Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
_itle
FORCE MEASURING DE~ICE
Technical Field:
The invention relates to a force measuring device for measuring
a force exerted to a force introduction member arranged in
spaced relationship to a support member the space therebetween
being filled with elastomeric material in contact with a
pressure sensor. Particularly, the force measuring devices
according to the invention are adapted to be used for supporting
a scale platform of a truck or car weighing apparatus or for
supporting of huge bins or coal bunkers.
Background Art:
When using force measuring devices for supporting scale plat-
forms or huge bins such force measuring devices must have
certain degrees of -freedom or resiliency which enables vertical,
horizontal or angular movements of the bin or the platform. On
the other hand, such movements should be limited in order to
prevent damaging of the force measuring device. In this
connection, it has become known to permit a lateral movement of
the force measuring device by moun-ting it on a spherical
projection and by providing an upper force introduction means
in the -form of a spherical recess into which a sphere or ball
is placed. Despite these measures it is s-till necessary to
support the force measuring device by levers and bumpers or
abutments against overloading due to angular and horizontal
forces. Also, it has become known to provide an elastomeric
plate as an intermediate layer at the Force introduction point.
However, a static friction must be overcome which is in the
range of 5%. Such a static friction deteriorates the accuracy
and overloads the force measuring cells in lateral direction.
Again, equalizing elements as levers or the like were necessary.
Summary of the Invention:
It is an object of the present invention to provide
force measuring devices adapted for weighing very
high loads.
It is a further object of the present invention to
provide force measuring devices -for very high loads
with a simple construction.
It is a still further object of the present invention
to provide force measuring devices of~ering different
degrees of freedom when used to support scale
platforms or very heavy bodies.
The force measuring device according to the invention
comprises: a force receiving member and a support
member spaced therefrom, one said member having a
peripheral rim and the other said member being fitted
into said rim so as to form a narrow and annular gap
between an inner peripheral surface of said rim and
an outer peripheral surface of the other said member;
elastomeric material provided in the space between
and adhered to said members said elastomeric material
essentially filling said gap; a pressure sensor in
contact with said elastomeric material; a base member
provided with a flat upward projection forming a
piston fitting in a bottom side recess of said
support member, said projection and said recess being
complementary to each other and concentrically
aligned to a longitudinal axis of said force
measuring device; and a disk of synthetic material
inserted in said recess and bearing against a top
surface of said projection when said support member
is placed on said base member.
7~
Accordin~ to another embodiment of the invention, a
force measuring device is comprised of a potlike hase
body, a piston inserted in the base body forming
space between an end surface of the piston, and a
bottom surface of the base body and between opposing
peripheral surfaces thereof, elastomeric material
essentially filling the space, a pressure sensor i.n
contack with the elastomsric material, and wherein
the end surface of the piston is concavely recessed
toward a central axis of the piston and the piston is
provided with a through-hole along the central axis,
which through-hole is closeable by a plug apparatus.
Brief Description of the Drawings,
Fig. 1 is a schematic sectional side view of a
firsk embodiment of a force measuring
device according to the invention;
7~6t~3
ig. 2 is a schematic sectional side view of a second
embodiment of a -force measuring device accorcling to
the invention; and
ig. 3 -is a schematic sectional side view of a -third
embodiment of a force measuring device according to
the invention.
etailled Description of the Embodiments of the Invention:
In principle, the invention uses a design of a force measuring
cell as disclosed in the European Patent Laid Open Publication
0145001 (corresponding to the US-Patent No. 4,644,805). Such
a force measuring, device uses a pot-like support member having
inserted thereto a piston-like force receiving member. Between
opposing end surfaces of the force receiving member and the
bottom of the support member and between the peripheral
surface of the force receiving member and the cylindrical inner
surface of the support member there is provided elastomeric
material being in contact with at least one pressure sensor.
~he embodiments o-f the present invention use the principal
design of such known force measuring devices. However, the
force measuring devices according to the embodiments have
specific designs for equalizing lateral and/or rotational
overloading of the force measuring devices when used in
connection with truck weighing devices or as a support for
huge bins.
Further requirements for such types of force rneasuring devices
are small height and simple design.
Figs. 1 to 3 show embodiments having differen-t degrees of free-
dom in lateral and/or rota-tional direction.
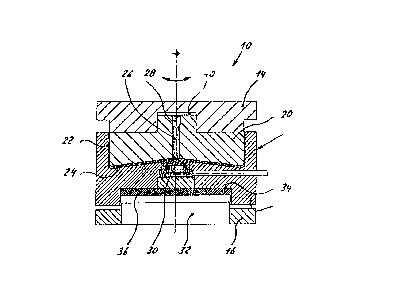
According to the Figs. 1 to 3 a force measuring device 10 of
the embodiments comprises an elastostatic force measurirlg de-
vice 12 similar to that explained in the European Patent Laid
Open Publication No. 0145001. The elastostatic -force measuring
device 12 comprises a potlike body 18 into which a piston 20 is
inserted forming a relatively narrow annular gap 22 with the
interior cylindrical sur-face of the potlike body 18. The
annular gap 22 and the bottom of the potlike body 18 are filled
with elastomeric material.
It should be noted, that in contrast to the known devices the
lower main surface 24 of the piston 20 has no conical pro-
jection but a conical recess with the bottom surface 24 ending
in a central bore 26 through the piston 20 which bore 26 is
closeable exemplary by a screw 28.
With the specific design of the force measuring device 12, in
manufacture any air bubbles are urged into the central bore
26 and may escape at its upper end which is closed at the end
of the manufacturing process. By avoiding the projecting cone
o-f the known devices the height of the force measuring device
is further reduced.
A pressure sensor 30 is mounted in contact with the elastomeric
material provided at -the bottom of the potlike body 18 .
Each of the embodiments of Figs. 1 to 3 comprise a base part
16 having an upwardly projecting central piston 32 which en-
gages a recess 34 complementary -to the piston provided at the
bottom side of the po-tlike body 18. The piston 32 urges against
a disk 36 made o-f elastomeric material.
At its top side the piston 20 is provided with a central pro-
jection 38 engaging a corresponding recess 40 provided at the
bottom side of a force introduction element 14. The force
introduction element 14 may have a plane upper surface connected
in any su;table manner to parts of the bin or a weighing
platform. The plane des;gn of the force introduction element
14 permits a stable connection to the bin or the weighing
platform, respectively, an~ a uniform Force introduction.
It should be noted, that with the embodiment according to Fig. 1
the piston 20 could be unitary with the force introduction
element 14 since the force measuring device according to this
embodiment only offers one degree of freedom i.e. a resiliency
or loose permitting a limited tilting of the bin or^weighing
platform, respectively.
Additionally, with the embodiment according to Fig. 3, there
is a further resiliency or loose in both the X-direction and
the Y-direction as indicated by the arrows at the top of the - -
Fig.. For this purpose a disk or layer 42 of synth'etic ma-
terial is interposed between the force introduction element 14
and the piston 20. The synthetic material may preferably be
Teflon,~ such that there is small friction between the metal
surfaces of the force introduction element 14 and of the piston
20. It shoùld be noted that with this embodiment (Fig. 3) there
is a sufficient distance between the surface of the'projection
38 and of recess 40, which distance permits a horizon-tal move-
ment of the force introduction element 40 relative to the force'
measuring device 12. Preferably, the disk 42 is placed in flat
recesses provided at the upper surface of the piston 20 and/or
the bottom surface of the force introduction element 14.
With the embodiment of Fig. 2 a lateral movement of the force
introduction element 214 relative to the force measuring device
212 is possible in only one direction, f.i. the X-direction.
In contrast to the embodiment according to Fig. 3 -there is no
free annular space around the projection 38. Rather, with the
projection 38 and the recess 40 having a rectangular, prefer-
ably square-like cross section a-t two opposite sides there is
provided a free space between opposing surfaces o-f the
., ~ .
~,~
~ - Trade Mark
projection 38 and the recess 40 whilst at the other opposite
sides the space is filled by Teflon~material 44 such that a
movemen~ of the force introduction element 14 in respec-t of
the force measuring device 12 is possible only in a direction
normal to the plane of the drawing. The disk 42 and the tef-
lon material 44 may be provided with lubricating recesses
offering the storage of lubricating material For permanent
lubrication of the sliding surfaces.
It should be noted that the embodiments of Figs. 2 and 3
provide the same resiliency as the force measuring device
according to Fig. 1 in addition to their resiliency in lateral
direction. However, there may be cases where force measuring
devices may be used having only a lateral resiliency in one
or both directions.
It will be appreciated that the combination of the piston 32
with the elastomeric disk 36 in the recess 34 constitutes a
potlike bearing which, in principle, is a fixed bearing, how-
ever, permitting rotational or tilting movements about a hori-
zontal axis which is possible due to the deformation of the
elastomeric disk 36. The volume of the elastomeric material
of the disk 36 is maintained constant independent of pressure
application. Thus it is incompressible. The piston 32 prevents
any squeezing out of the elastomeric material of the recess 34.
For supporting a huye bin or bunker or a weighing platform
appropriate support means will be selected. Exemplary, -for a
three point support the following devices are necessary:
One force measuring device according to Fig. 1,
one -force measuring device according to Fig. 2, and
one force measuring device according to Fig. 3.
m _ Trade Mark
. , .
~2~6~3
Using four support bearings an additional Force measuring de-
vice according to Fig. 3 is necessary.
It should be noted, that the force measuring device 12 oF the
embodiment of Figs. 1 -to 3 may be replaced by other force
measuring devices. The-force measuring device 12 has the advantage of
a relatively larye heigh-t of the gap 22 with a decreased
overall height of the device.
With all three embodiments essentially similar elements may be
used; this simplifies the manufacture and handling of -the de-
vices according to the invention.
As initially explained, it is an advantage of the force measur-
ing device according to the invention that any lateral forces
are transmitted by the elastomeric material in the annular
gap 22 from the piston 20 to the potlike body 18 and the
base part 16. Only considerably increased forces which over-
come the friction be-tween the metalic surfaces of the force
introduction element and the piston and the Teflon material
displace the force introduction element 14 in respect of the
force measuring device 12. Since there is no sagging of the
piston or the base par-t, -there is, in turn, no tilting of the
bin or the weighing platform. Force measuring devices according
to the invention may be loaded in the range of 100 tons and
may have a diameter of 200 mms. The central projection 38 at
the topside of the piston 20 and -the central recess 40 of -the
force introduction element 14 may be replaced by an annular
arrangement having the same function. Also, any other comple-
mentary combination may be used.
In the foregoing force measuring devices has been explained in
connec-tion with Fig. 1 to 3 which in view of the considerable
gap areas may compensate considerable lateral forces. Even
with a large overloading the force measuring device would not
be destroyed, but the relative movement is limited by the en-
~87~)68
gagement of the cylindrical surface of the pis-ton at the in-
terior cylindrical sur-face of the potlike body.
When manu-fac-turing the Force measuring devices according to
Figs. 1 to 3 there is a further advantage that when rotating
the devices with an apparatus according to the above mentioned
European Patent Laid Open Publication -the sectional angle
for a predetermined large diame-ter of a force measuring device
may be smaller than for devices having the bottom main
surface of the piston formed as a projecting cone.