Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 1 -
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR MANAGING TOKENS AND FILTERING DATA TO
CONTROL DATA ACCESS
Introduction
[0001] This disclosure is directed to systems and methods for managing tokens
and filtering
data to selectively control access to data. Specifically, techniques are
provided for providing
a token to a data recipient to enable the data recipient to request user
information, and
obtaining user information to be sent to the data recipient based on a token
received from a
data provider. In addition, techniques are provided for filtering data and
providing the filtered
data to a data recipient based on a data directive associated with a data
provider.
Summary
[0002] Technological advances in the transmission, storage and processing of
digital
information has had a profound impact on almost every aspect of life (e.g.,
commerce, social
interactions, internet of things (JOT) technology, etc.). For example, many
organizations
desire to obtain a consumer's electronic data for a variety of reasons, e.g.,
to tailor product
and service recommendations to the consumer based on the user's interests and
past
purchases. However, such organizations may provide little or no opportunity
for a user to
manage his or her data obtained by the organization. In some cases, an
organization may,
unbeknownst to the user, have an affiliation with a third party that holds
information of the
user for long periods of time, which may expose the user to security and/or
privacy risks with
respect to his or her personal information.
[0003] As an example, in the context of consumer financial data accessible
over the
Internet, the practice of screen scraping has long been utilized in which a
data aggregator is
compensated by a financial services company (e.g., a fintech) to capture a
user's login
credentials in plain text. For example, a user may have an online account with
a financial
institution (e.g., a bank) and when the user selects an option to connect his
or her account to a
fintech, a data aggregator acting on behalf of the fintech may prompt the user
to enter his or
her log-in credentials for the financial institution. Upon receiving the
user's log-in
credentials, the aggregator copies and stores the login credentials and uses
the captured login
credentials to access the user's online bank account and scrape all available
account
information and store such information, and may continue to scrape data from
the user's
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 2 -
account even after the request to connect the bank with the fintech is
completed. The data
aggregator may then share the user's bank account information with the fintech
(and possibly
other parties), and the fintech may also store such information and present
the information to
the user once the user has successfully connected his or her bank account to
the fintech. In
addition to the above-described data privacy concerns associated with screen
scraping, the
practice of screen scraping may require significant computing resources. For
example, screen
scraping is computationally intensive and requires significant bandwidth and
storage
resources for the storage of the scraped data for a large number of users.
[0004] In one approach, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) may be
employed as
an alternative to screen scraping for financial data access. For example, the
bank may receive
a user's login credentials and use APIs to provide the required data to an
aggregator or
directly to the fintech. However, APIs may be difficult to scale; while many
financial
institutions have negotiated "bilateral" agreements with aggregators and
fintechs to use APIs
for data access, there are over 10,000 financial institutions in North America
and thousands
of fintechs. Moreover, APIs face technical challenges (e.g., limited
standardization across
API specifications and formats), security challenges (e.g., multiple security
assessments and
scoring methodologies may result in lost time compared to a common vetting and
registration
process) and legal challenges (e.g., individual bilateral agreements with
differing terms may
cause expensive and prolonged negotiations). Thus, there is a need for a
convenient and
secure mechanism for providing a data recipient access to user data associated
with a data
provider in a manner that avoids one or more intermediary parties having
access to and
storing the data.
[0005] Moreover, while it is often desirable for a data provider (e.g., a
bank) to limit how
much user data is provided to a data recipient (e.g., a fintech) in response
to a user request to
share data with the data recipient, it may be difficult or time-consuming for
the data provider
or other entity to filter through the user data and extract only the data
suitable for the request.
In one approach, an intermediary entity, upon receiving incoming data, may
operate on the
entire payload of the data at the byte level to determine which data should be
filtered.
However, such approach is time-consuming when considered in the context of a
number of
operations on data such an entity is required to perform. In addition, the
intermediary entity
often retains any of the information operated on in persistent storage,
including confidential
and/or personal data of a user. Thus, there is a need for a better technique
for filtering user
data to ensure that no more data than necessary flows to a data recipient,
while at the same
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 3 -
time avoiding the practice of permitting unauthorized parties to maintain
confidential or
personally identifiable information data of a user, e.g., via the practice of
screen scraping, and
to avoid the aforementioned significant usage of computing resources
associated with the
widespread practice of screen scraping.
[0006] To overcome the above-mentioned problems, systems and methods are
provided
herein for, in response to receiving a user request to share certain
information of the user that
is associated with a data provider with a data recipient, employing one or
more tokens to
ensure each data recipient or data provider is authorized to access and/or
provide access to
user information data, without providing user credentials to unauthorized or
unnecessary
parties. In some embodiments, a token may be updated based on additional data
recipients
being granted access to the user information. In some embodiments, a key-value
map data
structure may be employed to filter data in accordance with a data directive
received from a
data provider, to efficiently analyze data received from the data provider and
provide only
data permitted by the data directive to a data recipient.
[0007] In some embodiments, processing circuitry may be configured to receive
a request
to grant authorization for a data recipient to access user information
associated with a data
provider, where the request is initiated by a user interacting with a service
associated with the
data recipient, and in response to receiving the request, re-direct the user
from the service
associated with the data recipient to an authenticator associated with the
data provider, where
the re-directing notifies the data provider of the request. The processing
circuitry may be
configured to receive a first token from the data provider indicating the user
has been
successfully authenticated by the authenticator, and provide a second token to
the data
recipient. In response to receiving the second token along with a request for
user information
from the data recipient, user information data may be obtained from the data
provider using
the first token and provided to the data recipient.
[0008] In some embodiments, the service associated with the data recipient is
a web page or
application, and the request to grant authorization is received by an
intermediary entity,
where executable instructions of the intermediary entity are executable to re-
direct the user to
the authenticator of the data provider. In some embodiments, receiving the
first token from
the data provider indicating the user has been successfully authenticated by
the authenticator
comprises: receiving an authorization grant code from the data provider, and
in response to
receiving the authorization grant code from the data provider, requesting the
first token from
the data provider. In some embodiments, prior to performing the re-directing,
the processing
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 4 -
circuitry may be configured to verify the data provider, and determine whether
the data
recipient, associated with the request to grant authorization, has been
authorized by the data
provider to access the user information, determine whether the data provider
is authorized to
provide access to the user information data. In some embodiments, the
processing circuitry
may be further configured to request, using the first token, a list of
accounts or products that
the user has with the data provider and receive the list of accounts or
products from the data
provider. The processing circuitry may be further configured to cause a
graphical user
interface to be generated for display, where the graphical user interface
comprises the list of
accounts or products that the user has with the data provider, and a
selectable option, for each
of the accounts or products, to selectively share with the data recipient
information associated
with respective accounts or products of the user with the data provider.
[0009] In some embodiments, the processing circuitry may be further configured
to request,
using the first token, a list of accounts or products that the user has with
the data provider,
and receive the list of accounts or products from the data provider, where the
list of accounts
or products specifies which accounts or products the data recipient is to be
granted access to
(which may be different from a list of accounts or products of the user with
the data provider
that other entities are to be granted access to). In some embodiments,
providing the second
token to the data recipient comprises generating the second token, wherein the
second token
is associated with a list of accounts or products that the user has with the
data provider to
which the data recipient is granted access, generating an authorization grant
code associated
with the second token, re-directing the user to the data recipient and
transmitting the
authorization grant code to the first data recipient, and in response to
receiving the
authorization grant code back from the data recipient, transmitting the second
token to the
data recipient. In some embodiments, the second token is generated by an
intermediary entity
and is stored by the intermediary entity without any personally identifiable
information of the
user, where re-directing the user from the service associated with the data
recipient to the
authenticator associated with the data provider may comprise providing an
indication to the
data provider that the intermediary entity is re-directing the user to the
data provider on
behalf of the data recipient, and the intermediary entity may be transparent
to the user within
user interfaces provided by the data recipient and the data provider.
[0010] In some embodiments, processing circuitry may be configured to receive
a first
request from a user to grant authorization for a first data recipient to
access user information
associated with a data provider and a second request from the user to grant
authorization for a
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 5 -
second data recipient to access user information associated with the data
provider. The
processing circuitry may be configured to receive an authentication token from
the data
provider, where the authentication token enables access to user information
associated with
the data provider, generate a first token for the first data recipient and a
second token (e.g.,
different from the first token) for the second data recipient, and provide the
first token to the
first data recipient and providing the second token to the second data
recipient. In response to
receiving the first token along with a request for user information from the
first data recipient,
the processing circuitry may be configured to obtain user information data
using the
authentication token and providing the user information data to the first data
recipient, and in
response to receiving the second token along with a request for user
information from the
second data recipient, obtain user information data using the authentication
token and
providing the user information data to the second data recipient.
[0011] In some embodiments, processing circuitry may be configured to receive
the first
request prior to the second request, where the authentication token is
received after the first
request and prior to the second request, and the authentication token
indicates that the first
data recipient is granted access to user information associated with the data
provider. In
addition, an updated version of the authentication token may be received after
the second
request, where the updated version of the authentication token indicates that
each of the first
data recipient and the second data recipient is granted access to user
information associated
with the data provider. In some embodiments, the first data recipient or the
second data
recipient also acts as a data provider. In some embodiments, an identity token
comprising
personally identifiable information of the user may be generated and embedded
in the first
token and the second token.
[0012] In some embodiments, the provided systems and methods further comprise
identifying, based on an indication from the data provider, that an account or
product that the
user has with the data provider should not be shared with the first data
recipient and the
second data recipient, and causing the identified account or product to be
omitted from a list
of accounts or products provided via the graphical user interface.
[0013] In some embodiments, the provided systems and methods further comprise,
for each
time a new request is received from the user to grant authorization to a new
candidate data
recipient to access user information associated with the data provider:
generating an updated
version of the authentication token, wherein the updated authentication token
indicates that
each of the first data recipient, the second data recipient, and the new
candidate data recipient
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 6 -
is granted access to user information associated with the data provider;
generating a third
token for the new candidate data recipient; and in response to receiving the
third token along
with a request for user information from the new candidate data recipient,
obtaining user
information data using the authentication token and providing the user
information data to the
new candidate data recipient.
[0014] In some embodiments, processing circuitry may be configured to receive
a byte
stream from a data provider, and identifying a plurality of data elements of a
data record
included in the byte stream. The processing circuitry may be configured to
transfer the
identified data elements to buffer memory, and generate a key-value map to map
the
identified data elements to their respective memory locations in the buffer
memory. The
processing circuitry may be further configured to perform, based on a data
directive (e.g.,
received from the data provider) and using the key-value map, filtering of the
data elements,
and provide the filtered data elements to a data recipient. In some
embodiments, the byte
stream is generated by converting data from a first format into the byte
stream, wherein the
first format comprises a plurality of data elements packaged into a data
record.
[0015] In some embodiments, the buffer memory is a temporary memory to which
the
filtered data elements are transferred for processing; and the filtered data
elements are deleted
from the temporary memory in response to performing the filtering. The
filtered data
elements may not include any personally identifiable information of a user. In
some
embodiments, the processing circuitry may receive the data directive from the
data provider
in advance, where the data directive specifies which data elements of the
plurality of data
elements are permitted to be provided to the data recipient. In some
embodiments, the
processing circuitry may be configured to receive a plurality of data
directives from the data
provider for respective data recipients, where each of the plurality of data
directives specifies
a different combination of data elements that are permitted to be provided to
a respective data
recipient. In some embodiments, the processing circuitry is further configured
to receive user
selection of an account of the data provider to provide the data recipient
access to, wherein
the filtered data elements provided to the data recipient comprise data from
the user selected
account.
[0016] In some embodiments, the processing circuitry may be configured to
perform the
filtering of the data elements by identifying, using the key-value map,
locations in memory of
data elements of the data record that match (and locations of data elements of
the data record
that do not match) permissible data elements specified in the data directive,
and delete from
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 7 -
memory the data elements of the data record that do not match permissible data
elements
specified in the data directive. In some embodiments, prior to providing the
filtered data
elements to the data recipient, the processing circuitry may be configured to
convert the data
elements to a format suitable for providing the data to the data recipient,
which may match
the first format from which the data is converted into the byte stream. In
some embodiments,
filtering of the data elements comprises masking a predefined number of
characters of a data
element of the identified data elements such that only a subset of the
characters of the data
element are readable.
[0017] In some embodiments, input/output circuitry may be configured to
receive at an
intermediary entity a token from a data provider that enables access to a
user's data at a data
provider, where the token is received without the intermediary entity
receiving user
credentials, and receive a request from a data recipient to receive data from
the data provider,
where the token is required to access the data. Processing may be configured
to receive data
from the data provider using the token, filter the received data, based on a
data directive
associated with the data provider, to identify which data the data recipient
is permitted to
access, and provide the identified data to the data recipient. Executable code
of the
intermediary entity may be executable to re-direct the user from respective
web pages or
applications associated with the data recipient to the provider.
[0018] In some embodiments, the processing circuitry may be configured to
receive a
request from a data recipient to access information from a data provider
associated with a
user, wherein the request comprises a data recipient token. The processing
circuitry may be
further configured to validate the request, and in response to validating the
request, transmit a
secondary token to the data provider. The processing circuitry may be further
configured to
receive the information from the data provider, generate a package of
authorized information
based on the information received from the data provider, and transmit the
package of
authorized information to the data recipient.
[0019] In some embodiments, the processing circuitry may be configured to
validate the
request by: validating the data recipient token; and determining whether the
data recipient is
authorized by the data provider. In some embodiments, the processing circuitry
is configured
to transmit the package of authorized information to the data recipient
further by: transmitting
as the package of authorized information only information from accounts or
products of the
user with the data provider having been previously authorized by the user for
the data
recipient. In some embodiments, the processing circuitry is further configured
to: identify,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 8 -
based on the information received from the data provider, certain categories
of data not
permitted to be shared with the data recipient; and remove the identified
categories of data
from the package of authorized information. In some embodiments, the data
recipient token is
generated by an intermediary entity; and the secondary token is generated by
the data
provider in response to authenticating the user. In some embodiments, the
processing
circuitry is further configured to receive the secondary token from the data
provider after the
user is authenticated, where the data provider authenticates the user in
response to executable
instructions of the intermediary entity being executed to re-direct the user
from a web page
or application associated with the data recipient to the data provider.
Brief Description of the Drawings
[0020] The above and other objects and advantages of the present disclosure
will be
apparent upon consideration of the following detailed description, taken in
conjunction with
the accompanying drawings, in which like reference characters refer to like
parts throughout,
and in which:
[0021] FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for selectively
providing data
to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure;
[0022] FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for selectively
providing data
to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure;
[0023] FIG. 3 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for enabling a
data provider
to connect to multiple data recipients, in accordance with some embodiments of
this
disclosure;
[0024] FIG. 4 shows a block diagram of token management system for selectively
providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of
this disclosure;
[0025] FIG. 5 shows exemplary interfaces provided to data recipients and data
providers, in
accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure;
[0026] FIG. 6 shows exemplary interfaces provided to users, in accordance with
some
embodiments of this disclosure;
[0027] FIG. 7 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for token
management and
selectively providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments of this
disclosure;
[0028] FIG. 8 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for selectively
providing data
to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure;
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 9 -
[0029] FIG. 9 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for selectively
providing data
to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure;
[0030] FIG. 10 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for managing
tokens for
selectively providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments of this
disclosure;
[0031] FIG. 11 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for managing
tokens for
selectively providing data to multiple data recipients, in accordance with
some embodiments
of this disclosure;
[0032] FIG. 12 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for filtering
data based on a
data directive to selectively provide data to a data recipient, in accordance
with some
embodiments of this disclosure;
[0033] FIG. 13 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for
transmitting a package of
authorized information to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments of this
disclosure; and
[0034] FIG. 14 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for
generating an identity
token, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure.
Detailed Description
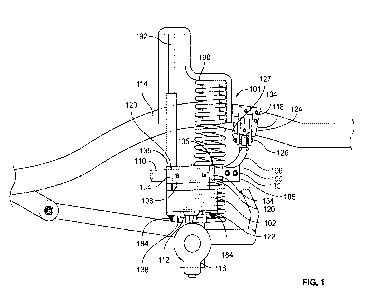
[0035] FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system 100 for
selectively providing
data to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this
disclosure. System 100
includes one or more data providers 104, 106, 108 which may comprise servers
and/or
databases associated with a particular entity (e.g., a financial institution
such as, for example,
a bank). User devices 118, 120, 122 may be associated with a user (e.g., user
204 of FIG. 2)
having an account with, or having purchased products associated with or
offered by, one or
more of data provider 104, 106, 108. For example, data provider 104 may store
information
related to a bank account of user 204, that user 204 previously subscribed to
with data
provider 104. Data access network 110 may be configured to act as an
intermediary between
data providers 104, 106, 108 and data recipients 112, 114, 116 (e.g., servers
and/or databases
associated with a financial services company, such as a fintech, an
aggregator, RIA platform,
payroll processing entity, credit card entity, other banking entity, etc.).
Network 102 may
comprise any suitable network (e.g., the Internet, including a WAN and/or a
LAN) over
which data access network 110, data providers 104, 106, 108, data recipients
112, 114, 116
and user devices 118, 120, 122 may communicate. In some embodiments, a
particular entity
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 10 -
may be capable of taking on a role as both a data provider and a data
recipient, depending on
the circumstances of a particular transaction or the entities involved in the
particular instance.
For example, in one instance, data provider 104 may act as a data provider,
but in another
instance data provider 104 may be configured to act as a data recipient.
[0036] FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system 200 for
selectively providing
data to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this
disclosure. At 202, user
device 118, 120 or 122 of FIG. 1, being operated by user 204, may be accessing
a website or
application associated with data recipient 112 of FIG. 1 (which may correspond
to data
recipient 212). User 204 may request to link one or more accounts he or she
has with data
provider 206 to data recipient 212. In some embodiments, data access network
210 (e.g.,
running at least in part on one or more of data access network servers 702;
and/or data
provider server 706; and/or user device 705; and/or data recipient server 712
of FIG. 7) may
be configured to cause such user request received by data recipient 212 to be
forwarded to
data provider 206 (which may correspond to data provider 106 of FIG. 1). For
example, one
or more executable instructions may be provided by data access network 210 to
data recipient
212 in order to facilitate re-directing user 204 from the service associated
with data recipient
112 to a service associated with data provider 206. For example, data access
network 210
(which may correspond to data access network 110 of FIG. 1) may provide code
(e.g.,
contained a URL address) to instruct data recipient 112 how to perform re-
directing (e.g., by
way of an HTTP instruction to a specified location) of a browser or
application being
accessed by user 204 to an authenticator service provided by data provider
206. In some
embodiments, data access network 210 may perform the re-directing of the user
request to
data provider 206, upon receiving an indication of the user request from data
recipient 212, or
data access network 210 may cause data recipient 212 to forward the user
request to data
provider 206 (e.g., to a particular URL address of data provider 206 specified
by data access
network 210). In some embodiments, the one or more executable instructions
provided by
data access network 210 may be running in the background, embedded or
otherwise
integrated in such data recipient 112 website or application.
[0037] Data access network 210 may determine that the user request received by
data
recipient 212 comprises a request from user device 118 indicating that user
204 desires to
share information associated with a user account at data provider 104, which
may correspond
to a website or an application associated with bank 206) with data recipient
212. In some
embodiments, data access network 210 may be transparent to user 204, e.g.,
from the user
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624 PC
T/US2022/047287
- 11 -
experience perspective, the websites or applications user 204 is interacting
with remain
associated with the data recipient 112 or data provider 104), and such
websites or
applications may not include an indication of the data access network 210. For
example,
respective user interfaces provided by data recipient 112 and data provider
104 may not
include an indication (e.g., a logo or text or other indicia) of data access
network 210.
[0038] In response to receiving the request from user device 118 indicating
that user 204
desires to share information associated with a user account at bank 206 with
data recipient
212, data access network 210 may re-direct user 204 (e.g., accessing the
service of data
recipient 112 by way of user device 118) to a website or application
associated with data
provider 206, which may be an authenticator application that prompts user 204
to enter his or
her account credentials for the account or profile of user 204 with data
provider 104. In some
embodiments, the re-directing may be performed by data access network 210
based on a
Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) determined by data access network 210 and/or
provided
by data provider 104 to data access network 210. In some embodiments, prior to
re-directing
user 204 operating user device 118 (e.g., running a browser or application of
data recipient
212) to the website or application associated with data provider 104, data
access network 210
may perform a check to ensure that data provider 104 has authorized its users
to share
information with data recipient 112, and/or a check to ensure that data
provider 104 is a
recognized data provider of data access network 210. For example, data access
network 210
may reference one or more databases (e.g., authorized data provider
information database 715
of FIG. 7 and/or authorized data recipient information database 717 of FIG. 7)
of authorized
data recipients and/or data providers in order to perform this determination.
In some
embodiments, data access network 210 may generate an intermediary header to be
placed at a
beginning portion of the re-direct request communicated to data provider 104,
to indicate to
data provider 104 that data access network 210 is re-directing a user from
data recipient 112
to data provider 104, and that there is a user requesting to share his or her
data stored at data
provider 104 with data recipient 112. In some embodiments, the re-directing
performed by
data access network 210 to a domain of data provider 206 may be over a front
channel (e.g.,
communicated via a browser or user-facing application at user device 118).
[0039] In some embodiments, at 208, the authenticator application of data
provider 104
(e.g., bank 206) may perform the authentication of user 204 (e.g., without the
involvement of
data access network 210), and thus the credentials of user 204 need not be
copied or stored
externally by data access network 210 or other third parties. Once user 204 is
authenticated,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 12 -
permissioned data may be passed by data provider 206 to data access network
210, where
data access network 210 and data provider 206 may have previously been
configured to
accept communications from each other. In some embodiments, data provider 206
and data
access network 210 may communicate via an Application Programming Interface
(API). As
.. referred to herein, an API should be understood as protocols for defining
interactions
between, and integrating, two pieces of software (which may have distinct
functions) by
providing expected requests, conventions, and data formats, enabling entities
to interact
without requiring knowledge of implementation details. In some embodiments,
the Financial
Data Exchange (FDX) specifications may be utilized to define the above-
mentioned APIs. In
some embodiments, the APIs may be RESTful APIs which may request and send data
in
various formats (e.g., JSON, XML, HTML, etc.). The FDX-based API may be
commonly
operable amongst a variety of entities. In some embodiments, data access
network 210 may
determine whether bank 206 is utilizing the FDX API, and the if data access
network 210
determines bank 206 is not utilizing the FDX-based API, data access network
210 may
.. convert data received from bank 206 into a format that is compatible with
the FDX API.
[0040] Data access network 210 may communicate the permissioned data received
from
bank 206 to one or more data recipients (e.g., one of fintech app 212, fintech
app 214, fintech
app 216 and aggregator 218). In some embodiments, data access network 210 may
filter the
data prior to transmitting the data to a data recipient, such as, for example,
in accordance with
a data directive (e.g., data directive 808 of FIG. 8) received from, or
otherwise generated by
data access network 210 at the direction of, bank 206, as discussed in more
detail above and
below. The data directive may be generated in any suitable manner, e.g.,
received by data
access network 210 from data provider 206; established by data provider 206 by
way of
management console 504 of FIG. 5 provided by data access network 210; and/or
data access
network 210 may generate the data directive based on instructions and/or a
written agreement
between data access network 210 and data provider 206. Thus, in some
embodiments, data
access network 210 may handle all third-party connections on behalf of bank
206, to enable
the data recipient 212 service (e.g., a website or application) to provide the
data received
from data access network 210 for presentation to user 204. For example, if the
information
relates to a user's bank account with bank 206, data access network 210 may
filter out certain
portions of the user's bank account information, and fintech app 212 may
present the filtered
user information data to the user to enable the user to perform desired
actions with his or her
information on fintech app 212.
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 13 -
[0041] FIG. 3 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system 300 for enabling
a data
provider to connect to multiple data recipients, in accordance with some
embodiments of this
disclosure. Data access network 310 may enable each of data providers 302,
304, 306 (e.g., a
financial institution such as a bank) to connect to one or more of multiple
data recipients 312,
314, 316 based on a single integration and implementation of data access
network 310. For
example, such integration enables data access network 310 to utilize API
connections and act
as an intermediary between data providers 302 and data recipients 312, 314,
316, to enable
data access network 310 to handle all downstream data recipient relationships
on behalf of
data providers 302, 304, 306, thereby providing reliable and secure FDX-
compatible API
connections for controlled data sharing between entities. In some embodiments,
data access
network 310 may provide to data provider 302 communications, e.g.,
notifications and
updates concerning maintenance, data recipient onboarding, and enhancements.
[0042] FIG. 4 shows a block diagram of token management system 400 for
selectively
providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of
this disclosure.
At 402, user device 420 (e.g., a mobile device, such as, for example, user
device 120 of FIG.
1) of user 404 accessing a website or application of data recipient 412
transmits a request to
grant data recipient 412 access to a data provider 406 (e.g., Mikomo Bank)
with which user
404 has one or more accounts, e.g., checking account 422, savings account 424,
basic savings
account 426, money market account 428. In some embodiments, the request may
contain
information regarding the scope of access data recipient 412 is requesting
(e.g., specify which
accounts of the user's with data provider 406) and/or data access network 410
may store
information indicating information typically required by data recipient 412 in
connection
with users accounts. In some embodiments, the request may contain information
regarding a
redirect URI (e.g., where to redirect the browser or application being
accessed by user 404 to
link his or her account with data provider 406 with his or her account with
data recipient 412,
after the user is authenticated at data provider 406).
[0043] In some embodiments, one or more executable instructions may be
provided by data
access network 410 (e.g., in an address URL) to be executable to redirect user
404 associated
with user device 420 to a login interface 414 of a website or application
associated with data
provider 406. In some embodiments, fintech service 412 may notify data access
network 410
of the request to link the accounts of user 404 associated with data provider
406, to enable
data access network 410 to process the request. In some embodiments, prior to
performing
the re-directing, data access network 410 may perform a check to ensure that
each of data
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 14 -
provider 406 and fintech app 412 is associated with an identifier indicating
that such services
are validated with data access network 410. Such re-directing may be performed
over a front
channel, e.g., a browser or application being accessed by user 404 may be re-
directed to a
domain of data provider 406. In some embodiments, data recipients verified by
data access
network 410 may by default be permitted to request user information from data
provider 406
via data access network 410, e.g., data provider 406 may be provided with an
interface (e.g.,
management console 504 of FIG. 5) to disable certain data recipients that data
provider 406
may not desire to provide user information to. Alternatively, data recipients
may not be
permitted to request user information associated with data provider 406 absent
receiving
affirmative permission to do so from data provider 406 by way of management
console 504
of FIG. 5.
[0044] Data provider 406 may authenticate user 404 based on login credentials
received
from user device 420. In some embodiments, OIDC, 0Auth 2.0 alone or in
conjunction with
Open ID Connect protocols, cookies, and/or SAML protocols may be implemented
for
authorization and/or authentication. In some embodiments, data access network
410 may be
configured to standardize multiple types of the authentication techniques used
by multiple
data providers into a common format, to enable data recipient 412 (and all
other data
recipients) to communicate with data access network 410 using a single
technique. That is,
regardless of an authentication format being employed by a particular data
provider that a
data recipient is requesting authorization to access user data at, the data
recipient may be
provided with a standard token format by data access network 410, with which
to
communicate with data access network 410. In some embodiments, collector 726
may be
utilized to perform this standardization, as discussed in more detail below.
[0045] Once user 404 is authenticated by data provider 406, data provider 406
may present
a user agreement of terms and conditions at interface 418, and data access
network 410 may
receive from data provider 406 authorization grant code 419 indicating that
user 404 has been
authenticated and consented to terms and conditions of data provider 406. Such
terms and
conditions may indicate to user 404 the consequences of permitting a third
party (e.g., data
recipient 412) access to his or her data with data provider 406. In some
embodiments, access
network 410 does not receive, along with the indication that user 404 has been
authenticated,
information regarding the login credentials (e.g., user name and password)
entered by user
404 at log-in interface 414 of data provider 406, e.g., data access network
410 is not able to
determine personally identifiable information or an identity of user 404. Data
access network
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 15 -
410 may transmit authorization grant code 419 back to data provider 406 in
order to initiate a
request for authentication token 421 from data provider 406. Authentication
token 421 may
be usable by data access network 410 to obtain a list of products or accounts
purchased or
subscribed to by authenticated user 404 with data provider 406. Data provider
406 may
transmit authentication token 421 to data access network 410 in exchange for
authorization
grant code 419. In some embodiments, the exchange of authorization grant code
419 and
authentication token 421 may occur over a backchannel, e.g., a secure
communication
channel enabling direct communication between one or more servers (e.g.,
server 702 of FIG.
7) of data access network 410 to and one or more servers (e.g., server 706 of
FIG. 7) of data
provider 406, without being transmitted through a browser or user-facing
application of user
device 420.
[0046] In some embodiments, using the received authentication token 421 of
data provider
406, data access network 410 may request a product and/or account list of user
404 for
selection and transmission to data recipient 412, and cause the product and/or
account list of
user 404 to be generated for display at graphical user interface (GUI) 423.
GUI 423 may be
provided by data access network 410 and/or data provider 406 and may permit
user 404 to
selectively indicate which accounts or products to share with data recipient
412 (e.g.,
checking account 422, savings account 424 and basic savings account 426) and
which
accounts or products not to share with data recipient 412 to access (e.g.,
money market
account 428). For example, each account or product may be associated with a
selectable
option (e.g., check mark) to specify whether a data recipient should be
granted access to
information associated with that account or product. In some embodiments, in
presenting
GUI 423, the look and feel, and/or formatting style of data provider 406 may
be employed,
e.g., even if being hosted by data access network 410. For example, data
access network 410
may store stylistic information (e.g., a logo and color scheme for each data
provider), and
cause display of GUI 423 based on the identified stylistic information of the
data provider.
[0047] In some embodiments, the website or application associated with data
provider 406
may query data access network 410 through APIs to receive and/or transmit
information
regarding how many and which accounts are selected. For example, data access
network 410
may cause, based on receiving an API call from data provider 406, GUI 423 to
be generated
for display by enabling data provider 406 to generate for display GUI 423 in
connection with
a webpage or application associated with data provider 406. For example, data
provider 406
may provide GUI 423, to enable user 404 to control which or how much data to
share with
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 16 -
data recipient 412. In some embodiments, GUI 423 may reflect each account user
404 has
with data provider 406, e.g., user 404 may have four total accounts with data
provider 406
from among each of the accounts or products offered by data provider 406
(e.g., 100 total
accounts or products). In some embodiments, GUI 423 may provide an option that
enables a
user to sign up or purchase new accounts or products from data provider 406,
e.g., where
selection of such option causes user 404 to be re-directed to an application
or website of data
provider 406 to subscribe to or purchase new accounts or products offered by
data provider
406. For example, upon selecting such option, data provider 406 may present
additional
account offerings, e.g., a college savings account, that the user does not
currently have with
data provider 406.
[0048] In some embodiments, data provider 406 may determine that information
related to
certain accounts or products should not be provided to any data recipient. For
example, if
data provider 406 determines that information related a particular product or
account (e.g., an
escrow account) should not be provided to any data recipients, an icon
associated with such
product or account may not be displayed at GUI 423 (or may be displayed as
grayed out icon
that is not selectable). In some embodiments, data provider 406 may determine
that
information related to certain accounts or products should not be provided to
a particular data
recipient. For example, if data provider 406 determines that a particular
product account type
(e.g., a health savings account) should not be provided to a particular data
recipient (e.g.,
Venmo), an icon associated with such product or account may not be displayed
at GUI 423
(or may be displayed as grayed out icon that is not selectable) if user 404 is
attempting to link
his or her products or accounts with data provider 406 with such particular
data recipient. In
some embodiments, upon receiving selection at GUI 423 of a particular account
from which
information may be shared with data recipient 412, such selections may be
stored at any
suitable data structure (e.g., an authorized accounts selection database),
such as, for example,
in connection with an account ID.
[0049] Once data access network 410 and/or data provider 406 receives
selection by user
404 of option 430 of GUI 423 to submit the selected products or accounts, data
access
network 410 may redirect user 404 back to data recipient 412 e.g., as shown at
interface 432
indicating that the user's request to link his or her accounts with data
provider 406 with data
recipient 412 has been successfully completed. Data access network 410 may
additionally
generate and transmit to data recipient 412 authorization grant code 434.
Authorization grant
code 434 may be associated with the indicated accounts and/or products 422,
424, 426 of user
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 17 -
404 with data provider 406 that data recipient 412 has been authorized to
access data from.
Data recipient 412 may transmit authorization grant code 434 back to data
access network
410, e.g., to call the APIs of data access network 410, causing data access
network 410 to
provide a token 436 (e.g., a first data access identifier token) to data
recipient 412 in
exchange for authorization grant code 434. In some embodiments, first data
access identifier
token 436 may be unique to the particular user, data provider and data
recipient combination,
e.g., a different data recipients linked to the user's accounts with the same
data provider may
be provided with a different data access identifier token. In some
embodiments, authorization
grant code 434 may be transmitted to data recipient 412 together when the user
is re-directed
back to data recipient 412.
[0050] In some embodiments, the exchange of authorization grant code 434 and
token 436
may occur over a backchannel, e.g., a secure communication channel enabling
direct
communication between a server (e.g., server 702 of FIG. 7) of data access
network 410 and
a server (e.g., server 706 of FIG. 7) of data provider 406, without being
transmitted through a
browser or user-facing application. In some embodiments, one or more of
authorization grant
code 434 and token 436 may indicate which data categories that data recipient
412 has been
permitted by user 404 to access and/or an information regarding when code 434
or token 436
expires. In some embodiments, no personally identifiable information of user
404 is stored in
association with, or is represented by, token 436. In some embodiments, data
access network
410 may generate an identifier or hash value associated with user 404, without
any
identifying information. Data access network 410 may cause token 436, and
other tokens
issued by data access network 410 and/or other entities, to be stored (e.g.,
at storage 710 of
FIG. 7). In some embodiments, token 436 is valid only for data recipient 412
and is
recognized by data provider 406 only if received from data access network 410,
e.g., if token
436 were to be received by data provider 406 directly from data recipient 412,
data provider
406 may refrain from providing user information data to data recipient 412.
[0051] Data recipient 412 may use token 436 received from data access network
410 to
request from data access network 410 account and/or product details of user
404 with data
provider 406 (e.g., by appending or otherwise attaching token 436 to the
request). In some
embodiments, data recipient 412 may include with the request a re-direct URI
indicating a
resource location at which data access network 410 may transmit permissioned
data to data
recipient 412. Data access network 410 may use authentication token 421,
received from data
provider 406, to request permissioned data associated with accounts and/or
products of user
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 18 -
404 with data provider 406. Upon receiving such permissioned data, data access
network 410
may reference a data entitlements directive associated with data provider 406,
which specifies
which data from the permissioned data is permissible to grant data recipient
412 access to.
The data directive may have been previously generated by data provider 406 and
provided to
data access network 410, and/or an updated version of the data directive may
be transmitted
from data provider 406 to data access network 410 along with the requested
permissioned
data. Additionally or alternatively, data access network 410 may generate the
data directive
based on instructions provided by data provider 406.
[0052] Data access network 410 may perform filtering of the received data
based on the
data directive, as discussed in more detail above and below. In some
embodiments, the
filtered data may be stored in a buffer (e.g., buffer memory 729 of FIG. 7),
and deleted from
the buffer after being transmitted to data recipient 412 (or in response to
determining a data
element is not authorized to be sent to a particular data recipient). For
example, a particular
data recipient may be determined by data access network 410 as unauthorized to
receive
certain data elements (e.g., based on a data directive associated with data
provider 406) and
such data elements may be deleted from buffer memory 729 prior to transmitting
the filtered
data to data recipient 412.
In some embodiments, deleting data from buffer memory 729 may correspond to
overwriting
the data with new incoming data so as to permanently remove, purge, or flush
the filtered or
unauthorized data from buffer 729 and render the filtered or unauthorized data
inaccessible.
In some embodiments, the filtered data elements may be deleted immediately
after
transmission to data recipient 412 or within a predefined period of time after
transmission
(e.g., any appropriate or suitable amount of time, such as, for example, less
than one second;
less than thirty seconds; or less than one minute). In some embodiments,
deleting the filtered
data from buffer memory 729 may correspond to replacing the filtered data with
a value
indicating the particular data field is eligible to be reallocated for other
purposes.
[0053] Data access network 410 may transmit the filtered data (e.g., user
information data)
to data recipient 412 to enable data recipient 412 to present such data via
interface 438 at user
device 420 of user 404. As discussed, the system of FIG. 4 may enable users to
authenticate,
select accounts, and permission data to flow from their data provider through
the data access
network and to a third-party data recipient (e.g., a fintech app), while
avoiding sharing with
third parties the login information of the user. In some embodiments, upon
expiration of one
or more of token 421 and 436, user 404 may be required to log-in and/or agree
to terms and
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 19 -
services at interface 418 to continue sharing permissioned information with
data recipient
412.
[0054] In some embodiments, data access network 410 may determine that user
404 desires
to link his or her account or product information associated with data
provider 406 to an
additional data recipient (e.g., data recipient 314 of FIG. 3), in addition to
data recipient 412.
For example, data access network 410 may provide one or more executable
instructions (e.g.,
in a URL address) to an application, website or other service associated with
data recipient
314, which may be executable to re-direct user 404 to data access network 410
and/or data
provider 406, which may receive a request to share with data recipient 314
account
information of user 404 with data provider 406. In some embodiments, data
recipient 314
may notify data access network 410 of this request. Data access network 410
may redirect
user 404 accessing the website or application of data recipient 314 to log-in
at interface 414
provided by data provider 406, and receive an indication from data provider
406 once data
recipient 314 has been successfully authenticated and agreed to terms and
services of data
provider 406 at interface 418. In some embodiments, interface 418 may not be
provided to
user 404 since user 404 may have previously agreed to the terms and conditions
of the user
agreement provided by data provider 406.
[0055] Data access network 410 may receive from data provider 406 an updated
version of
token 421 previously received from data provider 406 in connection with
granting data
recipient 412 access to information of user 404. For example, token 421 may be
updated to
include an indication that data recipient 314 is now being granted access to
at least some of
the user information, in addition to data recipient 412. In some embodiments,
either data
access network 410 or data provider 406 may perform the updating of the
tokens. Data access
network 410 and/or data provider 406 may use such updated version of token 421
to request
user information and present a screen similar to GUI 423, to permit user 404
to specify which
accounts or products data recipient 314 is to be granted access to. In some
embodiments, data
provider 406 may provide GUI 423 to user 404 at user device 420. In some
embodiments,
data access network 410 may perform the updating of authentication token 421,
based on
information or instructions received from data provider 406. Such updating of
authentication
token 421 may be performed by data provider 406 and/or data access network 410
each time
a new request is received from user 404 to grant authorization to a new
candidate data
recipient to access user information associated with data provider 406. That
is, authentication
token 421 may comprise an indication of each data recipient previously
authorized by the
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 20 -
user to access user data at a particular data provider 406 (e.g., first data
recipient 412, second
data recipient 314, any previously authorized candidate data recipients, and
the new
candidate data recipient). In some embodiments, authentication token 421 may
further
comprise an identity token associated with a particular user, as discussed in
more detail in
connection with FIG. 14, which may be employed to transmit PII data to one or
more data
recipients.
[0056] Data access network 410 may receive selections of certain products
and/or accounts
displayed at GUI 423, and may generate a second data access identifier token
associated with
data recipient 314 that is distinct from first data access identifier token
436 associated with
.. data recipient 412. That is, data access network 410 may, based on
instructions received from
data provider 406, maintain and issue separate data access identifier tokens
for each of data
recipient 412 and data recipient 314, although each of such data access
identifier tokens may
be associated with requesting access to data of user 404 stored in association
with data
provider 406. In some embodiments, authentication token 421 is associated only
with data
.. provider 406, e.g., a different data provider may be provided with a
different authentication
token in the event a user desires to link his or her account with such
different data provider to
a data recipient. In some embodiments, user 404 may specify at GUI 423 that a
different set
of accounts or products should be provided to data recipient 314 as compared
to data
recipient 412, and data access network 410 may separately track such differing
accounts or
products of user 404 with data provider 406 that the respective data
recipients have been
granted access to.
[0057] Data access network 410 may provide the second data access identifier
token from
data recipient 314, e.g., in exchange for a grant authorization grant code
previously
transmitted to data recipient 314, and may use the second data access
identifier token to
.. request user information of user 404 and associated with data provider 406.
In some
embodiments, data provider 406 may provide a data directive for data recipient
314 that
differs from the data directive for data recipient 412, which may result in
data access network
410 performing filtering of user information in a different manner depending
on the data
recipient. Thus, interface 438 provided by data recipient 314 may provide
different
information (e.g., user information data) from interface 438 for data
recipient 314 (e.g., based
on differing use selections at GUI 423 and/or differing data directives for
the data recipients).
It should be appreciated that data access control network 410 may provide
connections
between any number of users, data providers and data recipients. In some
embodiments, if a
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
-21 -
data recipient receives an indication from user 404 that its access to user
information
associated with data provider 406 is being terminated or revoked, the data
recipient may
notify data access network 410, which in turn may notify data provider 406.
[0058] Data access network 410 may employ a data access API based on Financial
Data
Exchange (FDX) specifications, to enable data recipients to request consumer-
permissioned
data to flow from a data provider through data access network 410. In some
embodiments,
through data mapping and API integration, data access network 410 may
translate responses
from data providers (even those with proprietary APIs) into a common format,
enabling
expected and standard API responses which may mitigate the need for
proprietary APIs,
thereby reducing development costs. Exemplary code which may be utilized by
the data
access API is shown below (e.g., corresponding to interface 438 of FIG. 4):
> curl --request GET \
--url https://akoya.com/akoya/access/fiId/accountsdetails/t1/v1 \
--header 'akoyaId: akoyaid-test'
>
"Accounts": {
"InvestmentAccount": [
"accountId": "1755093543",
"accountType": "CHK",
"displayName": "Checking Account",
"nickname": "Checking Account",
"accountNumber": "*****2431",
"currency": "USD",
"balanceType": "ASSET",
"balanceAsOf": 0,
"currentValue": 7398.45,
"availableCashBalance": 7158.96,
"transactions": [
"transactionId": "152652715",
"transactionTimestamp": "1588219200",
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 22 -
"description": "Megastore",
"status": "POSTED",
"amount": -65.98
"transactionId": "178426915",
"transactionTimestamp": "1587528000",
"description": "Coffee Shop",
[0059] FIG. 5 shows exemplary interfaces provided to data recipients and data
providers, in
accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure. Data access network 510
may be
configured to provide (e.g., via data access network server 110 of FIG. 1,
and/or installed at
least in part on data provider server 104 of FIG. 1) management console 504 to
enable data
providers to self-manage their connections and configure their settings in
data access network
510, e.g., to review and approve data recipients as well as determine which
use cases to
present to a given recipient. Management console 504 may include products
portion 516
where data provider 506 can manage information (e.g., Account ID, Account
Type, Balance
as of a certain date, Currency) related to a particular user account that data
recipient 512 has
been granted access to, a portion 518 regarding data recipients having been
granted access to
user accounts associated with data provider 506, and products portion 516
identifying
products of data provider 506 that one or more data recipients 512 have been
granted access
to. Data access network 510 may additionally or alternatively be configured to
provide (e.g.,
via data access network server 110 of FIG. 1, and/or installed at least in
part on data recipient
112 of FIG. 1) data recipient hub 505 to provide data recipients (e.g.,
aggregators and/or
fintechs) the ability to manage their connection to data providers, such as,
for example, data
provider 506. For example, data recipient 512 may view information regarding
checking
account 520, loan account 522, and savings account 524 that data recipient 512
may have
been granted access to by a user having such accounts with data provider 406.
[0060] In some embodiments, management console 504 may enable data provider
506
and/or data access network 510 to revoke access to a data recipient on-the-
fly, e.g., upon
determining the particular data recipient has been compromised. In some
embodiments,
management console 504 may enable data provider 506 to specify, or otherwise
instruct data
access network 510, that data (or requests to access user data stored at data
provider 506)
should not be sent to data provider 506 (or data recipient 512) at certain
times, or only certain
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 23 -
data should be sent at certain times. For example, a particular data provider
may prefer not to
be flooded with data traffic from the hours of 9 AM EST ¨ 10 AM EST of a
business day,
since many users may log into data provider 506 at this time to manage their
stock portfolio,
and the data provider may communicate this preference to data access network
510. In some
embodiments, data
[0061] FIG. 6 shows exemplary interfaces provided to users, in accordance with
some
embodiments of this disclosure. In some embodiments, data provider 606 may
provide user
interface 605 comprising permissions dashboard 604 to an authorized user
(e.g., user 204 of
FIG. 2) to enable the user to manage which of his or her accounts or providers
to grant data
recipients access to. In response to receiving a request from the user to
access permissions
dashboard 604, data provider 606 may, at 608, utilize a permission API (e.g.,
FDX API)
associated with data access network 610 to request permission data from data
access network
610, and data access network 610 may in response provide information allowing
the user or
consumer of data provider 606 to see which data recipients have access to
their permissioned
data, add new accounts, remove accounts, or remove access overall. For
example,
permissions dashboard 604 at interface 607 may enable the user to make changes
to account
selections, e.g., as adding new accounts or removing access to other accounts.
In some
embodiments, data provider 606 may send, at 609, the updated account
information of the
user to data access network 610, and data access network 610 may provide the
updated
information to data recipient 612 having been given permission by the user to
access the
products or services of the user with data provider 606, e.g., granting or
revoking access to
certain products or services of the user with data provider 606 based on the
user's selections
at interface 607.
[0062] FIG. 7 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system 700 for token
management
and selectively providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments of
this disclosure. System 700 may comprise one or more of data access network
server 702
(which may correspond to data access network 110 of FIG. 1), one or more of
data provider
server 706 (which may correspond to data provider server 104, 106, 108 of FIG.
1), one or
more of user device 705 (which may correspond to user device 118, 120, 122 of
FIG. 1), and
one or more of data recipient server 712 (which may correspond to, e.g., data
recipient server
112, 114, 116 of FIG. 1). Data access network server 702 may comprise
processing circuitry
704 which may comprise hardware, software or any combination thereof, such as,
for
example, one or more central processing units (CPUs), e.g., a processor,
configured to
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 24 -
execute non-transitory instructions stored (e.g., encoded) in computer-
readable media (e.g.,
non-transitory memory 713 and/or non-transitory storage 710) to implement
operating
system(s) and applications of data access network server 702 and perform
and/or control
various operations on data and other computations. For example, processing
circuitry 704
may be configured to execute instructions to implement data access network
110, 210, 310,
410, 510, 610, 810, 910, of FIGS. 1-6 and 8-10. Data access network server 702
may further
comprise input/output circuitry 707 and/or communications circuitry 708
configured to
receive input (e.g., from an operator or network administrator of data access
network server
702), receive communications or requests from, e.g., data provider 706, user
device 705, data
recipient 712), transmit requests to, e.g., data provider 706, user device
705, data recipient
712, database 715, database 717, and/or output information, e.g., to an
operator of network
operator or network administrator of data access network server 702. Storage
710 and/or
memory 713 of data access network server 702 may comprise one or more of, for
example,
Random Access Memory (RAM), Read Only Memory (ROM), EEPROM, ASIC, optical
storage, magnetic storage, flash memory, solid state memory, or any
combination thereof, or
any other suitable medium used to store data.
[0063] Memory 713 may be configured to store one or more applications
executable by
processing circuitry 704 to provide one or more of data recipient hub 714, key-
value map
716, admin dashboard 718, curator 720, management console 722, database
interface 724,
collector 726, and data recipient interface 728. Any suitable programming
languages may be
employed to implement such applications at the backend and/or the frontend,
e.g., Java, C,
Python, Go, JavaScript (e.g., React library), Typescript, Handlebar, React,
etc. Data recipient
hub 714 may correspond to data recipient hub 505 of FIG. 5, and may be
configured to
provide a portal for a data recipient associated with data recipient server
712, such as, for
example, by way of data recipient user interface portion 772, to enable data
recipients to
manage credentials and data access. Key-value map 716, e.g., an associative
array or hash
table, may generate (based on identified data elements having been transferred
to buffer
memory 729 by data access network 702) a plurality of key-value pairs, where
the key and
the value are linked such that the key may be a unique identifier indicative
of a location of a
data item, and the value corresponds to such data item. In some embodiments,
data received
from a data provider may be converted into the form of a key-value map to
enable efficient
retrieval and filtering of data, as is discussed in more detail below. Curator
720 may, in
association with authorized data provider information database 715, store
authorized data
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 25 -
providers (e.g., financial institutions), store products and account offerings
associated with
the authorized data providers, and manage data recipient subscriptions to data
provider
products and account offerings. In some embodiments, data recipient 712 may
utilize and
FDX API call to access elements stored in association with curator 720 and
authorized data
provider information database 715. Databases 715 and 717 may be implemented
using any
suitable combination or hardware and software to store and organize data in a
structured
format, and provide data in response to receiving a query, e.g., from data
access network
server 702.
[0064] Admin dashboard 718 may be configured to enable an operator or
administrator of
data access network server 702 to monitor elements of system 700 and/or
configure settings
of data access network server 702. For example, admin dashboard 718 permits
logging,
auditability, and traceability of data flows within system 700, and admin
dashboard 718
permits management of data recipients, data providers and data directives
received from data
providers, e.g., authorize or remove certain data providers or data
recipients, update data
directives associated with data providers, manage user accounts and/or user
permissions
granted. Management console 722 may be configured to provide management
console 504 of
FIG. 5, which may correspond to management console UI portion 740 of FIG. 7,
and may be
configured to provide one or more interfaces for data providers to manage
which data is made
available to which data recipients, e.g., which data directives apply to which
use cases and/or
users and/or data recipients for a particular data provider.
[0065] Database interface 724 may be configured to interface with authorized
data recipient
information database 717, which may store a record of which accounts each
consumer has
authorized each data recipient to access. Collector 726 may be configured to
be
communicatively coupled to authorized data provider information database 715
storing
information related to users having accounts or products with the data
provider. In some
embodiments, each data provider may be respectively associated with one or
more databases.
Collector 726 may be configured to communicate with data providers, e.g.,
translate requests
or responses received from data providers to an FDX compatible format, e.g.,
in the event
that such requests or responses are received in a format that is not FDX-
compliant. In some
embodiments, collector 726 may comprise a plurality of collector modules which
may be
respectively configured for specific data providers, e.g., to convert
authentication standards
of the respective data providers into a standardized format. In some
embodiments, each
collector module may contain software specific to a particular data provider
(e.g., settings,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 26 -
authentication protocol, and/or other specific software). In some embodiments,
each data
provider may be associated with a data flow and an authentication flow through
a
corresponding collector module of collector 726. The respective collector
module may utilize
whatever APIs the particular data provider is employing to collect data on the
fly, and
transform the data to the FDX format if the data is not in such format. In
some embodiments,
collector 726 may be configured to route data through a particular path for a
specific data
provider, and parallel processing and load balancing techniques may be
employed, e.g., if
multiple data recipients are requesting data from a particular data provider.
[0066] Data recipient interface 728 may comprise an externally facing API for
use by data
recipients to access permissioned consumer data (e.g., financial data). Memory
713 may
include a buffer memory 729 configured to store data in a transitory manner,
e.g., to store
byte stream 811 and/or user data 804 for a temporary period of time in order
to operate and
filter user data 804 of FIG. 8. In some embodiments, data access network
server 702 may
employ an identity provider (IdP) to handle user authentication for data
providers and admin
.. dashboard 718. In some embodiments, a third party service may be utilized
(e.g., data
recipients may utilize Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cognito for their IdP). In
some
embodiments, an abstraction layer may be provided by data access network
server 702 for
interaction with the data recipient user accounts (e.g., at AWS Cognito),
roles, and/or email
sending via a third party service (e.g., AWS SES). In some embodiments, data
access
network server 702 may provide a permissions API, which may be an externally
facing API
for data providers to build their own consumer permission management
dashboards against.
In some embodiments, access network server 702 may provide an interface to
handle end
user authentication workflows (e.g., to perform a handoff to the correct data
provider for
authentication). In some embodiments, role based permissions may be utilized,
e.g., to restrict
access by data recipients to unauthorized information. In some embodiments,
data access
network server 702 may employ security provisions, e.g., a Least Privilege
Zero-Trust
Model, secure application development implementing DevSecOps, NIST and FFIEC
frameworks, to ensure data is secure, and data access network server 702 may
employ each of
in-flight and at-rest encryption to ensure data is secure.
[0067] Data provider server 706 may comprise processing circuitry 730,
input/output
circuitry 732, communications circuitry 734, storage 736 and memory 738, which
may be
implemented in a similar manner as processing circuitry 704, input/output
circuitry 707,
communications circuitry 708, storage 710 and memory 713, respectively, of
data access
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 27 -
network server 702. Data provider server 706 may be communicatively coupled to
data
access network server 702, user device 705 and data recipient 712. For
example, data
provider server 706 may be associated with a financial institution such as,
for example, a
bank, that permits users to access their accounts to view information related
to their account
and subscribe to new products (e.g., a checking account). Processing circuitry
730 may be
configured to execute instructions stored in memory 738 and/or storage 736 to
provide
management console UI portion 740, user accounts 742 and directives 744.
Management
console UI portion 740 may be installed at, or otherwise provided to, data
provider server
706, which may correspond to management console 504 of FIG. 5, and which may
be
configured to provide data providers with the ability to view information
related to products
to self-manage their connections and configure their settings in connection
with data access
network 702, e.g., to review and approve data recipients as well as determine
which use cases
to present to a given recipient. In some embodiments, management console UI
portion 740
may enable data providers to specify which data directives 744 are to be
applied to certain
use cases and/or certain users and/or certain data recipients, and may enable
data providers to
monitor which data recipients have been granted access to which user
information stored in
association with data provider 706. For example, management console UI portion
740 may
permit an operator or administrator of the data provider to log in and
configure data elements
to be sent to certain data recipients. In some embodiments, management console
UI portion
740 may allow a provider to view data transmission in real time, including
system logs and
flow volumes. As used herein, data elements may be understood as any suitable
combination
of products (e.g., offered by data providers) and/or accounts (e.g., which may
be products
subscribed to by a user, and may be viewed by and selectable at GUI 423 of
FIG. 4). For
example, a product may be a mortgage, a checking account, a savings account,
etc., and data
elements related to the product may comprise an account number, an account
balance, an
interest rate, etc.
[0068] In some embodiments, data provider server 706 may provide information
to, and
update information stored at, authorized data provider information database
715. Data
provider server 706 may store information related to user accounts 742, such
as, for example,
which accounts or products of the data provider that a particular user is
subscribed to or has
with the data provider. In some embodiments, data provider server 706 may be
configured to
provide to user device 705 a permissions dashboard 604 and receive an
indication from user
device 705 of which accounts or products that a data recipient is to be
granted access. In
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 28 -
some embodiments, the data access network application is transparent to a user
accessing a
website or application provided by data provider server 706 (e.g., logos or
other indicia of the
data access network application may be omitted from user interfaces provided
by data
provider server 706). Data directives 744 may be set by data provider 706 for
a particular
data recipient 712. For example, data provider 706 may indicate that data
recipient 712
should not receive account balance information, and data provider 706 may
provide a data
directive indicating this information to data access network 702, which may
implement the
data directive by filtering out certain data, when a user requests data that
implicates the data
directive, as discussed in more detail below.
[0069] User device 705 may comprise processing circuitry 746, input/output
circuitry 748,
communications circuitry 750, storage 752 and memory 754, which may be
implemented in a
similar manner as processing circuitry 704, input/output circuitry 707,
communications
circuitry 708, storage 710 and memory 713, respectively, of data access
network server 702.
User device 705 may be communicatively coupled to data access network server
702, data
provider server 706 and data recipient server 712. In some embodiments, user
device 705
may correspond to a device of user 204 of FIG. 2, having requested to link a
data provider to
a data recipient, and may be used by user 204 to communicate which accounts or
products
that the user has with data provider 706 which data recipient 712 is to be
granted access. User
device 705 may also be an example of a device used by an administrator or
operator of data
provider 706 to configure settings or view which data recipients have been
granted access to
which users of data provider 706, and/or by an administrator or operator of
data recipient 712
to configure settings or view which data providers and which users of the data
providers data
recipient 712 has been granted access. User device 705 may comprise display
758, e.g., to
present information to user 204 or administrators of data provider 706 or data
recipient 712,
speaker 756, e.g., to output audio alerts regarding the data access network to
the user, and
camera 760, e.g., to permit the user to capture images of the surrounding
environment, or
receive login credentials by way of biometric data. Input/output circuitry 748
may be
configured to receive login credentials by way of any suitable method, e.g.,
text, audio,
tactile, or any combination thereof
[0070] Data recipient 712 server may comprise processing circuitry 762,
input/output
circuitry 764, communications circuitry 766, storage 768 and memory 770, which
may be
implemented in a similar manner as processing circuitry 704, input/output
circuitry 707,
communications circuitry 708, storage 710 and memory 713, respectively, of
data access
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 29 -
network server 702. Data recipient server 712 may be communicatively coupled
to data
access network server 702, data provider server 706 and user device 705. Data
recipient 712
may be associated with an entity (e.g., a fintech company) that provides
certain services (e.g.,
mobile payments) which require having access to a user's data (e.g., data
related to a bank
account of user 204, in order to obtain funds for the mobile payments). In
some
embodiments, an application provided by data access network server 702 may
provide one or
more executable instructions (e.g., contained in a URL address) to data
recipient server 712,
to instruct data recipient server 712 to notify data access network server 702
when a user
request is received by way of the URL, e.g., to link a bank account of the
user to a website or
application associated with data recipient 712. Data recipient hub UI portion
772, which may
correspond to data recipient hub 505 of FIG. 5, may be installed at, or
otherwise provided to,
data recipient 712 by data access network server 702, and may permit an
administrator or
operator of data recipient server 712 to view data provider and user pairs
that data recipient
server 712 has been authorized to access. User account portion 774 may store
information
regarding users having registered with data recipient 712 and data providers
associated with
the user that data recipient 712 has been granted access to.
[0071] FIG. 8 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system 800 for
selectively providing
data to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this
disclosure. Data access
network 810 may receive from data provider 806 user data elements or data
record 804
associated with a user (e.g., user 204 of FIG. 2) and data directive 808,
which may
correspond to which data items are permissible to provide to a particular data
recipient 812
for this particular user (or any particular user) of data having one or more
accounts or
products with data provider 806. In some embodiments, data directive 808 may
be received
by data access network 810 in advance, e.g., prior to receiving user data 804,
or data directive
808 may be received concurrently with user data 804. In some embodiments, data
access
network 810 may be configured to generate data directive 808 based on
instructions received
from data provider 806. In the example of FIG. 8, data elements 804 may relate
to a checking
account of a user with data provider 806, and more particularly to a medical
copay made by a
user, as indicated at data item 809. In some embodiments, data directive 808
may be provided
in the format of parentelement.childelement, e.g., FieldA.FieldAl, where Field
Al is a child
of parent field A.
[0072] The transfer of user data 804 from data provider 806 to data access
network 810
may be caused in response to receiving an indication from a user desiring to
share his or her
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 30 -
data (e.g., stored in association with data provider 806) with data recipient
812. Based on
such request, a data access API, which may be externally facing for use by
data recipients to
access user data, may communicate with data provider 806 to facilitate user
data elements for
a particular product (e.g., checking account or VISA account) to be sent to
collector 726 of
FIG.7, where the data and its format may vary based on bank and product type.
Such user
data elements may be filtered by data access network 810 based on data
directive 808, prior
to being provided to data recipient 812. In some embodiments, data access
network 810 may
define and configure the attributes and fields of various accounts and account
types from the
various data providers 806, based on information received from data provider
806, in order to
implement rules and entitlements of each data provider when providing data to
data recipient
812. In some embodiments, data 804 may be stored in any suitable structured or
semi-
structured data format (e.g., JSON, XML).
[0073] User data 804 and/or data directive 808 may be transmitted from data
provider 806
to data access network 810 in the form of a byte stream 811 over a
communication channel
(e.g., a wired or wireless connection), and byte stream 811 may correspond to
a sequence of
8-bit portions of data flowing through the communication channel. In byte
stream 811, plain
text may be represented by a string of alphanumeric digits (e.g., 54 46 82 af
aa a5 db b7 47 2e
b2 50 61 75 4d 6d d8 b8 32).
[0074] Data access network 810, upon receiving byte stream 811, may convert
byte stream
811 into objects of the data elements for transfer into buffer memory 729, in
order to perform
certain data operations, e.g., to facilitate and speed up filtering of user
data. In some
embodiments, the data objects transferred to transient buffer memory 729 may
comprise a
unique identifier and metadata in addition to the data elements themselves.
Data access
network 810 may generate, based on the data objects of such converted byte
stream 811, key-
value map structure 816 in buffer memory 729, where key-value map 816 may
correspond to
key-value map 716 of FIG. 7. Key-value map 816, e.g., an associative array or
hash table,
may be generated to hold, on a temporary or transient basis at buffer 729 of
FIG. 7, a
plurality of key-value pairs, where the key and the value may be linked such
that the key may
be a unique identifier indicative of a pointer to a location of a data item,
and the value may
correspond to such data item. While data item values 818 are shown as part of
key-value map
816 in the example of FIG. 8, this is merely illustrative and key-value map
816 may store
pointers to locations of data item values 818 in buffer memory 729.
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 31 -
[0075] Key-value map 816 may temporarily store user data elements in a
hierarchical
manner to store certain data fields at predefined memory locations (e.g.,
corresponding to a
memory address of buffer memory 729) such that a memory location of certain
data fields
may be known and indexed. Thus, user data that complies with data directive
808, and user
.. data that does not comply with data directive 808, may be identified using
index key
identifiers in key-value map 816 without having to process the entirety of the
received chunk
of user data, thereby reducing the time and processing power required to
perform filtering of
data. In some embodiments, processing time may be reduced from around 1 second
to
process an entire chunk of data in identifying unauthorized data items, to
around 10 ms by
employing key-value map 816 in identifying unauthorized data items. Data may
be stored in
key-value map 816 in any suitable format, e.g., JSON, XML, etc. In some
embodiments, a
particular data field (e.g., accountType) may consistently be stored in the
same memory
location (e.g., for a particular data provider) to enable the particular data
field to be quickly
identified or retrieved. Additionally or alternatively, data access network
810 may use
information from various data providers 806 to optimize key-value map 816,
e.g., data access
network 810 may store data from different data providers in different ways
based on how
data access network 810 typically receives data from the data providers.
[0076] Data access network 810 may determine based on data directive 808 that
certain
data associated with transaction 820 is not permitted to be provided to data
recipient for this
particular data provider and/or user and/or product combination. For example,
data directive
808 may only include permitted data fields and omit restricted data fields, or
may specify
only restricted data fields or only permitted data fields. In response to
determining that data
associated with unauthorized data elements (e.g., transactions 820) is present
in the data
received from data provider 806 but is not permitted by data directive 808,
data access
network 810 may delete (e.g., purge or remove of flush) data not permitted by
data directive
808 by, e.g., clearing values of the data associated with transactions 820
(e.g., zeroing both
the value and the key of the entries associated with transactions data 820).
In some
embodiments, data indicative of an unauthorized field may be used to replace
and overwrite
the data fields associated with transactions 820. In addition, filtered data
elements (e.g.,
determined as permissive to transmit to data recipient 812) may be deleted
immediately after
transmission to data recipient 412 or within a predefined period of time after
transmission
(e.g., any appropriate or suitable amount of time, such as, for example, less
than one second;
less than thirty seconds; or less than one minute). Incoming data, e.g., for a
next transaction,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 32 -
may be used to overwrite the filtered data in buffer memory 729, thereby
permanently
deleting (e.g., removing, purging, flushing) the filtered data and rendering
it inaccessible. In
some embodiments, a technique may be employed to reallocate the memory
associated with
the unauthorized fields to be used for other purposes, once the reference to a
particular
memory location is removed, deleted and/or purged.
[0077] In some embodiments, data directive 808 associated with data provider
806 may
exclude certain data elements (e.g., transactions 820), based on such data
element (e.g.,
transactions 820) including information 821 related to a medical copay made by
a user. For
example, such data element may be excluded due to being related to sensitive
personal health
information not suitable to be provided to, and potentially stored by, data
recipient 812. Thus,
data provider may be provided with balance information 825 but not
transactions information
820 related to medical copay 821. In this way, data access network 810 may not
only provide
for filtering of data received from data provider 806 based on data directive
808, but may
additionally provide for data security for the user by withholding certain
sensitive personal
information. In some embodiments, data provider 806 may not have provided data
access
network 810 a data directive for each potential scenario or use case of the
user data. Data
access network 810 may nonetheless store information indicating that for a
particular data
provider 806 and data recipient 812 combination, data recipient 812 is
permitted access to
certain information (e.g., bank account number) in all instances, but may
never be permitted
access to other information, and data access network 810 may take this
information into
account when providing user data to data recipient 812.
[0078] Data 823 may correspond to the remaining data fields that may be
present after
filtering is performed. In some embodiments, once the filtered data is
obtained, data access
network 810 may perform a check to ensure that no other data directives have
been received
from data provider 806, and may perform filtering if an intervening data
directive is detected.
Data access network 810 may convert data 823 into a format (e.g., JSON or XML)
that is
suitable for data recipient 812. In some embodiments, data access network 810
may consume
data in any format, perform any suitable filtering on the data, and provide
data in a suitable
format to data recipient 812 on the downstream side. In some embodiments, data
of byte
stream 811 may flow encrypted into data access network 810, and data may be
provided to
data recipient 812 in an encrypted manner, where data may be encrypted and
decrypted by
respective parties using any suitable method (e.g., using private-public key
pairs). In some
embodiments, a header portion of data may indicate a type of data included in
the payload,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 33 -
while the payload may be encrypted. In some embodiments, once data is
transmitted to data
recipient 812, data 823 may be removed from buffer memory 729 after a
predefined period of
time, and data access network 810 may only store identifiers or hash values
for the data
provider and the user (e.g., in order to log a transaction), where an identity
of the user is not
discernable based on the identifier or hash value. Data provided to data
recipient 812 may be
provided in the same format, or a different format, from a format of data 804.
In some
embodiments, rules and data directives received from data provider 806 may be
dynamically
applied to received user data one or more times per day (e.g., four times a
day, based on how
often a data provider provides updates to data directives).
[0079] In some embodiments, data access network 810 may perform filtering
based on a
specific product type (e.g., health savings accounts) for a particular data
provider. For
example, each data recipient desiring to obtain user information from data
provider 806 may
not be permitted to access any information related to the specific account,
e.g., based on a
global data directive associated with a data provider. In some embodiments,
data recipient-
specific data directives associated with a data provider may prohibit specific
data recipients
from accessing information for certain types of products or accounts of data
provider 806. In
some embodiments, data elements may be pre-filtered (e.g., based on the global
data directive
and/or the data recipient specific data directive and/or user selections
associated with an
authorized accounts selection database) by other components of data access
network 810
and/or the associated data provider, prior to the generation of key-value map
816. In some
embodiments, data access network 810 may request that data provided by data
providers be
in a specific format (e.g., account type and account ID in payload). In some
embodiments,
byte stream 811 may contain personally identifiable information, and such P11
may be filtered
out by data access network 810, e.g., based on data directive 808.
[0080] In some embodiments, data access network 810 may be configured to
perform one
or more of a variety of masking operations on data elements 804 received from
data provider
806. For example, data provider 806 may instruct data access network (e.g., by
way of data
directive 808) to mask certain data elements, e.g., based on the identify of
data recipient 812.
For example, a predefined number of digits or characters of an account number
may be
masked (e.g., replaced with an asterisk or star character) such that only a
subset of the digits
are readable. In some embodiments, masking may be performed on data elements
received in
a particular format (e.g. J SON) to mask private information (e.g., social
security numbers of a
user). Such masking operation may be used by data access network 810 to
perform the
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 34 -
filtering operation. For example, any suitable syntax (*.accountId) may be
used to specify
that a particular data element (e.g., accountID) should be returned regardless
of a parent
element in which it is contained (e.g., InvestmentAccount). As another
example, the masking
operation may define the number of characters that should be exposed in the
output, the
masking character to be used, and the position within the data element where
the masking
should start (e.g., 4 digits from start or end of string). For example, the
command of
investmentAccount.accountNumber::mask(4,*,$) may mask all but the last four
digits (e.g.,
*****2431) of the account number (12342431), and the command
investmentAccount.accountNumber::mask(4,*,e) may mask all but the first four
digits (e.g.,
1234*****) of the account number (12342431). In some embodiments, an allow
operation
filter may be employed to filter out a parent element based on a value of the
child element,
e.g., the allow operation may accept a list of strings as parameters, and if
the value of the
child element is not one of the values in the list passed to allow operation,
parent element
may be removed from the payload. Such allow operation may be used for product
filtering
such that the allow list may contain the products or accounts allowed by a
particular data
provider, and if an account type is not an allowed product code, the whole
account may be
removed from the payload. For example, for the command:
investmentAccount.accountType::allow(I,checking) if a user has any account
that does not
belong to the list of products (I, checking), such accounts may be removed
from the data.
.. [0081] FIG. 9 shows a block diagram of an illustrative system for
selectively providing data
to a data recipient, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure.
Data access
network 910 may convert filtered data 923, e.g., filtered based on data
directive 808 of FIG. 8
received from data provider 806, into a data format 925 (e.g., JSON, XML, or
other
structured or semi-structed data format) suitable for data recipient 912.
Converted filtered
data associated with format 925 may be packaged into byte stream 927 for
transmission to
data recipient 912. Upon receiving byte stream 927, data recipient 912 may use
convert byte
stream 927 into a readable format and present user data represented by byte
stream 927 to the
user having requested to link his or her products or account with data
provider 806 with data
recipient 912.
[0082] FIG. 10 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process 1000 for
managing tokens for
selectively providing data to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments of this
disclosure. In various embodiments, the individual steps of process 1000 may
be
implemented by one or more components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9.
Although
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 35 -
the present disclosure may describe certain steps of process 1000 (and of
other processes
described herein) as being implemented by certain components of the devices
and systems of
FIGS. 1-9, this is for purposes of illustration only, and it should be
understood that other
components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9 may implement those steps
instead.
[0083] At 1002, user device 1001 may transmit, based on an indication from a
user (e.g.,
user 204 of FIG. 2) a request to grant authorization for data recipient 1003
to access user
information (e.g., user information 804) associated with data provider 1007.
In some
embodiments, the user information may correspond to financial information of
user 204. User
device 1001 may correspond to, e.g., one of computing device 118, 120, 122 of
FIG. 1 of user
204.
[0084] At 1004, data access network 1005 may receive such request. In some
embodiments,
data access network 1005 may provide executable instructions (e.g., by way of
a URL
address) to instruct data recipient 1003 of a location to which to forward the
request, or may
otherwise receive the request from data recipient 1003. In some embodiments,
data recipient
1003 may be, for example, a fintech organization that user 204 is interested
in creating an
account with or purchasing a product from, and data provider 1007 may be, for
example, a
financial institution (e.g., a bank) at which user 204 has an existing
account, where certain
information from the account of user 204 with data provider 1007 may be
required to
establish the account with data recipient 1003.
[0085] At 1006, data access network 1005 may perform a verification of each of
data
recipient 1003 and data provider 1007, e.g., to ensure that each of data
recipient 1003 and
data provider 1007 previously registered with data access network and that
data recipient
1003 is authorized to receive data from data provider 1007. For example, data
access network
1005 may reference one or more of databases 715, 717 to compare identifiers of
data
recipient 1003 and data provider 1007 to a list of authorized entities in
performing such
verifications.
[0086] At 1008, if data access network 1005 determines that each of data
recipient 1003
and data provider 1007 is a verified entity with data access network 1005,
data access
network 1005 may re-direct the user operating user device 1001 to data
provider 1007. For
example, if user device 1001 is accessing data recipient 1003 via a web
browser, data access
network 1005 may cause the web browser to be re-directed to a website of data
provider
1007, or if user device 1001 is accessing data recipient 1003 by way of a
mobile application,
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 36 -
data access network 1005 may cause the mobile application to launch the mobile
application
of data provider 1007 in place of (or within ) the mobile application of data
recipient 1003.
[0087] At 1010, user 204 operating user device 1001 may be prompted by an
authenticator
portion of a service (e.g., website or application) of data provider 706 to
enter his or her
credentials for his or her account with data provider 1007. User device 1001
may be
configured to receive input of the user credentials in any suitable format
(e.g., text, voice,
tactile, biometric, or any combination thereof). In some embodiments, the user
may be
required to agree to certain terms and conditions associated with data
provider 1007 and/or
data access network 1005.
[0088] At 1012, data provider 1007 may receive the user credentials entered at
user device
1010 and transmitted to data provider 1007, and determine whether the user
credentials
correspond to an authorized user of data provider 1012.
[0089] At 1014, in response to authenticating user 204 operating user device
1001, data
provider 1007 may transmit an authorization grant code (e.g., authorization
grant code 419 of
FIG. 4) to data access network 1005. At 1016, data access network 1005 may use
such
authorization grant code received from data provider 1007 having authenticated
user 204 in
requesting an authentication token (e.g., authentication token 421 of FIG. 4)
from data
provider 1007. At 1018, data provider 1007 may provide the authorization token
to data
access network 1005, responsive to the request of 1016, and data access
network 1005, at
1020, may request user information of the authenticated user 204 using such
authentication
token 421.
[0090] At 1022, data provider 1007 may transmit the requested list of user
information
(e.g., information related to checking account 422, savings account 424, basic
savings
account 426, money market account 428 of FIG. 4) to data access network 1005,
which may
in turn transmit such user information to user device 1001. At 1026, data
access network may
receive an indication from user device 1001 that user 204 desires to share
certain user data
(e.g., information related to checking account 422, savings account 424, basic
savings
account 426) with data recipient 1003, but does not wish to share other user
data (e.g.,
information related to money market account 428) with data recipient 1003.
Such indications
may be received in the form of user selection (e.g., checking or unchecking
respective boxes
of the accounts of products included in the user information). In some
embodiments, data
access network may recommend which accounts to share, e.g., to help the user
share no more
than necessary with data recipient 1003. In some embodiments, data provider
1007 may
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 37 -
directly transmit the user information to user device 1001, and receive user
selection of one
or more accounts or products to share with data recipient 1003 from user 204
of user device
1001.
[0091] At 1028, data access network 1005 may re-direct user device 1001 to the
website or
.. application associated with data recipient 1003 along with a data access
network
authorization grant code (e.g., grant code 434 of FIG. 4). In some
embodiments, an indication
may be presented (e.g., at interface 432) to the user by data recipient 1003
that the accounts
or products specified at 1026 have been successfully linked. While the
accounts may have
been successfully linked, data recipient may nonetheless be required to
request access to the
.. user information by transmitting data access network authorization grant
code (e.g., code 434
of FIG. 4) to data access network 1005.
[0092] At 1030, data access network 1005 may, responsive to receiving data
access
network authorization grant code from data recipient 1003, provide a token
(e.g., a first data
access identifier token 436) to data recipient 412. At 1032, data recipient
1003 may use the
received token 436 to request permissioned user information (e.g., information
related to
checking account 422, savings account 424, basic savings account 426) of user
204 with data
provider 1007.
[0093] At 1034, data access network 1005 may use authentication token 421,
previously
received from data provider 1007, to request the permissioned data of user 204
with data
provider 1007 and having been requested by data recipient 1003 at 1032. At
1036, data
access network 1005 may receive the permissioned user data from data provider
1007, after
data provider verifies authentication token 421 received from data access
network 1005.
[0094] At 1038, data access network 1005 may perform filtering of the
permissioned user
information of user 204 based on a data directive (e.g., data directive 808 of
FIG. 8) of data
provider 1007, as discussed in more detail in connection with FIG. 12. For
example, based on
data directive 808, data access network 1005 may convert user information
received in the
form of byte stream 811 into a key-value map data structure 816, and may
remove data (e.g.,
related to transactions 820 and medical copay 821 of FIG. 8) that is not
permitted to be sent
to data recipient 1003 based on data directive 808.
[0095] At 1040, data access network 1005 may transmit filtered user
information 823 to
data recipient 1003, and at 1042, data recipient may in turn provide filtered
user information
823 to user device 1001 for presentation within the service (e.g., application
or website) of
data recipient 1003.
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 38 -
[0096] FIG. 11 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process 1100 for
managing tokens for
selectively providing data to multiple data recipients, in accordance with
some embodiments
of this disclosure. In various embodiments, the individual steps of process
1100 may be
implemented by one or more components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9.
Although
the present disclosure may describe certain steps of process 1100 (and of
other processes
described herein) as being implemented by certain components of the devices
and systems of
FIGS. 1-9, this is for purposes of illustration only, and it should be
understood that other
components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9 may implement those steps
instead.
[0097] At 1102, the data access network (e.g., data access network 310 of FIG.
3) may
receive a first request from user 204 of FIG. 2 to grant authorization for
data recipient 312 of
FIG. 3 to access user information (e.g., data elements 804 of FIG. 8)
associated with a data
provider 302 of FIG. 3. For example, user device 118 may be operated by user
204 to
transmit the first request to data recipient 302, and data access network 310
may be
configured to detect such request (e.g., by receiving an indication from data
recipient 302,
such as via a URL address provided by data access network 310 to data
recipient 302) or
otherwise notified or forwarded the first request. The first request may be
based on a desire of
user 204 to link his or her accounts or products with data provider 302 with a
new or existing
account with data recipient 302.
[0098] At 1104, data access network 310 may re-direct user 204 operating user
device 118
to a service provided over network 102 by data provider 302, where data
provider may
prompt user 204 to enter his or her log-in credentials. In response to
authenticating user 204
based on the received log-in credentials, data provider may transmit
authentication token 421
of FIG. 4 to data access network 310.
[0099] At 1106, if authentication token 421 is received, data access network
310 may
further receive user selection of which user data is to be shared with data
recipient 302, and at
1008, generate first token 436 for data recipient 302 which may be indicative
of the
permissioned user data for data recipient 302.
[0100] At 1110, data access network 310 may provide first token 436 to data
recipient 312,
where data recipient 312 at 1112 may transmit first token 436 along with a
request for the
permissioned user information to data access network 310.
[0101] At 1114, data access network 310 may obtain the requested permissioned
user
information from data provider 302 using authentication token 421 previously
received from
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 39 -
data provider 302, perform filtering on such data as described in further
detail in connection
with FIG. 12, and provide such filtered user data to data recipient 312.
[0102] At 1116, data access network 310 may receive a second request from user
204, e.g.,
operating one of user device 118, 120, 122 to grant authorization for data
recipient 314 to
access user information associated with data provider 302. In some
embodiments, the user
information requested to be shared with data recipient 314may be the same or
different from
the user information requested to be shared with data recipient 312.
[0103] At 1118, data access network 310 may re-direct user 204 operating one
of user
device 118, 120, 122 from the website or application of data recipient 314
(e.g., at which user
204 initiated the second request) to a website or application associated with
data provider
302.
[0104] At 1120, in response to data provider 302 authenticating user 204, an
updated
version of authentication token 421 may be received by data access network 310
from data
provider 302. For example, the updated version of authentication token 421 may
be modified
to include an indication that each of data recipient 312 and 314 are permitted
to access certain
user data associated with data provider 302.
[0105] At 1122, data access network 310 may generate a second token, based on
data
recipient 314 having been authorized to access user data of accounts or
products of user 204
with data provider 302. The second token may be generated in response to data
access
network 310 receiving an indication that certain accounts or products have
been selected that
data recipient 314 is permitted to access (e.g., one or more of checking
account 422, savings
account 424, basic savings account 426, money market 428). In some
embodiments, even if
each of data recipient 312 and data recipient 314 is granted access to the
same accounts or
products, data access network 310 may nonetheless generate separate tokens for
each of data
recipient 312 and data recipient 314.
[0106] At 1124, data access network 310 may provide the generated second token
to data
recipient 314, and data recipient 314 may transmit such second token along
with a request for
user information back to data access network 310.
[0107] At 1126, if data access network 310 receives the second token along
with the
request for user information from data recipient 314, processing may proceed
to 1128. At
1128, data access network 310 may obtain user information data using the
authentication
token and provide the user information data to data recipient 314. In some
embodiments, data
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 40 -
access network 310 may perform filtering of data based on a data directive of
data provider
302 prior to providing such user information data to data recipient 314.
[0108] FIG. 12 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process for filtering
data based on a
data directive to selectively provide data to a data recipient, in accordance
with some
embodiments of this disclosure. In various embodiments, the individual steps
of process 1200
may be implemented by one or more components of the devices and systems of
FIGS. 1-9.
Although the present disclosure may describe certain steps of process 1200
(and of other
processes described herein) as being implemented by certain components of the
devices and
systems of FIGS. 1-9, this is for purposes of illustration only, and it should
be understood that
other components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9 may implement those
steps
instead.
[0109] At 1202, data access network 810 may receive from one or more data
providers 806
one or more data directives 808. In some embodiments, each data directive 808
may
correspond to a particular use case or circumstance for a particular type of
user with a
particular data recipient. Additionally or alternatively, a data provider 806
may provide a
generic data directive for each transaction with a particular data recipient.
[0110] At 1204, data access network 810 may receive a request to grant
authorization for a
data recipient 812 to access user information associated with data provider.
For example, a
user (e.g., user 204 of FIG. 2) accessing a website or application of data
recipient 812 via a
user device 118, 120, 122 may transmit a request to link his or her accounts
with data
provider 806 with data recipient 812.
[0111] At 1206, data access network 810 may request user information from data
provider
806 based on received request. For example, such request may be transmitted
after
authenticating user 204 and receiving an authorization token from data
provider 806.
[0112] At 1208, data access network 810, in response to transmitting the
request to data
provider 806 for the user information, may receive byte stream 811 from data
provider 806.
In some embodiments, byte stream 811 is generated by converting data from a
first format
(e.g., JSON or XML format) into byte stream 811. Such first format may
comprise a plurality
of data elements (e.g., the fields of "balanceType", "availableCashBalance"
and
corresponding values) packaged into data record 804 of FIG. 8.
[0113] At 1210, data access network 810 may identify the plurality of data
elements of the
data record included in byte stream 811. For example, data access network 810
may convert
byte stream 811 into a set of objects (e.g., by parsing a JSON string
corresponding to byte
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
-41 -
stream 811) and analyze the set of objects to identify (e.g., by way of
processing circuitry
704) the various data elements (e.g., the fields of "balanceType",
"availableCashBalance"
and corresponding values) of data record 804. At 1212, data access network 810
may store
the identified data elements converted to objects in buffer memory 729 of FIG.
7. In some
embodiments, the data objects may be stored in a transitory manner in buffer
memory 729
and may comprise a unique identifier and metadata in addition to the data
itself
[0114] At 1214, data access network 810 may generate a key-value map 816 to
map the
identified data elements to their respective memory locations in buffer memory
729. Such
key-value map 816 may temporarily store user data in a hierarchical manner to
store certain
data fields at predefined memory locations (e.g., corresponding to a memory
address of
buffer memory 729) such that a memory location of certain data fields is known
and indexed.
In some embodiments, key-value map 816 may itself be a data object that holds
key-value
pairs, where the set of objects corresponding to the identified data elements
may correspond
to a key or value of key-value map 816.
[0115] At 1216, data access network 810 may identify data directive 808
associated with
data provider 806 and data recipient 812 associated with the request received
at 1204. For
example, data access network 810 may determine that, based on the products or
accounts
selected by the user at GUI 423, and based on one or more attributes of data
recipient 812 and
how it intends to use the data, that data directive 808 is appropriate for
this particular
transaction.
[0116] At 1218, data access network 810 may determine, using key-value map
816,
whether certain data elements are to be removed from the data record based on
the identified
data directive 808. For example, data access network 810 may determine that
none of the data
elements associated with transaction 820 are included in data directive 808
and thus are not
permitted to be provided to data recipient 812. Key-value map 816 enables data
access
network 810 to ascertain the memory location of each of the prohibited data
elements and
perform filtering at 1220 to delete (e.g., purge and/or flush and/or remove)
the prohibited data
elements associated with transaction 820, thereby leaving only the permitted
data elements in
buffer memory 729. Data access network 810 may perform filtering in any
suitable manner.
In some embodiments, filtering may be performed based on storing data received
from data
provider 806 in a defined and structured manner, generating key-value map 816,
comparing
fields of key value map 816 to the permitted fields of data directive 808 to
extract only
permissible data, and packaging the extracted permissible data for
transmission as up and
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 42 -
sending as byte stream 927 of FIG. 9. In some embodiments, data access network
810 may
perform filtering by removing or deleting or purging data fields, e.g.,
associated with
transactions 820, from key-value map 816 that do not comply with data
directive 808, such
that the memory location of the unauthorized data is not identifiable. In some
embodiments,
data access network may, based on comparing fields of key value map 816 to the
permitted
fields of data directive 808, delete and/or overwrite the unauthorized data in
memory.
[0117] At 1222, data access network 810 may convert filtered data elements 923
to a
format 925 that is suitable for data recipient 912. For example, filtered data
elements 923
may be converted to JSON or XML format and subsequently converted into byte
stream 927
for transmission to data recipient 912.
[0118] At 1224, data access network 810 may provide the filtered data elements
923
converted into the suitable format to data recipient 812. Data recipient 912
may present to
user 204 the permissioned data elements, e.g., as shown at interface 438 of
FIG. 4. In some
embodiments, the filtered data elements may be stored for less than a
predetermined period of
time after transmission to data recipient 912 (e.g., one hour, 10 minutes, 5
minutes, 1 minute,
10 seconds, or 1 second) or may be immediately deleted (e.g., purged from
memory, so as to
render the data inaccessible) once the filtered data elements 823 are provided
to data recipient
812. In some embodiments, the identified data elements may be stored without
any
personally identifiable information of user 204. For example, an identifier or
hash may be
assigned to the user and/or transaction.
[0119] FIG. 13 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process 1300 for
transmitting a
package of authorized information to a data recipient, in accordance with some
embodiments
of this disclosure. In various embodiments, the individual steps of process
1300 may be
implemented by one or more components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9.
Although
the present disclosure may describe certain steps of process 1300 (and of
other processes
described herein) as being implemented by certain components of the devices
and systems of
FIGS. 1-9, this is for purposes of illustration only, and it should be
understood that other
components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9 may implement those steps
instead.
[0120] At 1302, data access network (e.g., data access network 810 of FIG. 8)
may receive
a request from a data recipient 112 to access information from data provider
104 associated
with user 204 of FIG. 2. Such request may comprise a data recipient token
(e.g., first data
access identifier token 436 of FIG. 4). In some embodiments, data recipient
112 may have
previously been authorized by the user, data provider 104 and data access
network 810 to
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 43 -
receive user information associated with data provider 104. In some
embodiments, the
request from data recipient 112 may be received by way of Access API 1310,
e.g., an
externally facing API used by data recipients to access user data (e.g.,
consumer financial
data). In some embodiments, secure token service 1312 may be used to validate
the data
recipient token, and check whether data recipient 112 is permitted by data
provider 104 to
access user data, e.g., by querying curator 1319, which may store records of
data providers,
data provider products and accounts, and manage data recipient subscriptions
to such
provider products and accounts. Curator 1319 may correspond to curator 720 of
FIG. 7.
[0121] At 1304, data access network 810 may collect the requested data from
one or more
data providers 106. In some embodiments, collector 1316 (which may correspond
to collector
726) may be employed to standardize data from data provider 106 into a common
format
(e.g., FDX). In some embodiments, only accounts approved to be shared (e.g.,
by way of GUI
423 by user selection and permitted by data provider 106 to be shared for a
particular data
recipient product) may be retrieved, whereas accounts not permitted to be
shared may be
ignored for the purposes of the request received from data recipient 112. In
some
embodiments, data access network 810 may query data service 1317 (e.g.,
authorized
accounts database), which may store a record of which accounts each user has
authorized
each data recipient to access.
[0122] At 1306, filtering portion 1318 (e.g., of data access network 810
described in
connection with FIG. 8) may apply data provider directives, e.g., defined by
data provider
administrators by way of management console 1320, which may correspond to
management
console UI portion 740 of FIG. 7, to generate a package of authorized
information based on
the information received from data provider 106. In some embodiments,
filtering portion
1318 may be employed in conjunction with curator 1319 and admin tool 1322
(which may
correspond to admin dashboard 718 of FIG. 7) to apply the data provider
directives. In some
embodiments, admin tool 1322 may correspond to a tool to enable data access
network 810 to
specify data attributes that a data provider can provide to data access
network 810, and may
be used as an onboarding tool for data providers and/or to facilitate the
connection of data
providers and data recipients.
[0123] At 1308, data access network 810 may be configured to transmit the
package of
authorized information to data recipient 112, e.g., by way of Access API 1310.
Such
information may be usable by data recipient 112 to provide the user access to
desired
accounts, products or services provided by the data recipient 112 platform.
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 44 -
[0124] FIG. 14 is a flowchart of a detailed illustrative process 1400 for
generating an
identity token, in accordance with some embodiments of this disclosure. In
various
embodiments, the individual steps of process 1400 may be implemented by one or
more
components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9. Although the present
disclosure may
.. describe certain steps of process 1400 (and of other processes described
herein) as being
implemented by certain components of the devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9,
this is for
purposes of illustration only, and it should be understood that other
components of the
devices and systems of FIGS. 1-9 may implement those steps instead.
[0125] As shown in FIG. 14, end user 1402 may request to share his or her
account or
product information from one or more of data provider 1408, 1410, 1412 (e.g.,
banks, which
may play a role as an identity provider to enable generation of an identity
token of a user)
with data recipient 1404. Data recipient may desire detailed personal
information (e.g., social
security number, full name, address, date of birth, etc.) of end user 1402 in
order to set up an
account for end user 1402 (e.g., associated with a mortgage application).
[0126] Data access network 1406 may receive the request initiated by end user
1402, to link
his or her account data with data provider 1408 with data recipient 1404. In
some
embodiments, data access network 1406 may provide executable code to data
recipient 1404
(e.g., contained in a URL address) that is executable to re-direct a browser
or application of
data recipient 1404 being access by user 1402 to data access network 1406,
which may in
turn cause the user session to be forwarded to data provider 1408. Data
provider may perform
an authentication process to authenticate end user 1402. In some embodiments,
multi-factor
authentication techniques may be utilized (e.g., requiring entry of a password
associated with
data provider 1408, as well as entry of a pin code received via SMS or email
associated with
the user account with data provider 1408).
[0127] If end user 1402 is successfully authenticated at data provider 1408,
data access
network 1406 may be provided with a token (e.g., indicative of identifying
information of
end user 1402), and data access network 1406 may generate an identity token
comprising the
identifying information of end user 1402. In some embodiments, token 436
(e.g., a first data
access identifier token associated with a first data recipient) and/or a
second data access
identifier token associated with a second data recipient, as discussed in
connection with FIG.
4, may be updated or enriched to include such identity token embedded therein.
In some
embodiments, the identity token may be generated in advance by data access
network 1406
and persistently stored (e.g., in storage 710 of data access network server
702), based on
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 45 -
information received from data provider 1408, e.g., prior to receiving user
request to share
user information with data recipient 1404 from the user's account with data
provider 1408. In
some embodiments, the generating of the identity token may be performed in
response to
receiving the user request to share user information with data recipient 1404
from the user's
account with data provider 1408.
[0128] Once the identity token is generated by data access network 1406, the
identity token
may be forwarded to data recipient 1404, which may in turn validate end user
1402 on its
platform. In some embodiments, the identity token may be usable by data
recipient 1404 to
automatically populate information fields of one or more sign up screens of a
desired product
or account of data recipient 1404, and validate end user 1402. The identity
token may provide
assurance and evidence for data recipient 1404, as part of a trust framework
with data access
network 1406 and data provider 1408, of the authenticity of the user's
identifying
information, and proof of the identity of end user 1402.
[0129] In some embodiments, the generated identity token may be transmitted to
other data
recipients requesting identifying information of end user 1402 in connection
with products or
accounts of end user 1402 with data provider 1408. In some embodiments, the
identifying
information of end user 1402 may be received by data access network 1406 in
masked or
encrypted form. In some embodiments, since identifying information of user
1402 may differ
from data provider to data provider (e.g., data provider 1408 may have on
record different
information for user 1402 than does data provider 1410), each data provider
may request data
access network 1406 to generate a respective identity token for the
corresponding data
provider. In some embodiments, identifying information of user 1402 in the
generated
identity token may be deleted or removed by data access network 1406 once the
user is
verified at data recipient 1404.
[0130] While the examples of above have been described with reference to
filtering data to
be provided from a financial instruction (e.g., a bank) to a fintech service,
it should be
appreciated that the described systems and methods can be employed in any
number of
contexts or scenarios. For example, the described data access network may be
employed to
make decisions on whether an individual should be approved for a mortgage,
based on
criteria provided by a mortgage lender and mortgage loan applicant information
provided by
a mortgage loan applicant, without requiring the mortgage loan applicant to
provide the
mortgage lender with personally identifiable information, and the data access
network may
remove data related to the transaction after a predetermined period of time
(e.g., a 90 day
CA 03236147 2024-04-22
WO 2023/069624
PCT/US2022/047287
- 46 -
time window, or a one day time window). For example, data provided to the
mortgage lender
may be filtered to only provide relevant data to the transaction, e.g., the
mortgage lender may
only need information regarding large cash inflows or outflows into or out of
an applicant's
bank account within a predefined time period prior to the transaction (e.g.,
one month), but
information related to the applicant's mutual fund positions may be deemed
unnecessary and
filtered out of the information provided to the mortgage lender. That is, the
data access
network may provide to the mortgage lender only the information that is needed
to process
the application of the loan applicant.
[0131] It should be appreciated that the above-described systems and methods
may be used
in different contexts and for different types of information. For exampleõ the
described data
access network may be employed in healthcare, education, government, etc., or
any other
context where it may be beneficial to withhold certain information (e.g., a
social security
number included in a particular document) and provide a subset of such
information (e.g., a
GPA of a student included in the particular document) to a data recipient.
[0132] The processes discussed above are intended to be illustrative and not
limiting. One
skilled in the art would appreciate that the steps of the processes discussed
herein may be
omitted, modified, combined and/or rearranged, and any additional steps may be
performed
without departing from the scope of the invention. More generally, the above
disclosure is
meant to be exemplary and not limiting. Only the claims that follow are meant
to set bounds
as to what the present invention includes. Furthermore, it should be noted
that the features
and limitations described in any one embodiment may be applied to any other
embodiment
herein, and flowcharts or examples relating to one embodiment may be combined
with any
other embodiment in a suitable manner, done in different orders, or done in
parallel. In
addition, the systems and methods described herein may be performed in real
time. It should
also be noted that the systems and/or methods described above may be applied
to, or used in
accordance with, other systems and/or methods.