Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
ELECTRIC MOTOR CONTROL UNIT HAVING REDUNDANT CONTROL AND
ASSEMBLY METHOD THEREFOR
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] The disclosure relates to a motor control unit having redundancy
control and a
combination method thereof.
BACKGROUND
[0002] An air-conditioner outdoor or indoor unit typically includes a
centrifugal blower,
a furnace blower motor, a compressor motor, or an axial-flow fan motor. The
parameters
of these motors, such as voltage, power, signal communication, or torque, vary
with
manufacturers. As shown in FIGS. 2-4, a brushless AC motor or an
electronically
commutated motor (ECM) typically includes a main body la and a motor
controller 2a;
the main body la comprises a stator assembly 12a, a rotor assembly 13a, a
housing
assembly 11a, and a bearing; the motor controller 2a typically comprises a
control box
21a and a control board 22a; and the control board 22a is the integration of
function
circuits. When an important part breaks down, many technicians choose to
replace the
whole motor controller or the whole motor instead of repairing the damaged
part. This
often translates to high replacement costs.
[0003] Electronic components are typically integrated onto one or two circuit
boards in
the conventional motor controller, which increases hard to meet the needs of
different
customers. For examples, a customer may need a 5-speed PWM motor controller, a
0-
10VDC motor controller, a 10-speed motor controller matching 0-10VDC, a single
motor
controller in an outdoor unit, a plurality of motor controllers in an outdoor
unit, or a 3 HP
motor controller; the circuit board or the control box typically has a fixed
size; and the
circuit board only offers limited functions.
[0004] Thus, it is necessary to consider a motor controller with convenient
production
and assembly, short design and production cycle, and easy maintenance and
replacement,
and the maintenance cost of the motor controller in the after-sales market is
very low.
1
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0005] When damage occurs to a motor control unit, the broken part should be
replaced
with a new one that can immediately respond to a control system, thus
increasing the
operational reliability of the motor control unit.
SUMMARY
[0006] The disclosure provides a motor control unit having redundancy control
and a
combination method thereof, so as to solve the problems of inflexible and
inconvenient
production of the motor controller in the after-sales market, long research
and
development time and production time, inconvenient after-sales maintenance and
high
maintenance cost.
[0007] The disclosure adopts the following technical solutions.
[0008] The motor control unit having redundancy control comprises:
[0009] a first function module, referring to a power supply module that is
connected to an
electric supply and converts alternating current to direct current to supply
for other
function modules;
[0010] a second function module, referring to a motor control module that
controls the
operation of a motor; the motor control module comprises a motor control
microprocessor, an IGBT inverter, and a heat sink; the motor control module
receives DC
power and control signals and supplies power to the main body of the motor so
as to
control the rotational speed, torque, or air volume of the motor;
[0011] a third function module, referring to an I/0 module that allows signal
transmission between a main control board or a peripheral device and the motor
control
module; wherein the motor controller comprises at least one third function
module, and a
plurality of third function modules is optionally disposed between a main
control board
or a peripheral device and the motor control module for signal transmission;
[0012] a fourth function module, referring to a redundancy control module that
starts a
spare function module when the first, second or third function module has an
emergency;
and
2
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0013] a fifth function module, referring to at least one spare function
module that
performs the same function as the first function module, the second function
module, or
the third function module.
[0014] The above function modules are combined into a single motor control
unit.
[0015] The redundancy control module comprises a redundancy control
microprocessor,
a plurality of relays, a screen circuit, and a bus access circuit; the bus
access circuit
allows signal communication between the redundancy control microprocessor and
other
function modules; the redundancy control microprocessor starts the spare
function
module via the plurality of relays; and the screen circuit is configured to
display the
working status of other function modules.
[0016] Optionally, the first function module, the third function module, and
the spare
function module further independently comprise a network communication unit;
the
network communication unit comprises a bus microprocessor, a bus communication
access circuit, and a function detection circuit; the function detection
circuit performs a
function inspection to its function module and transmits the signal to the bus
communication access circuit; and data is transmitted between the bus
microprocessor
and the redundancy control microprocessor via the bus communication access
circuit and
a data bus.
[0017] Each function module comprises an independent shell, a first circuit
board, an
interface connector, and a heat sink; the shell comprises metal or plastic;
the first circuit
board is disposed in the shell; the interface connector is partially disposed
on the first
circuit board to allow the transmission of power and control signals; and the
heat sink is
disposed outside or inside the shell.
[0018] The 1/0 module comprises at least one module selected from the group
comprising:
[0019] a multi-speed 24VAC input module that receives a 24VAC signal from the
main
control board and sends the signal to the motor control module;
[0020] a PWM input module that receives a PWM signal from the main control
board
and sends the signal to the motor control module;
3
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0021] a 0-10VDC input module that receives a 0-10VDC signal and sends the
signal to
the motor control module;
[0022] a RS485 serial communication module that implements a communication
protocol
supported by a driver for the motor control module;
[0023] a Bluetooth module that allows the motor control module to communicate
with an
app or a computer for motor configuration;
[0024] a pulse output module that outputs a pulse for representing a motor
parameter;
and
[0025] an Ethernet local area network module that supports a TCP/TP protocol
for
allowing the motor control module to connect into a building control network
or to
monitor and control the motor parameters over network;
[0026] a human-machine interface (HMI) function module that comprises a color
and
monochrome screen for offering a high resolution display; the HMI function
module is
used to display information about the rotational speed, torque or air volume
of the motor,
making it convenient for the user to perform a configuration setting or
experimental test;
and
[0027] a DIP switch module that is connected to motor control module by the
interface
connector; and the DIP switch module comprises a set of switches for changing
the motor
parameters.
[0028] The motor control unit further comprises a mechanical mounting base and
a
second circuit board disposed in the mechanical mounting base; the above
function
modules are connected to each other via the second circuit board or a
plurality of flexible
cables so as to allow the transmission of power and control signals.
[0029] The motor control unit comprises two second function modules for
controlling the
operation of two motors, respectively.
[0030] The at least one spare function module is optionally used as a backup
of the
power supply module, the motor control module, and the 1/0 module.
4
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0031] A combination method of the motor control unit comprises dividing the
motor
control unit into a plurality of function modules according to functions of
the motor
control unit; and the plurality of function modules comprises:
[0032] a first function module, referring to a power supply module that is
connected to an
electric supply and converts alternating current to direct current to supply
for other
function modules; optionally, different power supply modules are formed to
match the
input voltage and power;
[0033] a second function module, referring to a motor control module that
controls the
operation of the motor; the motor control module comprises a microprocessor,
an IGBT
inverter, and a heat sink; when receiving VDC power and control signals, the
motor
control module supplies electricity to the motor so as to control the
rotational speed,
torque, or air volume of the motor; optionally, different motor control
modules are
formed to match the input power;
[0034] a third function module, referring to at least one I/0 module that
allows signal
transmission between the motor control module and a main control board or a
peripheral
device;
[0035] a fourth function module, referring to a redundancy control module that
starts a
spare function module when the first, second or third function module has an
emergency;
and
[0036] a fifth function module, referring to at least one spare function
module that
performs the same function as the first function module, the second function
module, or
the third function module.
[0037] The power supply module, the motor control module, the at least one I/0
module,
the redundancy control module, and the spare function module are combined into
a motor
control unit that matches the parameters of the motor.
[0038] The I/0 module comprises at least one module selected from the group
comprising: a multi-speed 24VAC input module for receiving a 24VAC signal from
the
main control board and sending the signal to the motor control module; a PWM
input
module for receiving a PWM signal from the main control board and sending the
signal
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
to the motor control module; a 0-10VDC input module for receiving a 0-10VDC
signal
and sending the signal to the motor control module; a RS485 serial
communication
module for implementing a communication protocol that is supported by a driver
for the
motor control module; a Bluetooth module for allowing the motor control module
to
communicate with an app or a computer for motor configuration; a pulse output
module
for outputting a pulse that represents a parameter of the motor; an Ethernet
local area
network module for supporting a TCP/TP protocol that allows the motor control
module
to connect into a building control network or monitors and controls the motor
parameters
over network; a human-machine interface (HMI) function module that comprises a
color
and monochrome screen for offering a high resolution display to show the
rotational
speed, torque or air volume of the motor, making it convenient for the user to
perform a
configuration setting or experimental test; and a DIP switch module connected
to the
motor control module via the interface connector, and the DIP switch module
comprises a
set of switches for changing the motor parameters.
[0039] Each function module comprises an independent shell, a first circuit
board, and
other electronic components; the shell comprises metal or plastic; the first
circuit board
and other electronic components are disposed in the shell; the motor control
unit further
comprises a mechanical mounting base and a second circuit board disposed in
the
mechanical mounting base; the above function modules are fixedly disposed on
the
mechanical mounting base, and connected to each other via the second circuit
board to
allow the transmission of power and control signals.
[0040] The second circuit board comprises a DC power supply interface and a
bus
interface, both of which are used to connect the function modules to the
second circuit
board.
[0041] The following advantages are associated with the motor control unit of
the
disclosure:
[0042] 1. The motor control unit is divided into a plurality of function
modules based on
function, comprising: a first function module referring to a power supply
module that is
connected to an electric supply and converts alternating current to direct
current to supply
for other modules, and different power supply modules may be formed to match
the input
6
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
voltage and power; a second function module referring to a motor control
module that
controls the speed, torque or air flow of a motor by receiving VDC power and a
control
signal, and by supplying a UVW three-phase electric current to the main body
of motor;
the motor control module comprises a microprocessor, an IGBT inverter
component, and
a heat sink; different motor control modules are formed to match the input
power; a third
function module referring to an I/0 module that allows signal transmission
between a
main control board or a peripheral device and the motor control module; a
fourth function
module, referring to a redundancy control module that starts a spare function
module
when the first function module, the second function module, or the third
function module
has an emergency; and a fifth function module, referring to at least one spare
function
module that performs the same function as the first function module, the
second function
module, or the third function module.
[0043] 2. Other advantages associated with the motor control unit are
described with
reference to the following embodiments.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0044] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a conventional HVAC system;
[0045] FIG. 2 is a perspective view of a conventional BLDC motor;
[0046] FIG. 3 is a perspective view of a conventional BLDC motor controller;
[0047] FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of a conventional BLDC motor;
[0048] FIG. 5 is a block diagram of a motor controller according to Example 1
of the
disclosure;
[0049] FIG. 6 is a block diagram for function modules according to Example 1
of the
disclosure;
[0050] FIG. 7 is a block diagram of a redundancy control module according to
Example
1 of the disclosure;
[0051] FIG. 8 is a perspective view of a function module according to Example
1 of the
disclosure;
7
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0052] FIG. 9 is an exploded view of a redundancy control module according to
Example
1 of the disclosure;
[0053] FIG. 10 is a perspective view of a mechanical mounting base according
to
Example 1 of the disclosure;
[0054] FIG. 11 is an exploded view of a mechanical mounting base according to
Example
1 of the disclosure;
[0055] FIG. 12 is an exploded view of a combined motor control unit according
to
Example 1 of the disclosure;
[0056] FIG. 13 is a perspective view of a combined motor control unit
according to
Example 1 of the disclosure;
[0057] FIG. 14 is a perspective view of a motor control unit comprising a
redundancy
control module according to Example of the disclosure;
[0058] FIG. 15 is a block diagram of a network communication unit according to
Example 1 of the disclosure;
[0059] FIG. 16 is a block diagram of a power supply module according to
Example 1 of
the disclosure;
[0060] FIG. 17 is a block diagram of a RS485 serial communication module
according to
Example 1 of the disclosure;
[0061] FIG. 18 is a block diagram of a PWM input module according to Example 1
of
the disclosure; and
[0062] FIG. 19 is a block diagram of a 5-speed 24VAC input module according to
Example 1 of the disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0063] To further illustrate the disclosure, embodiments detailing the motor
control unit
and the combination method thereof are described below. It should be noted
that the
following embodiments are intended to describe and not to limit the
disclosure.
8
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
Example 1
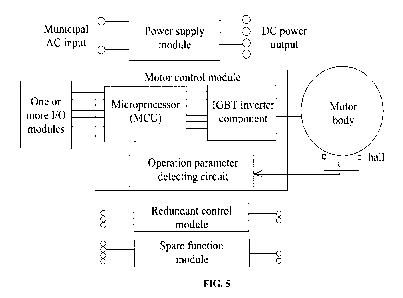
[0064] Referring to FIGS. 5 and 6, a motor control unit comprises:
[0065] a first function module, referring to a power supply module that is
connected to an
electric supply and converts alternating current to direct current to supply
for other
function modules;
[0066] a second function module, referring to a motor control module that
controls the
operation of a motor; the motor control module comprises a motor control
microprocessor, an IGBT inverter, and a heat sink; the motor control module
receives
VDC power and control signals and supplies power to the motor so as to control
the
rotational speed, torque, or air volume of the motor;
[0067] a third function module, referring to at least one 1/0 module that
allows signal
transmission between the motor control module and a main control board or a
peripheral
device;
[0068] a fourth function module, referring to a redundancy control module that
starts a
spare function module when the first function module, the second function
module, or the
third function module has an emergency; and
[0069] a fifth function module, referring to at least one spare function
module that
performs the same function as the first function module, the second function
module, or
the third function module.
[0070] The above function modules are combined into a single motor control
unit.
[0071] Referring to FIG. 7, the redundancy control module comprises a
redundancy
control microprocessor, a plurality of relays, a screen circuit, and a bus
access circuit; the
bus-communication access circuit allows signal communication between the
redundancy
control microprocessor and other function modules; when a function module is
broken,
the redundancy control microprocessor starts the spare function module via the
plurality
of relays; and the screen circuit comprises a plurality of LED lights, such as
an 8-segment
LED screen or a color screen, used to display the running status of each
function module
(that is, to indicate which function module is broken or running). The
redundancy control
module further comprises a signal input interface circuit for receiving an
external signal.
9
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
The signal input interface circuit further comprises at least one 5-speed
24VAC signal
input interface. Optionally, the redundancy control module further comprises a
PWM
signal input interface circuit, a 0-10VDC signal input interface circuit, a
serial
communication interface circuit, or a combination thereof. As shown in FIGS. 6
and 7,
the redundancy control module comprises N relays numbered JK1, JK2õ JKN; and
the N relays are used to start the power supply module, the motor control
module, the I/0
module, and the spare function module.
[0072] The function modules are packaged together to form a motor control unit
that
offers advantages such as high levels of flexibility and adaptability, easy
replacement of a
single function module, low maintenance cost, and short product development
cycle.
[0073] Each function module comprises an independent shell, a first circuit
board, an
interface connector, and a heat sink; the shell comprises metal or plastic;
the interface
connector is partially disposed on the first circuit board to allow the
transmission of
power and control signals; the heat sink is disposed outside or inside the
shell.
[0074] The I/0 module comprises at least one module selected from the group
comprising:
[0075] a multi-speed 24VAC input module that receives a 24VAC signal from the
main
control board and sends the signal to the motor control module;
[0076] a PWM input module that receives a PWM signal from the main control
board
and sends the signal to the motor control module;
[0077] a 0-10VDC input module that receives a 0-10VDC signal and sends the
signal to
the motor control module;
[0078] a R5485 serial communication module that implements a communication
protocol
supported by a driver for the motor control module;
[0079] a Bluetooth module that allows the motor control module to communicate
with an
app or a computer for motor configuration;
[0080] a pulse output module that outputs a pulse for representing a parameter
of the
motor; and
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0081] an Ethernet local area network module that supports a TCP/TP protocol
for
allowing the motor control module to connect into a building control network
or monitor
and regulate the motor parameters over network;
[0082] a human-machine interface (HMI) function module that comprises a color
and
monochrome screen for offering a high resolution display; the HMI function
module is
used to display information about the rotational speed, torque or air volume
of the motor,
making it convenient for the user to perform a configuration setting or
experimental test;
and
[0083] a DIP switch module that is connected to the motor control module
through the
interface connector; the DIP switch module comprises a set of switches for
changing the
motor parameters.
[0084] The motor control unit further comprises a mechanical mounting base and
a
second circuit board disposed in the mechanical mounting base. The above
function
modules are fixedly disposed on the mechanical mounting base, and connected to
each
other via the second circuit board or a plurality of flexible cables to allow
the
transmission of power and control signals.
[0085] The motor control unit comprises two second function modules for
controlling the
operation of two motor controllers in an indoor or outdoor unit, respectively.
[0086] The at least one spare function module refers to a spare power supply
module, a
spare motor control module, a spare I/0 module, or a combination thereof.
[0087] As shown in FIGS. 8-14, the first function module, the second function
module,
the third function module, the fourth function module, and the fifth function
module are
fixedly disposed on the mechanical mounting base 100; the mechanical mounting
base
comprises a plurality of power supply bus interfaces 103a and a plurality of
data bus
interfaces 103b, both of which allow the transmission of power and control
signals
between the function modules.
[0088] As shown in FIGS. 8-14, each function module comprises an independent
shell
lb, a first circuit board 2b, a power supply interface 3a, and a bus interface
3b, and a
plurality of signal interfaces 3c; the shell comprises metal or plastic; the
first circuit board
11
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
is fixedly disposed in the shell; the number of the signal interfaces is
determined
according to that of the I/0 modules connected to the motor control module 3c;
the motor
control module further comprises a power interface and an output terminal, and
the
output terminal is connected to the main body of the motor.
[0089] Each of the power supply interface 3a and the bus interface 3b are
partially
disposed on the first circuit board and exposed on the face of a panel on the
shell so as to
be electrically connected to one of the plurality of power supply bus
interface 103a or the
data bus interface 103b.
[0090] The mechanical mounting base 100 comprises a first shell 101, a second
shell
102, and a second circuit board 104; the first shell 101 is integrated with
the second shell
102 to form a chamber; the second circuit board 104 is disposed in the
chamber, and
comprises a plurality of power supply bus interfaces 103a and a plurality of
data bus
interface 103b, both of which are partially inserted through the second
circuit board 104
and disposed in multiple rows on the mechanical mounting base 100, each row
with one
power supply bus interface 103a and one data bus interface 103b.
[0091] When the power supply interface 3a is connected to the power supply bus
interface 103a, the electricity is released to the input terminal of the power
supply
module, and the output terminal of the power supply module outputs the DC
power to a
plurality of power supply buses. Vcc 1 represents the high DC bus voltage
(e.g., 325VDC)
supplied to the IGBT inverter component; Vcc2 represents the low DC bus
voltage (e.g.,
+5VDC) supplied to the motor control microprocessor; and GND represents the
ground.
As shown in FIG. 6, the plurality of data buses and the plurality of power
supply buses
are mounted on the second circuit board inside the mechanical mounting base
100; and
the second circuit board further comprises a function circuit for bus
communication.
[0092] As shown in FIG. 15, each of the first function modules, the third
function
module, and the spare function module further comprises a network
communication unit;
the network communication unit comprises a bus microprocessor, a bus
communication
access circuit, and a function detection circuit; the function detection
circuit performs a
function inspection to the function module in which it is disposed, and
transmits the
signal to the bus microprocessor; and data is transmitted between the bus
microprocessor
12
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
and the redundancy control microprocessor via the bus communication access
circuit and
the data bus. Optionally, the motor control module further comprises the bus
communication access circuit which enables the motor control microprocessor to
access
the data bus for data transfer between the motor control microprocessor and
other
function modules.
[0093] As shown in FIGS. 12 and 13, the power supply module 7, the motor
control
module 8, the Bluetooth module 9 (i.e., one I/0 module), and the PWM input
module
(i.e., another I/0 module) are disposed sequentially to form a motor control
unit.
Optionally, the motor control unit further comprises an Ethernet local area
network
module, a DIP switch module, or other function modules.
[0094] As shown in FIG. 14, the motor control unit further comprises a
redundancy
control module and a plurality of spare function modules so as to keep the
motor (or an
air conditioning system) running smoothly. The power supply module 7, the
motor
control module 8, the Bluetooth module 9 (i.e., one I/0 module), the PWM input
module
(i.e., another I/0 module), the redundancy control module 11, a first spare
function
module 12 (i.e., a spare power supply module), and a second spare function
module 13
(i.e., a spare motor control module), and a third spare function module (i.e.,
a spare
Bluetooth module) are disposed sequentially to form a motor control unit. For
example,
when the Bluetooth module 9 is broken, the redundancy control module 11 starts
the third
spare function module 14 to ensure the motor runs smoothly; when the motor
control
module 8 is broken, the second spare function module 13 starts running under
control of
the redundancy control module. The screen circuit is used to display the
status of the
function modules (that is, to indicate which function module is broken or
running).
[0095] When the network communication unit is unnecessary, the redundancy
control
module continuously sends a query to the motor control module to check if the
DC bus
voltage, rotational speed, torque, air volume and other parameters of the
motor are in the
present ranges.
[0096] FIG. 16 is a block diagram of a power supply module of the disclosure.
The
power supply module comprises a surge protection circuit, a filter circuit, a
DC/DC
converter circuit, and a network communication unit; the network communication
unit
13
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
comprises a bus microprocessor, a bus communication access circuit, and a
function
detection circuit; the function detection circuit performs a function
inspection to the
function module in which it is disposed, and transmits the signal to the bus
microprocessor; and data is transmitted between the bus microprocessor and the
redundancy control microprocessor via the bus communication access circuit and
a data
bus. The power supply module supplies direct current Vccl (e.g., 325VDC), Vcc2
(e.g.,
15VDC), Vcc3 (e.g., 5 VDC), and the ground GND; Vcc 1 represents the DC bus
voltage
supplied to the motor. Vcc2 supplies 15VDC to the IGBT inverter component; and
Vcc3
supplies 5VDC to the motor control microprocessor. The function detection
circuit is a
universal voltage detection circuit that can check if the voltage is in a
specific range.
[0097] FIG. 17 is a block diagram of a RS485 serial communication module of
the
disclosure. The RS485 serial communication module comprises a network
communication unit through which the RS485 serial communication module can be
inspected for function and allowed to access the data bus. And the signal
communication
is achieved between the RS485 serial communication module and the redundancy
control
microprocessor or the motor control module.
[0098] FIG. 18 is a block diagram of a PWM input module of the disclosure. The
PWM
input module comprises a network communication unit through which the PWM
input
module can be inspected for function and allowed to access the data bus. And
the signal
communication is achieved between the RS485 serial communication module and
the
redundancy control microprocessor or the motor control module.
[0099] FIG. 19 is a block diagram of a 5-speed 24VAC input module of the
disclosure.
The 5-speed 24VAC input module comprises a network communication unit through
which the 5-speed 24VAC input module can be inspected for function and allowed
to
access the data bus. And the signal communication is achieved between the
RS485 serial
communication module and the redundancy control microprocessor or the motor
control
module.
[0100] A spare function module and its redundancy control module are necessary
for
redundancy control of a function module. In certain examples, a motor control
unit
comprises a redundancy control module, a motor control module, and a spare
motor
14
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
control module. The motor control module and the spare motor control module
are
connected to a DC bus of a power supply and a three-phase line of a motor.
Under normal
conditions, as the motor control module runs, the spare motor control module
is
disconnected from the three-phase line by the relay of the spare motor control
module
and the three-phase line of the motor.
[0101] The redundancy control module continuously communicates with the motor
control module via a communication bus so as to check if the motor control
module is
operated normally. When the redundancy control module does not receive a
status code N
consecutive times that is sent by the motor control module based on a
communication
protocol, the motor control module is considered broken. Then the redundancy
control
module disconnects the relay of the motor control module, and connects to the
relay of
the spare motor control module to keep the motor running. To display the
status of each
function module, an 8-segment LED screen is used to display different numbers
or a
color LED screen is used to display a prompt or a pattern.
[0102] In certain examples, a motor control unit comprises a motor control
module, a
redundancy control module, a power supply module, and a spare power supply
module.
The power supply module and the spare power supply module are connected to an
external power supply (e.g., 460V three-phase AC) and the motor control
module. Under
normal conditions, the relay of the redundancy control module switches on the
power
supply module while switching off the spare power supply module.
[0103] The redundancy control module continuously communicates with the power
supply module via a communication bus so as to check if the power supply
module is
operated normally. Understandably, the power supply module comprises a network
communication unit. When detecting that the DC bus voltage exceeds a preset
threshold
N consecutive times, the redundancy control module disconnects the relay of
the power
supply module and connects to the relay of the spare power supply module. To
display
the status of different function modules, an LED screen is used to display a
prompt or a
pattern.
[0104] Other function modules adopt the same redundancy control scheme as the
5-speed
function modules of the disclosure, and accordingly not described herein. The
motor
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
control unit further comprises a 5-speed 24VAC thermometer that transfers a
signal to a
5-speed input module, a 5-speed spare input module, and the redundancy control
module.
When a 24VAC signal does not cause the motor to run, the redundancy control
module
checks N consecutive times the rotational speed, torque, or air volume of the
motor so as
to confirm the disabled status of the motor. Then the 5-speed input module is
switched off
and the 5-speed spare input module is switched on.
[0105] The number of the spare power supply module, the spare motor control
module,
and the 1/0 module is determined by demand and even not required.
[0106] The motor control unit in an indoor unit may be the same part number
for used in
an outdoor unit so as to match the input voltage and power. The following
function
module may be taken into account for OEM mass production and aftermarket.
[0107] The first function module, referring to the power supply module,
comprises a
surge protection circuit, a filter circuit, and a DC/DC converter circuit; and
the power
supply module converts alternating current to direct current. The following
power supply
modules with different part numbers are described:
[0108] Part number A101: 120/230/277VAC/60Hz/1Ph, used in a motor of equal to
or
less than 1/4 HP;
[0109] Part number A102: 120/230/277VAC/60Hz/1Ph, used in 1/3 and 1/2 HP
motor;
[0110] Part number A103: 120/230/277VAC/60Hz/1Ph, used in 3/4 and 1 HP motor;
[0111] Part number A104: 460VAC/60Hz/3Ph, used in 1.2 - 2 HP motor;
[0112] Part number A105: 460VAC/60Hz/3Ph, used in 2.3 - 3.5 HP motor;
[0113] Part number A106: 460VAC/60Hz/3Ph, used in 5 HP motor;
[0114] .............
[0115] Part number Al ON: 575VAC/60Hz/3Ph, in 5 HP motor;
[0116] A power supply module is selected from different part numbers so as to
match the
input voltage and power; for example, a 1 HP power supply module supplies
enough
power for two 1/2 HP motors.
16
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0117] The second function module, referring to a motor control module, that
controls
the speed, torque or air flow of a motor by receiving DC power and a control
signal, and
by supplying a UVW three-phase (or multiple-phase) electric current to the
main body of
the motor; the motor control module comprises a microprocessor, an IGBT
inverter
component, and a heat sink. The motor control module further comprises a Hall
element
and a Hall signal interface; and the Hall element is configured to detect the
rotor position
based on a Hall signal.
[0118] The motor control module further comprises a first port through which a
driver is
updated and compatible with an output or input module, thus allowing the user
to correct
defects or add new functions to the motor control unit. The motor control
module further
comprises a second port used to connect a computer that allows the user to
adjust the
motor parameters through programming. The following motor control modules with
different part numbers are described:
[0119] Part number B101: used in a DM2 motor of equal to or less than 1/4 HP;
[0120] Part number B102: used in a DM3 motor of equal to or less than 1/4 HP;
[0121] Part number B103: used in a DM2 motor of 1/3 and 1/2 HP;
[0122] Part number B104: used in a DM3 motor of 1/3 and 1/2 HP;
[0123]
[0124] Part number B120: used in a DM2 motor of 5 HP;
[0125] Part number B131: used in a DM3 motor of 5 HP;
[0126] The multiple-speed 24VAV input module comprises a plurality of module
components that matches a speed grade and a voltage grade. A corresponding
driver is
essential for the motor control module to work.
[0127] The RS-485 serial communication module implements a communication
protocol,
such as Modbus and ClimateTalk, supported by a driver for the motor control
module.
[0128] The I/0 module further comprises a specified communication module for
date
transmission with a client communication module.
17
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0129] The I/0 module comprises at least one module selected from the group
comprising:
[0130] a multi-speed 24VAC input module that receives a 24VAC signal from the
main
control board and sends the signal to the motor control module; and the part
number may
be C101;
[0131] a PWM input module that receives a PWM signal from the main control
board
and sends the signal to the motor control module; and the part number may be
C102;
[0132] a 0-10VDC input module that receives a 0-10VDC signal and sends the
signal to
the motor control module; and the part number may be C103;
[0133] a RS485 serial communication module that implements a communication
protocol
supported by a driver for the motor control module; and the part number may be
C104;
[0134] a Bluetooth module that allows the motor control module to communicate
with an
app or a computer for motor configuration; and the part number may be C105;
[0135] a pulse output module that outputs a pulse for representing a parameter
of the
motor; the part number may be C106;
[0136] an Ethernet local area network module that supports a TCP/TP protocol
for
allowing the motor control module to connect into a building control network
or to
monitor and control the motor parameters over network; and the part number may
be
C107;
[0137] a human-machine interface (HMI) function module that comprises a color
and
monochrome screen for offering a high resolution display; the HMI function
module is
used to display information about the rotational speed, torque or air volume
of the motor,
making it convenient for the user to perform a configuration setting or
experimental test;
the part number may be C107; and
[0138] a DIP switch module that is connected to motor control module by the
interface
connector; the DIP switch module comprises a set of switches for changing the
motor
parameters; and the part number may be C108.
[0139] The examples detailing the above function modules are described as
follows:
18
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0140] Test 1: a commercial air conditioner comprises a 3 HP indoor motor and
two 1/3
HP outdoor motors; and each motor operates at five speed levels. A motor
control unit for
controlling the commercial air conditioner comprises:
[0141] a power supply module (or two or three smaller power supply modules)
with a
part number for supplying enough power for the three motors;
[0142] a 3HP motor control module with a part number;
[0143] two 1/3 HP motor control modules with part numbers; and
[0144] three 5-speed input modules with part numbers.
[0145] The function modules are integrated to form a motor control unit that
shortens the
development circle, saves cost, and allows easy maintenance of the motor
control unit.
[0146] Test 2: a residential air conditioner comprises a 1/2 HP indoor motor
and a 1/4 HP
outdoor motor; the indoor motor operates at 0-10VAC and ten speed levels; and
the
outdoor motor operates at three speed levels. The indoor motor outputs a pulse
signal to a
main control board for adjusting the motor speed. A motor control unit for
controlling the
residential air conditioner comprises:
[0147] a power supply module for supplying enough power for the two motors;
[0148] a 1/2 HP motor control module;
[0149] a 1/4 HP motor control module;
[0150] two 5-speed input modules;
[0151] a 0-10VDC input module; and
[0152] a pulse output module.
[0153] Test 3: a commercial air conditioner comprises a 5 HP indoor motor and
two 1/3
HP outdoor motors; and each motor operates at five speed levels. The air
conditioner is
operated under poor working conditions such as thunderstorms and poor power
grid
quality, and even its power supply or IGBT inverter component has burned out
in the
past. A motor control unit for controlling the residential air conditioner
comprises:
[0154] a power supply module for supplying enough power for the three motors;
19
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0155] a spare power supply module;
[0156] a 5 HP motor control module;
[0157] a 5 HP spare motor control module;
[0158] two 1/3 HP motor control modules;
[0159] two 1/3 HP spare motor control modules;
[0160] three 5-speed input module; and
[0161] a redundancy control module.
[0162] The function modules are disposed on a mechanical mounting base 100 and
connected to the data bus and the power supply bus on the second circuit board
to allow
the transmission of power and data, thus forming a motor control unit.
[0163] Compared to a conventional motor control unit, the motor control unit
of the
disclosure comprises a plurality of independent function modules that allow
for easy
replacement of a damaged function module, thus reducing the maintenance cost.
Optionally, the function modules are disposed in different positions to
satisfy user
requirements.
Example 2
[0164] As shown in FIGS. 5 and 16, a combination method of the motor control
unit
comprises dividing the motor control unit into a plurality of function
modules; and the
plurality of function modules comprises:
[0165] a first function module, referring to a power supply module that is
connected to an
electric supply and converts alternating current to direct current to supply
for other
function modules; optionally, different power supply modules are formed to
match the
input voltage and power;
[0166] a second function module, referring to a motor control module that
controls the
operation of the motor; the motor control module comprises a microprocessor,
an IGBT
inverter, and a heat sink; when receiving VDC power and control signals, the
motor
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
control module supplies electricity to the motor so as to control the
rotational speed,
torque, or air volume of the motor; optionally, different motor control
modules are
formed to match the input power;
[0167] a third function module, referring to at least one 1/0 module that
allows signal
transmission between the motor control module and a main control board or a
peripheral
device;
[0168] a fourth function module, referring to a redundancy control module that
starts a
spare function module when the first, second or third function module has an
emergency;
and
[0169] a fifth function module, referring to at least one spare function
module that
performs the same function as the first function module, the second function
module, or
the third function module.
[0170] The power supply module, the motor control module, the at least one 1/0
module,
the redundancy control module, and the spare function module are combined into
a motor
control unit that matches the parameters of the motor.
[0171] The 1/0 module comprises at least one module selected from the group
comprising:
[0172] a multi-speed 24VAC input module that receives a 24VAC signal from the
main
control board and sends the signal to the motor control module;
[0173] a PWM input module that receives a PWM signal from the main control
board
and sends the signal to the motor control module;
[0174] a 0-10VDC input module that receives a 0-10VDC signal and sends the
signal to
the motor control module;
[0175] a RS485 serial communication module that implements a communication
protocol
supported by a driver for the motor control module;
[0176] a Bluetooth module that allows the motor control module to communicate
with an
app or a computer for motor configuration;
21
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12
[0177] a pulse output module that outputs a pulse for representing a parameter
of the
motor; and
[0178] an Ethernet local area network module that supports a TCP/TP protocol
for
allowing the motor control module to connect into a building control network
or to
monitor and control the motor parameters over network;
[0179] a human-machine interface (HMI) function module that comprises a color
and
monochrome screen for offering a high resolution display; the HMI function
module is
used to display information about the rotational speed, torque or air volume
of the motor,
making it convenient for the user to perform a configuration setting or
experimental test;
and
[0180] a DIP switch module that is connected to motor control module by the
interface
connector; the DIP switch module comprises a set of switches for changing the
motor
parameters.
[0181] Each function module comprises an independent shell, a first circuit
board, and
other electronic components; the first circuit board and other electronic
components are
disposed in the shell; the shell comprises metal or plastic; the motor control
unit further
comprises a mechanical mounting base 100 and a second circuit board disposed
in the
mechanical mounting base; the above function modules are fixedly disposed on
the
mechanical mounting base, and connected to each other via second circuit board
104 to
allow the transmission of power and control signals.
[0182] The second circuit board 104 comprises a plurality of power supply bus
interfaces
103a and a plurality of data bus interface 103b so as to be electrically
connected to the
mechanical mounting base.
[0183] It will be obvious to those skilled in the art that changes and
modifications may be
made, and therefore, the aim in the appended claims is to cover all such
changes and
modifications.
22
CA 03164562 2022- 7- 12