Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
HYDRAULIC EXCAVATOR CONTROL SYSTEM AND METHOD
Technical Field
The present invention relates to a hydraulic excavator control system and
method, and belongs
to the technical field of hydraulic excavators.
Background
Working conditions for the hydraulic excavator are extremely complicated, and
loads are
greatly changed. When the load of a hydraulic pump is increased, an engine
increases an oil
injection quantity, and an output torque is increased; due to mechanical
transmission, the engine
would have a relatively long hysteresis quality The following working states
would frequently
occur to the engine: one is that when the engine is suddenly loaded in a low
load state, the loading
time would be excessively long, rendering reduction of the working efficiency;
the second one is
that when the engine is suddenly loaded in an idle state, a problem of black
smoke would occur.
Most manufacturers would reduce the loading time of the engine by changing a
mixture ratio of
oil to gas in a combustion chamber of the engine; however, at the same time,
the problems of
inadequate combustion and black smoke of the engine would occur; when the
problem of the black
smoke occurs when in the idle speed, most manufacturers would improve the idle
rotation speed
of the complete machine, rendering energy consumption and wastes.
Summary
The purpose of the present invention is to overcome disadvantages in the prior
at and provide
a hydraulic excavator control system and method to solve the technical
problems of reduction of
the working efficiency when the engine is suddenly loaded in a low load state
and the occurrence
of black smoke when the engine is suddenly loaded in an idle state.
To resolve the technical problems above, the technical solution adopted in the
present
invention is as follows.
For a first aspect, the present invention provides a hydraulic excavator
control method,
including the following steps:
collecting, by a controller, an oil path pressure signal of a hydraulic
excavator, and calculating
a required main pump power according to the oil path pressure signal;
_ a _
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
sending, by the controller, the required main pump power to an engine ECM; and
first adjusting, by the engine ECM, an engine oil injection quantity according
to the
required main pump power, and then adjusting, by the controller, a main pump
power
according to the required main pump power.
By combining with the first aspect, furthermore, the oil path pressure signal
includes a
main oil path pressure value of the hydraulic excavator and each pilot
pressure value
corresponding to a current action of the hydraulic excavator.
By combining with the first aspect, furthermore, the time for the engine ECM
to start to
adjust the engine oil injection quantity is ahead of the time for the
controller to start to adjust
the main pump power by 0.05-0.6 second.
For a second aspect, the present invention provides a hydraulic excavator
control system
including a controller, an engine ECM, and an oil path pressure collection
unit, where the
engine ECM and the oil path pressure collection unit are respectively
communicationally
connected to the controller;
the controller calculates, according to an oil path pressure signal of a
hydraulic excavator
collected by the oil path pressure collection unit, a required main pump power
of the hydraulic
excavator, and sends the required main pump power to the engine ECM; and
the engine ECM first adjusts an engine oil injection quantity according to the
required
main pump power, and then the controller adjusts a main pump power according
to the
required main pump power.
By combining with the second aspect, furthermore, the controller is
communicationally
connected to the engine ECM using a CAN bus.
By combining with the second aspect, furthermore, the oil path pressure
collection unit
includes a first pressure sensor configured to collect a main oil path
pressure value of the
hydraulic excavator and a second pressure sensor configured to collect each
pilot pressure
value corresponding to a current action of the hydraulic excavator.
As compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects achieved by the present
invention
are the time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine oil injection
quantity is earlier
- 2 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
than the time for adjusting the main pump to the required main pump power, so
as to greatly reduce
a loading response time of the engine, improve a working efficiency of the
whole machine, avoid
the problem of black smoke from idle loading, and may further reduce an idle
rotation speed of
the engine and reduce fuel oil consumption. In addition, the control method
further has advantages
of simple implementations, low costs, and high reliability.
Brief Description of the Drawings
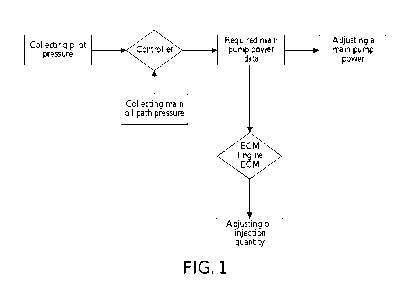
FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a hydraulic excavator control method according to an
embodiment of
the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a hydraulic principle diagram of a hydraulic excavator control
system according to
an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a relation diagram between an engine oil injection quantity of a
hydraulic excavator
and time in the prior art.
FIG. 4 is a relation diagram between an engine oil injection quantity of a
hydraulic excavator
and time according to an embodiment of the present invention.
10-engine; 11-main pump; 12-pilot pump; 13-electromagnetic proportional valve;
14-main
value; 15-hydraulic pilot handle; 16-controller; 17-traveling valve core; 18-
rotation value core;
19-moving arm valve core; 20-scraper pan valve core; 21-pan rod valve core;
and 22-
electromagnetic valve.
Detailed Description
The following further describes the hydraulic excavator control system and
method provided
in the present invention in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings
and specific
embodiments. It should be explained that the accompanying drawings all adopt a
quite simplified
mode, all use imprecise proportions, and only conveniently and clearly assist
the explanation of
the purposes of the embodiments of the present invention. Same or similar
reference numerals in
the accompanying drawings represent same or similar members.
Embodiment I
FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a hydraulic excavator control method according to an
embodiment of
the present invention. The method mainly includes the following steps:
- 3 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
collecting a main oil path pressure value of the hydraulic excavator and each
pilot
pressure value corresponding to a current action of the hydraulic excavator;
obtaining, by the
controller, a required main pump power according to the main oil path pressure
value and each
pilot pressure value corresponding to the current action of the hydraulic
excavator, and
sending the required main pump power to an engine ECM; the controller being
capable of
adjusting the main pump power according to the required main pump power; the
engine ECM
being capable of adjusting an engine oil injection quantity according to the
required main
pump power, and the time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine oil
injection being
earlier than the time for the controller to start to adjust the main pump
power.
The time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine oil injection being
earlier than
the time for the controller to start to adjust the main pump power can greatly
reduce a loading
response time of the engine, improve a working efficiency of the whole
machine, avoid the
problem of black smoke from idle loading, and may further reduce an idle
rotation speed of
the engine and reduce fuel oil consumption. In addition, the control method
further has
advantages of simple implementations, low costs, and high reliability.
More specifically, the time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine
oil injection
quantity is ahead of the time for the controller to start to adjust the main
pump power by 0.05-
0.6 second, which matches and is consistent with the hydraulic system
requirements, and
improves the working efficiency of the entire machine by 1-5%.
Embodiment II
FIG. 2 is a hydraulic principle diagram of a hydraulic excavator control
system according
to an embodiment of the present invention. The system includes an engine 10, a
main pump
11, a pilot pump 12, an electromagnetic proportional valve 13, a main value
14, a hydraulic
pilot handle 15, a controller 16, a first pressure collection unit, and a
second pressure
collection unit.
The engine 10 is connected to the main pump 11 and the pilot pump 12 for
providing
power for the main pump 11 and the pilot pump 12.
The main valve 14 includes a traveling valve core 17, a rotation value core
18, a moving
arm valve core 19, a scraper pan valve core 20, and a pan rod valve core 21.
After an outlet of
- 4 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
the main pump 11 is connected to an inlet of the main valve 14 through a
pipeline, it is sequentially
connected to the traveling valve core 17, the rotation value core 18, the
moving arm valve core 19,
the scraper pan valve core 20, and the pan rod valve core 21 for providing oil
for each action valve
core and constituting a main oil path; an oil return port of the main valve 14
is connected to an oil
tank after passing through an electromagnetic valve 22.
The pilot pump 12 is connected to an inlet of the electromagnetic proportional
valve 13; a path
of an outlet of the electromagnetic proportional valve 13 is connected to a
tilting plate adjuster
control port of the main pump 11.
The hydraulic pilot handle 15 is separately connected to a pilot control oil
port of each action
valve core for controlling connection and disconnection of each action valve
core.
The first pressure collection unit and the second pressure collection unit are
respectively in
communicative connection to the controller 16. The first pressure collection
unit is used for
collecting the main oil path pressure value of the hydraulic excavator; the
second pressure
collection unit is used for collecting the pilot control oil path pressure
value of each action valve
core; the controller 16 can obtain the required main pump power according to
the main oil path
pressure value and the pilot control oil path pressure value of each action
valve core and adjust the
power of the main pump 11 of the hydraulic excavator according to the required
main pump power.
The controller 16 is communicationally connected to the engine ECM for
delivering the
required main pump power to the engine ECM of the hydraulic excavator.
The time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine oil injection
quantity is ahead of the
time for the controller to start to adjust the main pump power; the time
difference is generally 0.05-
0.6 second, which can match and be consistent with the hydraulic system
requirements, and
improve the working efficiency of the entire machine by 1-5%. FIG. 3 is a
relation diagram
between an engine oil injection quantity of a hydraulic excavator and time in
the prior art. FIG. 4
is a relation diagram between an engine oil injection quantity of a hydraulic
excavator and time
according to an embodiment of the present invention. The relation diagram is
obtained when the
difference between the time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine
oil injection and the
time for the controller to start to adjust the main pump power is 0.1 second;
as can be seen from
comparison and analysis that as compared with the hydraulic excavator in the
prior art, a hydraulic
- 5 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
excavator provided in embodiment II of the present invention can greatly
reduce a loading
response time of the engine 10, so as to improve a working efficiency of the
whole machine, and
avoid the problem of black smoke from idle loading, and may further reduce an
idle rotation
speed of the engine 10 and reduce fuel oil consumption. In addition, it
further has advantages
of simple implementations, low costs, and high reliability
The first pressure collection unit, the second pressure collection unit, and
the engine ECM
can be connected to the controller 16 through the CAN bus.
The first pressure collection unit and the second pressure collection unit are
pressure
sensors; as shown in FIG. 2, a pressure sensor is separately disposed on the
pilot control oil
path of the rotation value core 18, the moving arm valve core 19, the scraper
pan valve core
20, and the pan rod valve core 21.
In conclusion, the hydraulic excavator control system and method provided by
the
embodiment of the present invention includes: collecting a main oil path
pressure value of the
hydraulic excavator; obtaining, by a controller, a required main pump power
according to the
oil path pressure value; the controller being used for adjusting, according to
the required main
pump power, the power of the main pump and delivering the required main pump
power to an
engine ECM; the time for the engine ECM to start to adjust the engine oil
injection being
earlier than the time for the controller to start to adjust the main pump
power so as to greatly
reduce a loading response time of the engine, improve a working efficiency of
the whole
machine, avoid the problem of black smoke from idle loading, and further
reduce an idle
rotation speed of the engine and reduce fuel oil consumption. In addition, the
control method
further has advantages of simple implementations, low costs, and high
reliability.
It should be explained that each embodiment in this specification is described
in a
progressive manner; each embodiment mainly illustrates the difference from
other
embodiments; same and similar parts among the embodiments can refer to one
another. For
the control method disclosed in the embodiments, since the adopted control
device partially
corresponds to the device disclosed by the embodiments, the description of the
control device
involved therein is relatively simple and the relevance can refer to the
explanation of the
device part.
- 6 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2
The descriptions above are only used for describing the preferable embodiments
of the present
invention, rather than any limitation to the range of the present invention;
any change and
modification made by a person having ordinary skilled in the art of the
present invention according
to the contents disclosed above is within the scopes of protection of the
claims.
- 7 -
CA 03150007 2022-3-2