Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
An apparatus for simulating load-temperature coupling wear behavior of a
Polycrystalline
Diamond Compact cutter
Field and Background
[0001] The invention relates to an experimental apparatus for simulating load-
temperature coupling
wear behavior of a Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) cutter, falling
within the field of
mechanical wear experimental apparatus.
[0002] PDC bits are an important rock-breaking tool for oil and gas drilling,
geothermal well drilling,
coal drilling and other drillings. The advantages of low bit pressure and high
drilling rate of the
PDC bits increase their market share in terms of the oil and gas drilling
business. The PDC bits,
accounting for 80% of global oil and gas drilling market and more than 90% of
the world's total
drilling footage, have been the most popular bits in the field of petroleum
drilling, and
dramatically accelerated the drilling rate and development of the drilling
technology.
[0003] However, the lifetime and drilling efficiency of the bits are reduced
due to serious wear of PDC
cutters under the coupling effect of temperature and load when drilling into
complex high-
temperature hard formations. The development of the PDC bits is restricted by
the phenomenon.
At present, scholars at home or abroad do not make great efforts to researches
on the wear
behavior of the PDC cutters under the temperature-load coupling, and no
supporting
experimental apparatus is reported.
[0004] In addition, conventional experimental apparatus for frictional wear
behavior have three
shortcomings: firstly, they do not regulate the temperature of the PDC cutters
but the ambient
temperature; secondly, the chippings produced by grinding between metal and
rock are several
times as much as those produced by the grinding between metal and metal, and
the conventional
experimental apparatus for frictional wear behavior are difficult to handle
the large amount of
rock chips produced during the grinding process; and finally, the conventional
experimental
apparatus for frictional wear behavior only support single reciprocating
motions or
circumferential motions, while the cutters are required to perform compound
motions depending
on heavy wear on rocks.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-11-05
1 CA 03070032 2020-01-15
=
[0005] Therefore, in order to study the load-temperature coupling wear
behavior of the PDC
cutters, an experimental apparatus for simulating load-temperature coupling
wear behavior
of a PDC cutter is urgently needed to be developed, so as to provide basic
theory and
guidance for the developments of high-temperature wear-resistant PDC cutters
and
geothermal drill bits.
Summary
[0006] The purpose of the invention is to overcome the shortages of the prior
art, and provide an
experimental apparatus for simulating load-temperature coupling wear behavior
of a PDC
cutter, in order to realize the research on the wear behavior of the PDC
cutter under
coupling effects at different cutter body temperatures and cutting loads.
[0007] The invention relates to an experimental apparatus for simulating load-
temperature
coupling wear behavior of a PDC cutter, and the experimental apparatus
comprises a motor,
a hydraulic power source, a lower support, a left hydraulic cylinder, a left
guide loading
block, a micro power end, a left guide post, an upper support, a PDC cutter
traverse
mechanism, a right guide post, a right guide loading block, a temperature
measuring and
controlling device, a right hydraulic cylinder, a rock rotating mechanism, a
chip removal
device and a reduction gearbox. The PDC cutter traverse mechanism is composed
of a
transverse guide post, a PDC cutter fixture, a leading screw and a PDC cutting
tool. The
temperature measuring and controlling device is composed of a heating wire, a
water-
cooled tube and an infrared thermometer. The rock rotating mechanism is
composed of a
rock fixture, a fixed chassis, a thrust ball bearing and a pad. The chip
removal device is
composed of a water collecting sump, a chip removal pipe, a fixed seat and an
annular
groove.
[0008] The motor is thread fastened in the lower support, and the hydraulic
power source is
welded in the lower support to provide power for the left hydraulic cylinder
and the right
hydraulic cylinder; the left hydraulic cylinder is in threaded connection with
the lower
support, and an upper end of the left hydraulic cylinder is fastened with the
left guide
loading block; the left guide loading block is in clearance fit with the left
guide post, and
the left guide post has a role of orienting movement of the left guide loading
block; an
2
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
upper end of the left guide post is in threaded connection with the upper
support; the upper
support is welded on the lower support; an upper end of the right guide post
is connected
with the upper support, a lower end thereof is connected with the lower
support, and the
right guide post is in clearance assembly with the right guide loading block;
the right
hydraulic cylinder is in threaded connection with the lower support, and an
upper end
thereof is fastened with the right guide loading block; and the reduction
gearbox is
arranged in the lower support and connected with the thrust ball bearing rotor
and the
motor to transmit power and decelerate.
[0009] A connecting ring of the micro power end is in clearance fit with the
left guide post, the
welding block is welded with the left guide loading block, the micro power end
is
connected with the leading screw through a driving hole to provide a rotating
power for the
leading screw; the PDC cutting tool is arranged in a tooth slot of the PDC
cutter fixture,
and pin connected with the PDC cutter fixture through a pin hole; the PDC
cutter fixture is
in threaded connection with the leading screw through a threaded hole and in
clearance fit
with the transverse guide post through a guide hole; and the leading screw and
the
transverse guide post are arranged between the left guide loading block and
the right guide
loading block.
[0010] The heating wire, the water-cooled tube and the infrared thermometer
are arranged on the
PDC cutter fixture, and the PDC cutting tool is wrapped by the heating wire;
an end of the
water-cooled tube is opposite to a surface of the PDC cutting tool; and the
infrared
thermometer is configured to measure body temperatures of the PDC cutting
tool.
[0011] A cylindrical rock is arranged in a cylinder of the rock fixture, four
counterbores are
connected to a bottom of the cylinder and bolted with a fixed chassis, and
four bosses are
uniformly arranged around the cylinder; a threaded hole is configured on the
pad, a center
line of the threaded hole coincides with a center line of the boss, a plane
end surface of the
pad completely fits with the rock, a curved end surface of the pad completely
fits with the
cylinder; and a screw passes through the boss and the pad to fasten the
cylindrical rock;
and an inverted T-shaped groove and an annular groove are configured on the
fixed chassis,
the inverted T-shaped groove is bolted with the counterbores, and the fixed
chassis is
fastened with the thrust ball bearing.
3
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
[0012] The fixed seat of the chip removal device is in threaded connection
with the lower support,
the water collecting sump is arranged inside the chip removal device, a chip
removal pipe
is arranged outside the chip removal device, the annular groove is configured
on the inner
wall of the chip removal device, and an 0-type sealing ring is arranged
between the
annular groove of the chip removal device and the annular groove on the fixed
chassis.
[0013] 1. The invention overcomes a limitation of the single reciprocating
motions or
circumferential motions of the conventional experimental apparatus for
frictional wear
behavior, realizes compound rock-breaking motions of the PDC cutter in a
circumferential
direction, a transverse direction and a longitudinal direction through
comprehensive actions
of the PDC cutter traverse mechanism, the rock rotating mechanism and a
hydraulic
pressure, so as to adjust a longitudinal height and a lateral displacement of
the PDC cutter
according to rock cutting conditions when the PDC cutter scrapes rocks in the
circumferential direction; 2. the invention realizes temperature control of
the PDC cutter
body in a more accurate and reliable way than the conventional ambient
temperature
control by directly monitoring and controlling the body temperature of the PDC
cutting
tool; and 3. the chip removal device for the rocks broken by PDC cutter is
designed to
effectively remove a large amount of rock chips generated during the PDC rock-
breaking
wear behavior test.
Brief Description of the Drawings
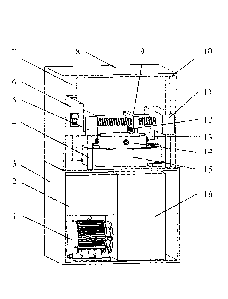
[0014] Figure 1 is a structural diagram of an experimental apparatus for
simulating load-
temperature coupling wear behavior of a PDC cutter of the invention.
[0015] Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a PDC cutter traverse mechanism of
the invention.
[0016] Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a temperature measuring and
controlling device of the
invention.
[0017] Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of a rock rotating mechanism of the
invention.
[0018] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of a chip removal device of the
invention.
[0019] Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of a micro power end of the invention.
4
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
[0020] Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of a PDC cutter fixture of the
invention.
[0021] Figure 8 is a structural diagram of a rock fixture of the invention.
[0022] Figure 9 is a view of a pad of the invention.
[0023] Figure 10 is a view of a fixed chassis of the invention.
[0024] Marks in the figures:
1. motor; 2. hydraulic power source; 3. lower support; 4. left hydraulic
cylinder; 5. left guide
loading block; 6. micro power end; 7. left guide post; 8. upper support; 9.
PDC cutter traverse
mechanism; 10. right guide post; 11. right guide loading block; 12.
temperature measuring and
controlling device; 13. right hydraulic cylinder; 14. rock rotating mechanism;
15. chip removal
device; 16. reduction gearbox; 17. transverse guide post; 18. PDC cutter
fixture; 19. leading screw;
20. PDC cutting tool; 21. heating wire; 22. water-cooled tube; 23. infrared
thermometer; 24. rock
fixture; 25. fixed chassis; 26. thrust ball bearing; 27. pad; 28. water
collecting sump; 29. chip
removal pipe; 30. fixed seat; 31. annular groove; 32. connecting ring; 33.
driving hole; 34. welding
block; 35. control terminal; 36. guide hole; 37. tooth slot; 38. pin hole; 39.
threaded hole; 40. boss;
41. counterbore; 42. cylinder; 43. threaded hole; 44. plane end surface; 45.
curved end surface; 46.
inverted T-shaped groove; 47. annular groove.
Detailed Description
[0025] The invention will be further described in combination with drawings
and embodiments.
[0026] As shown in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, the invention relates to an
experimental apparatus for
simulating load-temperature coupling wear behavior of a PDC cutter, and the
experimental
apparatus comprises a motor 1, a hydraulic power source 2, a lower support 3,
a left
hydraulic cylinder 4, a left guide loading block 5, a micro power end 6, a
left guide post 7,
an upper support 8, a PDC cutter traverse mechanism 9, a right guide post 10,
a right guide
loading block 11, a temperature measuring and controlling device 12, a right
hydraulic
cylinder 13, a rock rotating mechanism 14, a chip removal device 15 and a
reduction
gearbox 16; the PDC cutter traverse mechanism 9 is composed of a transverse
guide post
17. a PDC cutter fixture 18, a leading screw 19 and a PDC cutting tool 20; the
temperature
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
=
measuring and controlling device 12 is composed of a heating wire 21, a water-
cooled tube
22 and an infrared thermometer 23; the rock rotating mechanism 14 is composed
of a rock
fixture 24, a fixed chassis 25, a thrust ball bearing 26 and a pad 27; and the
chip removal
device 15 is composed of a water collecting sump 28, a chip removal pipe 29, a
fixed seat
30 and an annular groove 31.
[0027] As shown in Figure 1, the motor 1 is thread fastened in the lower
support 3, and the
hydraulic power source 2 is welded in the lower support 3 to provide power for
the left
hydraulic cylinder 4 and the right hydraulic cylinder 13; the left hydraulic
cylinder 4 is in
threaded connection with the lower support 3, and an upper end of the left
hydraulic
cylinder 4 is fastened with the left guide loading block 5; the left guide
loading block 5 is
in clearance fit with the left guide post 7, and the left guide post 7 has a
role of orienting
movement of the left guide loading block 5; an upper end of the left guide
post 7 is in
threaded connection with the upper support 8; the upper support 8 is welded on
the lower
support 3; an upper end of the right guide post 10 is connected with the upper
support 8, a
lower end thereof is connected with the lower support 3, and the right guide
post 10 is in
clearance assembly with the right guide loading block 11; the right hydraulic
cylinder 13 is
in threaded connection with the lower support 3, and an upper end thereof is
fastened with
the right guide loading block 11; and the reduction gearbox 16 is arranged in
the lower
support 3 and connected with the thrust ball bearing rotor 26 and the motor 1
to transmit
power and decelerate.
[0028] As shown in Figures 2, 6 and 7, a connecting ring 32 of the micro power
end 6 is in
clearance fit with the left guide post 7, a welding block 34 is welded with
the left guide
loading block 5, the micro power end 6 is connected with the leading screw 19
through a
driving hole 33 to provide a rotating power for the leading screw 19; the PDC
cutting tool
20 is arranged in a tooth slot 37 of the PDC cutter fixture 18, and pin
connected with the
PDC cutter fixture 18 through a pin hole 38; the PDC cutter fixture 18 is in
threaded
connection with the leading screw 19 through a threaded hole 39 and in
clearance fit with
the transverse guide post 17 through a guide hole 36; and the leading screw 19
and the
transverse guide post 17 are arranged between the left guide loading block 5
and the right
guide loading block 11.
6
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
[0029] As shown in Figure 3, the heating wire 21, the water-cooled tube 22 and
the infrared
thermometer 23 are arranged on the PDC cutter fixture 18, and the PDC cutting
tool 20 is
wrapped by the heating wire 21; an end of the water-cooled tube 22 is opposite
to a surface
of the PDC cutting tool 20; and the infrared thermometer 23 is configured to
measure body
temperatures of the PDC cutting tool 20.
[0030] As shown in Figures 4, 8, 9 and 10, a cylindrical rock is arranged in a
cylinder 42 of the
rock fixture 24, four counterbores 41 are connected to a bottom of the
cylinder 42 and
bolted with a fixed chassis 25, and four bosses 40 are uniformly arranged
around the
cylinder 42; a threaded hole 43 is configured on the pad 27, a center line of
the threaded
hole 43 coincides with a center line of the boss 40, a plane end surface 44 of
the pad 27
completely fits with the rock, a curved end surface 45 of the pad 27
completely fits with
the cylinder 42, and a screw passes through the boss 40 and the pad 27 to
fasten the
cylindrical rock; and an inverted T-shaped groove 46 and an annular groove 47
are
configured on the fixed chassis 25, the inverted T-shaped groove 46 is bolted
with the
counterbores 41, and the fixed chassis 25 is fastened with the thrust ball
bearing 26.
[0031] As shown in Figure 5, the fixed seat 30 of the chip removal device 15
is in threaded
connection with the lower support 3, the water collecting sump 28 is arranged
inside the
chip removal device 15, a chip removal pipe 29 is arranged outside the chip
removal
device 15, the annular groove 31 is configured on the inner wall of the chip
removal device
15, and an 0-type sealing ring is arranged between the annular groove 47 and
the annular
groove 31.
[0032] The invention relating to an experimental apparatus for simulating load-
temperature
coupling wear behavior of a PDC cutter has three main functions: rock scraping
by the
PDC cutter, temperature measurement and control and chippings removal. The
rock
scraping by the PDC cutter is realized by a combination of a circumferential
motion and a
linear motion. The motor 1 transmits a rotational energy to the rock rotating
mechanism 14
through the reduction gearbox 16 and the thrust ball bearing 26, and the rock
rotating
mechanism 14 drives the rock in the rock fixture 24 to do the circumferential
motion; and
the micro power end 6 drives the leading screw 19 to rotate to further realize
the transverse
displacement of the PDC cutting tool 20. The hydraulic power source 2 provides
a
7
=
CA 03070032 2020-01-15
hydraulic power for the left hydraulic cylinder 4 and the right hydraulic
cylinder 13, and
the left hydraulic cylinder 4 and the right hydraulic cylinder 13 drive the
left guide loading
block 5 and the right guide loading block 11 to move up and down to further
realize a
longitudinal load application and a longitudinal displacement of the PDC
cutting tool 20.
The control terminal 35 configured on the micro power end 6 regulates and
monitors
parameters of the transverse displacement and the longitudinal displacement of
the PDC
cutting tool. The temperature measurement and control is realized through the
heating wire
21, the water-cooled tube 22 and the infrared thermometer 23. The infrared
thermometer
23 is applied for monitoring the body temperatures of the PDC cutting tool 20.
When
overheating occurs, an end of the water-cooled tube 22 sprays a cooling liquid
to the
surface of the PDC cutting tool 20 to rapidly cool down the cutter body of the
PDC cutting
tool 20. When overcooling occurs, the heating wire 21 wrapped on the PDC
cutting tool 20
directly heats the cutter body. Cuttings generated by the rock scraping by the
PDC cutting
tool 20 are contained in the cooling liquid. The cooling liquid with the
cuttings flows to an
outside of the rock fixture 24, enters the water collecting sump 28 through
the fixed chassis
25, and then is discharged through the chip removal pipe 29. The 0-type
sealing ring is
arranged between the annular groove 47 and the annular groove 31 for the
purpose of
sealing between the fixed chassis 25 and the chip removal device 15, so as to
prevent the
chippings and the cooling liquid from entering the thrust ball bearing 26.
8