Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
CONVEYOR HAVING A CUSHIONED BELT AND HIGH SPEED DISCHARGE
CAPABILITIES
This application is a divisional application of Canadian Patent File No.
2,283,308 filed
April 16, 1998.
TECHNICAL FIELD
This invention relates generally to automated conveying and sorting of items
such as
packages from one or more loading sites to a variety of output destinations
and more
particularly relates to a conveying system which can eject packages to either
side of a high
speed conveyor onto designated output chutes, bins or subsequent conveyors
under programmed
or manual control.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Modern high volume package delivery systems often include package conveying
systems that accept packages from one or more loading stations and transport
the packages to
a variety of output destinations such as chutes, bins and subsequent conveyor
systems.
One of the most conventional types of conveyors is a belt conveyor, which
includes the use of an endless flexible belt which passes over at least two
cylindrical rollers,
one of which is a drive roller. Packages are placed atop the upwardly-directed
"working"
surface of the belt conveyor and are transported in a generally straight
direction from end of
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
2
the conveyor to the other. Another type of conveyor is a
"roller" conveyor which con include powered or idling rollers
which contact, support, and in certain instances propel the
bottom of the package along its path.
Some conveying systems include diversion features
which allow for the discharge of objects from a conveying
surface at selected stations located along the path of the
conveying surface. Some package diverting systems utilize a
pusher element mounted relative to a conveying surface which
1 0 when actuated ejects an adjacently placed package laterally
across the conveyor surface to the desired discharge station.
Some package diverting systems include the use of diversion .
elements which lie along the conveyor and provide the
diversion forces against the bottom surfaces of the package.
1 5 A modular diverter shoe and slat construction disclosed
in U.S. 'Patent No. 5,127,510 to Cotter describes a modular
diverter shoe for use in a slat conveyor. A diverter shoe is
mounted to each slat so that the shoe may~glide across the slat.
The movement of the diverter shoe is affected by a guide pin
2 0 and coaxial bearing which engages a network of guide tracks
located beneath the conveying surface. When a package is to
be diverted, a diverting switch is actuated to switch the guide
pins for the diverter shoe adjacent to the package onto a
diagonal track, which causes the diverter shoe to move across
2 S the slat and eject the package.
Another apparatus for sorting objects is disclosed in
U.S. Patent No. 4,732,260 to Canziani. In that system, a
conveyor belt is described in which each conveyor element has
a slit. The pusher elements are slidably inserted into the slits
3 0 and each pusher element is connected to a drive element that
extends beneath the conveyor surface. The drive element is '
attached to rollers and interacts with a series of cams or guide
rails located beneath the conveyor. The cams include an
electro-pneumatic two-position end portion. In one position,
3 5 the cam engages the drive element rollers and slides the pusher
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
3
element. In a second position, the rollers do not engage the
guide rails.
U.S. Patent No. 3,768,624, which issued to Kornylak,
discloses a flexible belt conveyor system. Referring to Fig. 3,
a flexible endless belt 6 travels between horizontal surfaces 16
and 18. A spring 20 extends downward from an object 14 to
engage a notch in the belt 6. As a result, the object 14 travels
with the belt 6 and slides across the surfaces 16 and 18. In
another embodiment depicted in Figs. 1 and 2, the traveling
1 0 belt 6 extends above the edges of a tube 2. A coat hanger hook
12 engages a notch (cleat 10) defined by the belt 6. As a
result, the coat hanger hook 12 travels with the belt and slides
upon upper portions of the tube 2 that are adjacent to the belt
6.
1 5 U.S. Patent No. 2,895,593, which issued to McKnight et
al., discloses another flexible belt conveyor. Referring
to
Figs. 10 and 11, anti-friction projections 61 or 63 can
be
mounted at either side of the driven belt 11:
U.S. Patent No. 3,857,487, which issued to Meeusen,
2 0 discloses another flexible belt conveyor. Referring to Fig.
3,
the surface of the conveyor belt includes resilient pads
4 with
deformable projections 5. Articles 2 being conveyed rest
upon
the pads 4.
U.S. Patent No. 1,781,750, which issued to Dodge et al.,
2 5 discloses a conveyor system for conveying lumber 36. As
depicted in Fig. 1, the lumber 36 travels upon multiple
flexible
belts 12.
U.S. Patent No. 3,138,238, which issued to De Good et
al., discloses a conveyor system with a powered diverter.
3 0 Referring to Figs. 1 and 3, the De Good et al. device includes
a
main powered conveyor 10 and a powered side conveyor 22
extending from a side of the main conveyor 10. A traveling
continuous belt 20 drives the rollers 16 (Fig. 1 ) of the
main
conveyor 10, and a drive belt 24 causes conveyance of objects
3 5 upon the side conveyor 22. An object traveling in the
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
4
direction defined from left to right on the main conveyor 10 is
diverted to the side conveyor 22 by a powered diverter. The
powered diverter includes an assembly of diverting wheels 48
{Fig. 3) that are oriented toward the side conveyor 22. The
group of diverting wheels 48 are normally positioned below
the tops of the rollers 16 of the main conveyor 10 so that
objects traveling on the main conveyor 10 are not contacted by
the diverting wheels 48. When it is desirable to divert an
object from the main conveyor 10 to the side conveyor 22, the
1 0 diverting rollers 48 are elevated so that they are slightly above
the top surfaces of the rollers 16 of the main conveyor 10.
The diverting rollers 48 are pushed upward by a device within
the box 32 (Fig. 1 ) which pushes the belt 20 upward
underneath the diverting wheels 48. The belt 20 causes the
1 5 diverting wheels 48 to rotate and drive an object onto the side
conveyor 22. The driven belt 24 of the side conveyor 22
draws the diverted object onto the side conveyor 22 and
propels the object along the side conveyor 22.
U.S. Patent No. 1,462,511, which issued to Lister,
2 0 discloses another conveyor diverter. Referring to Fig. l, a
side conveyor 37 extends perpendicularly from a main
conveyor. Referring to Fig. 8, rollers 36 of the main
conveyor are perpendicular to diverting rollers 41 that divert
objects from the main conveyor to the side conveyor 37 (Fig.
2 5 1 ). The bed of diverting rollers 41 are in a pivoted
configuration in Fig. 8 such that an object (not shown) upon
the diverting rollers 41 would roll under the force of gravity
across the bed of diverting rollers 41 onto the side conveyor
37 (Fig. 1 ).
3 0 U.S. Patent No. 5,477,955, which issued to Madden et
al., discloses a tilting tray conveyor system. Referring to Fig.
2, pivotably mounted trays 60 carry objects. A leg 67 extends
from each tray 60. A particular tray 60 is pivoted to
discharge an object when a lever 81 pushes the leg 67 of that
3 5 tray 60 upward.
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
Although the prior art includes some advantages, a need
always exists in the art for an improved conveyor sorting
system which allows for high speed travel of packages while
still allowing for effective side discharge, without the need for
5 side impact.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides an improved conveyor
1 0 sorting system which allows for high speed travel of packages
while still allowing for effective side discharge, without the
need for side impact.
Generally described, the invention relates to a conveying
apparatus comprising a belt having an deformable surface
1 5 defined by a soft urethane portion, and a slider bed positioned
adjacent the deformable belt, the cushioned belt and the slider
belt configured to combine to support the weight of the
packages, and the cushioned belt configured to urge the
package along the conveying axis.
2 0 The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
comprising a two-layer crowned deformable belt including an
upper deformable crowned portion and a lower, less
deformable, structural portion, and a slider belt positioned
adjacent the cushioned belt, the cushioned belt and the slider
2 5 belt configured to combine to support the weight of the
packages, and the cushioned belt configured to urge the
package along the conveying axis.
The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
comprising a conveyor belt with a crowned top, the belt
3 0 including an elongate substantially straight portion, and a first
and second elongate support means positioned on opposing
sides of the straight portion of the belt and configured to
provide support at a common plane, the belt and the support
means configured to combine to support the weight of the
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
6
packages, and the cushioned belt configured to urge
the
package along the conveying axis.
The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
for conveying a package having a substantially planar,
downwardly-directed lower surface, the conveying apparatus
comprising an endless belt having a portion lying along
a
substantially straight path having a longitudinal path
axis, the
belt defining an upper surface configured to contact
the
downwardly-directed lower surface of the package and
to
1 0 transport the package thereon while allowing the package
to be
tilted laterally thereon from an untilted neutral orientation
to a
tilted orientation, an ejection member configured to
contact
and urge the package such that the package is tilted
from the
neutral to the tilted orientation, and a withdrawal
member
1 5 positioned below the plane of and spaced from the
downwardiy-directed lower surface when the package
is in the
neutral orientation, but also positioned to be in frictional
contact with a portion of the downwardiy-directed lower
surface when the package is in the tilted orientation,
the
2 0 frictional contact being sufficient to allow the withdrawal
member to assist in the removal of the package from
the belt,
such that the package can be contacted and urged by
the
ejection member from the neutral to the tilted orientation
and
the withdrawal member can assist in the removal of
the
2 5 package from the belt.
The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
for conveying a package having a substantially planar
lower
surface, the conveying apparatus comprising an endless
belt
configured to transport a package along a conveying
path, the
3 0 endless belt having a crowned upper surface allowing
the
package to be tilted laterally atop the crowned surface
such
that the lower package surface can be in contact with
said
crowned surface yet can be tilted from a substantially
horizontal to an inclined orientation, a withdrawal
member
3 5 having a fractionally engaging member configured to
engage
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
7
the package only when tilted laterally, and means for tilting
the
package laterally across the longitudinal axis of the belt such
that the withdrawal member frictionaliy engages a portion of
the lower surface of the package and tends to remove the
package from atop the conveyor.
The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
for conveying a package having a substantially planar,
downwardiy-directed lower surface including first and second
spaced-apart lower surface portions, the conveying apparatus
1 0 comprising an endless belt having a portion lying along a
substantially straight path having a longitudinal path axis,
the
belt defining an upper surface configured to contact the
downwardly-directed lower surface of the package and to
transport the package thereon, the belt having a width less than
1 S that of the package to allow the package to extend laterally
therefrom on both sides of the belt to provide access from
below to the lower surface portions of .the planar Lower
surface and to allow the package to be tilted laterally thereon
from a neutral orientation to one of two tilted orientations,
the
2 0 orientations being a first and a second tilted orientation, a
first
ejection member configured to contact and urge the first lower
surface portion of the package such that the package is tilted
from the neutral to the first tilted orientation, an second
ejection member configured to contact and urge the second
2 5 lower surface portion of the package such that the package is
tilted from the neutral to the second tilted orientation, a first
withdrawal member positioned below the plane of and spaced
from the downwardly-directed lower surface when the
package is in the neutral orientation, but also positioned to
be
3 0 in frictional contact with the downwardly-directed lower
surface when the package is in the second orientation, the
frictional contact being sufficient to allow the withdrawal
member to assist in the removal of the package from the belt,
a
second withdrawal member positioned below the plane of and
3 5 spaced from the downwardly-directed lower surface when the
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
package is in the neutral orientation, but also positioned to be
in frictional contact with the downwardly-directed lower
surface when the package is in the second tilted orientation, the
frictional contact being sufficient to allow the withdrawal
member to assist in the removal of the package from the belt,
such that the package can be contacted and urged by the first
ejection member from the neutral to the first tilted orientation
and the first withdrawal member can assist in the removal of
the package from the belt in a first direction, and such that the
1 0 package can be contacted and urged by the second ejection
member from the neutral to the second tilted orientation and
the second withdrawal member can assist in the removal of the
package from the belt in a second direction.
The invention further relates to a conveying apparatus
1 5 for conveying a package having a substantially planar,
downwardly-directed lower surface including first and second
spaced-apart lower surface portions, the conveying apparatus
comprising an endless belt having a portion lying along a
substantially straight path having an upstream and downstream
2 0 portion both lying along a longitudinal path axis, the belt
defining an upper surface configured to contact the
downwardly-directed lower surface of the package and to
transport the package thereon, the belt having a width less than
that of the package to allow the package to extend laterally
2 5 therefrom to provide access to the lower surface portions of
the planar lower surface and to allow the package to be tilted
laterally thereon from a neutral position to a first tilted
position, a pair of slider beds on opposite sides of the first
portion of the belt, the slider beds each defining a plurality of
3 0 support portions all lying substantially in a first common
plane, a discharge station having two movable support means
each defining a plurality of support portions all lying
substantially in a second common plane, the movable support
means commonly selectively movable relative to the
3 5 longitudinal axis of the belt such that the plurality of support
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
9
portions can be selectively moved from a position in which the first common
plane is common
to the second common plane to a position in which the first common plane is at
an angle to the
second common plane.
Therefore, the present invention seeks to provide an improved automated
conveyor
sorting system.
Further, the present invention seeks to provide an improved ejection mechanism
for
ejecting items from a conveying surface.
Other aspects, features and advantages of the present invention will become
apparent
upon review of the following description of preferred embodiments and the
appended drawings
and claims.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
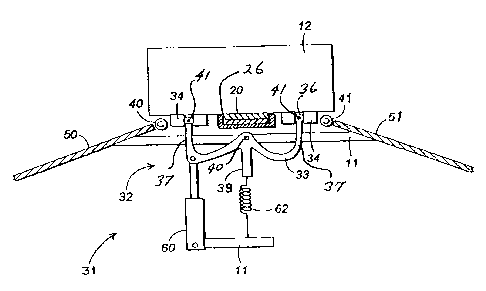
Fig. 1 is a top plan view of the conveyor assembly 10 according to the present
invention, showing packages moving upwardly along the page.
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
l0
Fig. 2 is a downstream end, partial cross-sectional view
of the apparatus 10 of Fig. l, showing the belt 20 in cross-
section. This view shows the pivoting fork assembly 32 in its
"neutral" pasition, which would allow packages to move
thereby without being discharged.
Fig. 3 is a view similar to that of Fig. 2, except that the
pivoting fork assembly has been pivoted to one side, the
''right" side as the figure is viewed, to a ''first" pivoted
position.
Fig. 4 is a view similar to that of Fig. 3, except the
pivoting fork assembly has been pivoted to its "left'' side as the
figure is viewed, to a "second" pivoted position.
Fig. 5 is an isolated view of a portion of the crowned_
belt 20 according to the prevent invention. It should be
1 5 understood that this substantially straight portion is part or an
endless belt which can be driven and guided by pulleys o r
other means such as known in the art.
Fig. 6 is a side elevationai~ view illustrating a package 12
atop the crowned belt 20, showing the deformation provided
2 0 thereby.
DET~Ii.ED DESCRIPTION
Reference is now made in mare detail tc ;~he drawings,
2 5 in which like numerals refer to like parts throughout the
several views,
General Discussion
Referring generally to Figs. 1-6, general discussion of
3 0 the operation of the conveyor apparatus 10 according to the
present invention is now made.
The conveyor assembly 10 includes an elongate crowned ,
conveyor belt 20 which conveys parcels 12 in a longitudinal
direction defined across slider beds 18, 19 and across
3 5 discharge stations such as 30. The parcels (which may also be
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
11
referred to as "packages" 12) can take three different routes once they reach
the discharge
stations. They may be allowed to pass the discharge stations 30 and continue
to be conveyed
by the crowned conveyor belt 20, or they can be selectively discharged off of
the crowned
conveyor belt and into discharge chutes 50, S 1 located to either side of the
substantially straight
path of the crowned conveyor belt 20.
Each of the discharge stations 30 includes a selectively indexable pivoting
fork
assembly 32 which includes a pair of upwardly-directed tines 37. A group of
idling rollers 34
are mounted proximate each of the ends of the upwardly-directed tines 37.
The parcels 12 have sliding contact with the slider beds 18, 19 and "rolling
contact"
with the rollers 34 of the discharge sections 30. When a package is in the
desired position, the
fork member 32 can be indexed to cause one group of rollers 34, which are
already in contact
with the bottom surface of the package, to move upwardly and inwardly. This
causes the
package to tilt about the top of the crowned conveyor belt 20 until the
package contacts a
withdrawal roller 40 or 41 opposing the conveyor belt from the raised rollers.
The withdrawal
roller draws the parcels into one of two chutes 50, S 1 for sorting purposes.
In the following discussion, a "primary conveying axis" will be referenced.
This axis
is an imaginary axis which is parallel to the travel axis of all packages as
they travel under the
sole influence of the crowned conveyor belt 20. This axis will be assumed to
be horizontal,
although it could be at least slightly inclined under other applications of
the present invention.
The Slider Beds
The slider beds 18, 19 are positioned on opposite ends of the discharge
station 30
and each define an upwardly-directed substantially horizontal sliding surface.
In the preferred
r
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
12
embodiment the slider beds 18, 19 are slick pieces of sheet metal, or the
like.
The upper surface of the crowned conveyor belt 20 extends slightly above the
plane
defined by the top surfaces of the slider beds 18, 19. As described in further
detail later, this
allows the crowned conveyor belt 20 to pull packages such as 12 in Fig. 1 to
slide along the
tops of the slider beds 18, 19.
As may be understood, a package preferably does not touch both of the slider
beds
at the same time as it is being drawn along by the crowned conveyor belt 20;
instead, the
package preferably tilts to one side as it is positioned atop the crowned
conveyor belt 20, such
that only one slider bed is being contacted and is providing support.
The Center Belt
Fig. 5 is an isolated, partially cut-away, pictorial view of the endless
crowned
conveyor belt 20. The crowned conveyor belt 20 includes a lower structural
belt portion 24
and an upper deformable crowned belt portion 22. The term "crowned" is meant
to mean that
packages, when placed atop the crowned belt and resting on either of the
slider beds, do not
1 S touch a corner defined by the belt; instead the curved surface of the
crowned belt allows it to
"roll" along the lower surface of the package. For example, if a package was
placed upon the
crowned belt such that it only touched one slider bed and a person pushed down
on the
opposite, non-contacting, side of the package, the crowned surface would
laterally "roll" in
contact with the undersurface of the package as the package tilted to contact
the "other" side.
With the "crowned" nature of the belt, no corner would be encountered by the
package
undersurface.
When in place, the upper deformable belt portion 22 of the crowned conveyor
belt
20 fits within an associated guide channel 26 and has a top portion extending
above the plane
defined by the top surfaces of the slider beds 18, 19.
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
13
Referring momentarily also to Fig, 6, the deformable belt portion 22 of the
crowned
conveyor belt 20 deforms under the weight of a parcel 12 such that portions of
the deformable
belt portion adjacent to the parcel 12 extend slightly higher than the bottom
surface of the
parcel 12 to grip the parcel 12. This provides a "gripping" feature which is
believed to be
advantageous.
The deformable belt 20 is endless in the preferred embodiment, although the
portion
shown in the Figures is substantially straight and extends between two sets of
static slider beds
18 and the discharge station 30. The belt 20 is driven by means known in the
art.
The Belt Guide C.'hannel
The belt guide channel 26 is elongate and defines an upwardly-directed cavity
configured to accept a length of the crowned conveyor belt 20, such that the
upper crowned
surface extends upwardly therefrom.
The Discharge Station 30 Generally
Fig. 1 is a top plan view of the discharge station as used in conjunction with
the
conveyor and the slide beds. The discharge station 30 includes a package
tilting assembly 31
and a pair of withdrawal rollers 40, 41.
The tilting assembly 31 includes a pivoting fork assembly 32, a two-way
actuator
60 and a return spring 62.
The pivoting fork assembly 32 includes a fork member 33, a pair of parallel
support
rods 35, four idler roller stub shafts 36 and eight idler rollers 34. It may
be understood that
more than one tilting assembly may be used in conjunction with one.
The Withdrawal Rollers
The withdrawal rollers are positioned outside of the package tilting assembly
31.
These withdrawal rollers 40, 41 are also positioned at the inlets to the
discharge chutes 50, 51
and aid in the transfer of parcels 12 onto the discharge chutes S0, 51. - '
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
14
In the preferred embodiment, the withdrawal rollers 40, 41 are rotatably
mounted
along axes which are substantially horizontal and coparallel with the travel
axis of the crowned
conveyor belt 20. The withdrawal rollers 40, 41 can be driven to enhance the
transfer of
parcels 12 onto the discharge chutes 50, 51. As depicted in Fig. 2, the
withdrawal rollers 40,
41 do not make contact with the parcels 12 when the fork 33 is not pivoted to
a discharge
position. As depicted in Figs. 3 and 4, the withdrawal rollers 40, 41 do make
contact with the
parcels 12 when the fork 33 is pivoted to a discharge position, which results
in withdrawal of
the package by the withdrawal roller.
The Package Tilting Assembly
The package tilting assembly 31 includes a pivoting fork assembly 32, a two-
way
actuator 60 and a return spring 62.
Generally described, the package tilting assembly 31 is configured to tilt
packages
which are atop the crowned conveyor belt 20 such that the packages can engage
and be
withdrawn by the withdrawal rollers 40.
1 S The pivoting fork assembly 32 includes a fork member 33, a pair of
parallel support
rods 35, four idler roller stub shafts 36 and eight idler rollers 34.
The fork member 33 is generally W-shaped and is pivotably mounted at pivot 40
relative to the frame 11 of the apparatus 10 of the present invention about an
axis which is
generally parallel to the primary conveying axis. The fork member 33 includes
a pair of
upwardly-directed tines 37 and an elongate, downwardly--directed spring
mounting member
39.
Fixed at the end of each of the tines is one of two corresponding parallel
support rods
35, which have longitudinal axes which are substantially coparallel with the
primary conveying
axis. The ends of the tines attach to central portions of the parallel support
rods 35 as shown
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
in the Figures, such that the leading and trailing ends of the parallel
support rods 35 are
oriented respectively upstream and downstream relative to the conveying
direction.
Attached to the leading and trailing ends of the parallel support rods 35 are
the
5 shorter stub shafts 36, which are oriented such that their longitudinal axes
are parallel to each
other and perpendicular relative to the conveying axis. Two idler rollers 34
are rotatably
mounted to each stub shaft 36, one roller 34 at each end. The idler rollers 34
rotate about the
longitudinal axis of their associated stub shafts through pivots 41.
As discussed in detail later, the pivoting fork assembly 32 performs an
ejecting
10 function. For this reason, the pivoting fork assembly could be thought of
as having two
synchronized "ejection members", each of which includes one tine 37 of the
fork member, one
parallel support rod 35, two idler roller stub shafts 38 and four idler
rollers 34.
Also as discussed in detail later, when in their "neutral" locations as shown
in Fig.-
2, the idler rollers are positioned such that their uppermost surfaces are in
the same plane as
15 the top surfaces of the slider beds 18. However, when the pivoting fork
assembly 32 is indexed
to either side as shown in either of the configurations shown in Figs. 3 or 4,
some of the idler
rollers go above this plane and some go below the plane. The idler roller stub
shafts 36 are
pivotably attached relative to the parallel support rods 35, to allow the
above-the-plane rollers
34 to remain in contact with the underside of the packages 12. Again as shown
in Figs. 3 and
4, when the pivoting fork assembly 32 is indexed to either side, the stub
shafts pivot at 41
relative to the fork member 33 to accommodate the relative pivoting of the
package as it is
lifted.
As shown in Figs. 2, 3 and 4, a linear force actuator 60 has one end connected
to one
of the two tines 37 of the fork member 33 and its other end to the frame 11 of
the apparatus.
This is a double-acting actuator 60 and is configured to cause the pivoting of
the pivoting fork
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
1G
assembly 32 from its "neutral" position shown in Fig. 2 to either of its
"first" or "second"
pivoted positions shown respectively in Figs. 3 or 4. By expanding, the linear
force actuator
60 causes the pivoting fork assembly 32 to pivot from its "neutral" position
to its first pivoted
position shown in Fig. 3. By contracting, the linear force actuator 60 causes
the pivoting fork
assembly 32 to pivot from its "neutral" position to its second pivoted
position shown
in Fig. 4.
The actuator 60 is a dual-action pneumatic cylinder, although other motive
means
may be provided without departing from the spirit and scope of the present
invention.
As shown in Figs. 2, 3 and 4, the fork member 33 includes an elongate spring
mounting member 39 which extends downwardly from the pivot point location 40
of the fork
member 33. A tensile return spring 62 has one end attached to the lower end of
the spring
mounting member 39 and its other end attached to the frame 11 of the apparatus
10. Therefore
it may be seen that the pivoting fork assembly 32 is biased into its neutral
position by the
return spring 62, that seeks to maintain the top surfaces of the idler rollers
18 even with the
plane defined by the upper surfaces of the static slider beds 18, 19 (Figs. 1
and 2).
Operation
Operation is as follows. A package 12 is placed on the crowned conveyor belt
20
at an upstream location. The package is drawn towards the discharge station
30. At this point,
the parcels (which may also be referred to as "packages" 12) can take three
different routes
once they reach the discharge stations. They may be~ allowed to pass the
discharge station 30
and continue to be conveyed by the crowned conveyor belt 20, or they can be
selectively
discharged off of the crowned conveyor belt and into discharge chutes 50, S 1
located to either
side of the substantially straight path of the crowned conveyer belt 20. If
they are to be
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
17
allowed to pass the discharge station, the actuator 60 is simply not energized
and the package
slides off the first, "upstream" set of slider beds 18, 19 onto the idler
rollers 34 and then off
the idler rollers onto the second, "downstream" set of slider beds 18, 19.
However, if discharge is desired, the actuator 60 will have to be energized.
Actuation of the actuator to index the package tilting assembly 31 from its
neutral position in
Fig. 2 to its "left discharge" (as viewed) configuration in Fig. 4 is
discussed as an example,
although the "right discharge" would operate in a similar manner.
Referring now to Figs. 2 and 4, upon retraction of the actuator 60, the
pivoting fork
assembly 32 of the package tilting assembly 31 moves from its "neutral"
position shown in Fig.
2 to its pivoted positions shown in Fig. 4. By retracting, the linear force
actuator 60 causes
the left side idler rollers 34 to be moved downwardly and away from contact
with the bottom
of the package 12. Conversely, the right side rollers are urged upwardly and
slightly to the
left, lifting the right side of the package such that it tilts to its left and
eventually contacts the
left side powered withdrawal roller 40. It may be understood that the downward
movement
of the left side idler rollers 34 "clears the way" for such tilting, which
would not be possible
if the left side idler rollers 34 had not moved. This is an important feature
of the invention.
As noted above, the idler roller stub shafts 36 which support the idler
rollers are
pivotably attached at 41 relative to the parallel support rods 35, to allow
the above-the-plane
rollers 34 to remain in contact with the underside of the packages 12. Again
referencing Fig.
4, when the pivoting fork assembly 32 is indexed as shown, the stub shafts
pivot about pivot
41 relative to the fork member to accommodate the relative pivoting of the
package as it is
lifted.
Timing
The timing of the apparatus may 'be varied as
known in the art to provide suitable discharge characteristics. However, . '
CA 02468455 2004-06-16
1
for a belt speed of 500 FPM (feet per minute), it is believed
that a fork ejection cycle would be in the range of 1 second.
Construction
w The deformable belt portion 22 of the crowned
conveyor belt 20 is preferably made of soft urethane, which
slightly deforms during support of typical packages.
The lower structural belt portion 24 of the crowned
conveyor belt 20 is preferably made of conventional belt
material.
io The apparatus is configured to accept and manipulate
packages being 2 to 3 feet wide, and 2 to 5 feet long.
It should be understood that various alternates are
possible without departing from the spirit and scope of the
present invention. For example, instead of individual rollers,
15 belted rollers could be used.
Conclusion
While this invention has been described in specific detail
with reference to the disclosed embodiments, it will be
understood that many variations and modifications may be
2o effected within the spirit and scope of the invention as
described in the appended claims.
T