Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
- 1 -
04.26.2018
SP12145PCT
Scaffolding decking and method for its production
The invention concerns a scaffolding decking, such as this is used as a walk-
on
working platform for scaffolding, in particular for scaffolding. Also,
the invention concerns a process for manufacturing such a scaffolding decking.
Scaffolding decks available on the market have a supporting frame made of
longitudinal and transverse profiles that are welded or riveted together. The
support frame is usually made of metal and is used for the storage and support
a
walk-on covering plate, which can be made of wood, plastic or a composite
material, for example. The covering plate can be screwed or riveted to the
support frame. Such scaffolding decks are also known in the construction
industry as so-called frame panels or combination decks. The scaffolding decks
are cost-intensive to manufacture and, in the event of damage to the
longitudinal
or transverse profiles of the supporting frame, are difficult to repair,
especially as
the decking plate must be detached from the supporting frame and, in addition,
the rivet or welded connections of the transverse profiles must be destroyed
to
loosen them.
It is, therefore, the task of the invention to specify a durable scaffolding
decking
which has a sufficiently high load-bearing capacity for construction purposes
and
which is
easier and cheaper to manufacture. In addition, it is the task of the
invention to
specify a cost-effective process for manufacturing such a scaffolding decking.
Pen i GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372
-2 ¨
The scaffolding decking according to the invention is essentially
characterized by
the fact that the cross profile(s) is/are hooked into the two longitudinal
profiles of
the supporting frame and is/are held or secured in position solely by the
supporting or decking plate in its/their longitudinal profiles, i.e. is/are
hooked into
the longitudinal profiles. In other words, unintentional loosening of the hook
connection between the cross profile(s) and the longitudinal profiles is
prevented
113 or prevented by the covering plate attached to the two longitudinal
profiles. The
scaffolding decking according to the invention can thus be manufactured more
simply and cost-effectively overall. Welding or riveting the cross profile or
the
individual cross profiles to the longitudinal profiles is completely
unnecessary,
which means that the covering plate has a dual function. This connects the
longitudinal profiles to each other and thus enables sufficient bending and
torsional stiffness of the scaffolding decking.
On the other hand, it serves as a locking or securing device for the cross
profile
interlocked with the longitudinal profiles or the cross profiles interlocked
with the
zo longitudinal profiles, so that the cross profile or profiles are secured
against
unintentional disconnection from the longitudinal profiles. According to the
invention, each cross profile has two wall legs which are connected to each
other
via a back section. In this case, the transverse profile(s) therefore have a
substantially U-shaped cross-sectional shape and are/are preferably designed
open towards the covering plate. Such a U-shaped cross-section shape enables
the cross sections to be realised with a sufficiently high load-bearing
capacity.
According to the invention, the two wall legs have angled free edge sections,
preferably to the outside, to provide the largest possible contact or support
area
for the covering plate. After the invention, the load-bearing capacity and the
torsional rigidity of the scaffolding beam can be further improved by the fact
that
each transverse profile of the support frame is provided with several hooks,
which
engage in recesses in the longitudinal profiles corresponding to the hooks.
Pen GmbH
Date Rope/Date Received 2023-12-21
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-3-
04.26.2018
According to the invention, the recesses in the longitudinal member(s) for the
respective transverse profile(s) are preferably slot-shaped.
This reduces material weakening of the side members to a minimum. Slots can
also
be produced without great effort, for example using a laser cutting process or
using
machining, in particular by sawing, at low cost and with great dimensional
accuracy.
le With its hook(s), the cross-member(s) can be arranged advantageously in the
recesses of the side rails in the form fit of the sliding play. This prevents
unwanted
warping of the supporting frame during fabrication and use of the scaffolding
decking.
After the invention, the covering plate rests on a profile heel of the
longitudinal
profiles. This means that the longitudinal profiles can protect the decking
plate
laterally in the sense of a frame around its longitudinal edges. Unwanted
mechanical
damage to the decking plate during transport or the use of the scaffolding
decking
can be avoided.
The recesses or slots of the longitudinal profiles can extend from the profile
heel
of the longitudinal profiles into (inside) side wall area of the longitudinal
profiles.
This allows the cross profile or the cross profiles to be hooked into both
longitudinal profiles in a simplified manner, if necessary at the same time.
At the
same time, the cross profile(s) can be aligned with its/their supporting
surface(s)
to support the decking plate in alignment with a bearing surface of the
longitudinal profiles, for example, formed by the paragraph above. Overall, a
flat
contact and support of the covering plate on the longitudinal as well as on
the cross
profile or the cross profiles can be achieved.
Pen GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-4-
04.26.2018
After the invention, the covering plate rests on the cross profile or profiles
of the
support frame. This allows the decking plate to be supported in the area of
the cross
profile(s) (free of play). As a result, the covering plate can be realised in
total thinner,
thus lighter, or from a less load-stable and therefore cheaper material.
After the invention, the covering plate can be riveted, preferably solely, to
the
longitudinal profiles of the support frame. Such riveted joints can be
realised
cost-effectively and offer advantages not least due to the cost-effective
automation of riveting processes - especially for mass production of scaffold
decks.
According to the invention, the longitudinal profiles of the support frame are
preferably hollow profiles. This allows sufficient load-bearing scaffolding
decks to be
achieved with a low mass at the same time. Overall, this is advantageous for
the
handling of the scaffolding decking.
The ingenious process for the fabrication of a scaffolding decking described
above comprises the following steps:
- Provision of the longitudinal profiles and one or more cross profiles as
well as the
covering plate;
- Hook each cross profile into the longitudinal profile under the support
frame;
- Placing the decking slat on the longitudinal profiles of the support
frame; and
- Securing one cross profile or profiles in its/its position hooked into the
longitudinal profiles solely by fixing the covering plate to the longitudinal
profiles
of the support frame, in particular by riveting it firmly.
With the ingenious method, the scaffolding decking can be produced simply
and cost-effectively. Hereby eliminating the need for welding or time-
consuming and costly fastening of the cross profile(s) to the longitudinal
beams using separate fastening means, such as screws or rivets.
Pen i GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
- 5 -
04.26.2018
It should be noted that the inventive process can easily be automated so that
the scaffolding decking can be produced cost-effectively in mass production.
Hooking the cross profiles into the side members can be done simultaneously.
In summary, the invention concerns a scaffolding decking for scaffolding in
the
building sector, with a supporting frame with two longitudinal profiles and
with a
transverse profile or with several transverse profiles via which the
longitudinal
profiles are connected to each other.
The scaffolding decking has a decking plate which is attached to the
longitudinal
profiles, whereby the cross profile(s) is/are hooked into the two longitudinal
profiles and are held or secured solely by the decking plate in its/their
position
hooked into the longitudinal profiles. Moreover, the invention relates to a
cost-
effective and easy to carry out a method for producing a scaffolding above.
Further advantages of the invention result from the description and the
drawing. The
form of execution shown and described is not to be understood as an exhaustive
list,
but rather has exemplary character for the description of the invention.
Show in the drawing:
Fig.1 A scaffolding decking with a supporting frame and a walkable
decking plate in a view from below;
Fig.2 Scaffold decking according to Fig. 1 is a sectional view;
Fig.3 The scaffold decking as shown in Fig. 1 is a partial front view;
Fig.4 a cross beam of the scaffold decking according to Fig. 1 in an optional
detailed perspective view;
Pen i GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-6-
04.26.2018
Fig.5 A longitudinal member of the scaffold decking according to Fig. 1 in an
optional perspective detail view; and
Fig.6 a block diagram with individual process steps of a process for producing
the
scaffolding decking shown in Fig. 1.
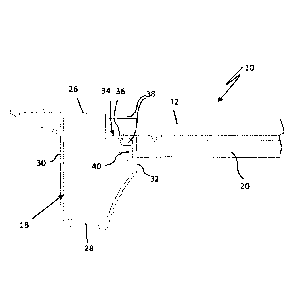
Fig. 1 shows a scaffold decking 10 for construction or working scaffold (not
shown) in a schematized subview. The scaffolding decking 10 has a walk-on
decking plate 12 which extends along the longitudinal axis 14 of the
scaffolding
decking 10. The covering plate 12 preferably consists of wood or a wood
material, but can also consist of plastic, composite material or metal.
io The scaffolding deck has a supporting frame, which is labelled 16 in
total. The
support frame 16 is used to support and stiffen the decking plate 12 and to
detachably attach the scaffolding decking 10 to other scaffolding parts of the
construction or working scaffolding. Support frame 16 has two longitudinal
beams or
longitudinal profiles 18 and one or more cross beams or cross profiles 20.
m The longitudinal profiles 18 can each have connecting means 24 at
their free end
sections 22, using which the scaffolding decking 10 can be attached in a known
manner to vertically running scaffolding standards or to horizontally running
scaffolding ledgers (not shown in each case), for example, hooked in. The
longitudinal profiles 18 are each connected via the cross profiles 20.
20 In the design example shown, the support frame 16 has four profiles
20 as
examples. However, the support frame 16 can also have less than four, for
example, 2 or three, or even more than four cross profiles 20. The scaffold
deck
can be provided at both ends with a profile fitting 25 preferably made of
metal,
as shown in Fig. 1 with a stroked line. The profile fitting 25 can be attached
at
25 both ends to the longitudinal profiles 18 and have or carry the
connecting means
24. If required, such a profile fitting 25 can be used to provide edge
protection on
the face of the covering plate 12.
30
In Fig. 2 the scaffold deck 10 is shown in a cut-out detailed view and in
Fig.3 in
a cut-out front view.
Pen i Gmbh
SPI2I4SPCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-7-
04.26.2018
18 longitudinal profiles are each designed as hollow profiles and preferably
consist of metal,
for example, aluminium. The longitudinal profiles 18 can be designed in
particular as
so-called extrusion profiles. The longitudinal profiles 18 each have an upper
side
26, an underside 28, an outside 30 and an inside. 32 The upper side 26 of the
longitudinal profiles 18 is of stepped design. As a result, the longitudinal
profiles 18 each
have a paragraph 34. Paragraph 34 forms a support area 36 for the covering
plate 12 and
the covering plate 12 is in direct contact with the support area 36. Here, the
covering plate 12
is fastened solely to the longitudinal profiles 18 and riveted via several
rivets 38 (Fig. 3) with
the longitudinal profiles (only). The rivets 38 of a longitudinal profile 18
are arranged spaced
apart in the axial direction. This holds the covering plate 12 permanently in
position on the
longitudinal profiles 18 of the support frame 16. 36 The support area can have
several ridges
or grooves. 39, each of which is arranged axially. The corrugations are
arranged laterally
offset to each other and serve to provide a non-slip and wobble-proof support
for the decking
plate 12 on the longitudinal profile 18 preferably into the material of the
covering plate 12.
The cross profiles 20 have several hooks 40 at both ends, over which the cross
profiles 20 are hooked to the two longitudinal profiles 18.
The hooks 40 are clearly visible in the detail view of a single cross profile
20 of
the support frame 16 as shown in Fig. 4 (Fig. 1). The hooks 40 are moulded
onto
the cross profile 20 and preferably of identical design. Because the hooks 40 -
relative to the longitudinal axis 14 of the scaffold deck 10 (Fig.1) - are
arranged in
the axial direction at a distance A from one another on the respective cross
profile 20, a particularly stable and torsionally rigid connection can be
achieved
between
the cross profiles 20 and the side members 18. The cross profiles 20 each have
a U-
shaped cross-section, Two parallel or essentially parallel wall legs 42 are
connected
to each other via a connection
or back section 44 of cross profile 20. It should be noted that the two wall
legs 42
may have
Pen i GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-8-
04.26.2018
free edge sections 46 angled or bent outwards. The covering plate (Fig. 1
3) to the scaffolding decking 10 can be additionally supported over a large
area
on the support or surface 48 of the edge sections 46 of the cross profiles 20
which is assigned to the decking plate 12. The surfaces 48 of the wall legs 42
of
the cross profiles 20 are aligned with the support area 36 of the longitudinal
profiles 18 (Fig. 3) in a direction orthogonal to the longitudinal axis 14 of
the
scaffold deck 10 (Fig. 1).
A groove 50 with a width B is formed between the hook 40 and the respective
assigned wall leg 42.
In Fig. 5 one of the longitudinal profiles 18 of the support frame 16 of the
scaffold
deck 10 according to Fig. 1 is shown in an exposed perspective detail section.
The recesses 52 are arranged in pairs on the respective longitudinal profile
18
and have a distance A corresponding to distance A of the hook 40 (Fig. 4). The
recesses 52 reach through each wall 54 of the longitudinal profiles 18. The
recesses 52 extend from the upper support area 36 of the longitudinal profiles
18
transversely to the longitudinal axis 14 into the inside 32 of the
longitudinal profile
18. This allows the cross profiles 20 to be simply hooked into the recesses
with
zo the longitudinal profiles 18 using the hooks 40 when assembling the
scaffold deck
10 (Fig. 1). The wall 54 of the longitudinal profiles 18 engages in one of the
grooves 50 of the respective cross profile 20 shown in Fig. 4. The width B of
the
groove is preferably matched to the material thickness (not indicated in the
25 drawing) of the wall 54 in order to allow the cross profiles 20 to be
mounted on
the two longitudinal profiles 18 in the in axial direction relative to the
longitudinal
axis 14 (Fig. 1) with little play or with a positive fit. The recesses 52 can
be
produced using a laser cutting process or purely by cutting, for example by
sawing.
Pen i GmbH
SP12145PCT
CA 03062372 2019-11-04
-9-
04.26.2018
The cross profiles 20 of the support frame are secured against disconnection
from the longitudinal beams 18 solely by the covering plate 12 riveted
directly to
the longitudinal beams 18. This eliminates the need for time-consuming and
cost-intensive riveting or welding of each cross profile 20 with
6 the longitudinal profiles 18.
In the event of damage to one or more cross profiles 20 or longitudinal
profiles 18
of support frame 16 (Fig. 1), only the rivet connections between the decking
plate
and the longitudinal beams (destructive) have to be loosened and the decking
plate 12 lifted from support frame 16 in order to be able to replace the
affected
profiles of support frame 16.
io The scaffolding decking 10 erected in the manner described above is
therefore
particularly easy and inexpensive to manufacture and repair.
In the following, the ingenious process for the fabrication of the above-
explained
scaffold decking 10 with additional reference to fig. 6 is explained.
In a first step 102 the longitudinal and cross profiles 18,20 (Fig.1) and the
covering plate 12 are provided. In step 104 the cross profiles 20 are hooked
into
the longitudinal profiles 18 to form the support frame 16 (Fig. 1). In step
106, the
covering plate 12 is placed on the longitudinal profiles 18 of the support
frame 16
and in step 108 the cross profiles are secured in their hooked position into
the
longitudinal profiles by fixing the covering plate to the longitudinal
profiles 18, in
particular, riveted to them.
PeriGmbH
SP12145PCT