Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1
Cutting device with lateral conveying aids
The present invention relates to a cutting device for attachment to an
agricultural harvesting
machine having a frame, at least one cutting element arranged on the side of
the cutting
device facing in the working direction and connected to the frame, stalk
dividers arranged
on the lateral opposite ends of the cutting device, which by their position
determine a
working width of the cutting device, rotationally drivable conveyor aids,
which are mounted
with their lower ends on the stalk dividers, a transfer opening arranged on
the side of the
cutting device opposite the working direction, at least one conveyor device
for conveying
cut crops from a cutting zone to the transfer opening, and drive devices for
driving the at
least one cutting element, the at least one conveyor device, and the conveyor
aids.
A generic cutting device is known from GB 684 829. The stalk dividers
positioned on the
opposite ends of the cutting device plunge into the standing crop in the
working direction as
the harvesting machine to which the cutting device is attached during the
harvesting
operation advances to, on the one hand, feed the stems and stalks of the crops
still to be
grasped by the working width of the cutting device to the cutting elements
and, on the other
hand, to keep away from the cutting elements the stems and stalks of harvested
crops which
are at the cutting edge and which are no longer to be grasped by the cutting
elements. If
separation of the crops along the cutting edge is clean, the cutting elements
cut the crops
cleanly at the side edges and transfer them to the conveying elements without
loss and
without disturbances in the crop flow.
To avoid the build-up of crop in the area of the stalk dividers, rotatably
driven conveying aids
in the form of spirally bent rods are located on the stalk dividers in front
of the front edges
.. of the side walls facing in the working direction of the cutting device.
The conveying aids
extend almost over the entire length of the cutting device and are
mechanically driven by V-
belts that are located on the rear of the cutting device frame. The rotatably
driven conveying
aids improve the placement of the cut conveyed crops on the conveying
elements.
The cutting device disclosed in GB 684 829 has a length and width that are
uncritical for
road transport. The problem of reducing the length and/or width of the cutting
device to
comply with the limit values applicable for road traffic approval did not
arise for this cutting
device.
However, cutting devices of the newer design have working widths that far
exceed the legal
limit values for road traffic approval. It is therefore customary to transport
the cutting devices
with their own cutting device trailers on public roads on which the cutting
devices are placed
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
2
in such a way that their working width extends along the longitudinal axis of
the cutting
device trailer. The length of the cutting devices in their working direction
is dimensioned in
such a way that they still comply with the legal requirements for the maximum
width
permitted for public transport. However, if the cutting devices are still
provided with stalk
dividers which protrude in the working direction over the cutting elements of
the cutting
device, such as a cutter bar, the length of such cutting devices exceeds the
maximum width
permitted for road traffic. To comply with the legal requirements, the stalk
dividers are
designed to be foldable, such that they can easily be swiveled up or folded
over the side
walls for road transport and, for example, placed against the cutter bar.
However, if the stalk divider is provided with a driven conveying aid, the
problem arises that
such a conveying aid cannot simply be pivoted because of the drives. Either
the conveyor
aid is therefore firmly attached to the cutting device in a position that is
disadvantageous for
its function and is set back to the rear, which ensures that the values for
the maximum
permissible width are complied with, or the drives must be separated from the
conveyor aids
each time before the conveyor aids can be swiveled into a position in which
they comply
with the maximum width permitted for public road traffic approval.
It is therefore the object of the present invention to find a solution for the
configuration and
arrangement of conveying aids with which the legal requirements regarding the
maximum
dimensions for road traffic approval can be complied with in the simplest
possible way.
The object is achieved for a generic cutting device in that the stalk
dividers, together with
the conveying aids mounted thereon, are connected to the frame so as to be
movable about
an at least approximately vertical axis of rotation from the working position
to a non-use
position, and the drives of the conveying aids are designed as hydraulic or
electrical drives
which are connected to the frame via flexible connecting cables.
Despite the conveyor aids mounted on the stalk dividers, the length of a
cutting device
placed on a cutting device trailer for road transport can easily be reduced by
pivoting the
stalk dividers together with the conveyor aids in a simple pivoting movement
from their
working position into a non-use position. While the stalk dividers extend in
the working
direction when in the working position, they are in a position transverse to
the working
direction after being pivoted about the at least approximately vertical axis
of rotation into the
non-use position. Since the drives of the conveyor aids are designed as
hydraulic or
electrical drives, which are connected to the frame and supplied with drive
power via flexible
connecting cables, it is not necessary to separate any drives for the pivoting
or to carry out
separate assembly work, as would be necessary for mechanical drives. The
flexible
connecting cables such as hydraulic hoses or electrical cables simply adapt to
the
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
3
respective new pivoting position when the stalk dividers pivot with the
conveying aids, if they
are long enough not to hinder the pivoting movement.
When installing a conveying aid on a stalk divider, there is the further
advantage that the
conveying aid can be attached to, or removed from, the cutting device in one
operation
together with the stalk divider. The connections between the frame of the
cutting device and
the stalk dividers can be designed for tool-free assembly and disassembly. The
interface
between the stalk dividers and the frame of the cutting device can also be
designed in such
a way that instead of a stalk divider, a rapeseed cutter or another attachment
can also be
attached to the interface, for example. The same connections as for the
conveyor aids can
then be used for driving the rapeseed cutter or other attachment.
The conveying aids on the stalk dividers, The height of the conveying aids is
also guided
via the stalk dividers if the conveying aids are supported and mounted on the
stalk dividers.
No separate height guidance is required. Height guidance can for example be
performed
via a sanding shoe attached to the respective stalk divider. With a vertically
movable
articulation of the stalk divider on the frame of the cutting device, The
stalk divider can then
follow the ground contour via the ground scanning with the sanding shoe if the
stalk divider
is articulated for vertical movement to the frame of the cutting device. The
conveying effect
of the conveying aids remains unchanged even if there are deflection movements
of the
stalk divider. The conveying aids can be driven from above or from below.
If the present description and the claims refer to "front," this means with
reference to the
cutting device the area which, viewed in the working direction of the cutting
device, is closest
to the crop to be harvested, while "rear" means the area of the cutting device
which is
farthest away from the crop to be harvested on the opposite side of the
cutting device. Width
of the cutting device always refers to the extension of the cutting device
transversely to the
working direction, while the length of the cutting device means the extension
in a direction
parallel to the working direction.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the conveying aids have a basic
shape of a
cone or truncated cone with a closed jacket and are mounted on the stalk
dividers with their
slimmer ends pointing downwards. Due to the widening of the basic shape
towards the top,
an increasingly stronger force component acting in a lateral direction is
generated with
increasing height at which the grain stalks or stems are in contact with the
surface of the
conveying aid, through which force the grain stalks or stems are increasingly
pushed away
to the side, namely, either towards the conveyor elements of the cutting
device or to the side
away from the cutting device. If the grain stalks or stems have already been
cut, the
conveying aids generate a force pulse through which the grain stalks or stems
are thrown
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
4
in the direction of the conveying units. The closed jacket prevents the crops
from getting
caught in any openings or components and then wrapping around the axle of the
conveyor
aid. The risk of a material build-up on the edges of the side walls pointing
in the direction of
travel is at least reduced as a result.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the conveying aids each rotate
about an axis
of rotation, which in the working position of the stalk dividers extends at
least approximately
in a direction parallel to the working direction, and the upper end of the
axis of rotation is
inclined in a direction opposite to the working direction. When the harvesting
machine drives
into the standing crops, the front end of the conveying aid plunges close to
the ground into
the crops, viewed in the working direction of the harvesting machine.
Particularly in the case
of lodged grain, the stock is grasped from below. As the harvesting machine
moves forward,
the contact surfaces of the conveyor aid move upwards at the same point in the
field. Flat-
lying grain stalks and stems are increasingly lifted and separated from one
another,
particularly if they are transverse to the working direction of the harvesting
machine. Due to
the inclined position of the axis of rotation, a gentle separation of the
crops lying in front of
the cutting device between the crops to be cut and the crops not to be cut is
possible.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the conveying aids are each held
in a support
frame which extends in an at least approximately parallel direction to the
axis of rotation of
the associated conveying aid, the lower end of which is rotsationally fixed on
the associated
stalk divider, but rotatably mounted in a pivot point, and which in a section
remote from its
front end is attached to the stalk divider or the frame with a coupling
element, wherein the
coupling element is connectable at different heights to the stalk divider or
the frame. The
conveying aids can be fixed and operated at different angles to the ground and
to the stalk
divider via the coupling elements that can be fastened at different heights.
Setting angles
between 40 and 70 have proven to be particularly suitable. If the setting
angle of the
conveying aids is changed, the setting angle of the stalk dividers on the
frame of the cutting
device can remain constant. An operator of the harvesting machine can
optimally adapt the
conveying aids to the respective harvesting conditions by selecting and
setting a suitable
setting angle. It is also possible to adjust the setting angle of the
conveying aids remotely
by a motor, in that an adjusting element of variable length by motor engages
the coupling
element.
According to one embodiment of the invention, one or more continuous
screwthreads are
placed on the jackets of the conveying aids. The screwthreads protruding from
the jackets
of the conveying aids make the conveying aids more active. For example, lodged
grain lying
in mats on the field can be better broken down and divided up.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
5
According to one embodiment of the invention, the conveying aids are held in
the stalk
dividers for more than half, preferably more than three quarters of their
length, more
preferably for their full length over the length of the cutting device in the
working direction in
front of the cutting element. Mounting of the conveying aids in the stalk
dividers enables the
front ends of the conveying aids to start dividing the crop at an operating
point which, viewed
in the working direction of the cutting device, is clearly advanced in front
of the cutting
element. It is advantageous to move the working point so far forward that more
than half,
preferably more than three quarters of the length, more preferably the full
length of the
conveying aids is in front of the cutting element. By moving the conveying
aids forwards, it
is possible to complete the division of the crops before the crops are then
cut by the cutting
element such as a cutter bar. This design enables a clean cut along a cleanly
separated
crop edge, even with lodged grain.
According to one embodiment of the invention, only the lower ends of the
conveying aids
are cantilevered in the stalk dividers. For this purpose, a receiving shoe is
formed in the
stalk dividers, which shields the lower ends of the conveying aids from the
outside in order
to prevent material build-up and wrapping around of the crops there. The drive
of the
respective conveying aid can be arranged in the receiving shoe, which is then
also protected
from the outside by the receiving shoe. The only one-sided cantilevered
mounting saves
weight and costs. The only one-sided mounting is sufficiently functional and
stable over the
long term, because the forces acting on the conveying aids from the harvested
crop are
comparatively low.
According to one embodiment of the invention, the drives are arranged on the
lower ends
of the conveying aids in the stalk dividers. The screwthread of the conveyor
aid can be
designed to be continuous. The stalk divider can be constructed flat and
light, it is not
necessary to provide an upwardly protruding bracket for the drive. The drive
can particularly
be arranged in the receiving shoe, by means of which the drive can be shielded
from contact
with foreign bodies. The drive can be pivoted together with the stalk divider
and the conveyor
aid. Separate set-up work for converting the drive from the harvesting
position to road
transport and back into the harvesting position is not required. The
adjustment takes place
with the pivoting of the stalk divider.
Further features of the invention can be derived from the claims, the figures
and the
following objective description. The features and feature combinations
mentioned in the
description above as well as the features and feature combinations mentioned
in the
description of the figures below and/or merely shown in the figures may be
used not only in
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
6
the combination specified, but also alone, without thereby departing from the
scope of the
invention.
The invention will now be explained in more detail using a preferred exemplary
embodiment
and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Wherein:
Fig. 1: shows an oblique view from the front of a cutting device,
Fig. 2: shows an enlarged view of a lateral end of the cutting device,
and
Fig. 3: shows a view of a lateral end of the cutting device from above,
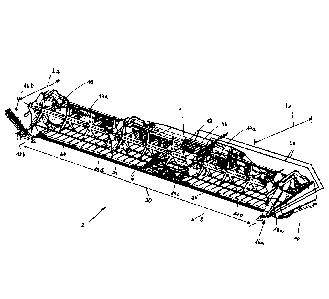
Fig. 1 shows an oblique view from the front of a cutting device 2. The cutting
device 2 has
a frame 4 which carries the components of the cutting device 2. The frame 4
can be used
to attach the cutting device 2 to a harvesting machine, not shown in detail in
the drawing,
such as a combine harvester or forage harvester.
At least one cutting element 6 is located on the front side of the cutting
device 2; in the
exemplary embodiment, this is a cutter bar which extends over the working
width 20 of the
cutting device 2. The cutting device 2 is moved in the working direction 8 by
the harvesting
machine to cut off the harvested crops and convey them away. The crop is cut
by the cutting
element 6, picked up by the conveying devices 14a, 14b, 14c, 14d, and
transported from
the cutting zone 24 to the transfer opening 12, where the crops are then
delivered to the
harvesting machine. In the exemplary embodiment, the conveyor devices are the
reel 14a
and three endlessly rotating belt conveyors 14b, 14c and 14d, of which the two
outer belt
conveyors 14b and 14d convey the crops from the ends 10 of the cutting device
2 to the
central belt conveyor 14c, which collects them there and then conveyes the
harvested crops
to the rear through the transfer opening 12 to the harvesting machine located
behind it.
Instead of belt conveyors 14b, 14c, 14d, other types of conveyor devices 14
can also be
used, for example screw conveyors and the like.
Stalk dividers 16a, 16b which protrude forwards in the working direction 8
over the front
edge of the cutting element 6 are located at the lateral ends 10 of the
cutting device 4. A
conveying aid 18a, 18b is placed on each of the two stalk dividers 16a, 16b.
In the
embodiment shown, the conveying aids 18a, 18b consist of frustoconical bodies
with a
closed jacket, which bodies can be driven in rotation. The stalk dividers 16a
16b with the
conveying aids 18a, 18b laterally limit the working width 20 of the cutting
device 2.
In Fig. 1, the stalk divider 16a is shown in the working position in which the
front tip of the
stalk divider 16a points in the working direction 8. The stalk divider 16b is
shown in a folded-
in position in which the stalk divider 16b has been pivoted about a vertical
axis of rotation
22 by 900 inward into a non-use position. By pivoting the stalk divider 16b
into the non-use
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
7
position, the length of the cutting device 2 is shortened from the dimension
L1 to the
dimension L2. With the dimension L2, the legal requirements for the maximum
permissible
width of trailers in road traffic can be complied with.
It can be seen in Fig. 1 that the conveying aid 18b has also been pivoted by
900 with the
stalk divider 16b. Since the conveying aids 18a, 18b are each mounted in the
stalk dividers
16a, 16b, it is not necessary to pivot them separately from the stalk dividers
16a, 16b to
reduce the length of the cutting device 2.
Fig. 2 shows an enlarged view of a lateral end 10 of the cutting device 2. In
this enlarged
view, the stalk divider 16a with the conveying aid 18a mounted thereon can be
clearly seen.
The conveying aid 18a has a basic truncated cone shape with a closed jacket.
It is mounted
on the stalk divider 16a with its slimmer end pointing downwards. The
conveying aid 18a
rotates about an axis of rotation 26 indicated by a dashed line in Fig. 2,
which axis in the
working position of the stalk divider 16a shown in Fig. 2 extends at least
approximately in a
direction parallel to the working direction 8. The conveying aid 18a is
positioned in its
working position in such a way that its axis of rotation 26 inclines with its
upper end in a
direction opposite to the working direction 8.
It can also be seen in the enlarged view in Fig. 2 that the conveying aid 18a
is held in a
support frame 28 which extends in a direction at least approximately parallel
to the axis of
rotation 26 of the associated conveying aid 18a. On its lower end, the support
frame 28 is
stationary on the associated stalk divider 16a, but is rotatably mounted at a
pivot point 32.
In a section remote from its front end, the support frame 28 is fastened to
the stalk divider
16 with a coupling element 30. The coupling element 30 can be connected to the
stalk
divider 16a at different heights, for example, via an elongated hole guide
(not shown in more
detail in the drawing). This makes it possible to align the conveying aid 18a
in different
angular positions in relation to the arable soil, as is indicated by the
double arrow in Fig. 2.
It can also be seen in Fig. 2 that a continuous screwthread 34 is placed on
the jacket of the
conveying aid 18a. When the conveying aids 18 rotate, the screwthreads 34
support the
separation of the crop into a fraction that is to be cut by the cutting
element 6 and another
fraction that is not yet to be cut as the cut edge of the crops as the
harvester continues to
advance.
The receiving shoe 40 with which the mounting of the conveying aid 18a in the
stalk divider
16a is covered can still be seen in Fig. 2. A drive 42 for the conveying aid
18 is also located
in the receiving shoe 40. The drive 42 is connected to the frame 4 of the
cutting device 2 via
flexible cables 44.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
8
Fig. 3 shows a view of a lateral end 10 of the cutting device 2 from above. It
can be seen in
the view from above that, in the working position of the stalk divider 16a,
the overall length
36 of the conveying aid 18a is still in front of the line 38, which is applied
to the front edge
of the cutting element 6 and is guided laterally over the end 10 of the
cutting device 2 in the
figure. The view from above makes it clear in this way that the division of
the crops located
in front of the cutting device 2 between a fraction that is to be cut by the
cutting element 6
and a second fraction that is to remain as the cutting edge is completed
before the cutting
element 6 reaches the respective grain stalks or stems as the harvesting
machine advances.
A hydraulic block 46 is located on the frame 4, to which the hydraulic lines
44, which are
hydraulic in the exemplary embodiment, can be connected to the hydraulic
circuit of the
cutting device 2.
The invention is not limited to the exemplary embodiments shown. A person
skilled in the
art will have no difficulty modifying the exemplary embodiments in a way that
appears
suitable to adapt it to a specific application.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17
9
List of reference numerals:
2 cutting device
4 frame
6 cutting element
8 working direction
ends of the cutting device
12 transfer opening
14 conveyor device
16 stalk dividers
10 18 conveying aid
working width
22 vertical axis of rotation
24 cutting zone
26 axis of rotation (conveying aid)
15 28 support frame
coupling element
32 pivot point
34 screwth read
36 overall length
20 38 line
pick-up shoe
42 drive
44 cable
46 hydraulic block
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-17