Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2047161
Bogies for railed vehicles
This invention relates to bogies for railed vehicles.
Known bogies for railed vehicles, such as commuter or short-
haul rail vehicles or tram cars, have primary springs which
operate against bogie frames to allow for relative upward and
downward movement of the bogie frames and the bogie wheels.
Secondary springs are provided between a bogie frame and a car
or vehicle body to provide a secondary spring action. In such
bogies, it is also conventional to provide wheels in sets with
the sets spaced longitudinally of the bogie and the wheels of
each set spaced laterally of the bogie. One set of wheels are
normally provided as idle or non-driven wheels which are rigidly
connected to a wheel mounting frame, for example by pedestal
bearings, with the wheel mounting frame extending transversely
of the bogie frame and coupling by bearing arrangements to a
transversely extending frame member of the bogie frame. The
bogie and wheel mounting frames are relatively immovable
longitudinally of the bogie except for vertical pivoting
movements of the mounting frame upon the bogie frame allowed for
by the bearing arrangements. The latter also permit lateral
movement of the mounting frame between limits, such lateral
movement, for instance, being caused by an axial load placed
against a flange of a wheel by a rail when the bogie is
travelling along rails.
Such a bogie is described in U.S. patent number 4,941,409
issued July 17, 1990, to which the reader is directed for
reference, and in its German equivalent, Offenlegungschrift
2047 1 6 1
number 3,808,593. The bogie structure described therein is
suitable for use when a vehicle or car is for travelling around
rail curvatures of large radius, but when travelling around small
radius curvatures, the movement available to the wheel mounting
frame may not enable its wheels to accommodate the curvature of
the rails without undue resistance. As a result, undue pressure
is applied either to one wheel flange or the other during travel
around curvatures of small radius. This pressure, assisted by
the slippage between the rail and the radial surface of the wheel
flange, results in inordinate wear of the engaging surfaces.
This undesirable result is found even though negligible wear
between rails and wheel flanges results when the bogie travels
in a straight line.
The present invention seeks to provide a bogie which is
capable of being used on rails having path curvatures of any
acceptable radius while mitigating the above problem.
Accordingly, the present invention provides a bogie
comprising:-
a bogie frame extending in a longitudinal direction of the
bogie; at least two bogie wheel sets spaced longitudinally of thebogie with the wheels of each set spaced apart laterally of the
bogie;
a wheel mounting frame extending transversely of the bogie
frame and rotatably carrying the wheels of one of the wheel sets;
an intermediate member; and
a coupling arrangement coupling the wheel mounting frame to
the bogie frame;
.
2047 1 6 1
said coupling arrangement permitting pivoting of the wheel
mounting frame about a vertical pivot axis;
said coupling arrangement including means for permitting
limited lateral movement of the wheel mounting frame relative to
the bogie frame; said coupling arrangement being configured so
as to translate lateral force exerted upon one or the other of
the wheels carried by the wheel mounting frame to provide a
component of force acting to rotate the wheel mounting frame
relative to the bogie and turn the wheel set mounted thereupon;
said coupling arrangement comprising resilient pivot means
coupling said intermediate member to said bogie frame and two
resilient coupling mechanisms coupling said wheel mounting frame
to said intermediate member, said coupling mechanisms being
spaced apart laterally of the bogie frame.
In a particularly practical and desirable arrangement, both
the intermediate member and the wheel mounting frame are disposed
at positions lower than the height of the bogie frame at
positions between the sets of wheels. This desirable arrangement
allows the car or vehicle body to be disposed at a particularly
low level, with floor height of as little as 30 cms. being
possible.
The pivot means may comprise two resilient connection
arrangements which are spaced-apart longitudinally of the bogie
to provide a pivot axis, for the wheel mounting frame, at a
position between the connection arrangements. With the
.-,i~
~0~71~1
connection arrangements disposed in tandem along the longitudinal
axis of the bogie frame, a pivoting movement of the wheel
mounting frame and accompanying set of wheels is possible up to
an angle of approximately 1.5 to 3 . The resilient connection
arrangements preferably each comprise a rigid spindle with an
upwardly extending (e.g. substantially vertical) major axis, a
resiliently deformable surround, for example of elastomeric
material, bonded to the spindle, and an outer rigid sleeve member
bonded to the surround. Such a structure advantageously allows
the rigid sleeve member and the spindle to tilt relative to each
other in any direction, i.e. universally.
The coupling mechanisms may each comprise a cylindrical
metal arbour, surrounded by an elastomeric layer which is encased
by a metal sleeve which is a press fit in a housing element,
specifically a journal boss, of the intermediate member. The
metal arbour may then have reduced diameter bearing journals
positively located in supports mounted to the intermediate
member.
The two coupling mechanisms connecting the wheel mounting
frame to the intermediate member may be disposed one on each side
of a longitudinal axis of the bogie. Interengaging parts of each
coupling mechanism may slide relative to each other along an axis
which is inclined at an angle, preferably 10 to 40, to the
longitudinal axis of the bogie. With this latter arrangement,
and with the directions of action being at opposite angles to the
longitudinal axis, any lateral movement of the wheel mounting
frame is accompanied by a slight pivoting movement of the wheel
2~471~
mounting frame. The force applied to the one wheel by a curved
rail will be transmitted to the inclined coupling mechanisms and
result in a component of force acting to pivot the wheel mounting
frame so as to tend to reduce the load upon the wheel flanges,
thereby reducing wear. The pivoting movement of the wheel
mounting frame upon the two coupling mechanisms is accommodated
by the coupling mechanisms until the limit of the elastic play
between the metal sleeves and supports is reached, whereupon the
lateral load is transmitted through the intermediate frame to the
central pivot between the intermediate frame and the bogie frame
member.
A compound movement of the wheel mounting frame is thus made
possible, with the pivoting movement of the wheel mounting frame
taking place about a pivotal point in the middle between the
centring bearings. The elastic coupling between the wheel
mounting frame and the intermediate beam on the one hand and the
intermediate beam and the bogie transverse beam on the other hand
cause a superimposed movement in opposite directions, through
which automatic radial adjustment of the wheel pairs is achieved.
It has been found that a suitable compound movement can be
achieved with the relationships between the various factors
adjusted as follows:-
the resiliently deformable sleeve has a Shore hardness of
from 50 to 80;
the resiliently deformable surround has a Shore hardness of
from 40 to 70;
2047~61
the angle of inclination between the longitudinal axis of
the bogie and the direction of action of each coupling mechanism
is from 10 to 40 with the directions of action oppositely
inclined;
5the distance between the coupling mechanisms is between 300
and 800 mm; and
the distance between axes of the resilient connection
arrangements of the central pivot is between 100 and 250 mm.
One embodiment of the invention will now be described, by
10way of example, with reference to the accompanying drawings, in
which:-
Figure 1 is a plan view of part of a bogie and showing the
bogie in a first position in full outline and in a second
position in chain-dotted outline; and
15Figure 2 is a horizontal sectional view of the bogie taken
along line A-A in Figure 1.
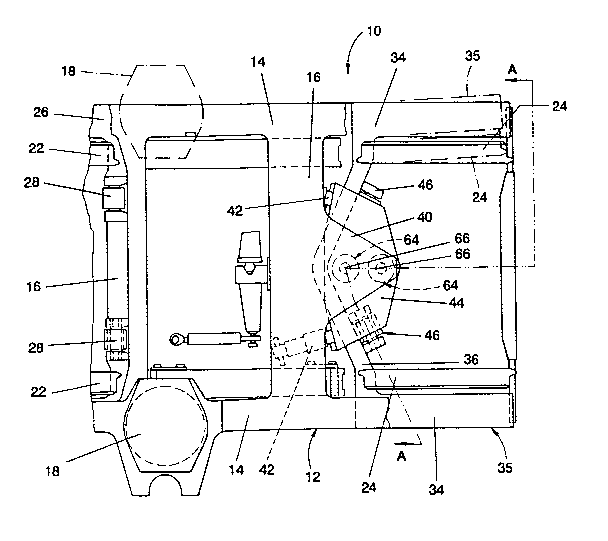
As shown by Figures 1 and 2, a bogie 10 comprises a rigid
bogie frame 12 having two laterally spaced longitudinally
extending side members 14 joined together by transversely
20extending frame members 16. Two springs 18 (referred to as
"secondary" springs) are supported by, and extend upwardly from,
the side members 14 for resiliently supporting a car or vehicle
body (not shown).
The bogie comprises two sets of wheels, a set of driven
25wheels 22 at one end of the bogie and a set of idle or non-driven
wheels 24 at the other end. The driven wheels 22 are rotatably
mounted independently of one another and laterally spaced in
204~
axial alignment upon a frame 26 which is pivoted at one end by
two axially spaced bearings 28 (Figure 1). The frame 26 has two
primary springs (not shown) acting between the frame 26 and
overhead parts of the bogie frame with which the primary springs
are vertically aligned.
The idle or non-driven wheels 24 are independently rotatably
mounted by pedestal bearings (not shown) upon two arms 34 of a
wheel mounting frame 35 which has a frame member 36 of chevron
shape in plan view. The frame member 36 extends transversely of
the bogie frame to interconnect one end of one arm 34 to an end
of the other arm 34.
The wheel mounting frame 35 extends with its frame member
36 extending horizontally and lower than the frame member 16,
which has a longitudinally extending projection 40 symmetrically
positioned relative to a longitudinal axis of the bogie and
overlying part of frame member 36. Two dampers 42, one on each
side of the longitudinal axis of the bogie, are provided to
dampen shock loads from the frame member 36 to the frame member
16. Between the frame members 36 and 16 is disposed a plate-like
intermediate beam member 44.
The wheel mounting frame 34 is suspended from the
intermediate frame member 44 by two resilient coupling mechanisms
46, disposed on respective arms of the chevron-shaped frame
member 36. These two coupling mechanisms are positioned at equal
distances apart, one on each side of the longitudinal axis of the
bogie, so that they are spaced laterally of the bogie frame. As
is more clearly shown by Figure 2, each resilient coupling
20471 61
mechanism comprises a rigid shaft element or arbour having a
large diameter axially extending centre section 50 and two
axially aligned journal ends 52 of smaller cross-section.
Surrounding and bonded to the centre section 50 is a resiliently
deformable sleeve 54 of elastomeric material. Surrounding the
deformable sleeve 54 is a metal sleeve 55. The metal sleeve 55
is disposed within and bonded to a rigid housing element 56. The
housing element 56 depends from the underside of the intermediate
member 44. The journal ends 52 of the shaft element 48 are non-
rotatably received by support brackets 58 attached to a sidesurface of the frame member 36. Each bracket 58 has an upwardly
open wedge-shaped recess. Each end 52 of each shaft 48 is
hexagonal in cross-section with two of its six surface portions
62 intimately engaged with the surfaces 60 of the recess as shown
by Figure 2.
In a stable first condition of each resilient coupling
mechanism 46, its metal sleeve 55 is spaced axially from each
support bracket 58 (Figure 2), but is slidable along the major
axis of the coupling mechanism which extends generally laterally
of the bogie. Thus an axial force of sufficient strength applied
to a wheel 24 will cause lateral movement of the wheel mounting
frame 35 relative to the bogie frame. This movement is permitted
by resilient axial shear movement of the sleeves 54 until the
metal sleeve 55 abuts the support bracket 58. The resiliently
deformable sleeves 54 have a Shore hardness preferably between
to 80 .
204711~1
As shown by Figure 1, the axial direction of each coupling
mechanism 46, and thus its direction of resilient action is
inclined to the transverse axis of the bogie at an angle of from
10 to 40. Thus, initial lateral movement of the wheel mounting
frame 35 is accompanied by a slight pivoting movement of the
wheel mounting frame, afforded by the elastomeric sleeve 54.
The pivotal connection between the intermediate member 44
and the projection 40 of frame member 16 comprises pivot means
in the form of two resilient centring bearings 64 which lie in
tandem along the longitudinal axis of the bogie. Each bearing
64 comprises a rigid spindle 66 secured to, and extending
substantially vertically downwardly from, the projection 40.
Around the spindle 66 is a metal sleeve held in position by a
retaining nut 69. Surrounding and bonded to the spindle 66 is
a resiliently deformable surround 68 of elastomeric material.
Surrounding and bonded to the surround 68 is an outer rigid
cylindrical member 70. The member 70 extends through and is
secured to the intermediate member 44. The surround 68 is made
from a material preferably with a Shore hardness of from 40 to
70 and with its thickness correctly chosen in relation to the
Shore hardness of the resiliently deformable sleeves 54 and to
other dimensions of the bogie, such as the distance between the
connection arrangements 64 and between the resilient coupling
mechanisms 46. The surround 68 is capable of allowing for
pivotal movement of the rigid cylindrical member 70 axially
around the spindle 66 and also allows for tilting of the member
70 in any plane, i.e. universally, relative to the spindle 66.
20~7161
Hence, the intermediate frame 44 is tiltable in any plane about
the pivot bearings 64. The pivoting action of the intermediate
frame 44 around the two bearings 64 may be complex. Any pivoting
action, either horizontally around the axes of the spindles 66
or in any vertical plane, actually occurs about a resultant axis
lying between the two bearings 64 as both of the surrounds 68 are
deformed simultaneously and to a required degree.
In use, lateral movement of the wheel mounting frame 35
takes place in the appropriate direction if a flange of a wheel
24 has a lateral load placed against it by the outside rail as
the bogie moves around a curve. Initially the lateral load will
displace wheel mounting frame 35 relative to the intermediate
member 44 until the sleeve 55 of the coupling mechanism abuts the
adjacent support bracket 58. When this occurs, the lateral load
is transmitted to the pivot assembly 64, 66. The centring
bearings 64, 66 are both elastically deformable a~d so the
intermediate member 44 pivots about an axis between them. As a
result, the wheel mounting frame moves laterally while being
pivoted to a small degree, steering the wheel pair 24 as
illustrated by chain dot lines in Figure 1. This movement,
results in reducing the load upon the wheel flanges, and turns
the wheels 22.
Embodiments of the invention thus allow automatic radial
adjustment of the wheel pair, enabling a bogie to negotiate rails
having small or large radius of curvature while minimising wear
upon wheel flanges and reducing the risk of derailment.