Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR DYNAMICALLY SYNCING FROM TIME-
SHIFTED FRAME TO LIVE STREAM OF CONTENT
Background
[0001] This disclosure is generally directed to dynamically synchronizing a
presentation of
a time-shifted frame of a content item to a live stream of the content item.
In particular,
methods and systems are provided for transitioning to the latest frame of the
live stream of
the content item by intelligently skipping a subset of time-shifted frames.
Summary
[0002] With the advent of the internet and the increasing popularity of
playing content
items over the internet, live streaming of a content item (e.g., media asset)
has become one of
the most popular content delivery types. Sometimes, a presentation of the
content item on a
user device may lag behind the live streaming of the content item, causing a
noticeable
latency of the presentation between what should have been presented and what
is currently
presented. In one example, the lag may occur due to an unstable or slow
network connection
or low computer performance. In another example, the lag may occur due to a
trick play
(e.g., rewind or pause) requested by a user.
[0003] To address such lag in the content item's presentation, in one
approach, the system
will simply keep playing the content item behind the live streaming without
ever catching up.
This approach is deficient because the user may be exposed to a spoiler via a
different content
delivery method. For example, the user may receive a notification showing an
up-to-date
soccer game score on a mobile phone while watching a delayed soccer game on a
laptop.
This may prevent the user from thoroughly enjoying the soccer game because
knowing the
game's outcome can diminish the full experience of watching a live sports
game.
[0004] In another approach, the system will allow the user to instantly catch
up to live (e.g.,
by pressing a "live" button). This approach is also deficient because the
instant catch-up will
entail simply not showing a large number of frames (e.g., if the lag was 2
minutes, then 2
minutes of the content may be not shown), which will cause the user to miss
important scenes
that are critical to the content item and end up not having enough context to
fully understand
the content.
[0005] To overcome such deficiencies, methods and systems are described herein
for
gradually catching the presentation of the content item up to the live stream
by skipping
subsets of missed segments of the content item while still presenting
important subsets of the
1
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
content item. For example, upon determining that the playing of the content
item lags behind
the live streaming of the content item, a streaming application determines a
skippable bit
value for a missed segment of the content item. The streaming application may
determine
skippable bit value from a manifest of the content item, which includes
segment information
and skippable bit value information for each segment. The skippable bit value
indicates
whether a presentation of a respective segment or a frame can be skipped to
catch up to live.
[0006] If a skippable bit value includes an enabled bit value, then the
streaming application
skips a presentation of a respective segment. If a skippable bit value
includes a disabled bit
value, then the streaming application does not skip a presentation of a
respective segment and
plays the respective segment because it is considered an important segment to
understand the
context of the content item. If a respective segment includes a disabled
skippable bit value,
then the data of the respective segment may be retrieved from a respective
network address,
and the respective segment may be played based on the data retrieved from the
respective
network address.
[0007] The present disclosure addresses the problems of both a) never catching
up orb)
instantly catching up. It may do so by, for example, identifying important
portions of the
missed segments (e.g., by disabling the skippable bit for those portions) and
determining
which segments to skip to eventually catch up to the live stream, thereby
enabling the user to
consume live video yet still presenting enough content of the missed segments
needed to
understand the context of the content item. The present disclosure further
addresses the
problems described above by, for example, saving the network bandwidth and
reducing
network traffic by not sending less important segments, for the purpose of
catching up to live.
[0008] In one embodiment, when the playing of a content item lags behind the
live
streaming, a user is often provided with limited catching-up options to
address the lagging
problem. For example, in one approach, the streaming application may display
an option for
the user to skip all the missed segments to go live instantly. In another
approach, the
streaming application may not present any options. These approaches may be
deficient
because each user may have different preferences for how much time they would
like to
spend watching the missed segments or how much content to consume to catch up
to live
based on the content item. Yet, these approaches do not give each user
different catching-up
options that meet each user's preferences and viewing situations.
[0009] The present disclosure addresses the problems of both a) never catching
up to live or
b) catching up instantly, by generating for display a user-selectable option
to choose a time
period during which to view the missed portion of the content item or to
specify a desired
2
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
amount of content to be presented to the user. For example, when playing of
the content item
lags behind the live streaming of the content item, a streaming application
may present user-
selectable options. The example selectable options include an option for a
user to select a
particular time period, which specifies how long the user wants the missed
segments to be
presented before catching up to live. Selecting the particular time period
(e.g., two minutes)
allows the user to skip only a certain portion of the missed segments and play
a user-
designated amount of the missed segments, such that the playing of the content
item catches
up to live in the selected particular time period.
[0010] In some embodiments, when playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming, the system takes various approaches to address the lagging problem.
In one
approach, the system caches all the remaining segments of the content item
from a server of a
content item source to store the segments in a cache. This approach may be
deficient,
because it may take up too much memory to store all the cached segments, some
of which
may never even be played.
[0011] In another approach, the streaming application may request segments of
the content
item from the server of the content item source directly in real time for data
transmission
without caching any of the segments. This approach may also be deficient,
because it may
strain the network in real time. Requesting segments of the content item in
real time may
lead to a more severe lag due to the network bandwidth consumption for
transmitting a large
amount of data during the period of the lag.
[0012] The present disclosure addresses the problems described above by
storing an
appropriate number of time-shifted segments (e.g., missed segments due to a
delay) in a way
that does not overuse the network resources. For example, methods and systems
are
described herein for storing a portion of segments of a content item in the
cache and playing
the portion of the segments from the cache. When playing of the content item
lags behind the
live streaming of the content item, the streaming application identifies a
duration of the lag
(e.g., two minutes) from a manifest of the content. The manifest may include
segment
information of the content item and priority level value information for each
segment (or a
frame). A priority level value may establish a relative position of a
respective segment or
frame with other segments or frames in determining whether the respective
segment or frame
needs to be stored in the cache for later presentation.
[0013] From the identified duration of the lag, the streaming application
determines a
priority threshold (e.g., five). A priority threshold may be used to determine
the number of
segments to store in the cache to provide a seamless viewing experience with
the content item
3
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
and still to catch up to live. For example, based on the duration of the lag,
the streaming
application determines a set of segments of the content item that fits within
the lag (e.g., three
segments within the two-minute lag).
[0014] Among the three identified segments (or frames), a subset of the
segments with a
priority level above the priority threshold is determined (e.g., segment 2
with a priority level
of seven is identified because its priority level is higher than the priority
threshold of five).
The streaming application stores a respective identified segment with a higher
priority level
than the priority threshold in the cache for later viewing. The present
disclosure addresses the
problems described above by, for example, caching only a portion of segments
that are
important enough to not miss the context of the missed segments that helps the
users to
understand the next segments of the content item, and also by minimizing use
of network
resources, bandwidth consumption, and amount of local storage dedicated to
caching.
Description of the Drawings
[0015] The above and other objects and advantages of the disclosure will be
apparent upon
consideration of the following detailed description, taken in conjunction with
the
accompanying drawings, in which like reference characters refer to like parts
throughout, and
in which:
[0016] FIG. 1 depicts an exemplary user interface for providing a content item
that has
fallen behind live streaming of the content item, in accordance with some
embodiments of the
disclosure;
[0017] FIG. 2 depicts an exemplary user interface for providing user-
selectable catching-up
options, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0018] FIG. 3 depicts an exemplary user interface for catching up to live
stream of the
content item, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0019] FIG. 4 depicts an exemplary user interface for presenting a live stream
of the content
item, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0020] FIG. 5 shows an exemplary embodiment for determining, by a client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of a missed segment based on a manifest of the
content item, in
accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0021] FIG. 6 shows an exemplary embodiment for determining, by the client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of the missed segment based on metadata of the
missed
segment that is received upon requesting the content item, in accordance with
some
embodiments of the disclosure;
4
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0022] FIG. 7 shows an exemplary embodiment for determining, by the client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of the missed segment based on metadata of each
missed
segment that is received upon requesting a respective missed segment, in
accordance with
some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0023] FIG. 8 shows an exemplary embodiment for determining, by a server,
whether to
skip a presentation of the missed segment based on metadata of the missed
segment, in
accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0024] FIG. 9 shows an exemplary embodiment for storing the missed segment in
the cache
based on the manifest, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0025] FIG. 10 shows an exemplary embodiment for storing the missed segment in
the
cache based on the received segment metadata, in accordance with some
embodiments of the
disclosure;
[0026] FIG. 11 shows an illustrative process for catching up to live based on
a user
selection, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0027] FIG. 12 shows an illustrative process for catching up to live based on
a skippable bit
value, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0028] FIG. 13 shows an illustrative process for caching a time-shifted
segment to catch up
to live, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure;
[0029] FIG. 14 shows a block diagram of an illustrative user device, in
accordance with
some embodiments of the disclosure; and
[0030] FIG. 15 shows a block diagram of an illustrative media system, in
accordance with
some embodiments of the disclosure.
Detailed description
[0031] FIG. 1 shows an example content instantiation 100 that shows a content
item that
has fallen behind live streaming of the content item, in accordance with some
embodiments
of the disclosure. Although FIGS. 1-4 depict user device 102, 202, 302, 402 as
a television, it
will be understood that any suitable device for displaying a live stream may
be used, such as
user television or gaming equipment 1502, user computer equipment 1504, or
wireless user
communications device 1506 discussed below in relation to FIG. 15. The user
device 102,
202, 302, 402 may have control circuitry 1404 of FIG. 14 configured to request
the live
stream of the content item from a server for display (e.g., on a display such
as display 1412
discussed later in more detail with reference to FIG. 14). FIGS. 1-4 depict
improved user
interface that includes exemplary content instantiation, which illustrate
catching-up
operations.
5
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0032] As shown in FIG. 1, user device 102 requests an audio-visual media
asset that
includes a group of segments. It will be understood that, consistent with the
present
disclosure, any content item may be requested for streaming from the media
server. As
referred to herein, the term "content item" should be understood to mean an
electronically
consumable user asset, such as an electronic version of a printed book,
electronic television
programming, as well as pay-per-view programs, on-demand programs (as in video-
on-
demand (VOD) systems), Internet content (e.g., streaming content, downloadable
content,
Webcasts, etc.), video clips, audio, content information, pictures, rotating
images, documents,
playlists, websites, articles, books, articles, newspapers, blogs,
advertisements, chat sessions,
social media, applications, games, and/or any other media or multimedia and/or
combination
of the same.
[0033] As shown in FIG. 1, a segment 104 of a content item (e.g., soccer game)
is streamed
on user device 102 via the streaming application. The streaming application
may be a stand-
alone application implemented on user equipment device 1400. The streaming
application
may generate a live status indicator 101 for display, which indicates whether
a segment that is
currently presented on user device 102 is a real time stream (i.e., live
segment). In exemplary
user interface 100, live status indicator 101 indicates that segment 104 is
not a live stream (by
showing "Not Live"). In another example, live status indicator 101 may be a
word "live" that
appears grayed out or otherwise altered.
[0034] The streaming application may generate for display a progress bar 108,
which
depicts the progress of the viewing history of the content item. Progress bar
108 may include
a current position bar 110, which indicates a current segment location in the
duration of the
content item and a live position bar 112 which indicates a live segment
location in the
duration of the content item. As indicated in FIG. 1, segment 104 currently
lags behind the
live stream of the content item as the current position bar 110 and the live
position bar 112
are not aligned together (current position bar 110 is located on the left side
of live position
bar 112).
[0035] FIG. 2 depicts an exemplary user interface 200 for providing user-
selectable
catching-up options on a user device 202, in accordance with some embodiments
of the
disclosure. Upon detecting a lag, the streaming application may display the
user selectable
options 204, 206, 210, which can be selected via user input. In some
embodiments, the
streaming application displays user selectable options 204, 206, 210 only when
the lag is
enough (e.g., when it exceeds a certain threshold, for example, when it's
longer than 1 minute
or longer than 5 minutes).
6
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0036] Selecting of each user-selectable option triggers the streaming
application to
perform different catching-up actions. User selection may be made by any
suitable type of
user interface input method, such as clicking, tapping, or voice input as
described in 1410 of
FIG. 14. In some embodiments, upon selecting a "Catch up to live immediately"
option 204,
the streaming application skips all of the missed segments of the content item
and catches up
to live instantly. As a result, the user will view the most up-to-date segment
of the content
item in real time. Upon selecting a "Stop live" option 210, the streaming
application may
keep playing the content item without ever caching up to live. As a result,
the user will
permanently remain behind the live streaming unless a further action is taken.
[0037] Upon selecting a "Catch up to live in X min" option 206, the streaming
application
may display a drop-down menu that offers a list of sub-options. In one
embodiment, the
drop-down menu may be pre-populated with a list of values. In another
embodiment, the
drop-down menu can be optional (e.g., it may not be displayed unless requested
by the user).
The sub-options may include a list of numbers (e.g., time periods) that the
user can choose
from. In some embodiments, the user can enter any value that is not displayed
in the list.
The particular time period may be a time basis for catching up on the missed
segments. For
example, if the user selects "1 min," then the streaming application will
catch up the
presentation of the content item to the live stream within 1 minute,
regardless of the duration
of the lag.
[0038] In some embodiments, the drop-down menu includes a system-configured
default
value. The streaming application determines the default value based on the
user's past
history or patterns for catching up to live. For example, the default value
may be determined
based on a user profile or a type of a content item (e.g., action v. romance).
The default value
may be determined based on a time of day that content item is played. The
default value may
be determined based on network connectivity and hardware condition. These are
exemplary
factors that may be used to determine the default value, but any suitable
factors may be used
to determine the default value. When the user selects the default value, then
the streaming
application catches up to live in the time period corresponding to the default
value.
[0039] FIG. 3 depicts an exemplary user interface 300 for catching up to the
live stream of
the content item on a user device 302, in accordance with some embodiments of
the
disclosure. Upon receiving user input specifying a value for the particular
time period of
option 206, the content item will be caught up to live in the particular time
period (e.g., 2
minutes). While catching up, the streaming application displays a live status
bar 301 which
indicates "Catching up to live" is in progress. The "Catching up to live"
progress can also be
7
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
shown by a progress bar 308. As shown in progress bar 308, a current position
bar 310 is
closer to a live position bar 312 in progress bar 308 compared to current
position bar 110 in
content instantiation 100.
[0040] FIG. 4 depicts an exemplary user interface 400 for presenting a live
frame 404 of the
content item on a user device 402, in accordance with some embodiments of the
disclosure.
Content instantiation 400 may be a resulting view of the user selecting "Catch
up in 2 min"
option 208 at 3:50pm in FIG.2. As a result, content item is catching up to
live at 3:51 pm in
FIG. 3 (showing a frame 304 where a soccer player is shooting a goal) and is
finally caught
up to live at 3:52 pm in FIG. 4 (showing live frame 404 where the soccer
player is scoring a
.. goal). When the content item is caught up to live, the streaming
application changes live
status bar 401 from "Catching Up to Live" to "Live." In some embodiments, the
live status
bar 401 includes a count-up or count-down countdown timer. The countdown timer
indicates
how much time is left or passed to catch up to live (e.g., by showing "in 3,
2, 1 seconds, live!)
The completion of catching up is also shown by a progress bar 408. As shown in
progress
bar 408 of FIG. 4, a current position bar 410 and a live position bar 412 are
aligned,
indicating that content item is caught up to live. Catching-up operations will
be explained in
connection with FIGS. 5-8.
[0041] FIG. 5 shows an exemplary embodiment 500 for determining, by a client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of a missed segment based on a manifest of the
content item, in
accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure. The client device can be
any user
television or gaming equipment 1502, user computer equipment 1504, or wireless
user
communications device 1506 discussed below in relation to FIG. 15. It should
be noted that
embodiments 500-1000 may be performed by control circuitry 1404 of FIG. 14 as
instructed
by the streaming application, which may be performed on any client device. In
addition, one
.. or more steps of embodiments 500-1000 may be incorporated into or combined
with one or
more steps of any other processes or embodiments described in the present
disclosure.
[0042] At step 502, the user may request a presentation of a content item
(e.g., an episode
of "Game of Thrones") via the streaming application on the client device. The
content item
consists of one or more segments. Each segment consists of one or more frames,
where the
length of each segment ranges approximately from zero to a few seconds (e.g.,
0-6 seconds).
A frame is one of the many still images that compose the content item. For
example, the
manifest may be an MPEG-DASH manifest.
[0043] At step 504, the streaming application requests a live streaming of a
content item to
a media server. The media server may reside in a content item data source 1518
of FIG. 15.
8
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
At step 506, in response to the request, the media server sends a manifest of
the content item.
The manifest contains information about sequential segments of the content
item, for
example, timing of each segment, location on the network such as a network
address from
where each segment can be retrieved, or a skippable bit value for each
segment. As shown in
the manifest, a time period for segment 1 is from 0:00 to 0:03, a network
address for
retrieving segment 1 is address 1, and a skippable bit value for segment 1 is
"False." These
are just example manifest parameters, and any suitable parameters or
variations may be used
for each component of the manifest.
[0044] The skippable bit value indicates whether a presentation of a
respective segment
may be skipped to catch up to live. For the delayed content item to catch up
to live stream,
some segments of the content item need to be skipped due to the time gap. The
skippable bit
value indicates which of the missed segments may be skipped to catch up the
time gap. If a
skippable bit value includes an enabled bit value, then the streaming
application skips a
presentation of a respective segment (only when the content item lags behind
the live). If a
.. skippable bit value includes a disabled bit value, then the streaming
application does not skip
a presentation of a respective segment, because it is considered as an
important segment to
understand the context of the content item. The data of the respective segment
may be
retrieved from a respective network address, and the respective segment may be
played based
on the data retrieved from the respective network address.
.. [0045] In some embodiments, the media server may determine a skippable bit
value based
on an importance level of a segment. The media server determines an importance
level of the
segment based on various factors, including a number of scheduled replays of
the segment in
a predetermined time period (e.g., sports highlights which are scheduled to be
played three
times this week), a type of content item (e.g., movie v. live sports game), or
a genre of the
segment (e.g., action v. romance).
[0046] In some embodiments, a machine learning algorithm is used to identify
skippable
segments. For example, a training set including segments that were commonly
skipped by a
large number of users may be compiled. The machine learning algorithm may then
take a
new segment as an input and compare it to known skipped segments. When the
similarity is
high, the machine learning algorithm may identify the new segment as a
skippable segment
and a skippable bit value may be enabled. The machine learning algorithm may
train a set of
data based on the user's preferences or past history. This is an example
method of
determining a skippable bit value, and any suitable methods may be used to
determine the
skippable bit value for the segment.
9
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0047] The skippable bit information for each segment may be inserted into the
manifest or
metadata of the segment by the media server either enabling or disabling the
skippable bit
value. The manifest or the metadata of the segment may be stored in a database
of the media
server.
[0048] In one embodiment, the skippable bit includes one of the two values,
such as an
enabled bit value (e.g., 1) or disabled bit value (e.g., 0). An enabled
skippable bit indicates
that a presentation of a respective segment may be skipped. A disabled
skippable bit
indicates that a presentation of a respective segment may not be skipped. In
another
embodiment, the skippable bit value includes a range of numbers. If a
respective segment has
.. a skippable bit value that is higher than an importance threshold, then the
respective segment
is determined to have a disabled bit value. On the other hand, if a respective
segment has a
skippable bit value that is lower than the importance threshold, then the
respective segment is
determined to have an enabled bit value.
[0049] In some embodiments, the importance threshold may be determined by the
media
server or the client device. The importance threshold may be determined based
on the user
profile or the content item in a similar technique and manner described above.
For example,
if the content item is an action movie, which the user indicated to be the
favorite genre, then
the importance threshold for the content item is determined to be higher than
a romance
movie about which the user cares less.
[0050] At step 508, upon receiving the manifest, which includes network
address
information for segment 1, the streaming application retrieves segment 1 of
the content item
from network address 1 and plays the retrieved segment 1 on the client device.
At step 510,
the streaming application determines whether playing of the content item lags
behind the live
streaming. One method of detecting the lag is described with respect to FIG.
11. In addition,
.. one or more steps of process 1100 described in FIG. 11 or embodiments 100-
400 of FIGS. 1-
4 may be incorporated into or combined with step 510. For example, upon the
user selecting
"catch up to live in X min" option 206 in FIG. 2, the streaming application
performs the steps
described in FIGS. 5-10.
[0051] At step 512, upon detecting the lag between the currently displayed
segment and the
.. live segment, the streaming application evaluates the next segment that
follows segment 1
(segment 2) and reads a skippable bit value from the manifest. As shown in the
transmitted
manifest at step 506, segment 2 has an enabled skippable bit, indicating that
a presentation of
segment 2 can be skipped. Therefore, the streaming application skips
retrieving of segment 2
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
from address 2 because the presentation of segment 2 is not necessary during
the catching up
to live operation.
[0052] After completing step 512, the streaming application reads a skippable
bit value for
a segment that follows segment 2: segment 3, at step 514. As indicated in the
manifest, the
skippable bit value for segment 3 is "false," a disabled bit value, indicating
that a presentation
of segment 3 cannot be skipped. Therefore, the streaming application retrieves
data for the
segment 3 from network address 3 and plays segment 3 from the network address
3.
[0053] At step 516, the streaming application determines whether the content
item is caught
up to live. If the streaming application determines that the content item is
caught up to live,
then the streaming application plays segment 4 regardless of the skippable bit
value. Since
there is no latency anymore, the streaming application does not skip any
segment of the
content item. If the streaming application determines that the content item is
not caught up to
live, then the streaming application repeats the steps in FIG. 5 until the
content item is caught
up to live.
[0054] FIG. 6 shows an exemplary embodiment 600 for determining, by the client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of the missed frame based on metadata of missed
frame that is
received upon requesting the content item, in accordance with some embodiments
of the
disclosure. The content item consists of one or more segments. Each segment
consists of one
or more frames, where the length of a frame ranges approximately from zero to
16.33
milliseconds. A frame is one of the many still images that compose the content
item.
[0055] Embodiment 600 is different from embodiment 500 in that the streaming
application
does not receive the manifest of the content item. Instead, the streaming
application receives
frame data and metadata upon requesting the live streaming of the content
item. The frame
data may include content data for the frame, such as digital pixel values. The
metadata
contains information about the skippable bit for each metadata, which
indicates whether a
presentation of a respective metadata may be skipped and a sequential location
data of a
frame in the content item.
[0056] At step 602, the user may request a presentation of the content item.
At step 604,
the streaming application requests live streaming of the content item to the
media server. At
.. step 606, unlike step 506 of embodiment 500, the media server sends frame
data and
metadata of the content item. The frame data and metadata may be a complete
packet with
all the content data necessary to play the content item from the beginning to
the end. The
frame data and the metadata may be stored in a database of the media server,
which may
reside in content item data source 1518.
11
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0057] At step 608, the streaming application plays frame 1 using the received
frame 1 data.
At step 610, the streaming application determines whether a lag is detected.
In some
embodiments, upon detecting the lag, the streaming application may generate
the user-
selectable "catching-up" options for display, as described in FIG. 2.
[0058] At step 612, based on the metadata, the streaming application
determines that a
presentation of frame 2 may be skipped because frame 2 has an enabled
skippable bit (e.g., or
when the user selects "catch up to live in X min" option 206 of FIG. 2). Thus,
the streaming
application skips the presentation of frame 2. At step 614, the streaming
application identifies
a next frame of the content item that follows frame 2 and performs similar
steps. For frame
3, the streaming application determines that a presentation of frame 3 cannot
be skipped
because frame 3 has a disabled skippable bit value. Thus, the streaming
application plays
frame 3 using the received frame 3 data.
[0059] At step 616, the streaming application determines whether the content
item is caught
up to live. If the content item is caught up to live, then the streaming
application plays frame
4 regardless of a skippable bit value for frame 4. If the content item is not
caught up to live,
then the streaming application repeats similar steps until the content item is
live.
[0060] FIG. 7 shows an exemplary embodiment 700 for determining, by the client
device,
whether to skip a presentation of the missed segments based on metadata that
is received
upon requesting a respective missed segment, in accordance with some
embodiments of the
disclosure. Embodiment 700 is different from embodiment 600 in that the
streaming
application does not receive the complete packet including all of the frame
data and the
metadata at once but receives individual frame data and metadata each time
when the
streaming application requests a respective frame from the media server.
[0061] At step 702, the user may request a presentation of the content item.
At step 704,
the streaming application requests live streaming of the content item from the
media server.
At step 706, unlike embodiment 600, the streaming application sends only frame
1 data and
metadata, instead of sending all the frame data and metadata of the content
item. Among
much other content information, the metadata contains information about a
skippable bit
value for each frame. At step 708, the streaming application obtains frame 1
data from the
media server and plays frame 1 using the received frame 1 data.
[0062] At step 710, the streaming application determines whether a lag exists
between the
live frame and the currently displayed frame on the client device. In one
embodiment, step
710 may be optional, and the streaming application may perform step 712
without performing
step 710.
12
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0063] At step 712, the streaming application requests frame 2 data and
metadata from the
media server. In one embodiment, the streaming application may only request
frame 2 data
without requesting metadata of frame 2 if a lag is not detected at step 710.
Upon receiving the
request for frame 2 from the streaming application, the media server sends
frame 2 data and
metadata to the streaming application.
[0064] At step 714, the streaming application receives frame 2 data and
metadata from the
media server. Based on the metadata, the streaming application determines that
frame 2 has
an enabled skippable bit ("true" skippable bit). The streaming application may
skip a
presentation of segment 2 based on the enabled skippable bit value. In one
embodiment, the
streaming application performs step 710 after receiving frame 2 data from the
media server.
Step 710 may be performed each time frame data is received at the streaming
application to
determine whether a respective received frame may be skipped to catch up to
live.
[0065] At step 716, the streaming application identifies the next frame (frame
3) and
requests frame 3 data and metadata from the media server. At step 718, the
streaming
application receives requested data from the media server and reads the
skippable bit value
for frame 3. As illustrated in the exemplary frame data connected to the media
server, frame 3
has a disabled skippable bit ("false" skippable bit), and based on this, the
streaming
application determines that a presentation of frame 3 cannot be skipped. At
step 720, the
streaming application plays frame 3 using the received frame data. The steps
in FIG. 7 may
be repeated until the content item is caught up to live.
[0066] FIG. 8 shows an exemplary embodiment 800 for determining, by a server,
whether
to skip a presentation of the missed segment based on metadata, in accordance
with some
embodiments of the disclosure. Embodiment 800 is different from embodiment 700
in that
embodiment 800 is performed by the media server that resides in the content
item data source
1518 of FIG. 15, compared to embodiment 700, which was performed by the client
device. In
embodiment 800, the media server determines which of the missed frames to be
sent to the
streaming application.
[0067] At step 802, the user may request a presentation of the content item.
At step 804,
the streaming application requests live streaming of the content item to the
media server. At
step 806, the media server sends frame 1 data and metadata. The respective
metadata contains
skippable bit information for corresponding frames. At step 808, the streaming
application
receives frame 1 data and metadata from the media server and streams frame 1
with the
received frame 1 data. At step 810, the streaming application detects a lag
between the
currently displayed frame and the live frame.
13
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0068] At step 812, the streaming application sends an indication to the media
server that
there is a lag between the currently displayed frame and the live frame. At
step 814, the
media server queries the database of the media server and determines that
frame 2 has an
enabled skippable bit ("true" skippable bit value). At step 816, the media
server determines
that segment 2 can be skipped for presentation and skips sending frame 2 data
to the
streaming application.
[0069] At step 818, the media server identifies a subsequent frame to frame 2
and
determines that frame 3 has a disabled skippable bit ("false" skippable bit).
Upon determining
that frame 3 has the disabled skippable bit, the media server sends frame 3
data and metadata
.. to the streaming application at step 820. In some embodiments, the media
server only sends
frame 3 data without the metadata for frame 3. Sending the metadata may be
optional.
[0070] At step 822, the streaming application receives frame 3 data and plays
frame 3 using
the received frame 3 data. The process of FIG. 8 may continue until the
content item is
caught up to live.
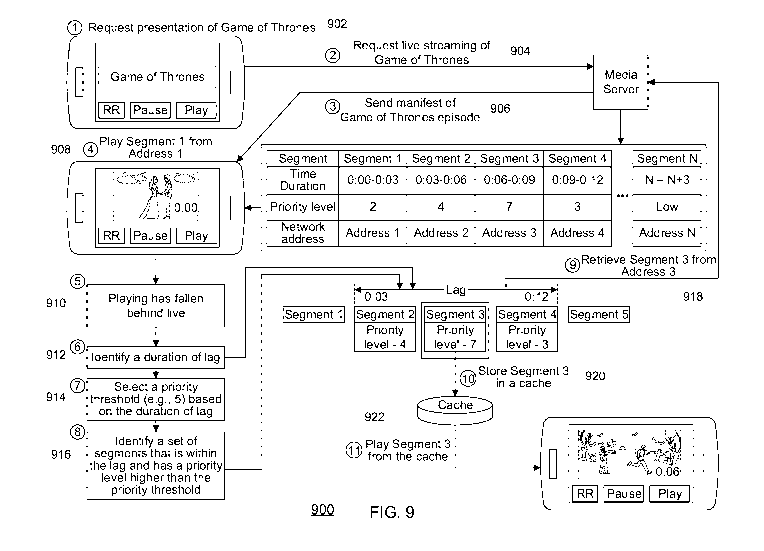
[0071] FIG. 9 shows an exemplary embodiment 900 for storing missed segments in
the
cache based on the manifest, in accordance with some embodiments of the
disclosure. At step
902, the user may request a presentation of the content item. At step 904, the
streaming
application requests live streaming of the content item to the media server.
At step 906, the
media server sends the manifest of the content item. The manifest contains
information about
the content item, such as a time duration of each segment, a priority level
value for each
segment, or a network address for each segment. The time duration of each
segment may be
associated with a respective timestamp of the segment, indicating the timing
of the segment
in the duration of the content item.
[0072] A priority level value may establish a relative position of a
respective segment with
other segments in determining whether the respective segment needs to be
stored in the cache
for a smooth presentation of the content item. The media server assigns a
priority level to
each segment based on the following factors. In one example, the media server
assigns a
priority level to each segment of the content item based on a respective
relevance level of the
segment. For example, the media server determines a respective relevance level
of a segment
.. to the user based on the user profile data, such that a segment of a higher
relevance (e.g.,
matching user's preference) is determined to be more relevant to the user than
other scenes. If
a particular segment is of high importance to the user (e.g., action scene),
then the media
server assigns a higher priority level value to the particular segment than a
segment that is
14
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
determined to be of lower relevance to the user (e.g., romance scene). In some
embodiments,
the media server assigns a priority level to each frame based on the similar
factors.
[0073] In another embodiment, the media server assigns a priority level to
each segment of
the content item based on a respective importance level of the segment in the
context of the
content item. For example, the media server determines a respective importance
level of a
segment, such that the segment includes scenes that are more important to the
content itself
than other scenes of the content (e.g., climax scene v. ending credits). The
media server
assigns a higher priority level value to a particular segment that has a
higher importance level
(e.g., climax) than a segment that has a lower importance level (e.g., ending
credits).
[0074] In one embodiment, the media server assigns a priority level to each
segment of the
content items based on a number of replays of the segment in a predetermined
time period.
For example, the media server calculates the number of times the segment is
streamed or
scheduled to be streamed in a particular time period. As an example, replays
of a previously
streamed segment affect the priority level of a respective segment adversely
because the user
is likely to have been exposed to the particular segment already, and the
particular segment
may not need to be presented to the user again.
[0075] In some embodiments, a machine learning algorithm is used to identify a
priority
level for a segment. For example, a training set including segments with
predetermined
priority levels may be compiled. The machine learning algorithm may then take
a new
segment as an input and compare it to known segments. When the similarity is
high, the
machine learning algorithm may assign to a new segment a priority level
similar to that of the
known segments. The machine learning algorithm may train a set of data based
on the user's
preferences or past history. This is an exemplary way of determining a
priority level, and any
suitable methods may be used to determine the priority level for the segment.
[0076] In some embodiments, the client device assigns a priority level to each
segment or a
frame of the content item using the similar techniques described above. The
client device
stores the priority level for each segment or frame in a database or storage
of the client
device. With this approach, the client device may determine which segment or a
frame needs
to be cached and make a request to the media server data for a corresponding
segment or a
frame.
[0077] At step 908, based on the manifest, the streaming application plays
segment 1 from
network address 1. At step 910, the streaming application detects a lag
between the currently
played segment and the live segment. In some embodiments, one or more steps of
process
1100 described in FIG. 11 or embodiments 100-400 of FIGS. 1-4 may be
incorporated into or
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
combined with step 910. For example, upon detecting the lag, the streaming
application may
generate the user-selectable "catching-up" options for display, as described
in FIG. 2.
[0078] At step 912, the streaming application identifies the duration of the
lag. For
example, the streaming application determines the duration of the lag based on
the timestamp
associated with each segment in the manifest. In embodiment 900, the duration
of the lag is
determined to be from 0:03 to 0:12, as shown in FIG. 9.
[0079] At step 914, the streaming application selects a priority threshold
based on the
duration of the lag. In some embodiments, the priority threshold may be
proportional to the
duration of the lag. In some embodiments, the priority threshold may be
dynamically
adjusted based on the user profile data and content item, based on the
techniques similar to
determining the importance threshold.
Lag Duration Priority
Threshold
<2 Mins 2
2-4 mins 3
5-6 4
>7 5
TABLE 1: Exemplary lag duration and priority threshold relationship
[0080] At step 916, the streaming application identifies a set of segments
that is within the
.. duration of the lag. In example embodiment 900, the streaming application
identifies, in this
example, three segments that match the length of the lag, segment 2 (0:03-
0:06), segment 3
(0:06-0:09), segment 4 (0:09-0:012). Among the three identified segments, the
streaming
application identifies a segment that has a priority level that is higher than
a priority
threshold. The streaming application determines that segment 3 has a priority
level of seven,
.. which is higher than the threshold of five.
[0081] At step 918, the streaming application retrieves segment 3 from network
address 3
based on the manifest. The streaming application may not retrieve segment 2
data and
segment 4 data as a presentation of segments 2 and 4 may be skipped based on
the priority
threshold. At step 920, the streaming application stores the retrieved segment
3 in a cache of
the client device for later presentation. A cache device may be implemented on
non-
transitory or transitory hardware of the client device. At step 922, the
streaming application
16
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
plays segment 3 from the cache. The steps in FIG. 9 may be repeated until the
content item
catches up to live.
[0082] FIG. 10 shows an exemplary embodiment 1000 for storing the missed
segments in
the cache based on the received segment metadata, in accordance with some
embodiments of
the disclosure. Embodiment 1000 is different from embodiment 900 in that the
media server
does not send the manifest to the streaming application, but the media server
sends segment
data to the streaming application when a request for a segment is received.
Furthermore, the
media server determines which of the missed segments of the content item need
be sent to the
streaming application and sends the determined segment data to the streaming
application.
Even though embodiment 1000 is described in the form of a segment, a frame may
be used.
[0083] At step 1002, the user may request a presentation of the content item.
At step 1004,
the streaming application requests live streaming of the content item to the
media server. At
step 1006, the media server sends segment 1 of the content item to the
streaming application.
[0084] At step 1008, the streaming application plays segment 1 from network
address 1. At
step 1010, the streaming application determines that playing of the content
item lags behind
the live streaming. At step 1012, the streaming application identifies the
duration of the lag.
At step 1014, the streaming application sends an indication to the media
server that playing of
the content item lags behind the live streaming.
[0085] At step 1016, upon receiving the indication, the media server
determines a threshold
based on the duration of the lag. At step 1018, the media server queries the
database of the
media server and determines that segment 2 has a priority level (e.g., 4) that
is below a
threshold. At step 1020, upon determining that segment 2 has the priority
level that is below
the priority threshold, the media server skips sending segment 2 data to the
streaming
application.
[0086] At step 1022, the media server identifies a segment of the content item
that follows
segment 2 and queries the database of the media server for the skippable bit
value for
segment 3. The media server determines that segment 3 has a priority level
(e.g., 7) that is
higher than the priority threshold (e.g., 5). At step 1024, upon determining
that segment 3
has the priority level higher than the priority threshold, the media server
sends segment 3 data
to the streaming application. At step 1026, the streaming application receives
segment 3 data
from the media server and stores segment 3 data in the cache. At step 1028,
the streaming
application plays segment 3 from the cache. The process 1000 may continue
until the content
item is caught up to live.
17
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0087] FIG. 11 shows an illustrative process 1100 for catching up to live
based on a user
selection, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure. It should be
noted that
process 1100 may be performed by control circuitry 1404 of FIG. 14 as
instructed by a
streaming application that maybe performed on any devices 1502, 1504, 1506 of
FIG. 15. In
.. addition, one or more steps of process 1100 may be incorporated into or
combined with one
or more steps of any other process or embodiment (e.g., process 1200 of FIG.
12 and process
1300 of FIG. 13). The process 1100 may be performed in accordance with the
embodiments
discussed in connection with FIGS. 1-4.
[0088] In some embodiments, the user requests the live stream of the content
item via the
streaming application on the user device. In response to the user request, the
streaming
application requests the live streaming of the content item from the media
server. At block
1102, the control circuitry generates the content item for live streaming. The
content item
includes one or more segments where each segment may have one or more frames.
[0089] At block 1104, the control circuitry determines whether playing of the
content item
lags behind the live streaming of the content item. One example of determining
the lag is by
calculating a hash of a segment of the content item. In some embodiments, the
streaming
application receives a manifest of the content item that contains information
about (a)
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of the content item, (b) hash code, and (c)
timestamp for
each segment. The streaming application calculates a hash code of a live
segment using a
timestamp of the live segment. The streaming application also determines a
hash code for a
segment that is currently displayed based on the manifest. The streaming
application
compares the calculated hash code of the live segment to the determined hash
code of the
currently displayed segment. If there is a mismatch, then the streaming
application
determines that there is a lag between the live segment and the currently
displayed segment.
[0090] At block 1106, if the control circuitry determines that playing of the
content item
lags behind the live streaming of the content item, then the streaming
application generates
one or more selectable "catching-up" options for display. The options include
(a) catch up to
live in a particular time period, (b) catch up to live immediately, and (c)
stop the live
streaming. On the other hand, if the control circuitry determines that playing
of the content
item does not lag behind the live streaming of the content item, then the
streaming application
does not present the user-selectable "catching-up" options for display.
[0091] The user-selectable options may include a graphical user interface
element that
prompts the user to select one of the presented options. At block 1108, the
streaming
application receives user input selecting one of the presented options. In
some embodiments,
18
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
the streaming application performs an action without receiving user input
selecting the
presented options. For example, based on the user profile data, the streaming
application may
perform one of the catching-up operations without receiving user input
selecting any of the
options (a), (b) or (c). The user profile data may include the user's
preferred catching-up
options and user history data on previously selected options.
[0092] At block 1110, if option (a) is selected, then the streaming
application presents a
sub-option for further user input. For example, the streaming application
displays a drop-
down menu or pop-up window that displays a list of values for the particular
time period in
the graphical user interface. In some embodiments, the graphical interface
element may
include a field where the user can provide a random value for the particular
time period. The
particular time period may be adjusted based on the user input. In some
embodiments, the
sub-option may be optional, and the list of values may be presented with the
option (a)
interface. In some embodiments, the streaming application determines a value
for the
particular time period based on user profile data and presents the system-
configured values
for display for the user to choose from. The user profile data includes user
preference
information for a preferred catching-up time period or past history of
catching-up patterns.
The streaming application may pre-populate the user's preferred particular
time period in the
sub-option.
[0093] Based on the selected particular time period, the streaming application
skips a
presentation of a portion of the missed segments, such that the playing of the
content item
eventually catches up to live in the particular time period. In one
embodiment, the streaming
application may skip a portion of the missed segment based on the user profile
data without
receiving user input specifying the particular time period.
[0094] At block 1112, if option (b) is selected, then the streaming
application presents a
frame corresponding to the live streaming of the content item (e.g., live
frame), such that the
playing of the content item catches up to live immediately. The missed frames
due to the lag
will not be displayed.
[0095] At block 1114, if option (c) is selected, then the streaming
application presents a
frame of the content item for when the content item was paused immediately
before when the
user-selectable options were presented. Selecting option (c) does not trigger
catching up of
the content item, such that the playing of the content item does not match the
live streaming.
The streaming application will continue presenting the content item that is
behind the live
streaming without ever catching up, and therefore, the content item will
remain behind the
live streaming.
19
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0096] FIG. 12 shows an illustrative process for catching up to live based on
a skippable bit
value, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure. It should be
noted that
process 1200 may be performed by control circuitry 1404 of FIG. 14 as
instructed by a
streaming application that maybe performed on any devices 1502, 1504, 1506 of
FIG. 15. In
addition, one or more steps of process 1200 may be incorporated into or
combined with one
or more steps of any other process or embodiment (e.g., process 1100 of FIG.
11 and process
1300 of FIG. 13). The process 1200 may be performed in accordance with the
embodiments
discussed in connection with FIGS. 5-8.
[0097] In some embodiments, the user requests the live stream of the content
item via the
streaming application on the user device. In response to the user request, the
streaming
application requests the live streaming of the content item from the media
server. At block
1202, in response to the request to live stream the content item, the control
circuitry receives
a manifest of the content item. The manifest identifies a plurality of
sequential segments of
the content item. For each segment of the content item, the manifest contains
information
about a respective skippable bit value and a respective network address.
[0098] At block 1204, based on the manifest, the control circuitry identifies
a first segment
as a last-played segment of the content item on the user device. The control
circuitry also
identifies a second segment of the content item as a segment that follows the
first segment of
the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item.
[0099] At block 1206, the control circuitry determines that playing of the
content item lags
behind the live streaming of the content item. In one embodiment, unstable
network
connectivity causes the lag in the live streaming of the content item. When
playing of the
content item is paused, the control circuitry determines that the playing of
the content item
lags behind the live streaming of the content item.
[0100] At block 1208, the control circuitry determines whether a respective
skippable bit
value of the second segment comprises a first skippable bit value based on the
manifest of the
content item. The first skippable bit value may indicate that the respective
segment may be
skipped for presentation (e.g., enabled skippable bit). At block 1210, upon
determining that
the respective skippable bit value of the second segment comprises the first
skippable bit
value, the control circuitry skips requesting data from a respective network
address of the
second segment. Skipping a presentation of a segment may cause the content
item to catch up
to the live streaming.
[0101] At block 1212, upon determining that the respective skippable bit value
of the
second segment does not comprise the first skippable bit value, the control
circuitry requests
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
data from a respective network address of the second segment. The control
circuitry plays
the second segment from the respective network address of the second segment
on the user
device. The control circuitry identifies a third segment as a subsequent
segment that follows
the second segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments
of the content
item.
[0102] At block 1214, the control circuitry determines whether a respective
skippable bit
value of the third segment comprises a second skippable bit value based on the
manifest. The
second skippable bit value may indicate that a presentation of a respective
segment cannot be
skipped (e.g., disabled skippable bit).
[0103] At block 1216, upon determining that the respective skippable bit value
of the third
segment comprises the second skippable bit value, the control circuitry
requests data from a
respective network address of the third segment. The control circuitry plays
the third segment
from the respective network address of the third segment on the user device.
[0104] At block 1218, upon determining that the respective skippable bit value
of the third
segment does not comprise the second skippable bit value, the control
circuitry skips
requesting data from the respective network of the third segment. In one
embodiment, the
third segment comprises the first skippable bit value different from the
second skippable bit
value. In another embodiment, the third segment comprises a skippable bit
value that is
different from both the first skippable bit value and the second skippable bit
value.
[0105] In some embodiments, the control circuitry identifies a fourth segment
of the
content item as a segment that follows the third segment of the content item
in the plurality of
sequential segments of the content item. Upon determining that the playing of
the content
item no longer lags behind the live streaming, the control circuitry requests
data from a
respective network address of the fourth segment of the content item
regardless of a
respective skippable bit value of the fourth segment. For example, even though
the fourth
segment comprises the first skippable bit value (e.g., enabled skippable bit),
the control
circuitry nevertheless plays the fourth segment of the content item based on
the data
requested from the respective network address of the fourth segment of the
content item,
because the content item is no longer lagging.
[0106] FIG. 13 shows an illustrative process for caching a time-shifted frame
to catch up to
live, in accordance with some embodiments of the disclosure. It should be
noted that process
1300 may be performed by control circuitry 1404 of FIG. 14 as instructed by
the streaming
application that maybe performed on any devices 1502, 1504, 1506 of FIG. 15.
In addition,
one or more steps of process 1300 may be incorporated into or combined with
one or more
21
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
steps of any other process or embodiment (e.g., process 1100 of FIG. 11 and
process 1200 of
FIG. 12). The process 1300 may be performed in accordance with the embodiments
discussed
in connection with FIGS. 9-10.
[0107] In some embodiments, the user requests the live streaming of the
content item via
the streaming application on the user device. In response to the user request,
the streaming
application requests the live streaming of the content item to the media
server. At block
1302, in response to the request to live stream the content item, the control
circuitry receives
a manifest of the content item. The manifest identifies a plurality of
sequential segments of
the content item. Each segment is associated with a timestamp, which
identifies the location
of each segment in the content item. The manifest contains information about a
network
address and a priority level value for each segment. The manifest may be
stored in a database
of the media server. In some embodiments, sending the manifest to the
streaming application
is optional and may only be performed when the lag is identified by the
streaming
application.
[0108] In one embodiment, the media server assigns a priority level to each
segment of the
content item based on a number of replays of the segment in a predetermined
time period. For
example, the media server calculates the number of times the segment is
streamed or
scheduled to be streamed in a particular time period. As an example, replays
of a previously
streamed segment affect the priority level of a respective segment adversely
because the user
is likely to have been exposed to the particular segment previously, and the
particular
segment may not need to be presented to the user again.
[0109] In another embodiment, the media server assigns a priority level to
each segment of
the content item based on a respective relevance level of the segment. For
example, the media
server determines a respective relevance level of a segment to the user based
on the user
profile data, such that a segment of a higher relevance (e.g., matching user's
preference) is
determined to be more relevant to the user than other scenes. If a particular
segment is of high
importance to the user (e.g., action scene), then the media server assigns a
higher priority
level value to the particular segment than a segment that is determined to be
of lower
relevance to the user (e.g., romance scene).
[0110] In a related embodiment, the media server assigns a priority level to
each segment of
the content item based on a respective importance level of the segment in the
context of the
content item. For example, the media server determines a respective importance
level of a
segment, such that the segment includes scenes that are more important to the
content itself
than other scenes of the content (e.g., climax scene vs. ending credits). The
media server
22
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
assigns a higher priority level value to a particular segment that has a
higher importance level
than a segment with a lower importance level.
[0111] At block 1304, the control circuitry determines whether the playing of
the content
item lags behind the live streaming of the content item. If the playing of the
content item does
not lag behind the live streaming of the content item, then the control
circuitry streams the
content item in real time at block 1320. If the playing of the content item
lags behind the live
streaming of the content item, process 1300 continues to block 1306.
[0112] At block 1306, the control circuitry identifies a duration of the lag
from the
timestamp of the segment included in the manifest. The control circuitry
calculates the
duration of the lag based on a time difference between when the content item
is paused and
when the content item is resumed. If there is more than one lag, the control
circuitry
calculates the total length of the lags.
[0113] At block 1308, the control circuitry selects a priority threshold based
on the duration
of the lag. In some embodiments, the priority threshold may be proportional to
the duration
of the lag. For example, if the duration of the lag is extended, then the
priority threshold
becomes high as the streaming application may present only a few of the highly
important
segments to catch up within a limited amount of time.
[0114] At block 1310, the control circuitry identifies a set of segments of
the plurality of
segments where a total length of the set of segments matches the duration of
the lag. For
example, when there is more than one lag, the control circuitry identifies,
based on the
manifest, all of the missed segments to match the total length of the delay.
[0115] At block 1312, the control circuitry identifies a segment that has a
priority level
value that is higher than the priority threshold based on the received
manifest from the media
server. In some embodiments, the media server sends the priority level
information of the
identified segment upon receiving an indication of the lag from the streaming
application at
block 1312. For example, upon receiving an indication of the lag, the media
server calculates
priority level information for the segments that fall within the total length
of the lag to
minimize the pre-calculation process of the priority level values and the
network data
transmission. This way, the media server does not have to calculate priority
level values for
all of the segments of the content item. Instead, the media server only
calculates the priority
level values for a limited number of segments that matches the length of the
delay.
[0116] At block 1314, the control circuitry retrieves a respective segment of
the subset
using a respective network address. The control circuitry skips retrieving a
respective
segment of the subset with a priority level lower than the priority threshold.
At block 1316,
23
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
the control circuitry stores each of the retrieved subset of the segments in a
cache of the user
device. The control circuitry may store the identified segments until the
content item is
caught up to live. The segments with priority level values lower than the
priority threshold
may not be stored in the cache as the presentation of those segments will be
skipped.
[0117] At block 1318, the control circuitry plays each of the stored subsets
of segments
from the cache. The control circuitry fetches the cached segments and causes
the content
item to catch up to live.
[0118] In one embodiment, upon determining that the playing of the content
item no longer
lags behind the live streaming, the control circuitry requests data from a
respective network
address of the set of segments of the plurality of content items regardless of
a respective
priority level value of the set of segments that follow the stored subset of
the plurality of
sequential segments in the content item, and stores the retrieved set of
segments in the cache
of the user device. For example, even though the retrieved set of segments
comprises a
priority level value that is lower than the priority threshold, the control
circuitry nevertheless
stores the retrieved set of segments in the cache and plays the set of
segments from the cache.
In another embodiment, upon determining that the playing of the content item
no longer lags
behind the live streaming, the control circuitry does not cache any of the
segments.
[0119] FIG. 14 depicts a generalized embodiment of an illustrative device
(e.g., user device
102, 202, 302, 402) that displays a live video stream. User equipment device
1400 may be
any of a plurality of user devices such as a smartphone, a tablet, personal
computer, set-top
box, etc. (discussed further below with respect to FIG. 15). User equipment
device 1400 may
receive the video stream and data via input/output (hereinafter "I/0") path
1402. I/0 path
1402 may provide the video stream (e.g., on-demand programming, Internet
content, content
available over LAN or WAN, and the like) and data to control circuitry 1404,
which includes
processing circuitry 1406 and storage 1408. Control circuitry 1404 may be used
to send and
receive commands, requests, and other suitable data using I/0 path 1402. I/0
path 1402 may
connect control circuitry 1404 (and specifically processing circuitry 1406) to
one or more
communications paths (described below in relation to FIG. 15). I/0 functions
may be
provided by one or more of these communications paths but are shown as a
single path in
FIG. 14 to avoid overcomplicating the drawing.
[0120] Control circuitry 1404 may be based on any suitable processing
circuitry such as
processing circuitry 1406. Processing circuitry should be understood to mean
circuitry based
on one or more microprocessors, microcontrollers, digital signal processors,
programmable
logic devices, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), application-specific
integrated
24
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
circuits (ASICs), etc., and may include a multi-core processor (e.g., quad-
core). In some
embodiments, processing circuitry may be distributed across multiple separate
processor or
processing units, for example, multiple of the same type of processing units
(e.g., two Intel
Core i7 processors) or multiple different processors (e.g., Ryzen processor
with integrated
CPU and GPU processing cores) or may include a multi-core processor (e.g.,
dual-core,
quad-core, hexa-core, or any suitable number of cores) or supercomputer. In
some
embodiments, control circuitry 1404 executes instructions for an application
stored in
memory (e.g., memory 1408). Specifically, control circuitry 1404 may be
instructed by a
media application to perform the functions discussed above and below. For
example, the
media application may provide instructions to control circuitry 1404 to
request a video stream
from server. Moreover, the media application may also collect user profile
information and
send to server prior to the encoding process. In some implementations, any
action performed
by control circuitry 1404 may be based on instructions received from the media
application.
[0121] Control circuitry 1404 may include tuning circuitry, such as one or
more analog
tuners, one or more MP3 decoders or other digital decoding circuitry, or any
other suitable
tuning or audio circuits or combinations of such circuits. Encoding circuitry
(e.g., for
converting analog or digital signals to signals for storage in storage 1408)
may also be
provided. Control circuitry 1404 may also include scaler circuitry for
upconverting and
downconverting content into the preferred output format of user equipment
device 1400, and
converter circuitry for converting between digital and analog signals. The
tuning and
encoding circuitry may be used by user equipment device 1400 to receive, play,
and buffer
content. The circuitry described herein, including, for example, the tuning,
audio generating,
encoding, decoding, encrypting, decrypting, scaler, and analog/digital
circuitry, may be
implemented using software running on one or more general purpose or
specialized
processors. If storage 1408 is provided as a separate device from user
equipment device 1400,
the tuning and encoding circuitry may be associated with storage 1408.
[0122] Storage 1408 may be any device for storing electronic data, such as
random-access
memory, solid state devices, quantum storage devices, hard disk drives, non-
volatile memory
or any other suitable fixed or removable storage devices, and/or any
combination of the same.
Control circuitry 1404 may allocate portions of storage 1408 for various
purposes such as
caching application instructions, recording media assets, storing portions of
a media asset,
buffering segments of media, etc. As described herein, storage 1408 may be
used to store
one or more LUTs storing a number of MAC addresses associated with a plurality
of user
equipment devices and their corresponding profile information.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
[0123] A user may send instructions to control circuitry 1404 using user input
interface
1410. User input interface 1410 may be any suitable user input interface, such
as a remote
control, mouse, trackball, keypad, keyboard, touchscreen, touchpad, stylus
input, joystick,
voice recognition interface, or other user input interfaces. Instructions to
control circuitry
1404 may be transmitted through I/0 path 1402, which could consist of a video
tracking and
detection mechanism, Internet of Things (IoT) and home automation triggers,
emergency
alert systems, and software or hardware communication pipelines and/or
notification centers.
[0124] Display 1412 may be provided as a stand-alone device or integrated with
other
elements of each one of user equipment device 1400. For example, display 1412
may be a
touchscreen or touch-sensitive display, a projector, or a casting device. In
such
circumstances, user input interface 1410 may be integrated with or combined
with display
1412. Display 1412 may be one or more of a monitor, a television, a liquid-
crystal display
(LCD) for a mobile device, silicon display, e-ink display, light-emitting
diode (LED) display,
or any other suitable equipment for displaying visual images. Graphics
processing circuitry
may generate the output to the display 1412. In some embodiments, the graphics
processing
circuitry may be external to processing circuitry 1406 (e.g., as a graphics
processing card that
communicates with processing circuitry 1406 via I/0 path 1402) or may be
internal to
processing circuitry 1406 or control circuitry 1404 (e.g., on a same silicone
die as control
circuitry 1404 or processing circuitry 1406). In some embodiments, the
graphics processing
circuitry may be used to receive, display, and play content.
[0125] Speakers 1414 may be provided as integrated with other elements of user
equipment
device 1400 or may be stand-alone units. The audio component of videos and
other content
displayed on display 1412 may be played through speakers 1414. In some
embodiments, the
audio may be distributed to a receiver (not shown), which processes and
outputs the audio via
speakers 1414. The speakers 1414 may be part of, but not limited to, a home
automation
system.
[0126] Streaming applications may be, for example, stand-alone applications
implemented
on user devices. For example, the streaming application may be implemented as
software or a
set of executable instructions, which may be stored in non-transitory storage
1408 and
executed by control circuitry 1404 of a user device 1502, 1504, 1506. In such
an approach,
instructions of the streaming application are stored locally (e.g., in storage
1408), and data for
use by the application is downloaded on a periodic basis (e.g., from an out-of-
band feed, from
an Internet resource, or using another suitable approach). Control circuitry
1404 may retrieve
instructions of the streaming application from storage 1408 and process the
instructions to
26
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
generate any of the displays discussed herein. Based on the processed
instructions, control
circuitry 1404 may determine what action to perform when user input is
received from input
interface 1410.
[0127] FIG. 15 depicts an exemplary media system in accordance with some
embodiments
of the disclosure, in which user equipment device 102, 202, 302, 402, and user
equipment
device 1400 can be implemented in the media system 1500 of FIG. 15 as user
television
equipment 1502, user computer equipment 1504, wireless user communications
device 1506,
or any other type of user equipment suitable for accessing media. For
simplicity, these
devices may be referred to herein collectively as user equipment or a user
device. User
equipment, on which the media application or the streaming application is
implemented, may
function as a stand-alone device or may be part of a network of devices.
Various network
configurations of devices may be implemented and are discussed in more detail
below.
[0128] User television equipment 1502 may include a set-top box, an integrated
receiver
decoder (IRD) for handling satellite television, a television set, a digital
storage device, or
other user television equipment. One or more of these devices may be
integrated to be a
single device, if desired. User computer equipment 1504 may include a PC, a
laptop, a
streaming content aggregator, a PC media center, or other user computer
equipment. It may
include devices like digital assistance, smart speakers, and/or home
automation. Wireless
user communications device 1506 may include a smartphone, a portable video
player, a
portable music player, a portable gaming machine, a tablet, a wireless
streaming device or
other wireless device. It should be noted that the lines are blurred when
trying to classify a
device as one of the above devices and one device may be categorized into one
or more of the
categories listed above.
[0129] In system 1500, there are typically more than one of each type of user
equipment,
but only one of each is shown in FIG. 15 to avoid overcomplicating the
drawing. In addition,
each user may utilize more than one type of user equipment (e.g., a user may
have a computer
and a tablet) and also more than one of each type of user equipment device
(e.g., a user may
have multiple television sets).
[0130] The user equipment may be coupled to communications network 1514.
Namely,
user television equipment 1502, user computer equipment 1504, and wireless
user
communications device 1506 are coupled to communications network 1514 via
communications paths 1508, 1510, and 1512, respectively. Communications
network 1514 is
used by the user equipment to obtain the video stream. Communications network
1514 may
be one or more networks including the Internet, a mobile phone network, ad-hoc
network, or
27
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
other types of communications network or combination of communications
networks. Paths
1508, 1510, and 1512 may separately or together include one or more
communications paths,
including any suitable wireless communications path. Path 1512 is drawn as a
dotted line to
indicate it is a wireless path. Communications with the user equipment may be
provided by
one or more of these communications paths but are shown as a single path in
FIG. 15 to avoid
overcomplicating the drawing. The user equipment devices may communicate with
each
other directly through an indirect path via communications network 1514.
[0131] System 1500 includes content item source 1516 and content item data
source 1518
coupled to communications network 1514 via communications paths 1520 and 1522,
respectively. Paths 1520 and 1522 may include any of the communications paths
described
above in connection with paths 1508, 1510, and 1512. Communications with the
content
item source 1516 and content item data source 1518 may be exchanged over one
or more
communications paths but are shown as a single path in FIG. 15 to avoid
overcomplicating
the drawing. In addition, there may be more than one of each of content item
source 1516
and content item data source 1518, but only one of each is shown in FIG. 15 to
avoid
overcomplicating the drawing. In some embodiments, content item source 1516
and content
item data source 1518 are integrated as one source device. Although
communications
between sources 1516 and 1518 with user equipment are shown as through
communications
network 1514, in some embodiments, sources 1516 and 1518 may communicate
directly with
user equipment devices 1502, 1504, and 1506 via communications paths (not
shown) such as
those described above in connection with paths 1508, 1510, and 1512.
[0132] Content item source 1516 or content item data source 1518 may include
one or more
types of media distribution equipment such as a media server, cable system
headend, satellite
distribution facility, intermediate distribution facilities and/or servers,
Internet providers, on-
demand media servers, and other media providers. Content item source 1516 or
content item
data source 1518 may be the originator of media content or may not be the
originator of
media content. Content item source 1516 or content item data source 1518 may
also include
a remote media server used to store different types of media content
(including a media asset
selected by a user), in a location remote from any of the user equipment.
Systems and
methods for providing remotely stored media to user equipment are discussed in
greater
detail in connection with Ellis et al., U.S. Patent No. 7,761,892, issued July
20, 2010, which
is hereby incorporated by reference herein in its entirety.
[0133] System 1500 is intended to illustrate a number of approaches, or
network
configurations, by which user equipment devices and sources of media content
and guidance
28
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
data may communicate with each other for the purpose of accessing media and
data related to
the media. The configuration of the devices and paths in system 1500 may
change without
departing from the scope of the present disclosure.
[0134] The processes discussed above are intended to be illustrative and not
limiting. One
skilled in the art would appreciate that the steps of the processes discussed
herein may be
omitted, modified, combined, and/or rearranged, and any additional steps may
be performed
without departing from the scope of the invention. More generally, the above
disclosure is
meant to be exemplary and not limiting. Only the claims that follow are meant
to set bounds
as to what the present invention includes. Furthermore, it should be noted
that the features
and limitations described in any one embodiment may be applied to any other
embodiment
herein, and flowcharts or examples relating to one embodiment may be combined
with any
other embodiment in a suitable manner, done in different orders, or done in
parallel. In
addition, the systems and methods described herein may be performed in real
time. It should
also be noted, the systems and/or methods described above may be applied to,
or used in
accordance with, other systems and/or methods. For example, processes 1100,
1200 and
1300 can be performed on any of the devices shown in FIGS. 14-15.
Additionally, any of the
steps in processes 1100, 1200 and 1300 can be performed in any order, can be
omitted, and/or
can be combined with any of the steps from any other process.
[0135] This specification discloses embodiments, which include, but are not
limited to, the
following:
1. A method comprising:
generating a content item for live streaming, the content item comprising a
plurality of
frames;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming of the content item, presenting a selectable option for a user
input, the option
comprising: (a) catch up to live in a particular time period; and
in response to receiving the user input via a corresponding option to (a)
catch up to
live in the particular time period:
skipping presentation of a portion of the plurality of frames, such that the
playing of the content item catches up to live in the particular time period.
2. The method of item 1, further comprising:
29
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
receiving a user input selecting a particular value for the particular time
period,
wherein the particular time period is adjusted based on the user input.
3. The method of item 1, wherein the option comprises: (b) catch up to
live immediately,
wherein the method further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (b) catch
up to live
immediately:
presenting a frame corresponding to the live streaming of the content item,
such that the playing of the content item catches up to live immediately.
4. The method of item 1, wherein the option comprises: (c) stop the
live streaming,
wherein the method further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (c) stop
the live
streaming:
presenting a corresponding frame of when determining that the playing of the
content item lags behind the live streaming, such that the playing of the
content item
does not match the live streaming of the content item.
5. The method of item 1, further comprising:
receiving a manifest of the content item, wherein the manifest identifies the
plurality
of frames of the content item;
wherein for each respective frame of the content item, the manifest comprises:
(a) a respective Uniform Resource Locator (URL);
(b) a respective hash code; and
(c) a respective timestamp.
6. The method of item 5, further comprising:
identifying a first frame of the content item as a last played frame of the
content item;
identifying a second frame of the content item that follows the first frame of
the
plurality of frames; and
identifying a third frame of the content item that is currently being
presented that is
different from the second frame.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
7. The method of item 6, wherein determining that the playing of the
content item lags
behind the live streaming of the content item comprises:
determining that the third frame does not match the second frame.
8. The method of item 7, wherein determining that the third frame does not
match the
second frame comprises:
determining a respective hash code for the second frame based on the manifest;
calculating a respective hash code based on a respective timestamp of the
third frame;
and
determining that the respective hash code for the second frame does not
correspond to
the calculated hash code of the third frame.
9. The method of item 1, further comprising:
determining, based on user profile data, user preference information for
skipping
presentation of the portion of the plurality of frames; and
presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
10. The method of item 9, wherein presenting a corresponding frame based on
the user
preference information is performed without receiving a user input specifying
the option.
11. A system comprising:
control circuitry configured to:
generate a content item for live streaming, the content item comprising a
plurality of frames;
user interface circuitry configured to:
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming of the content item, present a selectable option for a user input,
the option
comprising: (a) catch up to live in a particular time period; and
wherein the control circuitry is further configured to:
in response to receiving the user input via a corresponding option to (a)
catch
up to live in the particular time period:
skip presentation of a portion of the plurality of frames, such that the
playing of the content item catches up to live in the particular time period.
31
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
12. The system of item 11, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
receive a user input selecting a particular value for the particular time
period, wherein
the particular time period is adjusted based on the user input.
13. The system of item 11, wherein the option comprises: (b) catch up to
live
immediately, wherein the user interface circuitry is further configured to:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (b) catch
up to live
immediately:
present a frame corresponding to the live streaming of the content item, such
that the playing of the content item catches up to live immediately.
14. The system of item 11, wherein the option comprises: (c) stop the
live streaming,
wherein the user interface circuitry is further configured to:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (c) stop
the live
streaming:
present a corresponding frame of when determining that the playing of the
content item lags behind the live streaming, such that the playing of the
content item
does not match the live streaming of the content item.
15. The system of item 11, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
receive a manifest of the content item, wherein the manifest identifies the
plurality of
frames of the content item;
wherein for each respective frame of the content item, the manifest comprises:
(a) a respective Uniform Resource Locator (URL);
(b) a respective hash code; and
(c) a respective timestamp.
16. The system of item 15, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
identify a first frame of the content item as a last played frame of the
content item;
identify a second frame of the content item that follows the first frame of
the plurality
of frames; and
identify a third frame of the content item that is currently being presented
that is
different from the second frame.
32
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
17. The system of item 16, wherein the control circuitry, wherein
determining that the
playing of the content item lags behind the live streaming of the content
item, is further
configured to:
determine that the third frame does not match the second frame.
18. The system of item 17, wherein the control circuitry, wherein
determining that the
third frame does not match the second frame, is further configured to:
determine a respective hash code for the second frame based on the manifest;
calculate a respective hash code based on a respective timestamp of the third
frame;
and
determine that the respective hash code for the second frame does not
correspond to
the calculated hash code of the third frame.
19. The system of item 11, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
determine, based on user profile data, user preference information for
skipping
presentation of the portion of the plurality of frames; and
present a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
20. The system of item 19, wherein presenting a corresponding frame based
on the user
preference information is performed without receiving a user input specifying
the option.
21. A system comprising:
means for generating a content item for live streaming, the content item
comprising a
plurality of frames;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming of the content item, means for presenting a selectable option for a
user input, the
option comprising: (a) catch up to live in a particular time period; and
in response to receiving the user input via a corresponding option to (a)
catch up to
live in the particular time period:
means for skipping presentation of a portion of the plurality of frames, such
that the playing of the content item catches up to live in the particular time
period.
22. The system of item 21, further comprising:
33
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
means for receiving a user input selecting a particular value for the
particular time
period, wherein the particular time period is adjusted based on the user
input.
23. The system of item 21, wherein the option comprises: (b) catch up to
live
immediately, wherein the system further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (b) catch
up to live
immediately:
means for presenting a frame corresponding to the live streaming of the
content item, such that the playing of the content item catches up to live
immediately.
24. The system of item 21, wherein the option comprises: (c) stop the
live streaming,
wherein the system further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (c) stop
the live
streaming:
means for presenting a corresponding frame of when determining that the
playing of the content item lags behind the live streaming, such that the
playing of the
content item does not match the live streaming of the content item.
25. The system of item 21, further comprising:
means for receiving a manifest of the content item, wherein the manifest
identifies the
plurality of frames of the content item;
wherein for each respective frame of the content item, the manifest comprises:
(a) a respective Uniform Resource Locator (URL);
(b) a respective hash code; and
(c) a respective timestamp.
26. The system of item 25, further comprising:
means for identifying a first frame of the content item as a last played frame
of the
content item;
means for identifying a second frame of the content item that follows the
first frame
of the plurality of frames; and
means for identifying a third frame of the content item that is currently
being
presented that is different from the second frame.
34
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
27. The system of item 26, wherein means for determining that the
playing of the content
item lags behind the live streaming of the content item comprises:
means for determining that the third frame does not match the second frame.
28. The system of item 27, wherein means for determining that the third
frame does not
match the second frame comprises:
means for determining a respective hash code for the second frame based on the
manifest;
means for calculating a respective hash code based on a respective timestamp
of the
third frame; and
means for determining that the respective hash code for the second frame does
not
correspond to the calculated hash code of the third frame.
29. The system of item 21, further comprising:
means for determining, based on user profile data, user preference information
for
skipping presentation of the portion of the plurality of frames; and
means for presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference
information.
30. The system of item 29, wherein means for presenting a corresponding
frame based on
the user preference information is performed without receiving a user input
specifying the
option.
31. A non-transitory computer readable medium having non-transitory computer-
readable
instructions encoded thereon, comprising:
instructions for generating a content item for live streaming, the content
item
comprising a plurality of frames;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming of the content item, instructions for presenting a selectable option
for a user input,
the option comprising: (a) catch up to live in a particular time period; and
in response to receiving the user input via a corresponding option to (a)
catch up to
live in the particular time period:
instructions for skipping presentation of a portion of the plurality of
frames,
such that the playing of the content item catches up to live in the particular
time period.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
32. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 31, further
comprising:
instructions for receiving a user input selecting a particular value for the
particular
time period, wherein the particular time period is adjusted based on the user
input.
33. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 31, wherein the
option
comprises: (b) catch up to live immediately, and wherein the non-transitory
computer
readable medium further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (b) catch
up to live
immediately:
instructions for presenting a frame corresponding to the live streaming of the
content item, such that the playing of the content item catches up to live
immediately.
34. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 31, wherein the
option
comprises: (c) stop the live streaming, and wherein the non-transitory
computer readable
medium further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (c) stop
the live
streaming:
instructions for presenting a corresponding frame of when determining that the
playing of the content item lags behind the live streaming, such that the
playing of the
content item does not match the live streaming of the content item.
35. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 31, further
comprising:
instructions for receiving a manifest of the content item, wherein the
manifest
identifies the plurality of frames of the content item; and
wherein for each respective frame of the content item, the manifest comprises:
(a) a respective Uniform Resource Locator (URL);
(b) a respective hash code; and
(c) a respective timestamp.
36. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 35, further
comprising:
instructions for identifying a first frame of the content item as a last
played frame of
the content item;
instructions for identifying a second frame of the content item that follows
the first
frame of the plurality of frames; and
36
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
instructions for identifying a third frame of the content item that is
currently being
presented that is different from the second frame.
37. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 36, wherein
instructions for
determining that the playing of the content item lags behind the live
streaming of the content
item comprises:
instructions for determining that the third frame does not match the second
frame.
38. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 37, wherein
instructions for
determining that the third frame does not match the second frame comprises:
instructions for determining a respective hash code for the second frame based
on the
manifest;
instructions for calculating a respective hash code based on a respective
timestamp of
the third frame; and
instructions for determining that the respective hash code for the second
frame does
not correspond to the calculated hash code of the third frame.
39. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 31, further
comprising:
instructions for determining, based on user profile data, user preference
information
for skipping presentation of the portion of the plurality of frames; and
instructions for presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference
information.
40. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 39, wherein
presenting a
corresponding frame based on the user preference information is performed
without receiving
a user input specifying the option.
41. A method comprising:
generating a content item for live streaming, the content item comprising a
plurality of
frames;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind the
live
streaming of the content item, presenting a selectable option for a user
input, the option
comprising: (a) catch up to live in a particular time period; and
37
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
in response to receiving the user input via a corresponding option to (a)
catch up to
live in the particular time period:
skipping presentation of a portion of the plurality of frames, such that the
playing of the content item catches up to live in the particular time period.
42. The method of item 41, further comprising:
receiving a user input selecting a particular value for the particular time
period,
wherein the particular time period is adjusted based on the user input.
43. The method of any one of items 41-42, wherein the option comprises: (b)
catch up to
live immediately, wherein the method further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (b) catch
up to live
immediately:
presenting a frame corresponding to the live streaming of the content item,
such that the playing of the content item catches up to live immediately.
44. The method of any one of items 41-43, wherein the option comprises:
(c) stop the live
streaming, wherein the method further comprises:
in response to receiving a user input via a corresponding option to (c) stop
the live
streaming:
presenting a corresponding frame of when determining that the playing of the
content item lags behind the live streaming, such that the playing of the
content item
does not match the live streaming of the content item.
45. The method of any one of items 41-44, further comprising:
receiving a manifest of the content item, wherein the manifest identifies the
plurality
of frames of the content item;
wherein for each respective frame of the content item, the manifest comprises:
(a) a respective Uniform Resource Locator (URL);
(b) a respective hash code; and
(c) a respective timestamp.
46. The method of any one of items 41-45, further comprising:
identifying a first frame of the content item as a last played frame of the
content item;
38
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
identifying a second frame of the content item that follows the first frame of
the
plurality of frames; and
identifying a third frame of the content item that is currently being
presented that is
different from the second frame.
47. The method of any one of items 41-46, wherein determining that the
playing of the
content item lags behind the live streaming of the content item comprises:
determining that the third frame does not match the second frame.
48. The method of item any one of items 41-47, wherein determining that the
third frame
does not match the second frame comprises:
determining a respective hash code for the second frame based on the manifest;
calculating a respective hash code based on a respective timestamp of the
third frame;
and
determining that the respective hash code for the second frame does not
correspond to
the calculated hash code of the third frame.
49. The method of any one of items 41-48, further comprising:
determining, based on user profile data, user preference information for
skipping
presentation of the portion of the plurality of frames; and
presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
50. The method of any one of items 41-49, wherein presenting a
corresponding frame
based on the user preference information is performed without receiving a user
input
specifying the option.
51. A method comprising:
receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
identifying a first segment of the content item as a last played segment of
the content
item;
39
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
identifying a second segment of the content item that follows the first
segment of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
determining that playing of the content item lags behind live streaming of the
content
item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value, skipping
requesting data
from a respective network address of the second segment of the content item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value, requesting
data from a
respective network address of the third segment of the content item, wherein
the third
segment of the content item follows the second segment of the content item in
the plurality of
sequential segments of the content item; and
playing the third segment of the content item based on the data requested from
the respective network address of the third segment of the content item.
52. The method of item 51, further comprising:
identifying a fourth segment of the content item that follows the third
segment of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
requesting data from a respective network address of the fourth segment of the
content item, wherein a respective skippable bit value for the fourth segment
of the content
item comprises the first skippable bit value; and
playing the fourth segment of the content item based on the data requested
from the respective network address of the fourth segment of the content item.
53. The method of item 51, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
determined
based on a respective importance level of a respective segment.
54. The method of item 53, wherein the respective importance level of the
respective
segment is determined based on at least one of a number of replays of the
respective segment
in a predetermined time period, a type of the content item, or a genre of the
respective
segment in the content item.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
55. The method of item 53, wherein the first skippable bit value is
below an importance
threshold and the second skippable bit value is above the importance
threshold, and wherein
the second skippable bit value is different from the first skippable bit
value.
56. The method of item 51, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
inserted into the
manifest and stored in a database.
57. The method of item 51, wherein the segment comprises one or more
frames.
58. The method of item 51, wherein skipping a presentation of the second
segment of the
content item causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
59. The method of item 51, wherein a lag of the live streaming of the
content item is
caused based on a network connectivity, and wherein playing the content item
for display is
paused, such that playing the content item falls behind the live streaming of
the content item.
60. A method comprising:
transmitting, by a server, a manifest of a content item to a client device,
wherein the
manifest identifies a plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
identifying, by the server, a first segment of the content item as a last
played segment
of the content item on the client device;
identifying, by the server, a second segment of the content item that follows
the first
segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the
content item;
receiving, from the client device, an indication that playing of the content
item on the
client device lags behind live streaming of the content item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value, causing the
client device to
skip requesting data from a respective network address of the second segment
of the content
item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value, causing
the client device
41
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
to send a request of data from a respective network address for the third
segment of the
content item, wherein the third segment of the content item follows the second
segment of
the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
and
causing the client device to play the third segment of the content item based
on
the data requested from the respective network address of the third segment of
the content
item.
61. A system comprising:
control circuity configured to:
receive a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
identify a first segment of the content item as a last played segment of the
content
item;
identify a second segment of the content item that follows the first segment
of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
determine that playing of the content item lags behind live streaming of the
content
item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value, skip
requesting data from a
respective network address of the second segment of the content item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value, request
data from a
respective network address of the third segment of the content item, wherein
the third
segment of the content item follows the second segment of the content item in
the plurality of
sequential segments of the content item; and
user interface circuitry configured to:
play the third segment of the content item based on the data requested from
the
respective network address of the third segment of the content item.
62. The system of item 61, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
42
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
identify a fourth segment of the content item that follows the third segment
of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
request data from a respective network address of the fourth segment of the
content item, wherein a respective skippable bit value for the fourth segment
of the content
item comprises the first skippable bit value; and
play the fourth segment of the content item based on the data requested from
the respective network address of the fourth segment of the content item.
63. The system of item 61, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
determined based
on a respective importance level of a respective segment.
64. The system of item 63, wherein the respective importance level of the
respective
segment is determined based on at least one of a number of replays of the
respective segment
in a predetermined time period, a type of the content item, or a genre of the
respective
segment in the content item.
65. The system of item 63, wherein the first skippable bit value is below
an importance
threshold and the second skippable bit value is above the importance
threshold, and wherein
the second skippable bit value is different from the first skippable bit
value.
66. The system of item 61, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
inserted into the
manifest and stored in a database.
67. The system of item 61, wherein the segment comprises one or more
frames.
68. The system of item 61, wherein skipping a presentation of the second
segment of the
content item causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
69. The system of item 61, wherein a lag of the live streaming of the
content item is
caused based on a network connectivity, and wherein playing the content item
for display is
paused, such that playing the content item falls behind the live streaming of
the content item.
43
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
70. The system of item 61, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to receive
metadata of the content item, wherein the metadata comprises (a) a respective
network
address; and (b) a respective skippable bit value.
71. A system comprising:
means for receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest
identifies a
plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
means for identifying a first segment of the content item as a last played
segment of
the content item;
means for identifying a second segment of the content item that follows the
first
segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the
content item;
means for determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming of
the content item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value, means for
skipping
requesting data from a respective network address of the second segment of the
content item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value, means for
requesting
data from a respective network address of the third segment of the content
item, wherein the
third segment of the content item follows the second segment of the content
item in the
plurality of sequential segments of the content item; and
means for playing the third segment of the content item based on the data
requested from the respective network address of the third segment of the
content item.
72. The system of item 71, further comprising:
means for identifying a fourth segment of the content item that follows the
third
segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the
content item;
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
44
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
means for requesting data from a respective network address of the fourth
segment of the content item, wherein a respective skippable bit value for the
fourth segment
of the content item comprises the first skippable bit value; and
means for playing the fourth segment of the content item based on the data
requested from the respective network address of the fourth segment of the
content item.
73. The system of item 71, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
determined based
on a respective importance level of a respective segment.
74. The system of item 73, wherein the respective importance level of the
respective
segment is determined based on at least one of a number of replays of the
respective segment
in a predetermined time period, a type of the content item, or a genre of the
respective
segment in the content item.
75. The system of item 73, wherein the first skippable bit value is below
an importance
threshold and the second skippable bit value is above the importance
threshold, and wherein
the second skippable bit value is different from the first skippable bit
value.
76. The system of item 71, wherein the respective skippable bit value is
inserted into the
manifest and stored in a database.
77. The system of item 71, wherein the segment comprises one or more
frames.
78. The system of item 71, wherein skipping a presentation of the second
segment of the
.. content item causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
79. The system of item 71, wherein a lag of the live streaming of the
content item is
caused based on a network connectivity, and wherein playing the content item
for display is
paused, such that playing the content item falls behind the live streaming of
the content item.
80. The system of item 71, further comprising:
means for receiving metadata of the content item, wherein the metadata
comprises (a)
a respective network address; and (b) a respective skippable bit value.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
81. A non-transitory computer readable medium having non-transitory
computer-readable
instructions encoded thereon, comprising:
instructions for receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest
identifies
a plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
instructions for identifying a first segment of the content item as a last
played segment
of the content item;
instructions for identifying a second segment of the content item that follows
the first
segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the
content item;
instructions for determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming of the content item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value,
instructions for skipping
requesting data from a respective network address of the second segment of the
content item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value,
instructions for
requesting data from a respective network address of the third segment of the
content item,
wherein the third segment of the content item follows the second segment of
the content item
in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item; and
instructions for playing the third segment of the content item based on the
data
requested from the respective network address of the third segment of the
content item.
82. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, further
comprising:
instructions for identifying a fourth segment of the content item that follows
the third
segment of the content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the
content item;
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
instructions for requesting data from a respective network address of the
fourth segment of the content item, wherein a respective skippable bit value
for the fourth
segment of the content item comprises the first skippable bit value; and
instructions for playing the fourth segment of the content item based on the
data requested from the respective network address of the fourth segment of
the content item.
46
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
83. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, wherein the
respective
skippable bit value is determined based on a respective importance level of a
respective
segment.
84. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 83, wherein the
respective
importance level of the respective segment is determined based on at least one
of a number of
replays of the respective segment in a predetermined time period, a type of
the content item,
or a genre of the respective segment in the content item.
85. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 83, wherein the
first skippable
bit value is below an importance threshold and the second skippable bit value
is above the
importance threshold, and wherein the second skippable bit value is different
from the first
skippable bit value.
86. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, wherein the
respective
skippable bit value is inserted into the manifest and stored in a database.
87. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, wherein the
segment
comprises one or more frames.
88. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, wherein
skipping a
presentation of the second segment of the content item causes the content item
to catch up to
the live streaming.
89. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, wherein a lag
of the live
streaming of the content item is caused based on a network connectivity, and
wherein playing
the content item for display is paused, such that playing the content item
falls behind the live
streaming of the content item.
90. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 81, further
comprising:
instructions for receiving metadata of the content item, wherein the metadata
comprises (a) a respective network address; and (b) a respective skippable bit
value.
47
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
91. A method comprising:
receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each respective segment of the content item, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective skippable bit value;
identifying a first segment of the content item as a last played segment of
the content
item;
identifying a second segment of the content item that follows the first
segment of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
determining that playing of the content item lags behind live streaming of the
content
item:
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for the
second
segment of the content item comprises a first skippable bit value, skipping
requesting data
from a respective network address of the second segment of the content item;
in response to determining that a respective skippable bit value for a third
segment of the content item comprises a second skippable bit value, requesting
data from a
respective network address of the third segment of the content item, wherein
the third
segment of the content item follows the second segment of the content item in
the plurality of
sequential segments of the content item; and
playing the third segment of the content item based on the data requested from
the respective network address of the third segment of the content item.
92. The method of item 91, further comprising:
identifying a fourth segment of the content item that follows the third
segment of the
content item in the plurality of sequential segments of the content item;
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
requesting data from a respective network address of the fourth segment of the
content item, wherein a respective skippable bit value for the fourth segment
of the content
item comprises the first skippable bit value; and
playing the fourth segment of the content item based on the data requested
from the respective network address of the fourth segment of the content item.
48
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
93. The method of any of items 91-92, wherein the respective skippable bit
value is
determined based on a respective importance level of a respective segment.
94. The method of any of items 91-93, wherein the respective importance
level of the
.. respective segment is determined based on at least one of a number of
replays of the
respective segment in a predetermined time period, a type of the content item,
or a genre of
the respective segment in the content item.
95. The method of any of items 91-94, wherein the first skippable bit value
is below an
importance threshold and the second skippable bit value is above the
importance threshold,
and wherein the second skippable bit value is different from the first
skippable bit value.
96. The method of any of items 91-95, wherein the respective skippable bit
value is
inserted into the manifest and stored in a database.
97. The method of any of items 91-96, wherein the segment comprises one or
more
frames.
98. The method of any of items 91-97, wherein skipping a presentation of
the second
segment of the content item causes the content item to catch up to the live
streaming.
99. The method of any of items 91-98, wherein a lag of the live streaming
of the content
item is caused based on a network connectivity, and wherein playing the
content item for
display is paused, such that playing the content item falls behind the live
streaming of the
.. content item.
100. The method of any of items 91-99, further comprising:
receiving metadata of the content item, wherein the metadata comprises (a) a
respective network address; and (b) a respective skippable bit value.
101. A method comprising:
receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
49
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming
of the content item:
identifying a duration of a lag from the manifest of the content item;
based on the duration of the lag, selecting a priority threshold; and
identifying, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the plurality of
segments of the content item, wherein a total time length of the set of
segments matches the
duration of the lag;
identifying a subset of segments from the set of segments, wherein each
respective segment in the subset comprises a respective priority level value
higher than the
priority threshold;
retrieving each respective segment of the subset using a respective network
address;
storing each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache; and
playing each of the stored subset of segments from the cache.
102. The method of item 101, further comprising:
identifying, based on the manifest, another subset of segments from the set of
segments, wherein each respective segment in another subset comprises a
respective priority
level value lower than the priority threshold; and
in response to identifying another subset;
skipping retrieving of the respective segment of another subset from a
respective network address.
103. The method of item 102, wherein skipping a presentation of the respective
segment of
another subset causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
104. The method of item 101, further comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of the plurality of
segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set of segments of
the content item
is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and (b) lower than
the priority
threshold;
storing the retrieved set of segments of the content item; and
playing the stored set of segments of the content item.
105. The method of item 101, further comprising:
determining, based on user profile data, user preference information for
storing the
retrieved subset of segments in the cache; and
presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
106. The method of item 105, wherein priority level value is determined based
on a
respective relevance level of the frame based on the user profile data.
107. The method of item 101, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a respective importance level of the segment in context of the
content item.
108. The method of item 101, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a number of replays of the respective frame in a predetermined time
period.
109. The method of item 101, wherein the segment comprises one or more frames.
110. A method comprising:
transmitting, by a server, a manifest of a content item to a client device,
wherein the
manifest identifies a plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to receiving an indication from the client device that playing of
the
content item lags behind live streaming of the content item:
identifying, by the server, a duration of a lag from the manifest of the
content
item;
51
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
based on the duration of the lag, selecting, by the server, a priority
threshold;
identifying, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the plurality of
segments of the content item, wherein a total time length of the set of
segments matches the
duration of the lag;
identifying a subset of segments from the set of segments, wherein each
respective segment in the subset comprises a priority level value higher than
the priority
threshold;
retrieving each respective segment of the subset of segments using a
respective network address;
storing each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache; and
causing the client device to play each of the stored subset of segments from
the cache.
111. A system comprising:
control circuitry configured to:
receive a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming
of the content item:
identify a duration of a lag from the manifest of the content item;
based on the duration of the lag, select a priority threshold;
identify, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the plurality of
segments
of the content item, wherein a total time length of the set of segments
matches the duration of
the lag;
identify a subset of segments from the set of segments, wherein each
respective segment in the subset comprises a respective priority level value
higher than the
priority threshold;
retrieve each respective segment of the subset using a respective network
address;
store each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache; and
52
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
user interface control circuitry configured to:
play each of the stored subset of segments from the cache.
112. The system of item 111, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
identify, based on the manifest, another subset of segments from the set of
segments,
wherein each respective segment in another subset comprises a respective
priority level value
lower than the priority threshold; and
in response to identifying another subset;
skip retrieving of the respective segment of another subset from a respective
network address.
113. The system of item 112, wherein skipping a presentation of the respective
segment of
another subset causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
114. The system of item 111, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
retrieve data for a set of segments of the content item of the plurality of
segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set of segments of
the content item
is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and (b) lower than
the priority
threshold;
store the retrieved set of segments of the content item; and
play the stored set of segments of the content item.
.. 115. The system of item 111, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
determine, based on user profile data, user preference information for storing
the
retrieved subset of segments in the cache; and
present a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
116. The system of item 115, wherein priority level value is determined based
on a
respective relevance level of the frame based on the user profile data.
117. The system of item 111, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a respective importance level of the segment in context of the
content item.
53
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
118. The system of item 111, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a number of replays of the respective frame in a predetermined time
period.
119. The system of item 111, wherein the segment comprises one or more frames.
120. The system of item 111, wherein the control circuitry is further
configured to:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
skip retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of the
plurality of
segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set of segments of
the content item
is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and (b) lower than
the priority
threshold.
121. A system comprising:
means for receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest
identifies a
plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming
of the content item:
means for identifying a duration of a lag from the manifest of the content
item;
based on the duration of the lag, means for selecting a priority threshold;
and
means for identifying, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the
plurality
of segments of the content item, wherein a total time length of the set of
segments matches
the duration of the lag;
means for identifying a subset of segments from the set of segments, wherein
each respective segment in the subset comprises a respective priority level
value higher than
the priority threshold;
means for retrieving each respective segment of the subset using a respective
network address;
means for storing each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache; and
54
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
means for playing each of the stored subset of segments from the cache.
122. The system of item 121, further comprising:
means for identifying, based on the manifest, another subset of segments from
the set
of segments, wherein each respective segment in another subset comprises a
respective
priority level value lower than the priority threshold; and
in response to identifying another subset;
means for skipping retrieving of the respective segment of another subset from
a respective network address.
123. The system of item 122, wherein skipping a presentation of the respective
segment of
another subset causes the content item to catch up to the live streaming.
124. The system of item 121, further comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
means for retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of the
plurality of segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set
of segments of the
content item is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and
(b) lower than the
priority threshold;
means for storing the retrieved set of segments of the content item; and
means for playing the stored set of segments of the content item.
125. The system of item 121, further comprising:
means for determining, based on user profile data, user preference information
for
storing the retrieved subset of segments in the cache; and
means for presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference
information.
126. The system of item 125, wherein priority level value is determined based
on a
respective relevance level of the frame based on the user profile data.
127. The system of item 121, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a respective importance level of the segment in context of the
content item.
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
128. The system of item 121, wherein the respective priority level value is
determined
based on a number of replays of the respective frame in a predetermined time
period.
129. The system of item 121, wherein the segment comprises one or more frames.
130. The system of item 121, further comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
means for skip retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of
the
plurality of segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set
of segments of the
content item is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and
(b) lower than the
priority threshold.
131. A non-transitory computer readable medium having non-transitory computer-
readable
instructions encoded thereon, comprising:
instructions for receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest
identifies
a plurality of sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming
of the content item:
instructions for identifying a duration of a lag from the manifest of the
content
item;
based on the duration of the lag, instructions for selecting a priority
threshold;
and
instructions for identifying, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the
plurality of segments of the content item, wherein a total time length of the
set of segments
matches the duration of the lag;
instructions for identifying a subset of segments from the set of segments,
wherein each respective segment in the subset comprises a respective priority
level value
higher than the priority threshold;
56
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
instructions for retrieving each respective segment of the subset using a
respective network address;
instructions for storing each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache;
and
instructions for playing each of the stored subset of segments from the cache.
132. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, further
comprising:
instructions for identifying, based on the manifest, another subset of
segments from
the set of segments, wherein each respective segment in another subset
comprises a
respective priority level value lower than the priority threshold; and
in response to identifying another subset;
instructions for skipping retrieving of the respective segment of another
subset
from a respective network address.
133. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 132, wherein skipping
a
presentation of the respective segment of another subset causes the content
item to catch up
to the live streaming.
134. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, further
comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
instructions for retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of
the
plurality of segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set
of segments of the
content item is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and
(b) lower than the
priority threshold;
instructions for storing the retrieved set of segments of the content item;
and
instructions for playing the stored set of segments of the content item.
135. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, further
comprising:
instructions for determining, based on user profile data, user preference
information
for storing the retrieved subset of segments in the cache; and
instructions for presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference
information.
57
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
136. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 135, wherein priority
level
value is determined based on a respective relevance level of the frame based
on the user
profile data.
137. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, wherein the
respective
priority level value is determined based on a respective importance level of
the segment in
context of the content item.
138. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, wherein the
respective
-- priority level value is determined based on a number of replays of the
respective frame in a
predetermined time period.
139. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, wherein the
segment
comprises one or more frames.
140. The non-transitory computer readable medium of item 131, further
comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
instructions for skip retrieving data for a set of segments of the content
item of
-- the plurality of segments, wherein a respective priority level value for
the set of segments of
the content item is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold;
and (b) lower than
the priority threshold.
141. A method comprising:
receiving a manifest of a content item, wherein the manifest identifies a
plurality of
sequential segments of the content item,
wherein for each segment of the plurality of sequential segments, the manifest
comprises:
(a) a respective network address; and
(b) a respective priority level value;
in response to determining that playing of the content item lags behind live
streaming
of the content item:
identifying a duration of a lag from the manifest of the content item;
based on the duration of the lag, selecting a priority threshold; and
58
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
identifying, based on the manifest, a set of segments of the plurality of
segments of the content item, wherein a total time length of the set of
segments matches the
duration of the lag;
identifying a subset of segments from the set of segments, wherein each
respective segment in the subset comprises a respective priority level value
higher than the
priority threshold;
retrieving each respective segment of the subset using a respective network
address;
storing each of the retrieved subset of segments in a cache; and
playing each of the stored subset of segments from the cache.
142. The method of item 141, further comprising:
identifying, based on the manifest, another subset of segments from the set of
segments, wherein each respective segment in another subset comprises a
respective priority
level value lower than the priority threshold; and
in response to identifying another subset;
skipping retrieving of the respective segment of another subset from a
respective network address.
.. 143. The method of any of items 141-142, wherein skipping a presentation of
the
respective segment of another subset causes the content item to catch up to
the live streaming.
144. The method of any of items 141-143, further comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of the plurality of
segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set of segments of
the content item
is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and (b) lower than
the priority
threshold;
storing the retrieved set of segments of the content item; and
playing the stored set of segments of the content item.
145. The method of any of items 141-144, further comprising:
59
CA 03204498 2023-06-07
WO 2022/125559
PCT/US2021/062226
determining, based on user profile data, user preference information for
storing the
retrieved subset of segments in the cache; and
presenting a corresponding frame based on the user preference information.
.. 146. The method of any of items 141-145, wherein priority level value is
determined based
on a respective relevance level of the frame based on the user profile data.
147. The method of any of items 141-146, wherein the respective priority level
value is
determined based on a respective importance level of the segment in context of
the content
.. item.
148. The method of any of items 141-147, wherein the respective priority level
value is
determined based on a number of replays of the respective frame in a
predetermined time
period.
149. The method of any of items 141-148, wherein the segment comprises one or
more
frames.
150. The method of any of items 141-149, further comprising:
in response to determining that playing of the content item no longer lags
behind the
live streaming:
skipping retrieving data for a set of segments of the content item of the
plurality of segments, wherein a respective priority level value for the set
of segments of the
content item is at least one of: (a) higher than the priority threshold; and
(b) lower than the
priority threshold.