Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
NEW CONTRACEPTIVE KIT
The invention is in the field of hormonal contraception and pertains to a
contraceptive
kit comprising means for the daily adnunistration of a contraceptive agent.
The
invention also pertains to certain steroid compounds having an outstanding
profile of
biological properties with respect to use as contraceptive agents. More
particularly,
the invention pertains to compounds having such a profile as to make them
suitable
for use in anticonception by "monotherapy," i.e. by administering to a female
of child-
bearing age a single active substance which on its own possesses the required
activity
for preventing pregnancy.
Many conventional contraceptive kits provide for the administration to a
female of
child-bearing age of two different agents, usually a progestagen and an
estrogen.
Depending on the specific kit, these agents can be administered in various
ways and
according to various regimens. Mast customary are kits providing a
contraceptive
regimen of the so-called "combined contraceptive" type, in which daily dosage
units
comprising both the pmgestagen and the estrogen are administered for usually
21
consecutive days, in one or more phases distinguished by different amounts and
ratio's of both active substances, while in the remaining days of the 28 days'
cycle
placebo's are administered or a "pill-free" interval is provided.
Contraceptive kits in which a single active substance is provided, are known.
These
are usually of the "progestagen only" type. While such "progestagen-only-
pills"
(POPS) have the advantage of avoiding the administration of an estrogen, they
have a
drawback in that cycle control frequently is unsatisfactory, as can be seen
from
irregular bleeding as well as from inherent amenorrhoe.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
z
Hence, it is desired to include an estrogenic component, for which usually
ethinyl
estradiol is taken. In the art, several less-desired properties (on
haemostasis and a risk
of cancer) of combined contraceptives are mainly attributed to this estrogenic
component. It is an object of the invention to provide, by taking a single
compound
having an activity profile including both the required progestagenic and the
required
estrogenic activity, a contraceptive which leads to good cycle control without
exposing the above-identified less-desired properties. Further, it is an
object of the
invention to provide a contraceptive which has the advantages of excluding
ethinyl
estradiol, but at the same time retains the favourable effect of ethinyl
estradiol on the
lipid profile.
In the art, estrogenic .receptor binding is usually described in relation to
steroids
which, just as estradiol, have an aromatic A-ring. Thus, e.g. a review paper
by
Anstead et al. in Steroids, 1997, vol. 62, pages 269-303, describes the in
vitro
estrogen receptor binding of a great many of such steroid structures, carrying
various
substituents. Such a disclosure, apart from not relating to in vivo activity,
does not
allow making any prediction on the estrogenic receptor binding of other, non-
aromatic
structures, let alone with respect to mixed estrogenic/progestagenic activity.
25 The present invention now provides a contraceptive kit comprising means for
the
daily administration of a contraceptive agent, characterised in that the
single
contraceptive agent is a steroid compound having an activity profile
inherently
combining progestagenic and estrogenic activity. The invention also resides in
the use
of a steroid compound having an activity profile inherently combining
progestagenic
and estrogenic activity for the manufacture of a contraceptive pharmaceutical
preparation in which said compound is the single contraceptive agent. More
particularly, the invention is in the use of a steroid compound selected from
the group
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
3
consisting of steroids satisfying structural formula I given below, prodrugs
thereof,
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for the manufacture of a
contraceptive
pharmaceutical preparation.
2. Detailed De crin~ ion
The present invention is made possible in particular by the unexp~ted finding
of a
type of compounds which possess a rare activity profile in that they are at
the same
time progestagenic (P) and estrogenic (E); and both activities are at a
relatively high
level. Thus, the single contraceptive agent to be used in the kit according to
the
invention is a steroid compound having an activity profile inherently
combining
progestagenic and estrogenic activity to such an extent that the Minimum
Active Dose
(MAD) in both the Allen-Doisy test for estrogenic activity and the McPhail
test for
progestagenic activity is < 250 ~g/kg. It will be apparent to the person
skilled in the
art that the term "single contraceptive agent" does not preclude said steroids
from
being combined with any other progestogen and/or estrogen, in a minor amount
that is
not contraceptively active, to the extent that such is desired for fine-tuning
of the
activity profile. It is preferred that the mixed-profile steroid is the only
active
compound present.
Suitable compounds according to the invention include those satisfying the
following
structural formula I:
O
formula I
wherein the dotted lines each independently indicate an optional additional
bond.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
4
In one embodiment, the invention pertains to the use of these compounds for
the
. manufacture of a contraceptive pharmaceutical preparation. In another
embodiment,
the invention is a contraceptive kit comprising means for the daily
administration of
any one of the above steroids as a contraceptive agent. In yet another
embodiment, the
invention provides a method of contraception comprising administering, to a
female
of child-bearing age, an effective amount of a steroid compound as described
above.
It is intended to include in the invention the compounds of formula I, as well
as
prodrugs thereof, i.e. related compounds the substituents of which are easily
metabolised to the active compound according to formula I, or are readily
cleaved to
such a compound upon being administered. Together.with the most regular
prodrugs,
the invention thus pertains to the compounds satisfying formula II, and
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
formula II
wherein wherein the dotted lines each independently indicate an optional
additional
bond, Y stands for (H,H), (O), (N-OH), or (H,OH); and X stands for (-H) or (-
CZ-C,
acyl), such as -C(=O)CH,. The 3-keto compounds, i.e. with Y being (O), are
preferred. The other possibilities for the substituent at carbon atom number 3
have as
their main property according to the invention that they are precursors
(prodrugs) of
the preferred 3-keto compounds. Similar considerations hold for the X
substituent, in
which the optional ester group is a precursor for the preferred active
compound, in
which the OX group is OH. For the sake of clarity, the invention is described
hereinafter with reference to the active compounds according to formula I, but
is
intended to include at least the prodrugs described with reference to formula
II.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
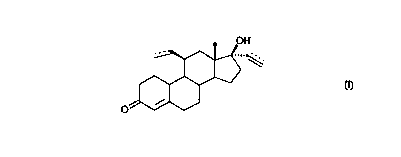
In a preferred embodiment, the compound used in the present invention is ( 11
(3,17a)
_ 11-ethyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one (Org 4060), which has the
following structural formula III:
structural fonmula N.
OH
",
O
5
formula III
This compound, which is known from US 3,325,520 as a component of a mixture,
from US 5,710,144 as a medicament in the treatment of menopausal complaints,
and
from GB 1,190,240 as a starting compound for the synthesis of other steroids,
surprisingly has properties which make it highly favourable for use in
contraception.
A yet further preferred embodiment of the invention, is the compound
satisfying the
O
OH
formula IV
This compound (11(3,17a)-11-Ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one
(Org 4325} is within a class of steroid compounds known in general from US
4,292,251. This document describes a group of compounds with a range of
possible
properties. The document does not pertain to compounds having a specific mixed
E/P
profile, nor to monotherapy contraception. In this preferred embodiment, the
invention now provides a compound which shows a marked difference with respect
to
the profile of biological properties compared with structurally related
compounds
known from US 4,292,251. This very difference, i.e. the unexpected mixed E/P
profile, makes Org 4325, as well as prodrugs thereof and pharmaceutically
acceptable
salts thereof, highly suitable for use in monotherapy contraception.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PGT/EP99/01404
6
According to the invention it is preferred to use the above steroids in
contraception
by monotherapy. However, it will be clear to the person skilled in the art
that the
outstanding biological properties of the steroids according to the invention
can also be
benefited from if one were to combine any one of these steroids with another
active
substance, e.g. a progestagenic or an estrogenic steroid.
The present invention further provides for a contraceptive kit in which a
single active
substance having both progestagenic and estrogenic properties is administered
for e.g.
18 to 30, and preferably 21 to 25 days, the remaining days of the cycle being
a "pill-
free" or placebo interval. In principle, any other number of days is possible,
but for
practical reasons this is less desired. It is also possible to refrain from a
pill-free or
placebo interval, i.e. to provide for the continuous (daily) administration of
the
aforementioned mixed estrogen/progestagen compound. Thus several advantages of
the above compounds may be enjoyed, but as such a continuous regimen will lead
to
inherent amenorrhoe, it is preferred to include a pill-free or placebo
interval.
The kits according to the invention provide contraception by "monotherapy"
rather
than by combination of components having separate activities, but include an
estrogenic component so as attain contraceptive efficacy and cycle control
comparable
to that of combined contraceptives. The pill-free or placebo interval will
make for a
withdrawal bleeding, which is generally considered desirable, inter alia
because thus
the natural cycle is mimicked as much as possible, and because it gives the
certainty
that no pregnancy has occurred.
The instant steroids can be administered in various ways. E.g., a means for
sustained
release can be chosen, but it is preferred if the means for administration is
in the form
of sequential daily dosage units, particularly tablets for oral
administration.
The term "dosage unit" generally refers to physically discrete units suitable
as unitary
dosages for humans, each containing a predetermined quantity of active
material
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PGT/EP99/01404
7
calculated to produce the desired effect, for instance tablets, pills,
powders,
suppositories, capsules and the like.
Methods and compositions for making such dosage units are well-known to those
skilled in the art. For example, conventional techniques for making tablets
and pills,
containing active ingredients, are described in the standard reference,
Gennaro et al.,
Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, ( 18th ed., Mack -Publishing Company,
1990,
see especially Part 8: Pharmaceutical Preparations and Their Manufacture).
For making dosage units, e.g. tablets, the use of conventional additives, e.g.
fillers,
colourants, polymeric binders and the like is contemplated. In general any
pharmaceutically acceptable additive which does not interfere with the
function of the
active compounds can be used in one or more of the compositions.
Suitable carriers with which the compositions can be administered include
lactose,
starch, cellulose derivatives and the like used in suitable amounts. Lactose
is a
preferred carrier. Mixtures of carriers can also be used.
A process of manufacturing the kit of the invention comprises mixing a
predetermined
quantity of one or more of the aforementioned steroid compounds having
progestagenic and estrogenic activity, optionally together with another
estrogenic or
progestagenic steroid, with predetermined quantities of excipients, and
converting the
mixture into dosage units. The resulting kits may contain any number of daily
dosage
units, but will generally be adapted to a defined length of the menstrual
cycle by
having 18-30, and preferably 20-28 daily dosage units. Preferred kits are in a
form
adapted to the normal length of the human menstrual cycle and contain 21-25,
most
preferably 21 of said daily sequential dosage units and optionally further
placebo
dosage units to make up a total of 28-32 daily dosage units.
Converting the mixture into dosage units generally involves moulding the
mixture
into a tablet, filling a capsule with a dried mixture, or filling a capsule
with a wet
mixture.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCTIEP99I01404
8
As indicated above, the means for administration of the steroids according to
the
invention may also be in a form other than that of a daily tablet, e.g an
implant or an
intravaginal article, such as a vaginal ring, or another type of sustained-
release device.
Methods of making sustained-release devices such as implants and vaginal rings
are
known in the art. In this respect, reference is made to Jorge Heller Drug
Delively in
the Plastics Aee, in "Innovations in Drug Delivery", Tom Sam and Jasper
Fokkens
ed., pages 134-145. For a preferred contraceptive implant, EP 303 306 is
referred to.
Many designs of a vaginal ring releasing two substances are known to the
person
skilled in the art. The preferably ring-shaped drug delivery system that can
be used in
the present invention comprises at least one compartment comprising a
thermoplastic
polymer core containing the mixed-profile steroid compound in an amount which
allows a direct release of the compound in physiologically required amounts.
The daily dosage of the steroids according to the invention, which may be up
to 1 mg,
generally is in the range of from SO to 500 pg, preferably of from 100 to 300
pg. For
the compounds according to formula III and N, the amount to be administered
preferably is 50-250 wg per day and more preferably 100-200 pg per day. The
most
preferred daily dosage in the case of monotherapy contraception is 140-160
p,g. For
Org 37678, which is the compound satisfying formula I wherein both of the
optional
additional bonds are absent, the doses typically are 1,5 to 2 times higher,
200-300 p,g
being chosen by preference.
The steroids used in the present invention can be prepared in accordance with
the
general teachings of US 5,710,144 and US 4,292,251.
The invention will be explained further with reference to the following
examples.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PGTIEP99/01404
9
EXAMPLE 1
(ll~i,l7a)-11-Ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one was prepared
from
(11(3)-11-ethenylestr-S-ene-3,17-dione cyclic 3-(1,2-ethanediyl acetal) as
follows:
i) - A suspension of 57.5 g of potassium tert-butoxide in 585 ml of dry THF
was ice-
cooled to 0 °C and subsequently acetylene was passed through this
mixture for 2
hours, at which point the ice-bath was removed. Next, a solution of 15.0 g of
(11~3)-
11-ethenylestr-5-ene-3,17-dione cyclic 3-(1,2-ethanediyl acetal) in 156 ml of
dry THF
was added dropwise and acetylene was passed through the resulting mixture at
mom
temperature. After 2 hours, 350 ml of a saturated aqueous solution of ammonium
chloride was slowly added and the resulting mixture was extracted twice with
ethyl
acetate containing ca. 2% of pyridine. The combined extracts were washed twice
with
a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate and once with a
saturated
aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), dried over sodium sulfate, and
concentrated under reduced pressure to afford 16.2 g of (11(3,17a)-11-ethenyl-
17-
hydroxy-19-norpregn-5-en-20-yn-3-one cyclic (I,2-ethanediyl acetal).
ii) - To a solution of 16.2 g of (11~i,17a)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-noipregn-
5-en-
20-yn-3-one cyclic (1,2-ethanediyl acetal) in 870 ml of acetone, 44 ml of 4N
HCl was
added and the resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature and under a
nitrogen
atmosphere for 3'/z hours. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was poured into
3'/z 1 of
water, which was extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The combined
extracts were
washed once with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate,
twice
with water and once with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride
(brine),
dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford
14.0 g of
crude material. This crude product was crystallised twice from a mixture of
methylene
chloride and acetone (K, : 1.2 g, K2: 4.8 g). The mother liquor of the second
crystallisation was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was
purified
by flash chromatography (toluene:ethyl acetate = 8:2) to afford another 3.8 g
of
product. This material was combined with K, and KZ and 50 ml of diethyl ether
was
added. The resulting suspension was refluxed for 4 hours, cooled for 60 hours
at 5 °C
and the crystals, after washing with 3 ml of cold diethyl ether, collected by
filtration
(9.0 g). Since repeating this procedure twice did not improve the purity of
the product,
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PGTlEP99/01404
flash chromatography (heptane:acetone = 7:3} was used as a final purification
step to
afford 6.3 g of pure (11 (3,17a)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-
3-one.
M.p. 186.8 °C. [a]oz° _ + 29.5° (c=1, ethanol).
5
EXAMPLE 2
(11(i,l7a)-17-Acetyloxy-11-ethenyl-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one was prepared
from (11/3,17a)-I1-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one as follows:
IO - To a solution of 460 mg of (11(3,17a)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-
en-
20-yn-3-one in 4.6 ml of acetic anhydride, 156 mg of para-toluenesulfonic acid
was
added and the resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature and under a
nitrogen
atmosphere for 4'h hours. Subsequently, 0.4 ml of 36% HCI was added and the
mixture was stirred overnight. The crude mixture was then poured into 46 ml of
water,
I S which was extracted four times with methylene chloride. The combined
extracts were
washed with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate, water
and a
saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), dried over sodium
sulfate, and
concentrated under reduced pressure to afford the crude product which was
still
contaminated with the corresponding 3-acetyloxy-3,5-diene.
The crude product was dissolved in a mixture of 28 ml of acetone and 0.2 ml of
36%
HCl and the resulting solution was stirred for 24 hours at room temperature
(after 3
and 7%Z hours, 0.7 ml of water was added). Next, another 0.2 ml of 36% HCI was
added and the resulting mixture was once more stirred overnight at room
temperature.
Finally, the crude mixture was poured into 275 ml of water, which was
extracted three
times with ethyl acetate. The combined extracts were washed with a saturated
aqueous
solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate, water and a saturated aqueous solution
of
sodium chloride (brine), dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under
reduced
pressure to afford 550 mg of crude product. Purification by flash
chromatography
(toluene:ethyl acetate = 4:6) yielded 165 mg of pure (11(3,17a)-17-acetyloxy-
11-
ethenyl-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one as an amorphous solid.
M.p. 14I.1-161.1 °C. [a]pz° _ -1° (c=0.5, dioxane).
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
11
EXAMPLE 3
(3E/Z,11 [i,17x)-11-Ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one oxime was
prepared from (11(3,17x)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one as
follows:
- To a solution of 500 mg of (11[i,l7a)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-
20-
yn-3-one in 2.6 ml of pyridine, 1.18 g of hydroxylamine.HCl was added and the
resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature and under a nitrogen
atmosphere for
1 hour. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was poured into 46 ml of water,
which was
extracted three times with methylene chloride. The combined extracts were
washed
with water and a saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), and
concentrated under reduced pressure to yield 480 mg of crude (3E/Z,11(3,17a)-
11-
ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one oxime.
Crystallisation from methylene chloride afforded 260 mg of a 85:15 mixture of
the
3E- and 3Z-oxime.
M.p. 257 °C. [a]DZ° _ + 58.4° (c=0.5, dioxane).
EXAMPLE 4
(11[3,17x)-11-Ethenyl-17-hydroxy-I9-norpregna-4,20-dien-3-one was prepared
from
(11[3,17x)-1 I-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one as follows:
- To a suspension of 175 mg Lindlar catalyst in 15 ml of ethanol, pre-treated
with
hydrogen gas for 25 minutes, a solution of SOO mg (11(3,17x)-11-ethenyl-17-
hydroxy
19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one in 5 ml of ethanol was added and the resulting
mixture
was hydrogenated at atmospheric pressure for 1 hour. Subsequently, the
catalyst was
removed by filtration of the crude mixture over dicalite and the filtrate
concentrated
under reduced pressure. Purification of the crude product by flash
chromatography
with toluene/ethyl acetate (4/6), using silver nitrate impregnated silica as
the
stationary phase, gave 162 mg of pure (11(3,17x)-11-ethenyl-I7-hydroxy-19-
norpregna-4,20-dien-3-one as an amorphous solid.
M.p. 62.9-70.3 °C. [a]p'° _ + 74.1° {c=0.5,
dioxane).
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
12
EXAMPLE 5
(3x,11 (3,17a)-11-Ethenyl-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yne-3,17-diol and (3 [3,11
(3,17a)-11-
ethenyl-19-nor-pregn-4-en-20-yne-3,17-diol were prepared from (I1(3,17a)-ll-
ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one as follows:
- To a solution of 2.0 g of (11(3,17a)-11-ethenyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-
20-
yn-3-one in 25 ml ~of dry THF, 3.14 g of Li(O'Bu),AIH was added and the
resulting
mixture was stirred at room temperature and under a nitrogen atmosphere for 2
hours.
Subsequently, the reaction mixture was poured into a saturated aqueous
solution of
ammonium chloride, which was extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was
washed
with water and a saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), and
concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification of the crude mixture by
flash-
chromatography with dichloromethane/acetone (95/5) gave, after crystallisation
from
diisopropyl ether, 100 mg ofpure (3a,11~i,17a)-11-ethenyl-19-norpregn-4-en-20-
yne-
3,17-diol and 700 mg of pure (3(3,11(3,17a)-11-ethenyl-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yne-
3,17-diol.
3a-isomer: M.p. 178.5 - 179.1 °C.
3 (3-isomer: M.p. 147.6 - 148.2 °C.
EXAMPLE 6
(Il~i,l7a)-11-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one was prepared as
follows from (11[3)-11-ethenylestr-5-ene-3,17-dione cyclic bis-(1,2-ethanediyl
acetal):
i) - To a solution of 100 g of the bisacetal mentioned above in 3.5 1 of dry
tetrahydrofi~ran was added S g of platinum(IV) oxide, and the mixture was
hydrogenated at room temperature until no more hydrogen was taken up. The
mixture
was filtered over celite, the residue washed twice with tetrahydrofuran, and
the
combined filtrates concentrated under reduced pressure to afford 93 g of crude
cristalline (11(3)-11-ethylestr-5-ene-3,17-dione cyclic bis-(1,2-ethanediyl
acetal),
which was used in the subsequent step without further purification.
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
13
ii) - The diketal from the previous step (10 g) was suspended in 50 ml of
acetone. To
this suspension was cautiously added a solution of 6,7 ml of water and 3,3 ml
of
sulfuric acid. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, and
then poured
into a solution of 20 g of sodium acetate in 100 ml of water. The mixture was
cooled
in an ice bath; the resulting precipitate was filtered off and the residue
washed with
water until the washings were neutral; the residue was then collected and
dried, giving
7.5 g of crude (ll~i)-11-ethylestr-4-ene-3,17-dione which was used in the
subsequent
step without further purification.
iii) - Acetylene gas was passed through a suspension of 16.5 g of potassium
tert-
butoxide in 100 ml of dry tetrahydrofiwan for 2 hours. To this suspension a
solution of
10 g of the diketone from the previous step in 50 ml of dry tetrahydrofuran
was added
dropwise. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours while
acetylene
was continuously passed through. Subsequently, a solution of 15 ml of sulfuric
acid in
30 ml of water was cautiously added and the mixture stirred for a fiuther 2
hours.
Thereafter, a sulution of 40 g of sodium acetate in 250 ml of water was slowly
added,
and the mixture heated at 75 °C for 15 minutes. The organic solvents
were then
distilled of and the residue cooled to room temperature. A precipitate was
formed,
which was removed by filtration and taken up in 600 ml of toluene. Active
charcoal
was added and the mixture heated to 65 °C, filtered and concentrated
under reduced
pressure. The crude product was recrystallized from ethanol/water to afford
6.5 g of
( 11 (i,17a)-11-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one.
M.p. 222 °C. [a]p2° _ _16.1° (c = 1, dioxane).
COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE
(A) Identical with Example II(b) of US 4,292,251.
(B) Identical with Example XIII of US 4,292,251 (including the procedures of
Example VI(a) and (b) therein).
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
14
EXAMPLE OF PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION
Pharmaceutical compositions are prepared containing a steroid in accordance
with the
present invention. By way of illustration, the compound of Example 6 (Org
4060) is
S chosen. The compound is mixed with the other ingredients in a standard way,
and the
mixture is subjected to granulation. The composition is as follows, the same
formulation being applicable to other compounds including Org 4325:
Org 4060 (active) 1-10 wt.%;
Corn Starch (disintegrant) 15 wt.%;
Hydroxy Propyl Cellulose (binder) 3 wt.%;
Lactose 200 M (diluent) up to 100 wt.%;
TEST EXAMPLE A
Several steroids, compounds according to the invention as well as compounds
not
according to the invention, were subjected to testing for relevant biological
properties,
viz. progestagenic activity and estrogenic activity. The progestagenic
activity was
determined by means of the McPhail test, the estrogenic activity by means of
the
Allen-Doisy test. Both tests are known in the art, and can be described as
follows:
In vivo test in rabbit used to evaluate test compounds for their
progestational activity
by histologically scoring the differentiation of endomefria1 tissue. Rabbits
are
primed with estradiol for 8 days and, subsequently, the progestagenic compound
is
orally administered for 5 days. The animals are euthanized (60 mg
pentobarbitonelrabbit i.v.) and transverse haematoxylin-eosin-stained sections
of
two different parts of each uterine horn are prepared. The progestin-dependent
endometrium development is evaluated microscopically and rated on a scale from
0-
4 (Van der Vies J., and De Visser, J. 1983. Endocrinological studies with
desogestrel. Drug Res. 33: 231-236).
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PCT/EP99/01404
In vivd test in rat used to evaluate test compounds for their estrogenic
activity by
scoring the cornification of the vaginal epithelium on vaginal smears. Mature
female
rats are ovariectomized and, in the third week thereafter, primed with a
single dose of
5 1 pg oestradiol (day 1). Seven days after priming, test compound is
administered once
on day 8 and twice on day 9. Vaginal smears are taken in the afternoon of day
10,
twice on day 11 and again in the morning of day 12. The smears are stained
with
Giemsa and the number of positive smears is determined (Van der Vies J., and
De
Visser, J. 1983. Endocrinological studies with desogestrel. Drug Res. 33: 231-
236).
The test results are indicated in the following table.
Compound Structure McPhail (p,g/kg)Allen-Doisy
(pglkg)
Comparison 63-125 2000
A
(Org 4433)
i
Comparison " >1000 >125
B
(Org 10436)
0
Example 6 "" 250 63-125
(Org 4060)
o '
Example 4 ~ 125 250
(Org 37678)
o~~
Example 1 ~ 63-125 32
,
(Org 4325)
0
CA 02319765 2000-08-O1
WO 99/45886 PGT/EP99/01404
16
TEST EXAMPLE B
The compound of Example 6 was employed in monkey studies.
Mature female stumptail monkeys (Macaca Arctoides) 5-20 years of age with
proven
regular menstrual cyclicity were used. The monkeys were housed in a colony of
approximately 35 females and one vasectomized male. Experiments were approved
by
the 'Animal Use Committee' (DEC, AEP nr. E97A0801PV E). To three of these
monkeys the compound of Example 6 was administered at a dose of 8 ~,g/kg per
day.
The first day of menstrual bleeding was considered to be day 1 of the cycle
and the
experiments started with the pre-treatment control cycle (day 1 of the
experiment).
Treatment (daily) started on day 2 of the treatment cycle until day 22.
Compounds
were administered orally via a catheter under light anaesthesia with ketamin~
(dose
depending on the monkey, i.m. s 10 mg/kg). Following administration animals
were
housed individually to regain consciousness and to check for regurgitation.
After two
hours the animals were allowed to return to the colony. The post-treatment
cycle
started after the (expected time of) menstrual bleeding of the treatment
cycle. Blood
samples for analysis of estradiol and progesterone levels were taken twice a
week
(Mondays and Thursdays) throughout the experiment. Blood samples were taken
from
the versa femoralis using Vacutainer tubes (Venoject). Cyclicity was also
monitored
by taking daily vaginal swabs with a cotton tip applicator. Vaginal bleedings
were
divided in clear bleedings (score = +) and minor bleedings (score = t).
All of the monkeys receiving the compound of Example 6 showed ovulation
inhibition; two out of three showed a withdrawal bleeding; none showed
intermittent
bleedings. These results show that this mixed E/P compound is highly suitable
as a
contraceptive: ovulation inhibition is excellent and, while a separate
estrogen is
dispensed with, the bleeding pattern and cycle control is good.