Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
EXTRUSION TYPE FROST HEAVE PREVENTING AND HEAT
GATHERING SELF-PROTECTIVE DEVICE AND SUBGRADE THEREOF
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The present invention relates to the technical field of preventing
and treating
engineering construction diseases in a seasonally frozen soil region, and
particularly to an
extrusion type frost heave preventing and heat gathering self-protective
device and subgrade
thereof.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] An area of seasonally frozen soil region in China is about 5.137
million square
kilometers, occupying 53.5% of the national territorial area. Seasonally
frozen soil is affected by
seasons, and is frozen in winters, and all melted in Summers. When seasonal
frozen layer and
seasonally thawed layer are melted in Summers, due to unevenness distribution
of ice layers and
ice lenses, an important reason why various buildings are deformed and
destroyed is the formation
of differential settlement of the soil layers. Characteristics of frost heave
and thaw settlement of
the seasonal frozen soil play a significant influence on engineering.
Therefore, engineering
construction or projects in the seasonally frozen soil region shall be
particularly noticed to consider
the influence of the seasonal frozen soil on engineering and prevention
measures thereof. As for
the subgrade, forms of frost damage of the subgrade are mainly frost heave,
thaw settlement, mud
pumping, and the like.
[0003] The Xining to Golmud section of Qinghai-Tibet Railway is at the
northeast part of
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and railway lines go across coastal plains, alluvial
plains,and ice platforms
at the north of Qinghai Lake, where an average altitude is 3220 m. The mean
annual precipitation
is 376 mm, precipitation is unevenly distributed, most concentrated in July to
September, the mean
annual temperature is -0.6 C, and the average temperature in the coldest month
January is -20.6 C.
At Xining to Golmud section of Qinghai-Tibet Railway, weather is cold, a
freezing capacity of the
temperature is strong, and a freezing depth is large, and the maximum freezing
depth may reach
1.8 m, which belongs to a typical seasonally frozen soil region. Accordingly,
engineering diseases
such as frozen heave and thaw settlement of the subgrade caused by freezing
and melting are
relatively severe.
[0004] Recently, due to a continuous increase of precipitation at Qinghai-
Tibet Plateau,
causing enrichment of underground water and rising of water table, as well as
the intensification
of climate and environmental change, the engineering disease of freeze-thaw in
such region is
further increased, resulting in an important influence on long-term stability
of the subgrade.
Although the previous study is made on diseases of the subgrade under action
of engineering in
1
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
seasonally frozen soil region, the study is mainly directed to issues such as
action and influence of
minor frozen heave engineering of the subgrade under working conditions of
highway engineering
or high-speed railway in regions such as northeast and northwest. However,
study on growth
features and distribution laws of engineering disease of freeze-thaw under
special conditions such
as a high water level, coarse filling, and strong freeze-thaw at Xining to
Golmud section of
Qinghai-Tibet Railway is still lacked. Application of methods such as
replacement of foundation
soil, building drainage facility for reducing water content of the subgrade
bed, stabilizing soil heat
preservation method with inorganic binder, artificial salinizing subgrade
soil, chemical grouting,
and waterproof curtain used in the common regions is difficult to satisfy
requirements of actual
engineering in such region, due to limitations of engineering conditions such
as normal driving of
trains without interruption of construction, and crack at processing positions
and extreme difficulty
in overall enclosure at a lower part of the subgrade caused by strong action
of soil freezing and
thawing. Since the previous study on engineering measures for treating such
engineering diseases
is weak, engineering issues affect stability and operating security of the
subgrade for a long time.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0005] An object of the invention includes providing an extrusion type
frost heave preventing
and heat gathering self-protective device and subgrade thereof, which can
realize balanced and flat
heating of the subgrade, thereby effectively avoiding generation of
engineering diseases such as
frost heave and uneven fluctuation of the subgrade in the seasonally frozen
soil region, and also
avoiding influence on stability and sealing performance of the device when the
circulating working
medium reaches a boiling point in Summers by controlling positions of the
circulating working
medium.
[0006] The embodiment of the invention can be implemented by:
[0007] In a first aspect, the invention provides an extrusion type frost
heave preventing and
heat gathering self-protective device, comprising a solar heat absorber, a
circulating tube, a heat
gathering tube and a circulating pump, the solar heat absorber, the heat
gathering tube and the
circulating pump being connected from head to tail sequentially through the
circulating tube to
form a circulating loop where a circulating working medium is filled, and the
heat gathering tube
is used to be inserted into a subgrade;
[0008] The solar heat absorber comprises a solar heat absorption panel, and
an upper
collecting tube, a lower collecting tube, row tubes and squeezing plugs
mounted below the solar
heat absorption panel, the upper collecting tube and the lower collecting tube
are connected to both
ends of the circulating tube, respectively, both ends of the row tubes are in
communication with
the upper collecting tube and the lower collecting tube, the squeezing plugs
are movable inside the
row tubes, the circulating pump is configured to push the circulating working
medium to flow in
2
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
a direction from the lower collecting tube to the upper collecting tube, and
when the circulating
pump stops working, the squeezing plugs press the circulating working medium
in the row tubes
into the lower collecting tube under action of gravity.
[0009] In such way, the heat absorbed by the solar heat absorber is
transferred to the heat
gathering tube via the circulating working medium, and heats soil around the
heat gathering tube
through heat release of the heat gathering tube inside the subgrade, such that
the subgrade is always
in a process of pure heat absorption and continuous accumulation of internal
heat, thereby reaching
heat gathering inside the subgrade and a state where the temperature is always
held to be positive,
and reaching objects of preventing and treating engineering diseases such as
soil freezing of the
subgrade and frost heave of the subgrade.
[0010] When the device works, the circulating working medium circulates in
the circulating
tube under driving of a pressure produced by rotation of the circulating pump.
As for the squeezing
plugs in the row tubes, they move upwardly under action of a circulating
pressure and a pushing
force of the circulating working medium, circulating channels are opened, and
the circulating
working medium starts circulation.
[0011] When the device stops working, such as, in summers, the circulating
working medium
stops circulation. Firstly, under action of gravity, the circulating working
medium flows back to
inside of the heat gathering tube through the circulating tube, and a liquid
level of the circulating
working medium in the row tubes starts decreasing till a height of a liquid
level of the device.
Secondly, the squeezing plugs further press the circulating working medium to
the lower collecting
tube under action of gravity, thereby further emptying the working medium in
the row tubes,
thereby avoiding a sharp rise of pressure of the whole device caused by
boiling and vaporization
of the circulating working medium under a high temperature condition of the
solar heat absorber
in the daytime of summers, and ensuring sealing performance, integrality and
security of the whole
device.
[0012] In an optional embodiment, the row tube comprises an upper half
section connected to
the upper collecting tube and a lower half section connected to the lower
collecting tube, the
squeezing plug is movable inside the upper half section and the lower half
section, an inner
diameter of the upper half section is greater than an inner diameter of the
lower half section, and
the inner diameter of the lower half section is greater than or equal to an
outer diameter of the
squeezing plug.
[0013] In such way, when the device works, the squeezing plug is pushed by
the circulating
working medium to move upward to the upper half section, such that the
circulating working
medium may pass through the row tubes, and when the device stops working, the
squeezing plug
falls into the lower half section under action of gravity, such that the
circulating working medium
can be discharged from the row tubes.
3
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
[0014] In an optional embodiment, a lower end of the squeezing plug is a
spiked shape.
[0015] In an optional embodiment, a gravity of the squeezing plug is
greater than a buoyancy
when the squeezing plug is totally immerged into the circulating working
medium.
[0016] In an optional embodiment, a height of a center of gravity of the
solar heat absorber, a
height of a center of gravity of the heat gathering tube and a height of a
center of gravity of the
circulating pump are lowered sequentially.
[0017] In an optional embodiment, when the circulating working medium and
the squeezing
plug are standing still, a liquid level of the circulating working medium does
not exceed a top
surface of the squeezing plug.
[0018] In an optional embodiment, the heat gathering tube comprises:
[0019] an outer tube;
[0020] a liquid inlet tube in communication with outside of the outer tube
and one end of the
circulating tube; and
[0021] a liquid outlet tube having one end inserted inside of the outer
tube and provided with
an opening in communication with the outer tube, and the other end extending
out of the outer tube
and in communication with the other end of the circulating tube.
[0022] In such way, a heat release flow channel of the circulating working
medium between
the outer tube and the liquid outlet tube is formed, and the circulating
working medium dissipates
heat in the heat release flow channel. The heat dissipation flow channel is
long, and a heat transfer
medium is only tube walls of the outer tube, so heat transfer efficiency is
high.
[0023] In a second aspect, the invention provides an extrusion type frost
heave preventing and
heat gathering self-protective subgrade, the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective subgrade comprises a subgrade and the extrusion type
frost heave
preventing and heat gathering self-protective device according to any of the
previous
embodiments, wherein the solar heat absorber is mounted outside the subgrade,
and the heat
gathering tube is inserted inside the subgrade.
[0024] In an optional embodiment, the extrusion type frost heave preventing
and heat
gathering self-protective subgrade further comprises a heat preservation
material layer disposed
on a slope of the subgrade.
[0025] In such way, under condition of no solar radiation at night, the
whole device stops
working, and meanwhile the heat preservation material layer on an outer side
of the subgrade
effectively prevents large loss of heat inside the subgrade.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0026] To clearly explain the technical solution in the embodiment of the
invention,
hereinafter the desired accompanying drawings in the embodiment are simply
introduced. It shall
4
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
be understood that hereinafter the drawings only illustrate some examples of
the invention, so it
shall not be viewed as definition to the scope. As for those ordinary in the
art, on the premise of
making no creative work, other relevant drawings also can be obtained based on
these drawings.
[0027] FIG. 1 is a structural diagram of the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective subgrade provided in one embodiment of the
invention.
[0028] FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective device provided in one embodiment of the invention.
[0029] FIG. 3 is a structural diagram of the heat gathering tube in FIG. 2.
[0030] FIG. 4 is a state diagram when the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective device is working.
[0031] FIG. 5 is a side view of the solar heat absorber in FIG. 4.
[0032] FIG. 6 is a state diagram when the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective device stops working.
[0033] FIG. 7 is a side view of the solar heat absorber in FIG. 6.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
[0034] To make objects, technical solutions and advantages of the
embodiments of the
invention clearer, hereinafter the technical solution in the embodiments of
the invention is clearly
and completely described with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of
the invention.
Obviously, the described embodiments are a part of the embodiments of the
invention, not all
embodiments. Generally, components in the embodiments of the invention
described and
illustrated in the drawings can be arranged and designed in various different
configurations.
[0035] Therefore, detailed descriptions of the embodiments of the invention
provided in the
drawings do not aim to limit the scope protected by the invention, but only
represent the selected
embodiments of the invention. Based on the embodiments in the invention, on
the premise of
making no creative work, all other embodiments obtained by those ordinary in
the art belong to
the scope protected by the invention.
[0036] It shall be noticed that similar reference signs and letters
represent similar items in the
drawings, so once one item is defined in one drawing, it is unnecessary to
make further definition
and explanation in subsequent drawings.
[0037] In the descriptions of the invention, it shall be noted that if
orientation or positional
relation indicated by terms "up", "down", "in" and "out" is orientation or
positional relation
illustrated based on the drawings, or common placed orientation or positional
relation when the
invention products are used, it is only to facilitate describing the invention
and simplifying the
descriptions, not indicating or suggesting that the device or element must
have a specific
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
orientation, and is constructed and operated in a specific orientation, so the
invention is not limited
thereto.
[0038] In addition, if there are terms "first" and "second", they are for
distinguishing only,
instead of indicating or suggesting relative importance.
[0039] It shall be noted that in the case of not conflicting, features in
the embodiments of the
invention can be combined with each other.
[0040] The embodiment of the invention is just proposed against the key
scientific issue in
frost heave of the subgrade, starting from "temperature of the subgrade" in
three indispensable
factors "water, soil and temperature" produced by frozen heave of the
subgrade, thereby reaching
objects of controlling the temperature and preventing frozen heave of the
subgrade through the
device provided in the embodiments of the invention.
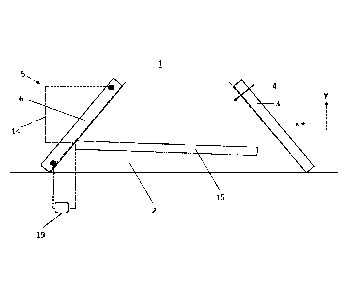
[0041] Referring to FIG. 1, this embodiment provides an extrusion type
frost heave preventing
and heat gathering self-protective subgrade 1, comprising a subgrade 2, a heat
preservation
material layer 3 and extrusion type frost heave preventing and heat gathering
self-protective
devices 5, wherein the extrusion type frost heave preventing and heat
gathering self-protective
devices 5 are evenly mounted on one side of a sunny slope or one side of a
shady slope of the
subgrade 2 at an interval.
[0042] The heat preservation material layer 3 is disposed on a slope of the
subgrade 2, can
cover the entire slope of the subgrade 2, and is fixed by an anchor rod 4. In
other embodiments,
the heat preservation material layer 3 also can be compacted and fixed by
covering a thin layer of
soil or other material on an outer surface of the heat preservation material
layer 3. The heat
preservation material layer 3 can select building rock wool heat preservation
material or an
integrated heat preservation plate. Specifically, the sunny slope and the
shady slope of the subgrade
2 can be provided with the heat preservation material layer 3, thereby
preventing heat loss inside
the subgrade 2, and effectively ensuring reservation of heat inside the
subgrade 2 in the process of
day-night change.
[0043] Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the extrusion type frost heave
preventing and heat
gathering self-protective device 5 comprises a solar heat absorber 6, a
circulating tube 14, a heat
gathering tube 15 and a circulating pump 19, wherein the solar heat absorber
6, the heat gathering
tube 15 and the circulating pump 19 are connected from head to tail
sequentially through the
circulating tube 14 to form a circulating loop where a circulating working
medium 20 is filled. The
circulating working medium 20 is a non-freezing refrigerating liquid, glass
water or other liquid
under a condition of -30 C, and has good flowability. The circulating tube 14
is a metallic tube or
a non-metallic tube resistant to wild solar radiation and aging.
[0044] The solar heat absorber 6 can be disposed in a natural surface
region close to a foot of
the sunny slope of the subgrade 2, and also can be disposed in a natural
surface region of the shady
6
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
slope of the subgrade 2 where sun can irradiate in winters, and the solar heat
absorber 6 is
configured to absorb solar energy and heats the circulating working medium 20.
[0045] The heat gathering tube 15 is used inserted the subgrade 2, and
transfers heat of the
circulating working medium to inside of the subgrade 2, such that the subgrade
2 is always in a
process of pure heat absorption and continuous accumulation of internal heat,
thereby reaching
heat gathering inside the subgrade and a state where the temperature is always
held to be positive,
and reaching objects of preventing and treating engineering diseases such as
soil freezing of the
subgrade 2 and frost heave of the subgrade 2.
[0046] The heat gathering tube 15 is inserted the subgrade 2 within a range
from a half to a
foot of the slope of the subgrade 2, and an insertion direction is
perpendicular to a length direction
of the subgrade 2. A length of the heat gathering tube 15 can be determined
according to actual
conditions of sites. On the same slope of the subgrade 2, an interval between
the two adjacent heat
gathering tubes 15 can be 1 m to 5 m. An angle between the heat gathering tube
15 and a horizontal
plane is within a range from -30 to 30 . In this embodiment, preferably, an
angle of the heat
gathering tube 15 upward lifting in a length direction from inside to outside
of the subgrade 2 is
0 to 30 , in particular, 5 to 10 . In other words, as shown in FIG. 1, an
angle of the heat gathering
tube 15 between extension along a direction x and upward lifting along a
direction y is 0 to 30 ,
such that a height of the heat gathering tube 15 is at a middle lower position
of the subgrade 2, and
the heat gathering tube 15 is across most regions of a width of the subgrade
2. In such way, it is
convenient to mount the heat gathering tube 15 in the subgrade 2, a drilling
depth is small and the
number thereof is few, and the original engineering structure of the subgrade
2 is not changed,
thereby ensuring stability of the original subgrade 2, having no influence on
normal driving of
trains during construction, and effectively solving difficulties in
engineering construction when
satisfying the condition of driving of the trains.
[0047] A height of a center of gravity of the solar heat absorber 6, a
height of a center of
gravity of the heat gathering tube 15 and a height of a center of gravity of
the circulating pump 19
are lowered sequentially. In such way, when the device stops working, the
circulating working
medium 20 in the solar heat absorber 6 flows out of the solar heat absorber 6
as much as possible
under action of gravity, and is stored in the heat gathering tube 15 or the
circulating pump 19.
[0048] Referring to FIG. 3, the heat gathering tube 15 comprises an outer
tube 16, a liquid
inlet tube 17 in communication with outside of the outer tube 16 and one end
of the circulating
tube 14, and a liquid outlet tube 18 at a bottom of the outer tube 16, having
one end inserted inside
of the outer tube 16 and provided with an opening in communication with the
outer tube 16, and
the other end extending out of the outer tube 16 and in communication with the
other end of the
circulating tube 14. In such way, a heat release flow channel of the
circulating working medium
20 is formed between the outer tube 16 and the liquid outlet tube 18, and the
circulating working
7
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
medium 20 dissipates heat in the heat release flow channel. The heat
dissipation flow channel is
long, and a heat transfer medium is only tube walls of the outer tube 16, so
heat transfer efficiency
is high. Design of the liquid inlet tube 17 and the liquid outlet tube 18
enables the circulating
working medium 20 to fill the heat gathering tube 15, such that more
sufficient heat exchange is
performed between the circulating working medium 20 and the tube walls,
thereby improving
heating efficiency of the heat gathering tube 15 to the subgrade.
[0049] Referring to FIGS. 4 and 5, arrows in FIG. 4 represent a flowing
direction of the
circulating working medium 20, and the solar heat absorber 6 comprises a solar
heat absorption
panel 7, and an upper collecting tube 8, a lower collecting tube 9, row tubes
10 and squeezing
plugs 13 mounted below the solar heat absorption panel 7.
[0050] The solar heat absorption panel 7 is mainly made of metallic or non-
metallic heat
absorption material, and has a thin thickness, and the specific thickness can
be 1 mm to 3 mm.
[0051] A section of the row tubes 10 is a cylindrical metallic tube, and
the row tubes 10 are a
diameter-varied structure. The row tube 10 comprises an upper half section 11
connected to the
upper collecting tube 8 and a lower half section 12 connected to the lower
collecting tube 9, the
squeezing plug 13 is movable inside the upper half section 11 and the lower
half section 12, and
an inner diameter of the upper half section 11 is greater than an inner
diameter of the lower half
section 12. Specifically, the inner diameter of the upper half section 11 can
be 1 to 2 times of the
inner diameter of the lower half section 12, and the inner diameter of the
lower half section 12 is
greater than or equal to an outer diameter of the squeezing plug 13.
[0052] A lower end of the squeezing plug 13 is a spiked shape. In such way,
in the process of
falling of the squeezing plug 13, the spiked shape can guide the squeezing
plug 13 to insert the
lower half section 12 of the row tubes 10. A gravity of the squeezing plug 13
is greater than a
buoyancy when the squeezing plug 13 is totally immerged into the circulating
working medium
20, such that when the device stops working, the squeezing plug13 can be
ensured to go down
freely, while extruding the circulating working medium 20 out of the row tubes
10.
[0053] Working principle of the extrusion type frost heave preventing and
heat gathering self-
protective device and subgrade thereof provided in this embodiment is as
follows:
[0054] Referring to FIGS. 4 and 5, when the device works, the circulating
working medium
20 circulates in the circulating tube 14 under driving of a pressure produced
by rotation of the
circulating pump 19. As for the squeezing plugs 13 in the row tubes 10, they
move upward to the
upper half section 11 of the row tubes 10 under action of a circulating
pressure and a pushing force
of the circulating working medium 20, circulating channels are opened, and the
circulating
working medium 20 starts circulation.
[0055] Referring to FIGS. 6 and 7, when the device stops working, such as,
in Summers, the
circulating working medium 20 stops circulation. Firstly, under action of
gravity, the circulating
8
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04
working medium 20 flows back to inside of the heat gathering tube 15 through
the circulating tube
14, and a liquid level of the circulating working medium 20 in the row tubes
10 starts decreasing
till a height of a liquid level of the device. Secondly, the squeezing plugs
13 further press the
circulating working medium 20 to the lower collecting tube 9 under action of
gravity, thereby
further emptying the working medium in the row tubes 10. Since the outer
diameter of the
squeezing plug 13 is substantially the same as the inner diameter of the lower
half section 12 of
the row tubes 10, the circulating working medium 20 in the lower half section
12 is substantially
emptied. Moreover, when the circulating working medium 20 and the squeezing
plug 13 are
standing still, the liquid level of the circulating working medium 20 (shown
by a dashed line in
FIG. 6) does not exceed a top surface of the squeezing plug 13, thereby
avoiding a sharp rise of
pressure of the whole device caused by boiling and vaporization of the
circulating working
medium 20 under a high temperature condition of the solar heat absorber 6 in
daytime of Summers,
and ensuring sealing performance, integrality and security of the whole
device.
[0056] Advantageous effects of the extrusion type frost heave preventing
and heat gathering
self-protective device and subgrade thereof provided in this embodiment
comprise:
[0057] 1. Heat absorbed by the solar heat absorber 6 is transferred to the
heat gathering tube
15 via the circulating working medium 20 to heat soil around the heat
gathering tube 15 through
continuous heat release of the heat gathering tube 15 inside the subgrade,
such that the subgrade
is always in a process of pure heat absorption and continuous accumulation of
internal heat, thereby
reaching heat gathering inside the subgrade and a state where the temperature
is always held to be
positive, and reaching objects of preventing and treating engineering diseases
such as soil freezing
of the subgrade and frost heave of the subgrade.
[0058] 2. The squeezing plugs 13 can empty the circulating working medium
20 from the row
tubes 10 by designing the row tubes 10 to be dimeter-varied tubes, and
disposing the squeezing
plugs 13 in the row tubes 10, thereby avoiding issues of sealing performance
and integrality of the
device threatened by an increase of pressure of the device caused by boiling
and vaporization of
the circulating working medium 20, enhancing stability of the device in
heating of the subgrade in
the seasonally frozen soil region, and better preventing and controlling frost
heave of the subgrade.
[0059] 3. The squeezing plugs 13 may select rubber to achieve the objects
of the device. The
device has characteristics of simple and useful and good stability, but can
better solve technical
and scientific difficulty of stability of the device.
[0060] The above disclosures are only detailed embodiments of the
invention, but the
protection scope of the invention is not limited thereto. Easily conceivable
change or substitution
for any skilled in the art within the technical range disclosed by the
invention shall be covered
within the protection scope of the invention. Therefore, the protection scope
of the invention shall
be subjected to the scope protected by the appended claims.
9
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-04