Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
NEW MEDICAL USE
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
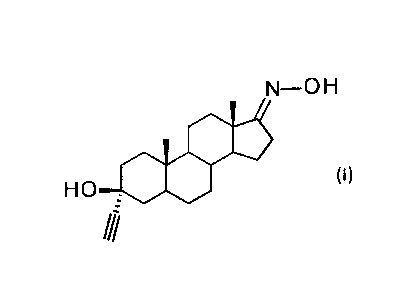
The present invention is directed to the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
for use in the
treatment of cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient with hepatic
encephalopathy (HE), said
patient having a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at
baseline (prior to treatment).
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is defined as brain dysfunction due to acute and
chronic liver disease
(Vilstrup H etal. Hepatology 2014;60:pp. 715-735). HE is a significant and
increasing health care
problem due to the large and increasing prevalence of chronic liver disease.
HE is characterized by
impairments in the sleep-wake cycle, cognition, memory, learning, motor
coordination,
consciousness, decreased energy levels and personality change, ranging from
minimal HE (MHE) to
overt HE (OHE).
Hepatic encephalopathy can also be classified as Type A, B and C (see e.g.
Prakash, R. & Mullen, K. D.
Nat. Rev. GastroenteroL HepatoL 7; pp. 515-525 (2010).
The GABA-system, the brain's major inhibitory neurotransmitter system,
regulates a variety of
functions including learning, memory, vigilance and sleep (Johansson Met al
2015; Am .1 Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol; 309: G400-409 and Johansson M et al 2016; J
Steroid Biochem Mol
Bio1;160: pp. 98-105). GABA-A receptors are ionotropic heteropentameric
assemblies with 20
distinct configurations, the functional characteristics of which vary
depending on receptor subtype
and cellular and subcellular localization (Johansson Met 012015; Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver
Physiol; 309: G400-409 and Johansson M et al 2016; J Steroid Biochem Mol
Bio1;160: pp. 98-105).
While the GABA-A receptor is a validated target with several agonist drugs
approved, development of
GABA-A antagonists has been hindered by their propensity to induce seizures
(Vilstrup H etal.
Hepatology 2014;60:pp. 715-735). In addition to GABA, endogenous neurosteroids
such as
allopregnanolone, are strong positive allosteric modulators of GABA-mediated
activation of GABA-A
receptors and are present in increased concentrations in the brain of patients
with HE (Johansson M
eta! 2016; J Steroid Biochem Mol Bio1;160: pp. 98-105). Allopregnanolone is a
potent anaesthetic
that alters the sleep-wake cycle and impairs memory and learning, and
allosteric activation of the
1
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
GABA-A system by neurosteroids is implicated in the pathogenesis of HE and
sleep disorders
(Johansson Metal 2016; J Steroid Biochem Mol Bio1;160: pp. 98-105).
The compound golexanolone, having the chemical name 3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime, is a compound currently in clinical Phase II for the treatment of
Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE).
This compound is dislosed in WO 2008/063128 for use in various CNS disorders.
WO 2015/114308
disclose the use of the compound 3a-ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime
for the treatment
of Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE). US patent application published as
US2017/0348323, discloses a
method for the treatment of hypersomnolence by administering the compound 3a-
ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime. WO 2019/102040 discloses a pharmaceutical
formulation of the
compound golexanolone.
The continuous reaction times method, is a computerized psychometric tool
introduced in the 1960s
(Renzi 1965; Brun and Parsons 1971), which method has been further developed
in the 1970s and
has been used in hepatology as a method for assessing cerebral dysfunction in
cirrhosis patients
since the 1980s (Elsass 1986b; Elsass etal. 1981,1985). Lauridsen et al
concludes in Metab Brain Dis
(2013) 28:pp. 231-234, that the CRT method is fast, easy to use, and that it
provides the physician
with a measure of the liver patient's reaction time stability, the CRT index.
Wernberg et al discloses La. a study for the Prediction of overt hepatic
encephalopathy by the
continuous reaction time method (PLOS ONE 14 (12): e0226283
https:fidoLord/10.1371/ioumal ,
published December 12 2019).
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is part of a spectrum of neurocognitive changes
and neuropsychiatric
abnormalities found in patients with portosystemic shunting and cirrhosis. HE
is divided into two
broad categories based on severity, covert (CHE) and overt (OHE). CHE has a
significant impact on a
patient's quality of life, driving performances, and has recently been
associated with increased risk of
OHE, hospitalizations and death. Likewise, OHE is associated with increased
rates of hospitalizations
and mortality, and poor quality of life (Kavish R. Patidar eta!; Clin
Gastroenterol HepatoL 2015;
November; 13(12): pp. 2048-2061).
Lauridsen M et al discloses a study in MHE patients with an abnormal CRT index
(PLOS ONE October 11,2017; https://doLord/10.1371/ioumal.pone.0185412).
2
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
HE is a neuropsychiatric complication of either acute or chronic hepatic
insufficiency. HE
results from impaired first-pass removal of ammonia, and potentially other gut-
derived toxins,
by a compromised liver, thus increasing their concentration in blood. HE can
be overt, with
characteristic neurological manifestations ranging from asterixis and
confusion to coma, or
covert (previously called minimal), with subtle mental changes that can be
detected only with
psychometric testing. Many and potentially most patients with clinically
decompensated liver
cirrhosis will develop some degree of HE during the course of their disease,
with up to 45%
developing overt HE and up to 80% developing CHE.
Present treatment options to reduce the risk of episodic OHE are mainly
directed toward
Reducing hyperammonemia (HA) by using non-absorbable disaccharides (lactulose)
and/or
antibiotics (rifaximin).
Although rifaximin has been shown to reduce the risk of OHE episode, there
remains a
substantial unmet need for patients with overt HE and there is no approved
treatment for
patients with the manifestations of cognitive impairment collectively referred
to as CHE
(Landis, C.S. et aL, Dig. Dis. Sci., 2016;61:1728-34).
There is therefore a need for new strategies to improve the neurological
alterations and to
further reduce the risk of HE recurrence
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
A problem underlying the present invention, is to find a novel therapy that
may be useful for the
treatment of cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient with hepatic
encephalopathy (HE), said
patient having a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at
baseline (prior to treatment).
An aspect of the present invention is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-
313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) of formula (I)
N-0 H
(I)
HO--C613
ill
3
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment of
cognitive impairment in a
cirrhotic patient with hepatic encephalopathy (HE), said patient having a CRT
index (continous
reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to treatment).
One aspect of the invention is a method for treatment of cognitive impairment
in a cirrhotic patient
with hepatic encephalopathy (HE), said patient having a CRT index (continous
reaction time index)
below 1.9 at baseline (prior to treatment), whereby the compound golexanolone
(3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) of formula (I)
N-0 H
(I)
HO-C613
ill
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, is administered to said
patient.
Yet an aspect of the invention is the use of the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) of formula (I)
N-0 H
(I)
HO.--C613
ill
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for the manufacture of a
medicament for use in the
treatment of cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient with hepatic
encephalopathy (HE), said
patient having a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at
baseline (prior to treatment).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
said patient having a
CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
4
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE),
said patient having a CRT
index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE),
said patient having a CRT
index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
wherein said patient
has a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior
to treatment) and
wherein said patient is at risk of developing overt hepatic encephalopathy
(OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient is at risk of developing overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
wherein said patient
has a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior
to treatment) and
wherein said patient is at risk of developing recurrent overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient is at risk of developing recurrent overt hepatic encephalopathy
(OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
5
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
wherein said patient
has a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior
to treatment) and
wherein said patient has had at least one prior episode of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient has had at least one prior episode of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
wherein said patient
has a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior
to treatment) and
wherein said patient has not had any prior episode(s) of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient has not had any prior episode(s) of overt hepatic encephalopathy
(OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient has had at least one prior episode of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
An aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one
oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in the treatment
of cognitive
impairment in a cirrhotic patient with overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE),
wherein said patient has
a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to
treatment) and wherein
said patient has not had any prior episode(s) of overt hepatic encephalopathy
(OHE).
6
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
One aspect of the invention, is the use of the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
for use in the
treatment of cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient suffering from any
one hepatic
encephalopathy conditions selected from minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE),
covert hepatic
encephalopathy (CHE) and overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE), wherein said
patient has a CRT index
(continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at baseline (prior to treatment).
In yet an aspect of the invention, the MHE, CHE or OHE patient as herein
described and claimed, has
not had any prior episode of OHE.
In yet an aspect of the invention, the MHE, CHE or OHE patient as herein
described and claimed, has
had at least one prior episode of OHE.
Still an aspect of the present invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
for use in reducing
the risk of a future episode or future episodes of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE) in a patient as
herein described and claimed, and wherein said patient has had no prior
episode of OHE.
Still an aspect of the present invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-
.. hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, for use in reducing
the risk of a future episode or future episodes of overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE) in patient as
herein described and claimed, and wherein said patient has had at least one
prior episode of OHE.
Still an aspect of the present invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
for use in reducing
the risk of hospitalization in patient suffering from MHE, CHE or OHE.
A cirrhotic patient as described throughout the specification and claims, may
be a patient with Child-
Pugh A, B, or C cirrhosis who has been diagnosed with hepatic encephalopathy
such as MHE, CHE or
.. OHE, and who has a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at
baseline (prior to
treatment).
Yet an aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use as described
herein, in combination
7
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
therapy with a compound and/or drug used as Standard of Care in the treatment
of a hepatic
encephalopathy.
In one aspect of the invention, a compound useful as Standard of Care in the
treatment of a hepatic
encephalopathy is an an ammonia-lowering compound. Examples of compounds or
drugs used as
Standard of Care in the treatment of a hepatic encephalopathy may be any one
selected from an oral
antioxidant, fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, ondansetron, colchicine, UDCA
(ursodeoxycholic acid), OCA
(obeticholic acid), ciclosporin, nalmefene, modafinil, rituximab, lactulose,
rifaximin, propranolol,
furosemide and methotrexate; or any combination thereof.
In one aspect of the invention, combination therapy may be as add-on therapy.
In yet an aspect of
the invention, the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) may be
administered as a fix combination (such as a pharmaceutical formulation) or by
administration
sequentially (i.e. after one another) or separately as a kit-of-parts
combination.
Also within the scope of the invention, is a pharmaceutical formulation
comprising the
compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) for use as
herein described and claimed.
The compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) may be
prepared according to the method of preparation disclosed in WO 2008/063128.
One aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) for use as described and claimed herein, wherein the covert hepatic
encephalopathy
(CHE) is Grade I HE.
One aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) for use as described and claimed herein, wherein the overt hepatic
encephalopathy
(OHE) is Grade II HE.
One aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) for use as described and claimed herein, wherein the overt hepatic
encephalopathy
(OHE) is Grade III HE.
8
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
One aspect of the invention, is the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) for use as described and claimed herein, wherein the overt hepatic
encephalopathy
(OHE) is Grade IV HE.
In one aspect of the invention, the hepatic encephalopathy is type A hepatic
encephalopathy.
In one aspect of the invention, the hepatic encephalopathy is type B hepatic
encephalopathy.
In one aspect of the invention, the hepatic encephalopathy is type C hepatic
encephalopathy.
Figure 1A is a line diagram illustrating change in CRT compared to baseline
for all study participants
with abnormal (<1.9) or normal W.9) CRT at baseline.
Figure 1B is a staple diagram illustrating change in CRT compared to baseline
for all study participants
with abnormal (<1.9) or normal W.9) CRT at baseline.
Figure 2A is a line diagram illustrating Change in CRT compared to baseline
for all study participants
with abnormal CRT (<1.9) at baseline.
Figure 2B is a staple diagram illustrating Change in CRT compared to baseline
for all study
participants with abnormal CRT (<1.9) at baseline.
9
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
DEFINITIONS
Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) is herein defined according to the The American
and European
Associations for the Study of the Liver 2014 practice guidelines recommend.
According to this
definition, hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is classified according to four
factors (American Association
for the Study of Liver Diseases; European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Hepatic
Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the
European
Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the
Study of Liver Diseases
(I HepatoL 2014;61(3): pp.642-659):
1. the underlying etiology as described previously ¨ Type A, B or C;
2. severity ¨ using grading system such as West Haven Criteria;
3. time course ¨ episodic, recurrent (>1 episode in 6 months) or persistent
(symptoms always present
and can have episodes of acute exacerbations); and
4. nonprecipitated or precipitated by factors such as infections, medications
or electrolyte disorders.
According to the West Haven criteria, symptoms and clinical findings involved
in Hepatic
Encephalopathy are divided by different grades of severity:
The wording "minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE)" is a milder form of hepatic
encephalopathy. It
comprises symptoms of psychometric or neuropsychological alterations of tests
exploring
psychomotor speed/executive functions, or neurophysiological alterations
without clinical evidence
of mental change. Clinical findings on routine examination are subtle to
absent, and cannot reliably
detect MHE.
The disease terminology and symptom terminology as used throughout the
specification and claims,
is terminology in the field of hepatic encephalopathy applicable at the
priority date of the present
.. patent application. Terminology such as minimal hepatic encephaopathy
(MHE), covert hepatic
encephalopathy (CHE) and/or overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) in the medical
field of cirrhosis
and hepatic encephalopathy, may evolve in the future. Any such change of
terminology will be be
acknowledged and recognised by medical authorities at drug approval, and
should not change the
scope of the claimed invention.
Grade I hepatic encephalopathy is one part of covert hepatic encephalopathy
(CHE) and comprises in
addition to MHE symptoms of trivial lack of awareness, euphoria, anxiety,
shortened attention span,
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
impairment of addition or subtraction, altered sleep rhythm. Clinical findings
involved are mild
asterixis or tremor.
The wording "overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE)" comprises Grade II OHE, Grade
III OHE and
Grade IV OHE.
Grade II overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) comprises symptoms of lethargy or
apathy,
disorientation for time, obvious personality change, and inappropriate
behavior. Clinical findings
involved are obvious asterixis, dyspraxia, and slurred speech.
Grade III overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) comprises symptoms of somnolence
to semistupor,
responsive to stimuli, confused, gross disorientation, and bizarre behavior.
Clinical findings involved
are muscular rigidity, clonus, and hyperreflexia.
Grade IV overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) is defined as a subject where the
major symptom is
coma. The major clinical finding is decerebrate posturing.
A cirrhotic patient is herein defined as a patient who has been diagnosed with
hepatic
encephalopathy such as MHE, CHE or OHE, and who has a CRT index (continous
reaction time index)
below 1.9 at baseline (prior to treatment).
The wording "normal CRT" is defined as a patient who has a CRT above 1.9
(>1.9).
The wording "abnormal CRT" is defined as a patient who has a CRT below 1.9
(<1.9).
The wording "Type A hepatic encephalopathy" (type A HE)" means HE which is due
to acute liver
failure.
The wording "Type B hepatic encephalopathy" (type B HE)" means HE which is due
predominantly to
portosystemic shunting (e.g.transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting
procedures).
The wording "Type C hepatic encephalopathy" (type C HE)" means HE which is due
to a complication
of liver cirrhosis.
11
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
Chronic hepatitis can result in cirrhosis with portal hypertension and liver
failure. Both chronic
hepatitis B (CHB) and chronic hepatitis C (CHC) are caused by a virus
infection characterised by
varying degrees of inflammation and hepatic fibrosis. The cause of liver
cirrhosis may also be due to
NAFLD (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease), NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis)
, PBC (primary biliary
cholangitis ) and other liver diseases.
The wording "a patient at risk of developing overt hepatic encephalopathy" is
defined as a patient
who has been diagnosed as having minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) or
covert hepatic
encephalopathy (CHE) and who is at risk of developing worsening of MHE
symptoms to overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE). A patient at risk of developing overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE) may also
be defined as a patient who has experienced prior OHE, or has risk factors for
OHE such as of minimal
hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) or covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE). One such
risk factor may be
excess levels of ammonia (NH3) in a patients blood (Vierlin J. etal. Pancreas,
biliary tract and liver;
Vol.14, issue 6; pp.903-906 El June 1 2015).
The wording "a patient who is at risk of developing recurrent overt hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE)" is
defined as a patient who has had at least one prior episode of OHE and wherein
the symptoms of
said patient have returned to a normal CRT index, defined as a CRT index above
1.9, or where the
patient remains at an abnormal CRT index below 1.9., but wherein the clinical
liver status of said
patient worsens and the CRT index changes into abnormal, defined as a CRT
index below 1.9.
The wording "CRT index" (continuous reaction time test) is a method for
assessing cerebral
dysfumction in cirrhosis patients, and is herein defined in accordance with
Lauridsen M et al (Meta,
Brain Dis (2013) 28:pp. 231-234). It provides the physician with a measure of
the liver patient's
reaction time stability, the CRT index. The CRT index is used in the diagnosis
of MHE and CHE, and
more particularly for OHE prediction in cirrhosis patients. A patient with a
CRT index above 1.9 (>1.9)
is considered to be "normal". A patient with a CRT index below 1.9 (<1.9) is
considered to be
"abnormal".
The wording "a patient who has had no prior episode(s) of overt hepatic
encephalopathy" is defined
as a patient who has had no prior episode of OHE and said patient having a CRT
index above 1.9
(>1.9). A patient who has had no prior episode(s) of overt hepatic
encephalopathy" may also be a
patient who has MHE and a CRT below 1.9, or a patient who has CHE and a CRT
below 1.9.
12
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
The wording "a patient who has had at least one episode of Overt Hepatic
Encephalopathy (OHE)" is
defined as a patient who has had at least one prior episode of OHE, and who
has OHE of Grade II, III
or IV of the current practice guidelines. OHE is a clinical diagnosis (Bajaj
.1.5; Metab Brain Dis. 2016
Oct;31(5):pp. 1081-1093).
The Child-Pugh classification is a universal scoring system of the degree of
liver failure in patients
with cirrhosis, and the Child-Pugh class (A, B, or C) has been used as a
predictive index for operative
mortality rate in adult patients undergoing portosystemic shunting procedures.
The estimated 1- and
5-year survival rates are 95% and 75% for patients with Child-Pugh class B,
and 85% and 50% for
patients with Child-Pugh class C. Child-Pugh Class A patients have the best
survival prognosis, Child-
Pugh Class B patients have a moderate prognosis of survival, whereas Child-
Pugh Class C patients
have a poor prognosis of survival.
The wording "treatment or therapy" as used throughout the specification and
claims, takes the
normal wording within the medical and pharmaceutical field, and herein means
treatment of
cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient who has been diagnosed as having
hepatic
encephalopathy and having a CRT index below 1.9 at baseline. The wording
"baseline" means prior to
treatment.
The wording "combination therapy" as used herein, means treatment (therapy)
with the compound
golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) in combination with
an agent (drug)
used as standard of care therapy (SOC) in the treatment of a hepatic
encephalopathy.
Combination therapy with an agent (drug) used as standard of care therapy
according to the
invention, means that the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime)
may be administered prior to, after (add-on) or simultaneously to the
administration of an agent
(drug) used as standard of care therapy in the treatment of a hepatic
encephalopathy.
Add-on therapy as used herein, is defined as combination therapy wherein the
compound
golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) is administered to
a cirrhotic patient
who is already being treated with a medication indicated for hepatic
encephalopathy such as minimal
hepatic encephalopathy (MHE), covert hepatic encephalopathy (MHE), or overt
hepatic
encephalopathy (OHE).
13
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
A fix combination as used herein, is defined as a combination where the
compound golexanolone
(3a-ethyny1-313-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) is formulated in admixture with
at least one more
compound useful in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy such as minimal
hepatic
encephalopathy (MHE), covert hepatic encephalopathy (CHE), or overt hepatic
encephalopathy
(OHE).
In yet an aspect, a fix combination may be defined as a "kit of parts"
combination where each active
ingredient or formulation may be administered simultaneously (i.e. in
parallell but as separate
formulations) or one after the other (sequentially).
As used throughout the present specification and claims, the compound
golexanolone is the
compound with the chemical name 3a-ethyny1-313-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime,
according to the
chemical formula (I),
N-0 H
HO.--C6113, (I)
ill
The International Nonproprietary Name (INN) is "golexanolone" and the CAS no.
is 2089238-18-4.
Also within the scope of the invention is a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
of the compound
golexanolone, for use as described and claimed herein.
PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATIONS AND ADMINISTRATION ROUTES
In certain aspects of the invention, the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) as used throughout the present specification
and claims, may be
administered in the form of a pharmaceutical composition, in admixture with
one or more
pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvants, diluents and/or carriers. Examples of
such
pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, carriers and/or diluents useful when
formulating the
compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-313-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) for use
in accordance
with the present invention, are thickeners, flavoring agents, diluents,
emulsifiers, dispersing aids,
carrier substances, lubricants or binders. Typical pharmaceutical carriers
include, but are not limited
14
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
to, binding agents (e.g., pregelatinised maize starch); fillers (e.g.,
lactose, glucose, sucrose and other
sugars, microcrystalline cellulose, pectin, gelatin, calcium sulfate, ethyl
cellulose, polyacrylates or
calcium hydrogen phosphate, etc.); lubricants (e.g., magnesium stearate, talc,
silica, colloidal silicon
dioxide, stearic acid, metallic stearates, hydrogenated vegetable oils, corn
starch, polyethylene
glycols, sodium benzoate, sodium acetate, etc.); disintegrants (e.g., starch,
and sodium starch
glycolate); wetting agents; diluents; coloring agents; emulsifying agents; pH
buffering agents;
preservatives; and mixtures thereof.
In one aspect of the invention, the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) may be administered by enteral administration when used as
disclosed and claimed
herein. Examples of enteral administration involves administration to the
esophagus, stomach, and
small and large intestines (i.e. the gastrointestinal tract). Methods of
administration include oral,
sublingual (dissolving the drug under the tongue), and rectal.
The physician will be able to determine the actual dosage of the compound
golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) which will be suitable for an
individual patient in
order to treat cognitive impairment in a cirrhotic patient with hepatic
encephalopathy (HE), said
patient having a CRT index (continous reaction time index) below 1.9 at
baseline (i.e. prior to
treatment). The dosage may vary with the route of administration, the severity
of hepatic
encephalopathy and the level of cognitive impairment as defined by the CRT
index in the patient
to be treated, as well as the species, age, weight, and sex, of the patient.
In one aspect of the invention, the compound golexanolone (3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-
one oxime) may be administered as a daily dose of from 1 mg to 200 mg, 10 mg
to 100 mg,
3 mg to 30 mg, 30 mg to 60 mg, 50 mg to 100 mg, 20 mg to 160 mg, 40 mg to 160
mg, or 80 mg to
160 mg.
The wording "daily dose" may be administration of the compound golexanolone
(3a-ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) once daily (Q.D.), or twice daily (B.I.D.).
Administration twice daily
(B.I.D.) means that the total daily dose is divided into two doses which in
total makes up the daily
dose. For example, a daily dose of 1 mg to 200 mg may be administered as a
dose of 1-200 mg once
daily (Q.D.), or as a dose of 0.5-100 mg twice daily (B.I.D.).
In one aspect of the invention, a daily dose of the compound golexanolone (3a-
ethyny1-30-
hydroxyandrostan-17-one oxime) which may be useful in accordance with the
present invention may
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
be selected from any one of 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 40 mg,
45 mg, 50 mg, 55 mg,
60 mg, 65 mg, 70 mg, 75 mg, 80 mg, 85 mg, 90 mg, 95 mg, 100 mg, 105 mg, 110
mg, 115 mg, 120 mg,
125 mg, 130 mg, 135 mg, 140 mg, 145 mg, 150 mg, 155 mg, and 160 mg.
BIOLOGICAL EVALUATION - CLINICAL PHASE II STUDY
Protocol EudraCT 2016-003651-30 was a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-
controlled study
consisting of four parts, where part D (partly) of the study is relevant to
the herein disclosed and
claimed invention. The aim of the study was to assess the potential efficacy
(Part D) of the compound
golexanolone in patients with cirrhosis. The study was performed at sites in
Sweden, Denmark,
Ukraine, Russia, Hungary and Poland.
Study design
Extended treatment (21 consecutive days) in cirrhotic patients defined as
Child-Pugh class A and B
with manifestation of CHE, was performed.
An objective of study part D (phase Ila, extended treatment) was to assess
preliminary efficacy of
treatment with the compound golexanolone on cognitive function, as measured by
the Continuous
Reaction time (CRT) test.
Inclusion criteria
In order to be eligible for the study, patients required evidence of cognitive
impairment defined as a
CRT index <1.9 at screening. CRT was re-assessed at baseline, prior to dosing
but was not required to
be abnormal at baseline.
Exclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria included uncontrolled infection, active gastrointestinal
bleeding, a history of
bleeding requiring transfusion, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
placement within the
past 90 days, hepatorenal syndrome, uncontrolled ascites, current malignancy,
evidence of overt HE
at screening or within 7 days of screening, use of psychoactive drugs, or any
other psychiatric or
medical comorbidity judged by the Investigator to preclude safe participation
and/or confound the
interpretation of study results.
Alcohol consumption was not allowed within two days prior to screening or for
24 hours prior to all
study visits. Moreover, subjects were required to have a negative alcohol
breath test at screening
16
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
and subsequent study visits, including Part D study days 10 and 21 at which
cognitive function was
measured.
The Investigational Medicinal Product (IMP) is self-administered by the
patient at home, except for
the study days of visiting the clinic (Days 1, 10 and 21), when the IMP is
administered under
surveillance. Assistance of a dedicated care-giver or family members/friends
is mandatory during the
extended treatment period. Intake of study medication, changes in concomitant
medications and
medical events between visits are registered in a diary on a daily basis by
the patient/care-giver and
a care-giver diary is completed. Efficacy parameters are evaluated. If
assessed as required for
practical reasons, a patient can be confined to the research clinic from the
evening before dosing on
Day 21. A follow-up visit is performed 5-10 days after (last) IMP
administration.
Change in CRT index from baseline (day 1) to 10 and 21 days respectively after
start of treatment, as
compared to placebo, is evaluated.
Investigational Medicinal Product(s), dosage and mode of administration
The Investigational Medical Product (clinical formulation) is supplied as a
lipid semi-solid filled in a
gelatine capsule for oral administration. For the present study, each capsule
contains 10 mg
golexanolone. The excipient is a mixture of mono -and diglycerides of
capric/caprylic glycerides
(Imwitor 742), which is of pharmacopoeia quality.
Placebo capsules contain the lipid excipient and is of identical appearance as
the golexanolone
capsules. The number of placebo capsules administered are adjusted to match
the number of
golexanolone capsules administered on each dose level. The clinical
formulation is described in the
table below:
r Amount Amount Clinical capsule dose
Capric/caprylic glycerides
(Imwitor 742)
Compound I 10 mg 490 mg 10 mg capsule
Placebo - 500 mg
17
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
U C07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
The manufacture of the Investigational Medical Product formulation of
golexanolone as used in the
present clinical study, may be prepared as described in Example 10 of
Applicant's published
application W02019/102040.
The Investigational Medical Product golexanolone is administered every twelve
(12) hours (i. e. twice
daily) for 21 consecutive days.
mg golexanolone BID (i.e. 20 mg per day) in combination with Standard of Care
therapy; or
40 mg golexanolone BID (i.e. 80 mg per day) in combination with Standard of
Care therapy; or
10 80 mg golexanolone BID (i.e. 160 mg per day) in combination with
Standard of Care therapy; or
placebo BID in combination with Standard of Care therapy.
Standard of Care therapy may be any one of an oral antioxidant, fluvoxamine,
fluoxetine,
ondansetron, colchicine, UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid), OCA (obeticholic acid),
ciclosporin,
nalmefene, modafinil, rituximab, lactulose, rifaximin, propranolol,
furosemide, methotrexate; or any
combination thereof.
The following results were obtained:
I. Change in CRT compared to baseline for all 45 patients with abnormal (<1.9)
or normal W.9) CRT
at baseline. Data for all patients irrespective of CRT at baseline. The
inclusion was based on an
abnormal CRT at screening but without further restrictions for inclusion at
baseline. Some patients
improved between screening and baseline.
Table 1
10 mg 40 mg 80 mg
Placebo Golexanolone Golexanolone Golexanolone
Time point N=12 N=10 N=10 N=13
¨
Baseline 0 0 0 0
Day 10 0.1435 0.2762 0.3035 0.4593
Day 21 0.3607 0.2792 0.4276 0.3505
N= number of patients.
Baseline means the day of study start (day of randomization) and prior to
treatment with the
compound golexanolone (IMP). Day 21 is the last day of the study.
These results are also illustrated in Figure 1A (line diagram) and Figure 1B
(stapel diagram).
18
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29
UC07-1 CA v.
25 OCT 2021
II. Change in CRT compared to baseline for all 36 patients with abnormal CRT
(<1.9) at baseline.
These are the patients that did not improve between screening and basline but
remained
"abnormal" with a CRT below 1.9.
Table 2
mg 40 mg 80 mg
Placebo Golexanolone Golexanolone Golexanolone
Time point N=9 N=8 N=10 N=9
Baseline 0 0 0 0
CRT<1.9
Day 10 0.2468 0.3504 0.3035 0.5109
Day 21 0.2559 0.4166 0.4276 0.5219
5 N= number of patients.
Baseline means the day of study start (day of randomization) and prior to
treatment with the
compound golexanolone (IMP). Day 21 is the last day of the study.
10 These results are also illustrated in Figure 2A (line diagram) and
Figure 2B (stapel diagram).
As shown by these results, a dose-dependent effect was seen in patients having
abnormal CRT (<1.9)
at baseline.
19
Date recue / Date received 2021-10-29