Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 ~ PCT/US99/30074
RIDGE CAP VENT
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to roof ventilating devices and, in particular,
the
s present invention relates to roof ventilating devices made of corrugated
materials used to
ventilate roofs with metal ridge caps.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Insufficient roof ventilation can result in a prolonged interface between
still moist
to air and a colder surface. Moisture condensation on the colder surface
occurs when these
conditions are present. The condensed moisture often spots and damages
ceilings. In
more severe cases, structural members such as rafters, truss chords, joists
and studs are
continually damp and become unsound. Buildings with insufficiently ventilated
roofs
also tend to be warmer in summer months due to the presence of solar-heated
air trapped
15 within. Because of the heat retained by inadequately ventilated roofs,
these buildings are
more expensive to maintain at comfortable temperatures than if these roofs
were
adequately ventilated. However, when adequate ventilation occurs, air is kept
in motion
by being circulated from outside the roof, through the attic, and out through
vents often
placed at or near the roof ridge. Such ventilation is continually necessary in
order to
20 prevent accumulation of hot air or condensed moisture.
Various products have been developed to provide forms of ventilation. These
products either provide separate ventilation structures or are themselves
building
materials with ventilating properties.
25 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A vent which is disposable on a roof is provided. The vent is disposable
proximate an edge of a gap formed proximate the roof peak. The vent may
include one
or more vent layers. Each vent layer may include a generally planar first ply
and a
second ply. The first and second plies are joined to define a multiplicity of
air passages
3o which enable air (or fluid) exchange between interior and exterior portions
of the roof.
The vent may be conformed to be disposable between an upper roof member or
ridge cap
and a lower roof member, the upper roof member overlaying the lower roof
member
when the upper roof member is in place. Exemplary second plies are convoluted
or may
include a multiplicity of cross-members extending between the first plies. The
vent may
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 2 PCT/US99/30074
further include means for adhering the vent to the roof when the vent is
installed thereon.
The adhering means may include an adhesive and the adhesive may be covered by
a
protective strip before the vent is installed. The vent may further include
means for
folding the vent. The folding means may include a flexible member hingably
joining a
pair of vent sections. The folding means may also include a hinge defined by
an intact
first ply, other first plies (if present) and the second ply being severed to
further define
the hinge. The folding means may be further defined by a fold extending
generally
transversely to a longitudinal axis of the vent. The vent may include one or
more layers.
If a plurality of layers are present, the layers may be fastened together in a
generally
1o stacked relationship.
There is also provided a vent operably disposable on a roof between an upper
roof
member and a, generally planar lower roof member. The vent may include at
least one
generally planar first ply, at least one second ply, and means for air
exchange between
-the interior and exterior of the roof. The air exchange means may be at least
partially
defined by a cooperation between the first and second plies. The air exchange
means
enables fluid exchange between the interior and the exterior of the roof. The
vent may be
conformed to be disposable between the upper roof member and the lower roof
member.
There is also provided a method of installing a vent on a roof, the roof with
a gap
defined proximate the peak of the roof. The method may comprise the steps of
providing
2o the vent; and placing the vent along the gap. The provided vent may include
a generally
planar first ply and a second ply, the first and second plies joined to define
a multiplicity
of air passages enabling air exchange between interior and exterior portions
of the roof.
If more than a single vent layer is present, adjacent pairs of layers may be
hingably
connected. The vent may be conformed to be disposable between an upper roof
member
and a lower roof member underlying the upper roof member. The method may
further
include the step of placing the upper roof member over the placed vent. The
vent may
further include an adhesive on an exterior vent surface. If the vent includes
the adhesive,
the method may further include the step of placing the vent such that the
adhesive will
contact the upper roof member or the lower roof member. The vent may further
include
3o a protective member or strip disposed over the adhesive. If the vent
includes a protective
member or strip, the method may include the step of removing the protective
member
from the adhesive prior to placing the vent on the roof. The method may
further include
the step of disposing a closure strip between the vent and the lower roof
member.
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 3 PCT/US99/30074
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
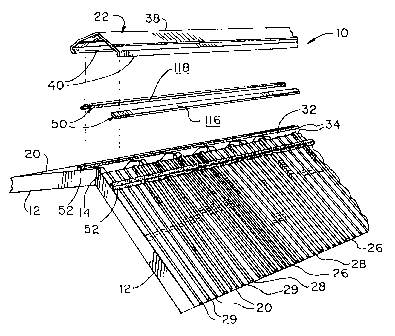
Figure 1 is a fragmentary, exploded, perspective view of an exemplary roof
including the ventilation device of this invention;
Figure 2 is a fragmentary, exploded, perspective view of the peak portion of
the
roof of Figure 1, depicting another embodiment of the ventilation device of
this
invention;
Figure 3 is a fragmentary, perspective view of the peak portion of the roof of
Figure 1, depicting installation of the ventilation device embodiment of
Figure 2;
Figure 4 is a fragmentary, cross-sectional view of two layers of a first
embodiment of the corrugated material used in the ventilation device of this
invention;
Figure 5 is a fragmentary cross-sectional view of a single layer of a second
embodiment of the corrugated material used in the ventilation device of this
invention;
Figure 6 is a fragmentary cross-sectional view of four layers of a third
w embodiment of~he-corrugated material used in the ventilation device of this
invention;
Figures 7a, 7b, 8a and 8b are perspective views depicting how the material of
Figure 4 is fashioned into an exemplary ventilating device of this invention;
Figure 9 is a fragmentary, cross-sectional view of one embodiment of a hinge
of
the ventilation device of this invention;
Figure 10 is a fragmentary, cross-sectional view of the hinged ventilation
device
of Figure 9 in a folded position; and
Figure 11 is a fragmentary, cross-sectional view of another embodiment of the
hinge of Figure 9.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Figure 1 depicts exemplary roof 10. The slope of exemplary roof 10 is defined
by
angular structural members, such as rafters 12. Opposing rafters 12 join at an
angle to
form peak (ridge) 14. Exterior or lower roof members of roof 10 overlaying
rafters 12
include generally planar sheets 20 and an upper member, such as ridge cap 22.
Each
sheet 20 includes first portion 26 and a second portion, such as lateral lip
28, extending
3o from one or both of the lateral edges of sheet 20. Lips 28 of adjacent
sheets 20 overlap
when sheets 20 are installed on roof 10 in this embodiment. While first
portion 26 is
generally planar, one or more ribs 29 may be present. Gap 32 is defined
between upper
edges of corresponding sheets 20 on opposing slopes of roof 10 and includes
lateral
edges 34. The central portion of gap 32 is coincident with peak 14 in this
embodiment.
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 4 PCT/US99/30074
Ridge cap 22 may be installed over gap 32. Ridge cap 22 may define ridge cap
peak 38
and include one or more lateral lips 40. Sheets 20 and ridge cap 22 are
usually fabricated
from materials such as galvanized metals and synthetic resins. The galvanized
metals
may be prefinished. The synthetic resins may include such materials as
fiberglass.
Figures 1-3 also depict exemplary ventilation devices 50 and closure strips
52.
Vents 50 are advantageously disposed between installed sheets 20 and ridge cap
22
along, or proximate, edges 34. In Figure 1, vents 50 are disposed directly
beneath one or
both lips 40 of ridge cap 22. A closure strip 52 may be disposed between each
vent 50
and installed sheets 20. Vent 50 is more fully described below and functions
to insure
that air exchange proximate peak 14 between the interior and exterior of roof
10 will
occur within vent 50. Closure strip 52 accomplishes this function by
accommodating the
nonplanar contours presented by lips 28 and ribs 29, thereby providing a
substantially
air-tight seal between vent 50 and sheets 20. Strip 52 may include materials
such as
foam rubber. Other structures equivalent to strip 52 are within the scope
of~this invention
and include caulking, as well as other materials which may be nominally
conformable to
achieve a sealable interface with abutting materials having regular and
irregular surface
contours.
Exemplary vent 50 of this invention includes at least one layer of a
corrugated
material which defines air passages extending generally perpendicularly, or
otherwise
transversely, to longitudinal axis 56 of vent 50. The embodiment of vent 50
depicted in
Figure 2 may include at least four layers. Each layer includes a corrugated
material more
fully discussed below. The material included each in layer defines a
multiplicity of air
channels extending generally transversely to longitudinal axis 56 of
ventilator S0. These
air channels serve to enable air (or fluid) exchange between the interior and
exterior of
roof 10.
Figure 4 depicts two exemplary layers of this invention, generally denoted as
60.
Each exemplary layer 60 includes planar plies 68 and 70 and convoluted ply 72.
Convoluted ply 72 is disposed between, and joined to (or otherwise cooperates
with),
planar plies 68 and 70 to define a multiplicity of air channels 64.
3o Referring to Figure 5, another exemplary corrugated layer denoted as 78
includes
planar plies 68 and 70, and a multiplicity of cross plies 80. Each cross ply
80 extends
between planar plies 68 and 70, thereby defining a multiplicity of air
channels 82
therebetween. The multiplicity of cross plies 80 is an alternate embodiment of
convoluted ply 72.
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 5 PCT/US99/30074
In Figure 6, four exemplary corrugated layers 88 are depicted. In this
embodiment, each layer 88 includes planar ply 68 and convoluted ply 72. Planar
ply 68
and convoluted ply 72 are joined and cooperate to define a multiplicity of air
channels 90
therebetween. When layers 88 are stacked such that convoluted plies 72 abut,
abutting
convoluted plies 72 cooperate to define another multiplicity of air channels
90
therebetween.
Stacked exemplary layers 60, 78, and 88 may be affixed to each other by such
means as stitching 96 as depicted in Figures 2, 3, 8a and 8b. However, layers
60, 78, and
88 may also be fastened to each other by such means as hot air welding (or
other bonding
1o means using thermal energy), ultrasonic welding, infrared bonding, staples,
glue, or by
other methods known to the art. In this embodiment, vent 50 comes in two four-
foot
strips or sections 106 and 108. Sections 106 and 108 may be joined by such
means as a
hinge technique (described below), folding along preformed creases, or folding
over
pliable hinges such as flexible (duct) tape. While orle embodiment of
exemplary vent 50
1s includes four layers such as layer 60, 78, or 90, any vent with one or more
such layers is
contemplated to be within the scope of this invention.
In one embodiment of the technique of defining exemplary layers 60 of this
invention, layers 60 are stacked after hinge lines 98 are defined by the nick-
scoring
technique. The nick-scoring technique is described in U.S. Patent No.
5,094,041, issued
2o to Kasner et al. on 10 March 1992, the entire contents of which are hereby
incorporated
by reference, and the teachings of which are meant to be included herein. In
the nick-
scoring technique, a sheet of a corrugated material, such as described above
in
conjunction with Figures 4, 5, and 6, is used. Individual hingelines 98 and
individual
layers 60 are defined by a series of generally linear perforations. In this
embodiment,
25 each perforation substantially extends through plies 68, 70, and 72.
Substantially intact
portions of plies 68, 70, and 72 remain between perforations. After these
perforation
lines are formed, layers 60 are accordion-folded along the hinge (perforation)
lines 98 to
form vent 50, as depicted in Figures 7a and 7b.
In another hinge-forming technique, layers such as layers 60, are stacked
after
30 hinge lines 98 are defined by the slit-scoring technique. The slit-scoring
technique is
described in U.S. Patent No. 4,803,813, issued to Fiterman on 14 February
1989, the
entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference, and the
teachings of which
are meant to be included herein. In the slit-scoring technique, layers 60 may
be defined
by slitting, or slicing alternately through one of planar plies 68 or 70, and
through
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
WO 00/37750 6 PCT/US99/30074
convoluted ply 72, leaving the other planar ply 70 or 68 intact. Intact planar
plies 68 and
70 enable layers 60 to be accordion-folded to form vent 50.
As depicted in Figures 8a and 8b, vent 50 may be further defined by the nick-
or
slit-scoring technique, in which sections 106 and 108 are formed so that vent
50 can be
folded for reasons such as more efficient storage and transportation. In one
embodiment,
sections 106, 108 and hingeline 110 are formed by extending slice 120
perpendicularly,
or generally transversely, to longitudinal axis 56, through all layers 60,
except for a
terminal layer denoted 112. In terminal layer 112, a single exterior planar
ply, denoted as
ply 114, is left intact. Intact ply 114 is the exterior planar ply of terminal
layer 112 when
vent 50 is assembled. In assembled vent 50 intact ply 114 becomes the hinge
upon which
sections 106 and 108 are folded along arrow 124. Alternately, an entire
terminal layer
112 may be left intact to serve as a hinge, or a pliable member 122, such as
flexible
(duct) tape, may connect two completely separate sections 106 and 108 as shown
in
Figure 11.
As depicted in Figures 2 and 3, one or both of upper and lower surfaces 116
and
118 of vent 50 may further include adhesive 102 to facilitate installation of
vent 50 by
readily mating upper and/or lower surfaces of vent 50 with either or both of
ridge cap 22
and closure strip 52. A protective strip 104 may be present over adhesive 102
during
storage and transportation to the installation site. Strip 104 may be peeled
from adhesive
102 prior to placing vent 50 into position on roof 10. In another embodiment,
vent 50
may be bonded to closure strip 52. If vent 50 and closure strip 52 are bonded
together in
a single piece, they may be installed in a single step rather than installing
vent 50 and
closure strip 52 separately.
While many materials having various specifications are suitable, exemplary
layers 60 may be made of a corrugated plastic (resin) material with varying
weight as
may be appropriate to the use. In one embodiment, a nominal weight of between
about
140 and 160 pounds per thousand square feet is useful for certain structures.
The
nominal weight may further be about 150 pounds per thousand square feet. The
plastic
resin may have a 4.0 to 4.5 millimeter profile. The plastic resin may still
further include
a profile of about 4.0 (t 0.2) millimeters. The plastic material may be black
and may
include ultraviolet (UV) inhibitors to enable the plastic resin to better
withstand extended
exposure to LJV light. The vent of this invention may include a high-density
polyethylene, corrugated resin with a brittleness temperature of about -
103° (~ 50) F, a
deflection temperature of about +162° (t 50) F at 66 (~ S) pounds per
square inch, a burn
CA 02356133 2001-06-15
W O 00/37750 7 PCT/US99/30074
rate of about 2.5 (~ 0.5) inches per minute, and a self ignition temperature
of about 734°
(t 500) F, and may also merit a label of "excellence" for smoke density of a
9.3 percent
average.
Exemplary vent SO may be about 5/8 (~ $ ) inches in thickness, three (t 0.5)
inches in width, and include two sections 106 and 108, each section 106 and
108 being
about 48 (t 0.5) inches in length. However, other dimensions are contemplated
to be
within the scope of this invention according to the structure environment, and
materials
selected for use.
Because numerous modifications may be made of this invention without departing
from
to the spirit thereof, the scope of the invention is not to be limited to the
embodiments
illustrated and described. Rather, the scope of the invention is to be
determined by
appended claims and their equivalents.