtained by
linking via the
linking arm nucleotide sequences which are modified from the nucleotide
sequences set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one
or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5; the linking arm comprises a moeity capable of inhibiting
polymerase
binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension during in
vitro nucleic acid
amplification.
[0112] The polymerase includes a polymerase that can be used for in vitro
nucleic acid
amplification.
[0113] The downstream primer comprises: the nucleotide sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 3,
or the nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence set
forth in SEQ ID
NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3.
[0114] The template comprises: the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:
6, or the
nucleotide sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 6
by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has the
same function as the
nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6.
[0115] The same function refers to enabling the amplification of the template.
-19-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0116] The linking arm comprises a compound having a long-chain structure.
[0117] Specifically, the linking arm is oxyethyleneglycol, and the chemical
structure of
oxyethyleneglycol is:
o o
o
1
0=P-0"
(1)
1 .
[0118] Specifically, the upstream primer is TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT-
oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-AACTATACAACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTT
TTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0119] Specifically, the downstream primer is a primer labeled with immune
marker, wherein
the immune marker comprises biotin, and the biotin is labeled on the first
nucleotide at the 5'
terminal of the downstream primer; and the labeling method belongs to a
conventional art; and
more specifically, the downstream primer is Biotin-TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC.
[0120] Specifically, the method further comprising at least one of the
following 1) to 2):
[0121] 1) the amplifying nucleic acid in vitro comprises ultra-rapid PCR,
wherein the reaction
process of the ultra-rapid PCR comprises: 90-98 C for 2-6s and 50-60 C for 2-
8s, for 20-40
cycles in total;
[0122] specifically, the reaction process of the ultra-rapid PCR comprises: 95
C for 2s and
58 C for 3s for 30 cycles in total;
[0123] more specifically, the concentration of the upstream primer and the
downstream primer
in the reaction system of the ultra-rapid PCR is more than 10 times of the
concentration of the
normal PCR, even more specifically, 20 times; the reaction system of the ultra-
rapid PCR further
comprises a DNA polymerase, and the concentration of the DNA polymerase is
more than 10
times of the concentration of the normal PCR, specifically, 60 times;
[0124] 2) the method further comprises a color reaction based on nucleic acid
self-assembly,
- 20 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
wherein the reaction system of the color reaction based on nucleic acid self-
assembly comprises a
hairpin sequence, wherein the hairpin sequence comprises hairpin sequence 1
and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the hairpin sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a
complementary
sequence D and three or more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the three or more
arbitrary
nucleotides are provided at the 5' terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the
hairpin sequence; the
hairpin sequence 2 comprises a complementary sequence E and a complementary
sequence F;
and the complementary sequence D and the complementary sequence F are
complementary
and/or reverse complementary to each other; the complementary sequence C is
complementary
and/or reverse complementary to the complementary sequence A and/or
complementary sequence
B , and the complementary sequence C and the complementary sequence E are
complementary
and/or reverse complementary to each other.
[0125] The numbering of sequences is used to distinguish different hairpin
sequences, not for
sorting; C, D, E, and F are only used to distinguish different complementary
sequences, not for
sorting.
[0126] Specifically, the hairpin sequence comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 2):
[0127] 1) the hairpin sequence 1 comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 9,
and/or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 9 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0128] 2) the hairpin sequence 2 comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO:
10, and/or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide
sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 10 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides
and has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0129] Specifically, the method further comprises: mixing the reaction system
and the hairpin
sequence according to at least one method for detecting Ag+ according to the
present disclosure,
and incubating at 37 C for 20 min; adding TdT enzymatic reaction system to
react at 37 C for
20 min, and heating at 75 C for 10 min; adding hemin and G-quadruplex inducing
buffer and
incubating at 37 C for 20min; and adding ABTS2- and hydrogen peroxide for
color reaction.
-21-
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0130] Specifically, before adding TdT enzyme to the reaction system, the
purification step is
further comprised; specifically, the purification step comprises attaching
biotin to the downstream
primer and then purifying target product with biotin through the binding of
biotin and avidin.
[0131] Specifically, in the reaction system of the color reaction based on
nucleic acid
self-assembly, the final concentration of each of the hairpin sequence 1 and
the hairpin sequence
2 is 21,1.M.
[0132] Determine the present of target to be detected in the object to be
detected by the color
change of the final reaction system.
[0133] Specifically, when the color of the reaction system changes, the object
to be detected
contains the target to be detected; more specifically, when the color of the
reaction system
changes to blue-green, the object to be detected contains the target to be
detected.
[0134] The concentration of the target to be detected in the object to be
detected is calculated
by a method of preparing a standard curve according to the color of the final
reaction system
[0135] Before the color reaction based on nucleic acid self-assembly,
purification of the in vitro
nucleic acid amplification product is performed.
[0136] Specifically, the purification is carried out by a kit purification or
magnetic bead
purification; the purification comprises removing other impurities other than
the in vitro nucleic
acid amplification products and hairpin sequence linking products in the
reaction system.
[0137] The present disclosure further aims to provide a kit and/or a biosensor
for detecting Ag+,
and the kit and/or the biosensor comprise at least one of the following 1) to
4):
[0138] 1) a upstream primer, wherein the upstream primer includes: a primer
obtained by
linking the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5
via the linking
arm, or a primer obtained by linking via the linking arm nucleotide sequences
which are modified
from the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by
substituting,
adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and have the same function as
the nucleotide
sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5; the linking arm
comprises a moeity
capable of inhibiting polymerase binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting
new strand
extension during in vitro nucleic acid amplification;
- 22 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
[0139] 2) a upstream primer, a downstream primer and a template, wherein
[0140] the upstream primer includes: a primer obtained by linking the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the linking arm, or a primer
obtained by linking
via the linking arm nucleotide sequences which are modified from the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or
deleting one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5; the linking arm comprises a moeity capable of inhibiting
polymerase
binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension during in
vitro nucleic acid
amplification;
[0141] the downstream primer includes: the nucleic acid sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 3,
or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0142] the template includes: the nucleic acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 6, or the
nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 6
by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has the
same function as the
nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6;
[0143] 3) a upstream primer and a hairpin sequence, wherein
[0144] the upstream primer includes: a primer obtained by linking the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the linking arm, or a primer
obtained by linking
via the linking arm nucleotide sequences which are modified from the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or
deleting one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5; the linking arm comprises a moeity capable of inhibiting
polymerase
binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension during in
vitro nucleic acid
amplification;
[0145] the hairpin sequence includes: hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the hairpin
sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary sequence D
and three or
- 23 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the three or more arbitrary nucleotides
are provided at the 5'
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B , and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other;
[0146] 4) a upstream primer, a downstream primer, a template and a hairpin
sequence, wherein
[0147] the upstream primer includes: a primer obtained by linking the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and SEQ ID NO: 5 via the linking arm, or a primer
obtained by linking
via the linking arm nucleotide sequences which are modified from the
nucleotide sequences set
forth in SEQ ID NO: 4 and/or SEQ ID NO: 5 by substituting, adding and/or
deleting one or more
nucleotides and have the same function as the nucleotide sequences set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4
and/or SEQ ID NO: 5; the linking arm comprises a moeity capable of inhibiting
polymerase
binding and/or a moeity capable of inhibiting new strand extension during in
vitro nucleic acid
amplification;
[0148] the downstream primer includes: the nucleic acid sequence set forth in
SEQ ID NO: 3,
or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence
set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 3 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has
the same function
as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0149] the template includes: the nucleic acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID
NO: 6, or the
nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 6
by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and has the
same function as the
nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6; and
[0150] the hairpin sequence includes: hairpin sequence 1 and/or hairpin
sequence 2; the hairpin
sequence 1 comprises a complementary sequence C, a complementary sequence D
and three or
more arbitrary nucleotides, wherein the three or more arbitrary nucleotides
are provided at the 5'
- 24 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
terminal and/or the 3' terminal of the hairpin sequence; the hairpin sequence
2 comprises a
complementary sequence E and a complementary sequence F; and the complementary
sequence
D and the complementary sequence F are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other; the complementary sequence C is complementary and/or reverse
complementary to the
complementary sequence A and/or complementary sequence B , and the
complementary sequence
C and the complementary sequence E are complementary and/or reverse
complementary to each
other.
[0151] The polymerase comprises a polymerase that can be used for in vitro
nucleic acid
amplification.
[0152] The same function refers to enabling the amplification of the template.
[0153] The linking arm comprises a compound having a long-chain structure.
[0154] Specifically, the linking arm is oxyethyleneglycol bridge, and the
chemical formula of
oxyethyleneglycol is:
o¨ P- 0-
j)
[0155] Specifically, the upstream primer is TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT-
oxyethyleneglycol bridge
-AACTATACAACCTACTACCTCA1-1"1-1TTTTT
TTGCACATAACACCCC.
[0156] Specifically, the downstream primer is a primer labeled with immune
marker, wherein
the immune marker comprises biotin, and the biotin is labeled on the first
nucleotide at the 5'
terminal of the downstream primer.
[0157] The labelling method is conventional art; more specifically, the
downstream primer is
Biotin-TC ATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC.
[0158] The numbering of sequences is used to distinguish different hairpin
sequences, not for
- 25 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
sorting; C, D, E, and F are only used to distinguish different complementary
sequences, not for
sorting.
[0159] Specifically, the hairpin sequence comprises at least one of the
following 1) to 2):
[0160] 1) the hairpin sequence 1 includes the nucleic acid sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 9
and/or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 9 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0161] 2) the hairpin sequence 2 includes the nucleic acid sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 10
and/or the nucleic acid sequence which is modified from the nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ
ID NO: 10 by substituting, adding and/or deleting one or more nucleotides and
has the same
function as the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0162] The same function comprises: the upstream primer can open the hairpin
structure of the
hairpin sequence 1 by base complementation, and the hairpin sequence I realize
a self-extension
of the nucleotide chain under the action of the TDT enzyme; the hairpin
sequence 2 can open the
hairpin structure of the hairpin sequence 1 by base complementation; the
hairpin sequence 1 and
the hairpin sequence 2 can mutually cyclically open each other's hairpin
structure and connect to
each other; the hairpin sequence 1 can realize the self-extension of the
nucleotide chain under the
action of the TDT enzyme at the same time in a linking body formed by the
hairpin sequence 1
and the hairpin sequence 2.
[0163] Specifically, the kit and/or the biosensor comprise the following 1) to
4):
[0164] 1) TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT- oxyethyleneglycol bridge -AA
CTATACAACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC;
[0165] 2) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6;
[0166] 3) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0167] 4) the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7, the nucleotide
sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 8, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9, and the
nucleotide
sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10;
- 26 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
wherein, the chemical structure of oxyethyleneglycol is:
_0......õ..õ.o....õ.....õ___.¨õ,,, ____,....-õ,,..,..õaõ..,õ.õ.....õ.õ ____.--
....õ........õõa..,,,
o o
cp-'
1
o ¨P-0-
0
1
[0168] Specifically, the kit and/or the biosensor further includes at least
one of TDT reaction
buffer, dATP, dGTP, TdT enzyme, hemin, G-quadruplex inducing buffer, ABTS2-
,hydrogen
peroxide, home-made XP beads, and magnetic beads modified with streptavidin on
the surface.
[0169] The present disclosure further aims to provide the use of at least one
of any of the
methods according to the present disclosure, and at least one of any of the
kits and/or biosensors
according to the present disclosure.
[0170] Specifically, the use comprises at least one of the following 1) to 4):
[0171] 1) detecting metals;
[0172] 2) producing products for use in metal detection and/or related
products;
[0173] 3) detecting two or multiple metals; and
[0174] 4) producing products for use in two or multiple metal detection and/or
related products.
[0175] Specifically, the metal includes Hg2+ and/or Ag .
[0176] Optionally, any one of the uses does not include the diagnosis and
treatment of the
disease described in Article 25 of the Chinese Patent Law.
[0177] A novel dual colorimetric sensing method based on ultra-rapid PCR is
established by the
present disclosure:
[0178] (1) an ultra-rapid PCR system is established, which reduces the
traditional PCR time
from about 3 hours to 2.5 minutes, significantly reducing the time spent on
PCRs;
[0179] (2) the ultra-rapid PCR system is equipped with an enzyme-linked
nucleic acid
self-assembly color module, which solves the problem, that the traditional PCR
is difficult to
- 27 -
13790822.1
34273/53
CA 03059246 2019-10-07
visualize and quantitatively detect; and
[0180] (3) the dual ultra-rapid PCR system is equipped with a dual enzyme-
linked nucleic acid
self-assembly color module to realize ultra-rapid, quantitative and visual
detection of two heavy
metals.
[0181] According to a specific embodiment of the present disclosure, a novel
dual colorimetric
sensing method is provided based on dual ultra-rapid PCR for use in a
visualized and
ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+ and Ag+. A dual amplification primer for
ultra-rapid polymerase
chain reaction (PCR) is designed based on a mercury ion thymine mismatch and a
silver ion
cytosine mismatch, and through the primer which can bind to the enzyme-linked
nucleic acid
self-assembly color module, an emerging method for nucleic acid detection
based on mismatched
mercury ion and silver ion dual target function is integrated and established.
[0182] The present disclosure has the following beneficial effects:
[0183] 1) the detection method and the biosensor established by the present
disclosure are
faster and more sensitive than the conventional method, and have the
advantages of high
.. specificity, high sensitivity, reliable detection results, etc., and can
simplify the analysis and .
detection steps, shorten the analysis time, and more importantly make the
online real-time
detection possible, easy to carry and field work, and has very good
application prospect in the
field of heavy metal rapid detection;
[0184] 2) the detection method and the biosensor established by the present
disclosure can
simultaneously realize the dual specific detection of Hg2+ and Ag+, the
detection has good
specificity, high sensitivity, reliable detection result, can be discerned by
the naked eye, and the
detection process is quick and convenient, which are of great significance in
daily monitoring or
market screening and other aspects. Specifically, the sensitivity experiment
results show that the
detection method and the biosensor established by the present disclosure have
a detection limit of
1.3 pM for Hg2+ and a detection limit of 2.5 pM for Ag+, and the detection
sensitivity is high;
[0185] the specificity experiment results show that the detection method and
biosensor
established by the present disclosure do not cross-react with Cu2+ and Mg2+,
and can realize dual
specific detection of Hg2+ and Ag+ at the same time; the experiment results of
spike recovery
- 28 -
13790822.1
34273/53
detection indicate that the detection values of the detection method
established by the present
disclosure for Hg2+ and Ag+ are close to the actual value of standard
substance added, and the
detection results are reliable and accurate; and
[0186] 3) the detection method and the biosensors established by the present
disclosure solve
the problem that the traditional PCR is difficult to visualize and
quantitatively detect, and realize
the ultra-rapid, quantitative and visual detection of the dual heavy metals
Hg2+ and Ag .
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[0187] Figure 1 is a schematic diagram showing the structure of ultra-rapid
PCR device.
101881 Figure 2 are the results of verification of the amplification of the
dual ultra-rapid PCR;
wherein, lane 1 is the result of only adding Ag+ in the reaction system; lane
2 is the result of only
adding Hg2+ in the reaction system; lane 3 and lane 4 are the results of
adding Hg2+ and Ag+ at the
same time in the reaction system; lane 5 is the result of a negative control
(without Hg2+ and Ag+
added to the reaction system); Figure 2a is an image showing the result after
magnetic bead
purification; Figure 2b is an image showing the comparison results before and
after the magnetic
bead purification, wherein lane 3 is the result without the magnetic bead
purification, and lane 4
is the result with the magnetic bead purification.
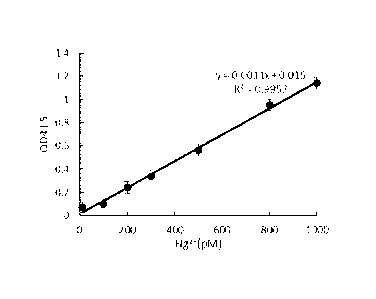
101891 Figure 3 is a standard curve of Hg2 .
101901 Figure 4 is a standard curve of Agt
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0191] The experimental methods used in the following examples are
conventional methods
unless otherwise specified.
101921 The molecular biology experimental methods not specifically described
in the following
examples are all carried out according to the specific methods listed in the
book "Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual" (third edition) by J. Sambrook, or carried out
according to the
instructions of kits and products.
- 29 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
[0193] The materials, reagents and the like used in the following examples are
commercially
available unless otherwise specified.
Example 1. Establishment of a dual colorimetric sensing method based on ultra-
rapid PCR for
detecting two heavy metals of He and Agt
I. Experimental materials
101941 The nucleotide sequences of primers designed in this example are shown
in Table 1 and
Sequence Listing.
Table 1
Primers Sequences (from 5' to 3')
AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAG- oxyethyleneglycol
Primerl
bridge-CTCTCTCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGTGAAATTATCGCCACGTTCGGTTTT
Primer2 Biotin-TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAACC
TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT-oxyethyleneglycol
Primer3
bridge-AACTATACAACCTACTACCTCATTTTTTTTTTTGCACATAACACCCC
T CATC GCAC C GT CAAAGGAAC C T CAGTAT CAGT GCTATAC GT C GATC AGTACCC C
Template
T GT TATGT GCAAAAAAAAAAATT T TCC GAAC GTGGC GATAATT TC AC
Hairpinl CTCTCTCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTCGGGGCAGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGTCTCT
Hairpin2 AGAGAGAGAGAGGGAAAGAGAGAGCTTTCCCTCTCTCTCTCTGCCCCG
Hairpin3 ACTTTGAACTATACAACCTACTTGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTTGTTTC
Hairpin4 AGTAGGTTGTATAGTTCAAAGTAACTATACAACCTACTACCTCA
[0195] In Table 1, the nucleotide sequence on the left side of the linking arm
(oxyethyleneglycol bridge) of the upstream primer Primer 1 is the nucleotide
sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 1 in Sequence Listing, and the nucleotide sequence on the right
side of the
linking arm is the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence
Listing, and the
chemical structure of linking arm is :
- 30 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
0
S.
0¨P-0'
=
101961 In Table 1, the downstream primer Primer 2 is obtained by labeling
biotin on the first
nucleotide at the 5' of the nucleic acid set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3 in Sequence
Listing.
[0197] In Table 1, the nucleotide sequence on the left side of the linking arm
(oxyethyleneglycol bridge) of the upstream primer Primer 3 is the nucleotide
sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 4 in Sequence Listing, and the nucleotide sequence on the right
side of the
linking arm is the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 5 in Sequence
Listing, and the
chemical structure of the linking arm is the same as the chemical structure of
the linking arm of
Primer 1.
101981 In Table 1, the nucleotide sequence of the template is the nucleotide
sequence set forth
in SEQ ID NO: 6 in Sequence Listing.
[0200] In Table 1, the hairpin sequences 1 to 4 (Hairpin 1,Hairpin 2,Hairpin
3,Hairpin 4) are
the nucleotide sequences respectively set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7, SEQ ID NO: 8,
SEQ ID NO: 9,
SEQ ID NO: 10 in Sequence Listing.
102011 The sequences listed in Table 1 are all artificially synthesized.
102021 SYBR Gold nucleic acid dye, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase(TdT),
10 X TdT
buffer, deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate
(dGTP), dNTP, Ex
Taq DNA polymerase, lox Taq buffer, hemin, mercury (III) chloride, silver
nitrate, magnetic
bead Sera-mag SpeedBeads, Magnetic bead Dynabeads MyOneTM Streptavidin T 1,
and nucleic
acid molecular weight marker ultra-low range DNA ladder are purchased from
Thermo Scientific
Life Technologies. Water used in experiment is obtained from Milli-Q water
purification system.
II. Construction of ultra-rapid PCR device
- 31 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
[0203] The main structure of the ultra-rapid PCR device is shown in Figure 1,
and its specific
structure, connection method, working principle and working process are
described below.
102041 Light Cycler model capillary (20 [IL, 04 929 292 001, Roche) was used
as a PCR
sample chamber for ultra-rapid PCR device. The samples were respectively
collected at one end
of each capillary by rapid centrifugation, and the capillary with the sample
was fixed to the
plastic holder after centrifugation. The plastic holder was connected to a
stepper motor
(42JSF630AS-1000, Just Motioin Control) which drove the capillary sample
chamber fixed on
the plastic holder to cyclically switch between a high-temperature water bath
at 95 C and a
medium-temperature water bath at 58 C to realize reaction temperature change
and control
during the ultra-rapid PCR. The stepper motor was powered by a switching power
supply
(S-100-24, Elecall), and the frequency or time control of the above-mentioned
cyclic conversion
of the stepper motor was realized by a DC servo motor driver (YZ-ACSD60,
Moving) and
Labview (version 2014). Temperature measurement was achieved by using a
thermocouple
encapsulated in a capillary. The amplification and linearization of the
thermocouple signal were
carried out using a temperature transmitter (SBWR-2260, K, Yuancheng) and
processed using the
Arduino UNO v1.0 chip. The Arduino UNO chip converted the received analog
signal into a
digital signal, which was then executed for calculation by the Arduino lDE
(version 1.8.1)
module.
III. Establishment of dual ultra-rapid PCR
[0205] 1) Preparing a dual ultra-rapid PCR system, which is shown in Table 2.
Table 2
Reaction component Final concentration
Template 0.05 [tM
Ex Taq DNA polymerase 1.5 U/mL
Hg2 /Ag+ 100 nM
Primer-1 2 [tM
Primer-2 4 [tM
Primer-3 2 [tM
dNTP 250 [tM
- 32 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
xEx Taq Buffer 1 xEx Taq Buffer
ddH20 Up to 10 [IL
[0206] Four groups of reactions were performed, wherein the reaction system of
the negative
control group was without adding Hg2+ and Ag ; only Ag+ was added in the
reaction system of
the experimental group 1; only Hg2+ was added in the reaction system of the
experimental group
2; Hg2+ and Ag+ were added simultaneously in the reaction system of the
experimental group 3,
wherein a parallel experiment of the experimental group 3 was performed.
Primer 1, Primer 2 and
Primer 3 were respectively the primers Primer 1, Primer 2 and Primer 3
described in the above
Table 1.
[0207] 2) Reaction process of the dual ultra-rapid PCR
[0208] According to Table 2, 10 [IL of the reaction system was prepared on
ice, and then
quickly placed in the ultra-rapid PCR device constructed in the step II for
temperature control.
The temperature control and cycle number are shown in Table 3.
Table 3
Reaction
Reaction time
temperature
95 C 2s
30cyc1es, 2.5min in total
58 C 3s
102091 After completing the ultra-rapid reaction, the magnetic beads "home-
made XP beads"
synthesized in the laboratory were used to purify the reaction system
according to the size of the
product fragment, and only the amplified product with metal ion binding was
obtained.
[0210] The magnetic beads "home-made XP beads" synthesized in the laboratory
were
obtained by treating magnetic bead Sera-magSpeedBeads with PEG-8000, NaCl,
Tris-HC1 and
EDTA according to the literature: Tian, Jingjing, et al "Visual Single Cell
Detection of
Dual-Pathogens based on Multiplex Super PCR (MS-PCR) and Asymmetric Tailing
HCR
(AT-HCR)." Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical (2018). Available online 3
January 2018.
[0211] 3) Verification the amplification results of dual ultra-rapid PCR
102121 After completing the above dual ultra-rapid PCR, agarose gel
electrophoresis
- 33 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
pre-stained with 2% ethidium bromide was used to verify the amplification of
the dual ultra-rapid
PCR system, and the conditions of electrophoresis: 120 V for 25 min, and
photographing system:
Molecular Imager Gel Doc XR (Bio-Rad).
[0213] The verification result of the dual ultra-rapid PCR amplification is
shown in Figure 2.
The results of Figure 2a show that the dual ultra-rapid PCR and the reaction
process established
by the present disclosure achieve template amplification when Hg2+ and Ag+ are
respectively
present or exist simultaneously; at the same time, it can be seen from the
results of Figure 2b that
the magnetic beads play a good role in removing impurities.
[0214] IV. Establishment of enzyme-linked nucleic acid self-assembly chromatic
module and
dual visual detection of Hg2+ and Ag+
102151 1) Sensitivity experiment
[0216] Standard curves of Hg2+ and Ag+ were plotted: the four hairpin probes
listed in Table 1:
Hairpin 1, Hairpin 2, Hairpin 3, Hairpin 4 were dissolved in ultrapure water
to a concentration of
100 [tM, heated at 95 C for 5 min, and then slowly cooled to room
temperature; the reaction
according to the dual ultra-rapid PCR system and the reaction process
(including the magnetic
bead purification step) described in the above step III were completed except
that only the Hg2+
or only the Ag+ was added to the reaction system described in Table 2, and the
final
concentrations of Hg2+ in different reaction systems were 10 pM, 100 pM, 200
pM, 300 pM, 500
pM, 800 pM, 1000 pM, respectively; the final concentrations of Ag+ were 10 pM,
100 pM, 200
pM, 400 pM, 800 pM, 1000 pM, respectively; in addition, Primer-3 in Table 2
was not added in
the reaction system with Hg2 , and Primer 1 was not added in the reaction
system with Ag .
[0217] After the completion of the reaction in multiple systems with different
concentrations of
Hg2+ or Ag+, Hairpin 1, Hairpin 2 prepared in ultrapure water above were added
to the reaction
system with Hg2+ before reaction, and Hairpin 3, Hairpin 4 prepared in
ultrapure water above
were added to the reaction system with Ag+ before reaction, then an self-
assembly buffer (8 mM
Na2HPO4, 2.5 mM NaH2PO4, 0.15 M NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, pH 7.4) was respectively
added to
each reaction system to make the total volume of each reaction system to 50
[IL and each hairpin
probe at a final concentration of 2pM; the obtained reaction systems were
incubated at 37 C for
- 34 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
20 min to obtain HCR products; then the magnetic beads with the surface
modification of one
layer of avidin (Dynabeads MyOneTM Streptavidin Ti) was used to bind to
biotinylated HCR
double-stranded product, and impurities such as hairpin probes not attached to
the HCR
double-stranded product were removed, and finally the magnetic beads were
removed by
high-salt elution to obtain a purified HCR product.
102181 A functional nucleic acid self-assembly system catalyzed by TdT enzyme
was
established, which comprised: 1 X TDT reaction buffer (purchased from Thermo
Fisher
Scientific), 0.4 mM dATP, 0.6 mM dGTP, 20 U/ [IL of TdT enzyme and 50 [IL of
purified HCR
product were reacted at 37 C for 20 min, and heated at 75 C for 10 min to
terminate enzymatic
reaction to form a G-rich sequence; 10 [tI_, of the enzymatic reaction product
was taken, and 1 [LL
of hemin stock solution (10 [tM) 32 [IL of G-quadruplex inducing buffer (100
mM
2-(4-morpholine) ethanesulfonic acid (IVIES), 40 mM KC1, 0.05% Triton X-100,
pH 5.5), 23 [EL
of ultrapure water were added and incubated at 37 C for 20 min to form G-
quadruplex; 8 [IL of
ABTS2- stock solution (20 mM) and 8 [EL of hydrogen peroxide (H202) stock
solution (20 mM)
were added and incubated at room temperature in the dark for 5 min.
[0219] After the reaction was completed, the OD value of the reaction solution
was measured
at 415 nm by a spectrophotometer, and the respective standard curves of Hg2+
and Ag+ were
plotted, and the results were shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
102201 Determination of the minimum detection limit: according to the obtained
standard curve
and the 3a principle, the detection limit of Hg2+ was 1.3 pM, and the
detection limit of Ag+ was
2.5 pM, indicating that the detection method established by the present
disclosure has a high
sensitivity.
102211 2) Accuracy experiment
[0222] Recovery of standard substrate experiment: the reaction was completed
according to the
dual ultra-rapid PCR and the reaction process described in the above step III,
the difference was:
only the final concentration of 400 pM Hg2+ was added to the reaction system
described in Table
2, without adding Primer 3 and Ag+ in Table 2. After the reaction, the color
was developed
according to the steps described in the above sensitivity experiment, after
completion, according
- 35 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
to the prepared standard curve, the concentration of Hg' detected by the
method established by
the present disclosure was calculated to be (400 5.33) pM, which was close to
the standard
substrate added, indicating that the detection method established by the
present disclosure has
reliable detection result and high accuracy.
[0223] The reaction was completed according to the ultra-rapid PCR and the
reaction process
described in the above step III, the difference was: only the final
concentration of 500 pM Ag+
was added to the reaction system described in Table 2, without adding Primer 1
and Hg' in Table
2. After the reaction, the color was developed according to the steps
described in the above
sensitivity experiment, after completion, according to the prepared standard
curve, the
concentration of Ag+ detected by the method established by the present
disclosure was calculated,
and the detection result was shown in Table 4.
[0224] The detection value (standard substrate recovery value) of the method
established by the
present disclosure in Table 4 is close to the standard substrate added,
indicating that the detection
method established by the present disclosure has reliable detection result and
high accuracy.
Table 4
Standard Substrate Added Standard recoverya +SDb
Sample
(PM) (PM)
400 400 5.33
Ag+ 500 500 2.87
[0225] 3) Specificity experiment
102261 The experimental group with Hg' and Cu' at a final concentration of 500
pM added to
the PCR ultra-rapid reaction system listed in Table 2 was counted as
experimental group a; the
experimental group with Ag+ and Mg' at a final concentration of 500 pM was
counted as
experimental group b; the experimental group with Hg' and Ag+ at a final
concentration of 500
pM was counted as experimental group c; the dual ultra-rapid PCR according to
the above step
III (except the type and concentration of metal ions in the system) were
carried out in three
groups (experimental group a, experimental group b, experimental group c), and
four identical
reactions were performed in each group.
- 36 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
[0227] The four hairpin probes listed in Table 1 above: Hairpin 1, Hairpin 2,
Hairpin 3, Hairpin
4 were dissolved in ultrapure water to a concentration of 100 [tM, and heated
at 95 C for 5 min,
then slowly cooled to room temperature for later use.
[0228] Each reaction system (10 111_, system) which completed the dual ultra-
rapid PCR was
separately added to color reaction system. The first reaction system of each
group (group a, group
b, group c) was added to three wells (labeled with number 1), in which Hairpin
1 and Hairpin 2
were dissolved in ultrapure water in advance). The second reaction system of
each reaction
system was added to three wells (labeled with number 1), in which Hairpin 3
and Hairpin 4 were
dissolved in ultrapure water in advance). The remaining two reaction systems
of each reaction
system were added to three wells (labeled with number 3) and another three
wells (labeled with
number 4) respectively. No hairpin was added to well 3 and well 4, as a
negative control.
Self-assembly buffer solution (8 mM Na2HPO4, 2.5 mM NaH2PO4, 0.15 M NaCl, 2 mM
MgCl2,
pH 7.4) was added to each well, and the final concentration of each hairpin
probe was 2 [EM, and
the volume of each well was 50 [IL. All the wells were incubated at 37 C for
20 min, and the
resultants were purified by magnetic beads to obtain purified HCR products.
[0229] The above purified HCR product was separately added to the wells
containing 1 x TDT
reaction buffer (purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific), 0.4 mM dATP, 0.6 mM
dGTP, and 20
U/[11_, TdT enzyme, and reacted at 37 C for 20 min. The enzymatic reaction
was terminated by
heating at 75 C for 10 min to form a G-rich sequence; 1 [IL of hemin stock
solution (10 [tM), 32
[IL of G-quadruplex inducing buffer (100 mM 2-(4-morpholine) ethanesulfonic
acid (IVIES), 40
mM KC1, and 0.05% Triton X-100, pH 5.5), and 23 [IL of ultrapure water were
added to the
enzymatic reaction system and incubated at 37 C for 20 min to form G-
quadruplex; 8 [11_, of
ABTS2- stock solution (20 mM) and 8 of [IL hydrogen peroxide (H202) stock
solution (20 mM)
were added and incubated at room temperature in the dark for 5 min.
[0230] The experimental results showed that the detection method and the
biosensor
established by the present disclosure do not cross-react with Cu2+ and Mg2 ,
and can
simultaneously realize the dual specific detection of Hg2+ and Ag .
102311 The examples described above are only illustrative of the embodiments
of the present
disclosure, and the description thereof is more specific and detailed, but is
not to be construed as
- 37 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12
limiting the scope of the present disclosure. However, any technical solution
obtained by using
equivalent replacement or equivalent transformation should fall within the
protection scope of the
present disclosure.
- 38 -
16442353.1
34273/53
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-02-12