Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
21 82344
BODY STRUCTURE FOR AN OPERATOR'S CAB OF A RAILROAD
2 VEHICLE
- BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
7 The present invention refers to a body structure for an operalor's cab of a
8 railroad vehicle, and in particular to a body structure formed of sections
9 members welded together for forming opposing sides, a front face, roof and
floor, and an external body sheeting of metal.
11
12 Operalor cabs for railroad vehicles are formed conventionally of a body
13 structure which is formed of section members of steel or aluminum that are
14 welded together and are covered on their inside and outside surfaces with asheeting of same material. The section members are suitable sp~ced from each
16 other at a distance that depends on- the thickness of the sheeting so as to avoid
17 a bulging or deformation when being subject to a load. Typically, the distance
18 between spaced-apart reinforcing sections ranges between 200 and 300 mm.
19 Thus, not only is a great number of section members required for the body
structure but frequently clirrerent lengths of section members are needed or
21 suitably cut sections are joined at their ends. This need for numerous
22 co",ponents renders the overall construction relatively expensive. In addition,
21 8234~
the sheeting must be thermally sllailled by mechanical tension after being
2 welded onto the section members and should exhibit heat insulating and sound
3 insulating properties through incorporation of an insulation and sound absorbing
4 components. Moreover, a covering must be mounted onto the inside surface of
the body structure.
7 It is also known to design the operator's cab in form of a sandwich8 construction of plastic material, including a rigid foam core through which inner
9 and outer support structures of fibrous-glass reinforced plastics (FRP) are held
in place at a suitable distance from one another. Such a sandwich construction
11 eliminates a need for a sound absorption, insulation, inner covering and section
12 ",embers. However, as this body structure for the operator's cab exhibits a
13 dirrerent thermal expansion coefficient than the remaining vehicle body, its
14 attachment can only be effected through elastic bonding, so that this cab body
structure cor,l, ibutes only to a limited extent to the strength of the vehicle.16
17 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
18
19 It is an object of the present invention to provide an improved body
20 structure for the operator's cab of a railroad vehicle, obviating the aforestated
21 drawbacks.
21 82344
In particular, it is an object of the present invention to provide an
2 improved body structure for an operator's cab of a railroad vehicle, exhibiting an
3 increased stability compared to conventional constructions while yet reducing
4 the overall manufacturing costs.
.
6 These objects and others which will become apparent hereinafter are7 attained in accordance with the present invention by providing a body structure
8 comprised of spaced section members, an external sheeting which is welded
9 onto the section members at weld lines, and a load-bearing sandwich structure
comprised of a batten plate and a tension-resistant and co,l,pression-proof inner
11 covering panel bonded interiorly to the sheeting.
12
13 The cab body structure according to the present invention unites the
14 advantages of welding with the advanlages of a sandwich construction. While
welding of the section members and the external sheeting to one another results
16 in a good flux of forces between these components, the sandwich construction
17 results in a required stiffness of the overall body structure. Thus, the sheeting is
18 prevented from deformations and bulging in a direction perpendicular to its
19 surface area when being subject to compressive strains or forces. To date, such
results were only attainable through complicated welding of section members.
21
22 The body structure for an operalor's cab according to the present
` 21 82344
invention eliminates the following process steps:
3 - Production and incor~oralion of numerous reinforcing sections through4 welding;
- Spraying of sound insulation onto the sheet;
6 - Cutting and bonding of a heat insulation onto the single sheets;
7 - Production and attachment of an inner covering.
9 Preferably, the batten plate is provided in form of a rigid foam panel which
is made of hardly infla,~"~,able polyurethane, or in form of a honeycomb panel
11 made of phenolic resin The inner covering panel may be formed as decorative12 high pressure laminate or may be made of fibrous-glass reinforced plastics.13
14 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
16 The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present
17 invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the
18 accompanying drawing in whi~:
19
FIG. 1 is a side view of a body structure for an operalor's cab of a
21 railroad vehicle, in accordance with the present invention;
2 1 82344
-
FIG. 2 is an exploded illustration of the body structure of FIG. 1
2 showing in detail the individual components of the operator s cab; and
3 .
4 FIG. 3 is a partial sectional view through the roof of the operatG, s
cab.
7 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
9 Throughout all the Figures the same or corresponding ele",e"ls are
ge"erally indicated by the same reference numerals.
11
12 Tuming now to the drawing and in particular to FIG.. 1 there is shown a
13 side view of a body structure for an operators cab of a railroad vehicle with the
14 body structure being formed of section members that are welded together to
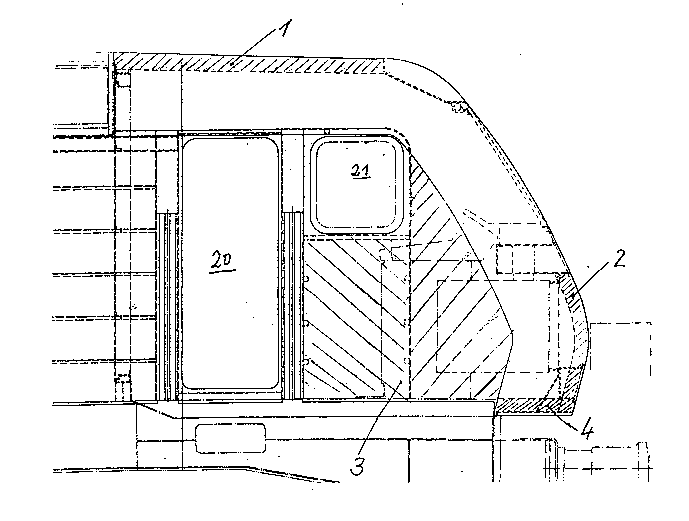
provide components such as roof 1 front face 2 opposing side walls 3 and
16 floor 4. These co",ponents of the body structure are illustrated in FIG. 1 through
17 respective hatching for ease of illustration. Further shown in FIG. 1 are cutouts
18 for an ~ccess door 20 and a window 21.
19
Turning now to FIG. 2 there is shown an exploded illustration of the body
21 structure, with additional illustration of a rear wall 5 formed of vertical and
22 longitudinal section me,nbers 5a 5b a side wall column 6 upper and lower
- 2182344
guard panels 7 8 upright section ",en,ber~i 9 for connection purposes a
2 subassembly 10 as well as a side wall 11 of the railroad vehicle. The roof 1 is
3 shown as comprised of transverse section members 14 and longitudinal
4 sectional members 14a (only one is shown of each). The arrows indicate the
5 direction of asse",bly of the individual cG"".o"ents of the body structure
6 Persons skilled in the art will understand the general mode of assembly of the
7 body structure as indicated in FIG. 2 so that a detailed description thereof is
8 ~milled for sake of simplicity.
Referring now to FIG. 3 there is shown an exemplified partially sectional
11 view of the body structure as described with reference to the roof 1. As shown in
12 FIG. 3 the roof 1 is formed by an external sheeting 12 which is welded onto the
13 section member 14 at weld line 13. At their forward end the external sheeting 12
14 is welded at weld line 13 to the side wall column 6 that is formed as hollow
15 girder. Through the welded connection between the sheeting 12 on the one
16 hand and the column 6 and the sections 14 on the other hand a good flux of
17 forces is ensured between these components.
18
19 A batten plate 16 is bonded by means of an adhesive 15 to the inside
20 surface of the external sheeting 12 and extends between the transverse section
21 member 14 and the side wall column 6. The batten plate 16 may be made in
22 form of a rigid foam panel of hardly inflan"~,able polyurethane or in form of a
2 1 82344
honeycomb panel of phenolic resin. Secured to the underside of the batten
2 plate 16 by means of adhesive 15 is a tension-resistant and compression-proof
3 covering panel 17 which together with the batten plate 16 forms a load-bea,i"g
4 sandwich board for the sheeting 12. A sealing is provided at the junction of the
5 sandwlch board comprised of batten plate 16 and covering panel 17 with the
6 side wall column 6 through incorporation of a sealing compound 18. Suitably the
7 inner covering panel 7 is made as decorative high pressure laminate or made of
8 fibrous-glass reinforced plastics.
As further shown in FIG. 3 the side wall column 6 is formed with a
11 cavity 19 which contains a suitable filler material.
12
13 Persons skilled in the art will understa"d that the desc, i,l~lion of the roof 1
14 is done by way of example only and should be considered only as representation
15 of the general structure of the cab body structure.
16
17 While the invention has been illustrated and described as embodied in a
18 body structure for an operator s cab of a railroad vehicle it is not intended to be
19 limited to the details shown since various modifications and structural changes
20 may be made without depa,lii1g in any way from the spirit of the present
21 invention.
2 1 82344
-
What is claimed as new and desi~d to be protected by Letters Patent is
2 set forth in the appended claims: