Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
1
MACHINE FOR MAKING A GROOVE INTO A CONCRETE SURFACE OR THE LIKE
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a machine for making a groove into a
concrete surface or the like, which can be floor, wall or a ceiling. This
machine is an
improvement to the machine disclosed and claimed in Canadian patent
no.1,253,420
granted on May 2, 1989, and its US counterpart no. 4,792,190 granted on
December,
1988, to the same applicant.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The machine disclosed and claimed in the above patent is designed for
cutting curbstones, sidewalks or the like. The movements of the saw are
restricted to
the cutting of floor-like surfaces. This machine does not permit enough
rotation of the
saw so as to be directed towards the upper portion of a wall or a ceiling for
cutting the
same. Moreover, this machine does not include any supporting means which are
appropriate to stabilize the saw while it is in operation, because such is
actually not
necessary when the saw is exclusively used to cut curbstones or sidewalks.
2 0 There is presently a need for a machine for the cutting of wall-like
surfaces and ceiling-like surfaces in order to, for example, make a groove
into the walls
and ceiling of a road tunnel.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The object of the present invention is to provide a machine for making a
groove into any kind of surface which is made of concrete or any other hard
material,
whatever be the position of such a surface (floor, wall or ceiling).
More particularly, the object of the present invention is to provide a
3 o machine including a powered truck-like vehicle having a support base and
an apparatus
mounted on the base for making a groove into a surface, the apparatus
comprising:
CA 02236811 2004-11-03
2
- two spaced-apart booms, the two booms being parallel to each other
and each having one end pivotally mounted on the base;
- tilting means mounted on the base.to tilt the parallel booms vertically in
unison about their one ends;
- a rail-structure-holding head slidably mounted on each of the parallel
booms;
- sliding means to slide each head separately along its respective boom;
- an elongated main rail having a pair of opposite ends;
- means for mounting the main rail on said heads for rotation about a
longitudinal axis parallel to said elongated main rail, the means for mounting
the main
rail comprising:
-- curved support members, each support member pivotally
connected to its respective head for rotation about said longitudinal axis,
and having a
first end on which the main rail is pivots lly mounted by support means about
a
transversal axis perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, and a second end;
-- power means extending between the second end of each
curved support member and the respective head for levering the first end of
the curved
support member and, therefore, for rotating the main rail about the
longitudinal axis;
- a saw carrier mounted on the main rail;
- displacing means for moving the saw carrier along the main rail along a
first direction parallel to the longitudinal axis;
- a motorized saw mounted on the saw carrier;
- means on the saw carrier for displacing the saw on the saw carrier in a
second direction perpendicular to the first direction, and
- a powered extendible leg mounted on each opposite end of the
main rail for stabilizing said apparatus whenever required, each leg being
mounted pivotally on the main rail so that each leg can be rotated with
respect to
the main rail, and each leg being fixable with respect to the main rail so
that
each leg can be rotated with the main rail around the longitudinal axis.
As can be appreciated, the machine according to the present invention,
gives the saw enough freedom to be directed towards an upper wall or a ceiling
and for
cutting therein.
CA 02236811 2004-11-03
2a
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the saw carrier of
the machine holds a motor which is offset with respect to the saw and operates
the saw
through a gearing. This feature makes it possible to cut relatively deep
grooves into a
surface since the motor operating the saw is offset with respect to the saw
and does not
interfere with the surrounding surFace.
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
3
According to another preferred embodiment of the invention, each
opposite end of the main rail of the machine includes a powered extendible leg
for
stabilizing the apparatus whenever required. Each leg has a remote end with a
foot
attached to it. Means are provided for orienting each leg in a third direction
perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and perpendicular to the surface in
such a way
that each foot lies on the surface and thus stabilizes the apparatus.
According to still another preferred embodiment of the invention, each
end of the main rail of the machine further includes a supporting element
extendable in
a given direction perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. This element
comprises a first
portion indirectly attached to the respective end of the main rail and a
second
telescopically mounted portion. The second portion has a remote end on which a
foot is
mounted, and fixation means on which the remote end of the leg is connected
after
removal of the corresponding foot.
These two preferred features are designed to stabilize the saw with the
legs which may lie on a floor for making a groove therein, or on a wall for
making a
groove in an adjacent ceiling.
The invention and its advantages will be better understood upon reading
the non restrictive description of a preferred embodiment thereof, made with
reference
to the appended drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
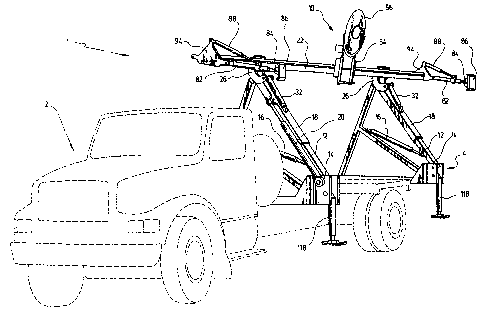
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a truck on which a machine according to
the invention is mounted.
Figure 2 is a top plan view of the machine shown in figure 1, with its
booms and saw in a lateral extension.
Figure 3 is a side elevational view of the machine according to the
invention showing the booms in horizontal and lifted up positions.
Figure 4 is another side elevational view of the machine according to the
invention, positioned for making a groove into a floor-like surface.
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
4
Figure 5 is a side elevational view similar to the one of figure 4, showing
the machine positioned for making a groove into a ceiling-like surface.
Figure 6 is a side elevational view similar to those of figures 4 and 5,
showing the machine positioned for making a groove into a wall-like surface.
Figure 7 is a partial perspective view of the machine shown in figure 2.
Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view taken along line VIII-VIII of figure 9
showing the spacer wheels and powered pinion wheel of the saw carrier.
Figure 9 is a partial cross-sectional view taken along a horizontal plane of
the saw.
Figure 10 is a cross-sectional view taken along line X-X of figure 9,
showing the other spacer wheels of the saw carrier.
Figure 11 is a partial front view taken along the plane defined by lines a-a
and b-b of figure 7, showing the leg with and exploded representation of an
adapter
piece.
Figure 12 is a partial front view taken along line a-a of figure 4, showing
the leg.
Figure 13 is a partial front view taken along the plane defined by lines a-a
and b-b of figure 7, showing the leg in a contracted position.
Figure 14 is a view similar to the one of figure 13, showing the leg in an
2 0 extended position.
Figure 15 is a partial front view of figure 6, showing the leg.
Figure 16 is a view similar to the one of figure 2, showing the main rail at
an angle slightly different than 90° with each boom.
Figure 17 is a partial exploded perspective view of the pivoting
connection of one of the curved support members of the machine according to
the
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
invention, showing the respective head and the support means for pivotally
mounting
the curved support member on the main rail.
NUMERAL REFERENCES USED FOR THE ELEMENTS SHOWN IN THE DRAWINGS
1 machine
2 powered truck-like vehicle
4 support base
apparatus
12 booms
10 14 one end of the booms
16 powered jacks of the tilting means
18 rail-structure-holding heads
powered jacks of the sliding means
22 main rail
23 opposite borders of the main rail
24 opposite end of the main rail
26 curved support members
28 first end of the curved support members
second end of the curved support members
2 0 32 powered jacks extending between curved support members and heads
34 pin extending along the longitudinal axis L
36 holes in the extensions of the head
38 extensions of the heads
holes in the curved support member
42 first plate of the support means
44 second plate of the support means
46 bolts
48 spacers
nuts
30 52 pivot pin extending along the transversal axis T
54 saw carrier
56 saw
58 first part of the saw carrier
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
6
60 second part of the saw carrier
62 powered jacks for displacing the saw in the second direction S
64 motor of the saw
66 gearing of the motor
68 toothed rack
70 powered pinion wheel
72 upper spacer wheels
74 lower spacer wheels
76 side spacer wheels
78 motor of the pinion wheel
80 rod of the pinion wheel
82 powered extendible legs
84 remote ends of the legs
86 foot of the legs
88 powered jack of the orienting
means
90 first place to attach the legs
92 second place to attach the legs
94 triangular support plate
96 first tip of the triangular
support plates
98 second tip of the triangular
support plates
100 third tip of the triangular
support plates
102 adaptors
104 third place to attach the supporting
elements
106 supporting elements
108 first portion of the supporting
elements
110 second portion of the supporting
elements
112 remote end of the second portion
114 foot of the supporting elements
116 fixation means of the supporting
elements
118 legs of the support base
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
7
As shown in figures 1 and 2, the machine (1 ) according to a preferred
embodiment of the invention includes a powered truck-like vehicle (2) having a
support
base (4). It also includes an apparatus (10) mounted on the base (4) for
making a
groove into a surface. The surface could be made of concrete or any other hard
material.
As is also shown in figures 3, 5 and 7, the apparatus (10) comprises two
spaced-apart booms (12) which are parallel to each other. Each of these booms
(12)
has one end (14) pivotally mounted on the base (4). The apparatus (10) also
comprises
tilting means mounted on the base (4) to tilt the parallel booms (12)
vertically in unison
about their one end (14). The tilting means preferably consist of powered
jacks (16)
Each of these jacks (16) interconnects the base (4) and a corresponding boom
(12) in
such way that the extension and contraction of the powered jacks (16) in
unison, permit
to tilt the booms (12) up and down as shown in figure 3.
The apparatus (10) also comprises a rail-structure-holding head (18)
slidably mounted on each parallel boom (12) and sliding means to slide each
head (18)
separately along its respective boom (12). The sliding means preferably
consist of
powered jacks (20). Each jack (20) interconnects one of the heads (18) and the
corresponding boom (12). These jacks (20) may expand and contract
independently in
such a way that each head (18) may be positioned differently from the other
along its
2 0 respective boom (12) as is shown in figure 16 in comparison with figure 2.
The apparatus (10) further comprises an elongated main rail (22) having
a pair of opposite ends (24) and means for mounting the main rail (22) on the
heads
(18) for rotation about a longitudinal axis (L) parallel to said elongated
main rail (22).
The longitudinal axis (L) and the means for mounting the main rail (22) are
clearly
shown in figure 17. The means for mounting the main rail (22) comprise curved
support
members (26). Each curved support member (26) is pivotally connected to a
corresponding head (18) for rotation about the longitudinal axis (L). Each
curved
support member (26) also has a first end (28) on which the main rail (22) is
pivotally
mounted by a support means about a transversal axis (T) perpendicular to the
3 0 longitudinal axis (L), and a second end (30). Power means are provided
between the
second end (30) of each curved support member (26) and the corresponding head
(18)
for levering the first end (28) of the curved support member (26) and,
therefore, for
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
8
rotating the main rail (22) about the longitudinal axis (L). Preferably, the
power means
include powered jacks (32). Referring to figure 17, the pivoting connection of
each
curved support member (26) to its corresponding head (18) includes a pin (34)
extending along the longitudinal axis (L) and passing through holes (36) into
an
extension (38) of the respective head (18) and holes (40) into the curved
support
member (26). As can be noticed, the means described hereinabove for mounting
the
main rail (22) on the heads (18) allow the main rail (22) to rotate about the
longitudinal
axis (L) within a wide angle of rotation. Two different positions of rotation
of the main rail
(22) are illustrated in figures 5 and 6. Thus, the means for mounting the main
rail (22)
on the heads (18) of the present invention is one of the main improvements of
the
present invention over the machine disclosed and claimed in Canadian patent
no. 1,253,420. It allows more rotation of the main rail (22) about the
longitudinal axis (L)
and thus allows the machine (1) to cut into a surface enclosed in a wider
area.
Referring more particularly to figure 17, the support means for pivotably
mounting the first end (28) of each curved support member (26) on the main
rail (22)
comprises a first plate (42) fixed on the main rail (22) and a second plate
(44) that is
rigidly connected to the first plate (42) in a spaced apart relationship by
four sets of
bolts and nuts. Each set includes a bolt (46), a spacer (48) and a nut (50).
The first and
second plates (42, 44) together define a gap in which the first end (28) of
the curved
support member (26) is pivotably mounted about a pivot pin (52) that extends
along the
transversal axis (T) from and between the first and second plates (42, 44).
The first end
(28) of each curved support member (26) is sandwiched between the first and
second
plates (42, 44) and may pivot around the pivot pin (52), thereby allowing the
main rail
(22) to make an angle slightly different than 90° with each boom (12)
when the heads
(18) are positioned differently along their respective booms (12) as is shown
in
figure 16.
Referring now to figures 8, 9 and 10, the apparatus (10) further
comprises a saw carrier (54) mounted on the main rail (22). Displacing means
are
provided for moving the saw carrier (54) along the main rail (22) in a first
direction (F)
parallel to the longitudinal axis (L). A motorized saw (56) is mounted on the
saw carrier
(54) and means are provided on the saw carrier (54) for displacing the saw
(56) on it in
a second direction (S) perpendicular to the first direction (F). The saw
carrier (54)
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
9
comprises a first part (58) mounted on the main rail and a second part (60)
carrying the
saw (56). The first and second parts (58, 60) are interconnected by the saw
displacing
means which preferably include two powered jacks (62) projecting in the second
direction (S). The saw displacing means disclosed hereinabove is another one
of the
improvements made to the machine disclosed and claimed in Canadian patent
no. 1,253,420. It provides a simple and solid way for displacing the saw (56).
The
second part (60) of the saw carrier (54) holds a motor (64) which is offset
with respect
to the saw (56) and operates the saw (56) through a gearing (66). Thanks to
the
particular structure and positioning, the saw (56) may penetrate more deeply
into the
groove that is being cut, because the motor (64) is offset with respect to the
saw (56).
The displacing means for moving the saw carrier (54) along the main rail
(22) along the first direction (F) comprises means for slidingly mounting the
saw carrier
(54) along the main rail (22). It also comprises a toothed rack (68) solid
with and
extending all along [of] the main rail (22), and a powered pinion wheel (70)
mounted on
the saw carrier (54) and adapted to engage the toothed rack (68). Preferably,
the
means for slidingly mounting the saw carrier (54) along the main rail (22)
includes four
upper spacer wheels (72) which extend on both sides of the main rail (22) and
are
spaced apart from each other. The upper spacer wheels (72) are mounted on the
saw
carrier (54) and positioned in such a way that they are lying on opposite
borders (23) of
the main rail (22) and may roll on it along the first direction (F). The means
for slidingly
mounting the saw carrier (54) along the main rail (22) also includes four
lower spacer
wheels (74) and four side spacer wheels (76). The lower spacer wheels (74) are
also
mounted on the saw carrier (54) and are positioned under each upper spacer
wheels
(72) in order to sandwich the borders (23) of the main rail (22) and also roll
on it along
the first direction (F). The side spacer wheels (76) also mounted on the saw
carrier (54),
separated on both sides of the main rail (22) and spaced apart from each
other, are
positioned in order to roll onto the edge of the borders (23) and guide the
saw carrier
(54) along the main rail (22). As illustrated in figure 8, a motor (78) is
mounted on one
side of the saw carrier (54) and operates the pinion wheel (70) through a rod
(80)
extending under the main rail (22) in such a way that the pinion wheel (70)
engages the
toothed rack (68) under the main rail (22). The toothed rack (68) is better
illustrated in
figures 11 and 12. Rotation of the powered pinion wheel (70) by means of the
motor
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
(78) moves the saw carrier (54) along the main rail (22). More particularly,
the saw
carrier (54) slides onto the borders (23) with the help of the spacer wheels
(72, 74, 76).
Referring to figures 13 and 14 among others, each opposite end (24) of
the main rail (22) includes a powered extendible leg (82) for stabilizing the
apparatus
(10) whenever required. Each leg (82) has a remote end (84) with a foot (86)
attached
on it. Means are provided for orienting each leg (82) in a third direction (H)
perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (L) and perpendicular to the surface in
such way
that each foot (86) lies on the surface and thus stabilizes the apparatus
(10). These legs
(82) are used to stabilize the apparatus (10) especially while the saw (56) is
in
10 operation. Preferably, the powered extendible legs (82) are powered jacks.
Figures 13
and 14 show the extendible legs (82) in contraction and extension
respectively.
As clearly illustrated in figure 7, each opposite end (24) of the main rail
(22) has a triangular support plate (94) rigidly connected thereto. The
triangular support
plate (94) extends in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (l_) and
has first and
second tips (96, 98) that are in opposite positions with respect to the second
direction
(S) in which the saw (56) is displaced. The triangular support plate (94) also
has a third
tip (100).
The means for orienting each leg (82) comprise a' powered jack (88)
pivotably connected to the third tip (100) of the triangular support plate
(94) and to the
corresponding leg (82), respectively. These means for orienting (the] the legs
(82) are
particularly helpful because they enable the operator of the machine (1 ) to
position each
leg (82) perpendicularly to the surface, at a distance. Such becomes a need in
the
position illustrated in figure 5 where the legs (82) are up. These orienting
means are
also another one of the improvements of the machine according to the invention
over
the one disclosed and claimed in Canadian patent no. 1,253,420. They give new
operational possibilities to the machine, especially for making grooves into a
ceiling or a
wall as well. They also simplify the operation for cutting a floor.
Each opposite end (24) of the main rail (22) further includes first and
second places (90, 92) to which the corresponding leg (82) is attached. The
first and
second places (90, 92) are spaced apart in such a way that when the leg (82)
is
attached to the second place (92) as shown in figure 12, it extends less than
when the
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
11
same leg (82) is attached to the first place (90) as shown in figure 1. The
first and
second places (90, 92) to attach the corresponding leg (82) are respectively
located at
the first and second tips (96, 98) of the triangular support plate (94). More
particularly,
the second places (92) are located indirectly at the second tip (98) by means
of
adaptors (102), while the first places (90) are located directly at the first
tip (96).
Preferably, the adaptors (102) are directly attached to the second tip (98) of
the triangle
support plate (94) and the main rail (22) as illustrated in figures 11 and 12.
Installation
of the legs (82) at the second places (92) allows the saw (56) to get closer
to a floor-like
surface and to make a deeper groove therein or with a lower angle as
illustrated in
figure 4. The option to less extend the legs (82) is also another improvement
made over
Canadian patent no. 1,253,420.
Referring more particularly to figures 6 and 15, each end (24) of the main
rail (22) further includes a third place (104) to receive and install a
supporting element
(106) extendable in a given direction perpendicular to the longitudinal axis
(L). Each
element (106) comprises a first portion (108) attached to the third place
(104) and a
second telescopically mounted portion (110). Each second portion (110) has a
remote
end (112) on which a foot (114) is mounted, and fixation means (116) on which
the
remote end (84) of the leg (82) is connected after removal of the
corresponding foot
(86). It is noteworthy that the foot (114) of each supporting element (106) is
designed to
be interchangeable with the foot (86) of each leg (82). The extension and
contraction of
the legs (82) force the second portion (110) to slide inside the first portion
(108). In
other words, the supporting element (106) performs as an extension of the legs
(82)
thereby allowing it to reach the floor-like surface when the saw (56) is
cutting high up
into the wall, and therefore stabilizing the apparatus (10) in such an
operation as
particularly illustrated in figure 6. When the legs (82) are connected to the
supporting
elements (106), the orienting means also permit to adapt the orientation of
each leg (82)
and thus of each supporting element (106) so that it is perpendicular to the
surface. The
option of extending more the legs (82) is a further one of the main
improvements of the
present invention over the one disclosed and claimed in Canadian patent
no.1,253,420.
Indeed, it allows for the stabilization of the apparatus (10) during its
operation whatever
its position.
CA 02236811 2001-05-28
12
The support base (4) of the machine (1 ) comprises at least two
extendible, ground-contacting legs (118) to stabilize the apparatus (10)
whenever
required. More particularly, the apparatus (10) is stabilized by four support
base legs
(118) as partially shown in figure 1, 3 or 7. These legs (118) also allow for
the
stabilization of the whole machine (1) during every movement of the apparatus
(10)
such as positioning or operating the saw (56).
As can be appreciated, the machine (1) according to the present
invention is designed to be able to make a groove into a floor-like surface as
well as a
ceiling or wall-like surface at almost any possible angle. This machine (1)
has been
construed especially for making a groove in a road tunnel in order to renovate
such a
tunnel. The machine (1 ) is preferably equipped with a circular diamond saw
(56) in such
a way that it can succeed to cut any hard material.
It should be noted that all powered jacks are preferably hydraulic
cylinders. However, use could also be made of endless screws. It should also
be noted
that the displacing means for moving the saw carrier (54) along the main rail
(22) could
alternatively consist of a chain system instead of the pinion wheel and
toothed rack
system disclosed hereinabove. It should be further noted that the machine
according to
the present invention could include only one of the very specific
improvements.
Thus, although a preferred embodiment of the invention has been
2 0 described in detail herein, and illustrated in the accompanying drawings,
it is to be
understood that the invention is not limited to the precise embodiment, and
that various
changes and modifications may be effected therein without departing from the
scope or
the spirit of the invention.