Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 1
PCT/JP2014/062969
SUPPORT LEG
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001]
The present invention relates to a support leg suitable for use when
assembling a large structure such as a fuselage of an aircraft or the like.
BACKGROUND ART
[0002]
When a large structure such as a fuselage of an aircraft is assembled. for
example, the structure is assembled using a jig installed on a floor surface.
At
this time, to ensure high-precision assembly, sometimes coordinates that serve
as absolute references are defined as reference positions on the floor
surface,
and assembly is performed in accordance with these reference positions.
Specifically, a body frame or the like assembled at a different location in
advance is first placed on the jig in accordance with the reference positions.
Then, the structure placed in accordance with the reference positions is
assembled by sequentially attaching various components and the like to this
body frame or the like.
Here, in this specification, the body frame or the like assembled at a
different location and placed on the jig is referred to as an object to be
supported.
[0003]
To place an object to be supported on a jig in accordance with reference
positions requires adjustment of the position of the object, and it is
extremely
difficult to subtly move the position of an object to be supported that is a
heavy
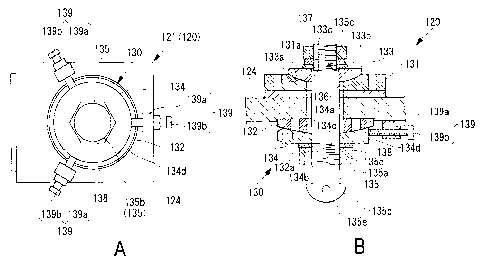
object. Hence, there is a bearing device that includes a support that moves
freely in the horizontal direction, as described in Patent Document 1, for
example.
CITATION LIST
Patent Literature
[0004]
Patent Literature 1: Japanese Unexamined Utility Model Application
Publication No. 2579974
SUMMARY OF INVENTION
Technical Problem
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 2
PCT/JP2014/062969
[0005]
Positioning an object to be supported with respect to a jig, however,
requires the provision of a positioning area on the object to be supported as
well. As illustrated in FIG. 12, for a fuselage of an aircraft, a temporary
support leg 2 is attached to a body frame 1, and this support leg 2 is
positioned
relative to a jig 3.
Here, a manufacturing error of several millimeters, for example, may
occur in the body frame 1 itself assembled at a different location.
Accordingly,
when the support leg 2 is attached to the body frame 1, an attachment position
and an angle of the support leg 2 need to be adjusted in accordance with the
manufacturing error.
To this end, a thin sheet-like shim plate is interposed or a filling material
4 such as resin is filled between an attachment surface 2a of the support leg
2
and the body frame 1.
[0006]
Nevertheless, adjusting the position and the angle of the support leg 2 of
course takes time and effort. In particular, when the filling material 4 such
as
resin is used, work must be stopped once the resin 4 has been filled between
the
attachment surface 2a of the support leg 2 and the body frame 1 until the
filling
material 4 cures and exhibits a required strength, resulting in work
stagnation.
[0007]
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and
an object of the present invention is to provide a support leg that can be
easily
and quickly attached to an object to be supported and efficiently positioned
relative to an assembly reference position of the object to be supported.
Solution to Problem
[0008]
To resolve the above-described problems, a support leg of the present
invention adopts the following means.
That is, an aspect of the present invention is a support leg for
positioning an object to be supported on a jig. The support leg includes a
support leg body detachably attached to the object to be supported, a leg
member supported so as to be pivotable with respect to the support leg body on
a spherical sliding surface, and a positioning portion provided on a lower end
portion of the leg member and positioned on the jig.
[0009]
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 3
PCT/JP2014/062969
According to such a support leg, when the support member is pivoted
with the support leg body attached to the object to be supported, the
positioning
portion provided on the lower end portion of the leg member is displaced. This
displacement makes it possible to absorb the manufacturing error of the object
to be supported and to position the positioning portion of the leg member on
the jig. Thus, even if the object to be supported is a large, heavy object, it
is
possible to position the object to be supported relative to the jig without
the
movement of the object to be supported itself, but simply with the
displacement
of the leg member.
Further, the support leg body may be directly provided to the object to
be supported without using a shim plate or a filling material such as resin,
making it possible to achieve easy and quick attachment.
[0010]
Further, this support leg may further include a support member that is
provided to the support leg body and includes the sliding surface, a sliding
member that faces the sliding surface, includes a spherical sliding surface
that
matches the sliding surface, and is slidable on the sliding surface, a first
through-hole formed through the support member, and a second through-hole
formed through the sliding member. In the support leg, the leg member is
provided so as to be fixed to the sliding member to extend downward through
the first through-hole and the second through-hole.
[0011]
The sliding member pivots on a spherical support surface of the support
member, causing the leg member to swing in an arc shape.
[0012]
Here, the above-described support leg may further include a fixing
member provided to an outer peripheral portion of the sliding member and
regulates the sliding of the sliding member by butting against the outer
peripheral portion of the sliding member.
[0013]
This fixing member is butted against the outer peripheral portion of the
sliding member, making it possible to regulate the sliding of the sliding
member and to fix the position of the sliding member, that is, the angle of
the
leg member.
[0014]
Further, the leg member may regulate the pivot angle by butting against
an inner peripheral surface of the first through-hole.
[0015]
CA 291253.6 2017-03-14
51258-100
4
The leg member can pivot within a range of clearance with the
inner peripheral surface of the first through-hole, thereby
making it possible to regulate excessive displacement of the
leg member.
[0015a]
According to an embodiment, there is provided a support leg for
positioning an object to be supported on a jig, comprising: a
support leg body detachably attached to the object to be
supported; a leg member supported so as to be pivotable with
respect to the support leg body on a first spherical sliding
surface, the leg member including a positioning portion which
is positioned on the jig, a support member provided on the
support leg body, the support member including the first
spherical sliding surface; a sliding member facing the first
spherical sliding surface, the sliding member including a
second spherical sliding surface that matches the first sliding
surface and being slidable on the first spherical sliding
surface; a first through-hole formed through the support
member; a second through-hole formed through the sliding
member; and a fixing member provided on an outer peripheral
portion of the sliding member, the fixing member regulating the
sliding of the sliding member by butting against the outer
peripheral portion of the sliding member, wherein the leg
member is provided so as to be fixed to the sliding member and
to extend downward through the first through-hole and the
second through-hole.
CA 2912516 2017-03-14
51258-100
4a
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0016]
According to the present invention, it is possible to easily
and quickly perform attachment to an object to be supported and
efficiently perform positioning with respect to an assembly
reference position of the object to be supported.
Brief Description of Drawings
[0017]
FIG. 1 is a side view illustrating a configuration when a
fuselage of an aircraft is assembled using a support leg of the
present invention.
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional elevational view illustrating a
configuration of a first jig.
FIG. 3 is a perspective developed view illustrating the
configuration of the first jig.
FIGS. 4A to 4D are diagrams illustrating a flow of operation
when an object to be supported is supported by the first jig.
FIG. 5 is a sectional elevational view illustrating a
configuration of a second jig.
FIG. 6 is a perspective developed view illustrating the
configuration of the second jig.
FIGS. 7A to 7D are diagrams illustrating a flow of operation
when the object to be supported is supported by the second jig.
FIG. 8 is a perspective view illustrating a configuration of a
C.4,1 291253.6 2017-03-14
=
,
51258-100
4b
support leg.
FIG. 9A is a side view, and FIG. 9B is a front view of the
support leg.
FIGS. 10A and 10B are diagrams illustrating a configuration of
a supported portion provided to the support leg, and FIG. 10A
is a view as seen from below of the support leg and FIG. 10A is
a cross-sectional view of the supported portion.
FIG. 11 is perspective view illustrating an example of the
first jig and an example of the second jig when a middle trunk
section is supported.
FIG. 12 is a schematic view illustrating an attachment
structure of a conventional support leg.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 5
PCT/P2014/062969
Description of Embodiments
[0018]
An embodiment of a support jig according to the present invention will
now be described with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 illustrates a configuration when a fuselage 100 of an aircraft is
assembled using a first jig (jig) 10 and a second jig (jig) 20 according to
this
embodiment.
As illustrated in this FIG. 1, the fuselage 100 of an aircraft is assembled
by sequentially assembling a main wing, a front trunk section, a rear trunk
section, and the like (not illustrated) of body sections formed by dividing
the
fuselage 100 in a longitudinal direction, using a middle trunk section (object
to
be supported) 110 that includes an attaching portion 111 of the main wing as
reference.
The first jig 10 and the second jig 20 support this middle trunk section
110 in accordance with a specific reference position determined in advance.
[0019]
As illustrated in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the first jig 10 includes a base 11, a
casing 12, a hydraulic cylinder 13, a tapered guide 14, a receiving portion
15, a
rolling element 16, and a support member 17.
The base 11 is formed in a plate shape and fixed on the floor surface.
The casing 12 is formed in, for example, a rectangular cylindrical shape
having an axis in the vertical direction, and a lower end portion thereof is
fixed
to a top surface of the base 11.
[0020]
The hydraulic cylinder 13 includes a rod 13b that is vertically retractable
with respect to a cylinder body 13a fixed to the base 11 within the casing 12,
and is adjustable in total length by feeding and discharging hydraulic oil to
and
from the cylinder body 13a by a hydraulic pump 18 that is provided outside.
Further, a flow rate adjustment valve 18v that adjusts a flow rate of the
hydraulic oil is provided between the cylinder body 13a and the hydraulic
pump 18, thereby making it possible to adjust an extending and retracting
speed
of the hydraulic cylinder 13 when the hydraulic pump 18 is operated.
[0021]
The tapered guide 14 is integrally provided on the casing 12, and an
outer peripheral surface thereof is a tapered surface (guide surface) 14a that
gradually decreases in diameter from the bottom to the top. This tapered
surface 14a, as described in detail below, guides the support member 17 to a
specific position in at least one direction within a horizontal plane by
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 6
PCT/JP2014/062969
interfering with the support member 17 when the hydraulic cylinder 13 causes
the support member 17 to descend. Further, a top of the tapered guide 14 is a
flat surface 14b.
A cylindrical straight surface 14d having the same diameter as that of a
lowermost portion of the tapered surface 14a is continuously formed on a lower
end of the tapered surface 14a.
A cylindrical portion 14e that has an outer diameter smaller than that of
the straight surface 14d and extends perpendicularly downward is formed
below the straight surface 14d. A step surface 14f between this cylindrical
portion 14e and the straight surface 14d is placed on a top surface 12a of the
casing 12, and the cylindrical portion 14e is inserted into the casing 12
through
a through-hole 12b formed through the top surface 12a.
Such a tapered guide 14 includes a through-hole 14c that extends
vertically through the tapered guide 14, at a center portion of the flat
surface
14b, allowing the rod 13b of the hydraulic cylinder 13 to protrude upward
through this through-hole 14c.
[0022]
The receiving portion 15 is formed of a disk-shaped plate portion 15a, a
peripheral wall 15b that is continually formed in a circumferential direction
on
an outer peripheral portion of the plate portion 15a and rises upward, and a
column portion 15c that is orthogonal to a surface of the plate portion 15a,
extends downward, and is inserted into the through-hole 14c of the tapered
guide 14. A lower end of the column portion 15c of this receiving portion 15
is
integrally attached to a tip of the rod 13b of the hydraulic cylinder 13, and
the
plate portion 15a is positioned within a horizontal plane.
[0023]
The rolling element 16 is a spherical element made of metal having a
diameter that is greater than a rising height of the peripheral wall 15b from
the
plate portion 15a. This rolling element 16 is, for example, formed of a high
carbon chromium bearing steel material, a stainless steel, a carbon tool
steel, or
the like. A plurality of the rolling element 16 are disposed on the inner side
of
the peripheral wall 15b of the receiving portion 15. When the number of
rolling elements 16 is too large, the rolling elements 16 bump into each other
on the receiving portion 15, causing an increase in a resistance to a sliding
movement of the support member 17 described below. When the number of
rolling elements 16 is too small, a load that acts on each individual rolling
element 16 increases, resulting in the possibility of damaging the plate
portion
15a or the like. Hence, these points are preferably taken into consideration
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 7
PCT/JP2014/062969
when determining the number of the rolling elements 16. For example, the
number of rolling elements 16 is preferably determined so as to ensure as
small
a load as possible and to prevent the plate portion 15a from being damaged by
measuring the load when the support member 17 is pulled in a direction along
the surface of the plate portion I5a and assessing the damage to the plate
portion 15a, with the rolling elements 16 placed on the plate portion 15a and
the support member 17 plced on top.
Further, the material of the rolling element 16 is preferably a material
having as high a hardness as possible and, among the materials described as
examples above, a carbon tool steel is preferably used.
[0024]
The support member 17 includes a plate-shaped plate portion 17a and a
cylindrical skirt portion 17b that extends downward from an outer peripheral
portion of the plate portion 17a. The plate portion 17a is formed with an
outer
diameter that is larger than that of the receiving portion 15. The skirt
portion
17b is formed with an inner diameter that is larger than an outer diameter of
the
straight surface 14d below the tapered surface 14a, and the outer diameter
that
is smaller than that of the top surface 12a of the casing 12. Accordingly, the
above-described tapered guide 14 is formed so that the diameter of the tapered
surface 14a comes closer and closer to the inner diameter of the skirt portion
17b from top to bottom.
Further, an inner peripheral edge portion of a lower end portion of the
skirt portion 17b is preferably rounded, or chamfered at an angle
corresponding
to the taper angle of the tapered surface 14a.
A convex portion 17c that protrudes upward is formed on a top surface
of the plate portion 17a, and a cone-shaped supporting concave portion 19
having a diameter that gradually decreases from top to bottom is formed in a
center portion of the convex portion 17c.
This support member 17 is placed on the rolling elements 16 that are on
the receiving portion 15.
[0025]
A fall prevention block 28 is mountable on both sides of the convex
portion 17c of the support member 17, with the supporting concave portion 19
therebetween. The fall prevention block 28 has an L-shaped cross section, and
is made of an upper surface plate portion 28a that extends along a top surface
of the convex portion 17c of the support member 17, and a side surface plate
portion 28b that is orthogonal to the upper surface plate portion 28a and
fixed
to a side surface of the convex portion 17c. This fall prevention block 28
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 8
PCT/JP2014/062969
prevents the support leg and the like of the object to be supported that is
inserted into the supporting concave portion 19 from coming out of the
supporting concave portion 19.
[0026]
As illustrated in FIGS. 4A to 4D, this first jig 10 causes the hydraulic
cylinder 13 to extend and retract with the help of the hydraulic pump 18,
thereby raising and lowering the support member 17. With the hydraulic
cylinder 13 extended and the skirt portion 17b of the support member 17 thus
raised a distance above the tapered guide 14, the rolling elements 16 roll on
the
receiving portion 15, allowing the support member 17 to move freely along the
plate portion 15a of the receiving portion 15, that is, within a horizontal
plane.
The amount of movement within the horizontal plane of the support member 17
is regulated by the interference between the skirt portion 17b of the support
member 17 and the peripheral wall 15b of the receiving portion 15.
Further, when the hydraulic cylinder 13 is retracted by the hydraulic
pump 18 with the support member 17 raised, the lower end portion of the skirt
portion 17b of the support member 17 interferes with the tapered surface 14a
of
the tapered guide 14, thereby guiding a center of the skirt portion 17b of the
support member 17 to a center of the tapered surface 14a and ultimately
placing
the skirt portion 17b on the top surface 12a of the casing 12.
Then, an ascending and descending speed of the support member 17 is
adjustable by adjusting an opening of the flow rate adjustment valve 18v.
[0027]
In the meantime, the second jig 20 has a basic configuration that is
similar to that of the above-described first jig 10, and components thereof
that
are common to those of the first jig 10 are denoted using the same symbols.
As illustrated in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, the second jig 20 includes the base
11, the casing 12, the hydraulic cylinder 13, a tapered block 24, the
receiving
portion 15, a guide member 22, the rolling element 16, and the support member
17.
[0028]
The guide member 22 includes a cylindrical portion 22a that is inserted
into the through-hole 12b formed through the top surface 12a of the casing 12,
a large diameter portion 22b that has an outer diameter larger than that of
the
cylindrical portion 22a and that is supported on the top surface 12a of the
casing 12, and a through-hole 22c that extends vertically through the guide
member 22 and that allows the column portion 15c of the receiving portion 15
to be inserted thereinto.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 9
PCl/JP2014/062969
The column portion 15c is inserted into this guide member 22, thereby
supporting the receiving portion 15 so that the receiving portion 15 can
ascend
and descend vertically.
[0029]
The tapered block 24 is made of block members (guide members) 24b,
24b that are positioned within a horizontal plane and disposed in parallel on
the
top surface 12a of the casing 12 on both sides of the through-hole 12b. On
each of the block members 24b, a slanted surface (guide surface) 25 is formed
on a side facing the other block member 24b, gradually increasing a space to
the other block member 24b from bottom to top. In other words, the tapered
block 24 includes a pair of slanted surfaces 25 that face each other with the
support member 17 therebetween in the plan view, and the space between the
pair of slanted surfaces 25 is formed so as to gradually come closer to the
outer
diameter of the skirt portion 17b from top to bottom.
[0030]
A plurality of rolling elements 16 are provided on the plate portion 15a
of the receiving portion 15 that is provided on the tip of the cylinder body
13a
of the hydraulic cylinder 13, and the support member 17 is placed on these
rolling elements 16.
[0031]
As illustrated in FIGS. 7A to 7D, this second jig 20 causes the hydraulic
cylinder 13 to extend and retract with the help of the hydraulic pump 18,
thereby raising and lowering the support member 17. With the hydraulic
cylinder 13 extended and the skirt portion 17b of the support member 17 thus
raised a distance above the tapered block 24, the rolling elements 16 roll on
the
receiving portion 15, allowing the support member 17 to move freely on the
plate portion 15a of the receiving portion 15, that is, within a horizontal
plane.
The amount of movement within the horizontal plane of the support member 17
is regulated by the interference between the skirt portion 17b of the support
member 17 and the peripheral wall 15b of the receiving portion 15.
Further, when the hydraulic cylinder 13 is retracted by the hydraulic
pump 18 with the support member 17 raised, the lower end portion of the skirt
portion 17b of the support member 17 interferes with the slanted surfaces 25,
25 of the tapered block 24, thereby guiding the center of the skirt portion
17b
of the support member 17 to the center of the block members 24b, 24b facing
each other and ultimately placing the skirt portion 17b on the top surface 12a
of
the casing 12.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
- 51258-100
=10
Then, the ascending and descending speed of the support member 17 is
adjustable by adjusting the opening of the flow rate adjustment valve 18v.
[0032]
To support the middle trunk section 110 using the first jig 10 and the
second jig 20 such as described above, a plurality of support legs (leg
portions)
120 that protrude downward are mounted at predetermined positions on the
bottom surface of the middle trunk section 110, as illustrated in FIG. 1,
FIGS.
4A to 4D, and FIGS. 7A to 7D.
As illustrated in FIG. 8, FIG. 9A, and FIG. 9B, each of the support legs
120 includes a support leg body 121, and a supported portion 130 provided on
the lower portion of the support leg body 121.
[0033]
The support leg body 121 is made of steel, and formed of a base block
122, and an attachment bracket 123 that is provided on the base block 122.
The base block 122 includes a baseplate 124, a rising wall 125 that rises
upward from three sides of an outer peripheral portion of the baseplate 124,
and
an upper plate 126 supported on the rising wall 125.
The attachment bracket 123 is formed of an attachment plate 127 that is
integrally provided to the upper plate 126, extends upward from the upper
plate
126, and is fixed to the middle trunk section 110, and a reinforcement plate
128
that is attached on a side opposite to the side facing the middle trunk
section
110 of the attachment plate 127 and positioned within a plane orthogonal to
the
attachment plate 127 and the upper plate 126. The attachment plate 127 has a
shape corresponding to a mounting area of the middle trunk section 110, and
can be fixed to a bolt hole (not illustrated) formed on the middle trunk
section
110 via a bolt (not illustrated). Further, the attachment plate 127 and the
middle trunk section 110 may be positioned by providing a positioning pin or
the like that is insertable into a pin hole (not illustrated) formed on the
middle
trunk section 110 to the attachment plate 127, and fitting the positioning pin
to
the pin hole. Here, a dimension and a shape of each component of the support
leg body 121, and a shape, an angle, and the like of the attachment plate 127
of
the plurality of support legs 120 are suitably set in accordance with an area
of
the middle trunk section 110 where each of the support legs 120 is to be
mounted, and there is no intention of specific limitation thereof.
It should be noted that while FIG. 8, FIG. 9A, and FIG. 9B illustrate a
= support leg 120A (refer to FIG. 1) installed on the first jig 10, a
support leg
120B installed on the second jig 20 has a shape different from that of the
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 11
PCT/JP2014/062969
support leg body 121, but has the same functional configuration as that of the
support leg 120A.
[0034]
As illustrated in FIG. 10A and FIG. 10B, the supported portion 130 is
provided on the baseplate 124 of the support leg body 121.
This supported portion 130 mainly includes an upper sliding base
(support member) 131, a lower sliding base (support member) 132, an upper
sliding member (sliding member) 133, a lower sliding member (sliding
member) 134, and a leg member 135.
[0035]
The upper sliding base 131 is integrally welded on the top surface of the
baseplate 124. A downwardly concave support surface (sliding surface) 131a
formed at a predetermined curvature is formed on a top surface of the upper
sliding base 131.
The lower sliding base 132 is integrally welded on the bottom surface of
the baseplate 124, facing the upper sliding base 131 with the baseplate 124
therebetween. A downwardly convex support surface (sliding surface) 132a
formed at a curvature concentric with the support surface 131a is formed on a
bottom surface of the lower sliding base 132.
Then, a through-hole (first through-hole) 136 having a center axis that
extends through a center of the concave support surface 131a and the convex
support surface 132a is formed through the upper sliding base 131, the
baseplate 124, and the lower sliding base 132.
[0036]
The upper sliding member 133 is circular in the plan view, with a bottom
surface thereof established as a downwardly convex sliding surface (sliding
surface) 133a formed at the same curvature as that of the concave support
surface 131a of the upper sliding base 131, and a top surface thereof
established as a flat surface 133b. The upper sliding member 133 is placed on
the upper sliding base 131 with the convex sliding surface 133a butted against
the concave support surface 131a of the upper sliding base 131. Accordingly,
the convex sliding surface 133a and the concave support surface 131a slide,
thereby allowing the upper sliding member 133 to slide along the concave
support surface 131a.
Further, the lower sliding member 134 is circular in the plan view, with
a top surface thereof established as a downwardly concave sliding surface
(sliding surface) 134a formed at substantially the same curvature as that of
the
convex support surface 132a of the lower sliding base 132, and a bottom
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 12
PCT/JP2014/062969
surface thereof established as a flat surface 134b. The lower sliding member
134 is disposed beneath the lower sliding base 132 with the concave sliding
surface 134a butted against the convex support surface 132a of the upper
sliding base 131. Accordingly, the concave sliding surface 134a and the convex
support surface 132a slide, thereby allowing the lower sliding member 134 to
slide along the convex support surface 132a.
Through-holes (second through-holes) 133c, 134c having an inner
diameter smaller than that of the through-hole 136 are formed through the
upper sliding member 133 and the lower sliding member 134.
[0037]
The leg member 135 includes a shaft portion 135a having a circular
cross-section, and a head portion 135b integrally formed with a lower end
portion of the shaft portion 135a.
The shaft portion 135a has an outer diameter that allows the shaft
portion 135a to be inserted into the through-holes 133a, 134a of the upper
sliding member 133 and the lower sliding member 134. Thread grooves 135c,
135d are respectively formed at least on an upper portion and a lower portion
of this shaft portion 135a.
The head portion 135b has a spherical portion (positioning portion) 135e
that has an outer diameter larger than that of the shaft portion 135a and that
is
formed in a downwardly convex hemispherical shape on the bottom surface of
the shaft portion 135a.
With a lower fixing screw 138 mounted on the thread groove 135d of the
shaft portion 135a in advance, the shaft portion 135a of this leg member 135
is
passed through the through-hole 134c of the lower sliding member 134, the
through-hole 136, and the through-hole 133c of the upper sliding member 133
from below, causing the section where the upper thread groove 135c is formed
to protrude above the upper sliding member 133. In this state, an upper fixing
screw 137 is mounted on the thread groove 135c. Then, the upper fixing screw
137 and the lower fixing screw 138 are tightened, allowing the upper sliding
member 133, the upper sliding base 131 and the lower sliding base 132 above
and below the baseplate 124, and the lower sliding member 134 to be fastened
between the upper fixing screw 137 and the lower fixing screw 138.
[0038]
Further, three fixing members 139 spaced apart in a circumferential
direction are provided on an outer peripheral side of the lower sliding base
132
and the lower sliding member 134, on the bottom surface of the baseplate 124.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
= a
WO 2014/203660 Al 13
PCT/JP2014/062969
=
Each of the fixing members 139 includes a fixing block 139a fixed to
the bottom surface of the baseplate 124, and a fixing bolt 139b that is
screwed
into a screw hole (not illustrated) formed in this fixing block 139a and a tip
of
which butts against an outer peripheral surface 134d of the lower sliding
member 134. The fixing bolt 139b can be moved back and forth along a radial
direction of the lower sliding member 134 with respect to the fixing block
139a
when rotated about an axis of the fixing bolt 139b by a tool or the like.
When the tip of each of the fixing bolts 139b of the three fixing
members 139 is butted against the outer peripheral surface 134d of the lower
sliding member 134, the lower sliding member 134 is fixed. Then, the angle of
inclination of the leg member 135 that extends through the lower sliding
member 134 as well as that of the upper sliding member 133 through which the
leg member 135 extends is fixed along with that of the lower sliding member
134.
Then, the upper fixing screw 137 and the lower fixing screw 138 are
slightly loosened, the fixing bolts 139b of the three fixing members 139 are
loosened and the tip portions thereof are separated from the outer peripheral
surface 134d of the lower sliding member 134, causing the lower sliding
member 134 to freely slide along the convex support surface 132a. When the
lower sliding member 134 slides, the lower sliding member 134, the leg
member 135, and the upper sliding member 133 slide along the concave support
surface 131a and the convex support surface 132a, that is, the leg member 135
swings, changing the angle of inclination of the leg member 135. At this time,
the angle of inclination of the leg member 135 is regulated by the leg member
135 interfering with an inner peripheral surface of the through-hole 136.
[0039]
The following describes the assembly of the fuselage 100 of an aircraft.
As illustrated in FIG. 1 and FIG. 11, a pair of the first jigs 10, 10 and a
pair of the second jigs 20, 20 are fixed in predetermined positions in an
assembly space where the fuselage 100 of an aircraft is to be assembled. The
installation spacing and positional relationship between the first jigs 10, 10
and
the second jigs 20, 20 match the designed installation spacing and positional
relationship of the support leg 120 provided on the middle trunk section 110.
It should be noted that the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20, 20 are
disposed so as to be spaced apart along a longitudinal direction S of the
fuselage 100. Then, the pair of the first jigs 10, 10 and the pair of the
second
jigs 20, 20 are arranged facing each other with the center of the fuselage 100
therebetween, along a width direction W of the fuselage 100. Further, the
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
=
WO 2014/203660 Al 14
PCT/JP2014/062969
=
block members 24b, 24b of each of the second jigs 20 are provided so as to
extend in the width direction W of the fuselage 100 and to face each other in
the longitudinal direction S of the fuselage 100.
[0040]
The middle trunk section 110 pre-assembled at a different location is
loaded onto a moving truck or suspended by a crane so as to be brought into
the
assembly space.
When the moving truck or the like is used, the middle trunk section 110
supported on the moving truck is inserted between the first jigs 10, 10 and
the
second jigs 20, 20. At this time, in the moving truck, the middle trunk
section
110 is supported in a position higher than the first jigs 10, 10 and the
second
jigs 20, 20.
When the crane is used, the middle trunk section 110 is lifted and
positioned perpendicularly above the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20,
20.
[0041]
Here, the above-described support leg 120 is mounted in a
predetermined position on the middle trunk section 110. The attachment plate
127 of the support leg 120 is made to face the predetermined position of the
middle trunk section 110 and the two are fastened to each other by a bolt and
the like. At this time, if there is an assembly error in the middle trunk
section
110, the attachment position and the angle of the support leg 120 may be
affected, causing the position of the spherical portion 135e of the leg member
135 to deviate from the designed position.
Additionally, the upper fixing screw 137 is loosened and the tip of the
fixing bolt 139b of each of the fixing members 139 is separated from the outer
peripheral surface 134d of the lower sliding member 134 on the support leg
120.
Accordingly, the leg member 135 of the support leg 120 can slide and swing
along the concave support surface 131a and the convex support surface 132a,
and the position of the spherical portion 135e that is the tip portion of the
leg
member 135 can be changed.
[0042]
As illustrated in FIG. 4A and FIG. 7A, with the support leg 120 of the
middle trunk section 110 positioned perpendicularly above the first jigs 10,
10
and the second jigs 20, 20, the hydraulic cylinder 13 of each of the first
jigs 10,
and the second jigs 20, 20 is extended by the hydraulic pump 18, thereby
raising the support member 17.
Then, as illustrated in FIG. 4B and FIG. 7B, the spherical portion 135e
of the support leg 120 of the middle trunk section 110 is inserted within the
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 15
PCT/JP2014/062969
=
supporting concave portion 19 of the support member 17. The support member
17 moves freely within a horizontal plane by the rolling of the rolling
elements
16 on the receiving portion 15 and thus, when the spherical portion 135e is
inserted within the supporting concave portion 19 while the support member 17
is raised, the spherical surface of the spherical portion 135e follows the
supporting concave portion 19, thereby automatically aligning a center of the
spherical portion 135e with a center of the supporting concave portion 19. At
this time, when the spherical portion 135e and the supporting concave portion
19 are deviated from each other in the horizontal direction just before the
spherical portion 135e is inserted into the supporting concave portion 19, a
worker can push and slide the support member 17 with his or her hands in the
horizontal direction, and align the spherical portion 135e with the supporting
concave portion 19. Further, on the support leg 120 side as well, the angle of
the leg member 135 changes when the spherical portion 135e is inserted into
the supporting concave portion 19, allowing the alignment to be made.
[0043]
Once the spherical portions 135e are inserted into the supporting
concave portion 19 for all of the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20,
20, the
moving truck and crane are withdrawn.
[0044]
Next, the hydraulic pump 18 is operated to retract the hydraulic
cylinders 13 of the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20, 20. Then, the
support members 17 of the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20, 20
descend.
At this time, the descending speed of the support members 17 is preferably
adjusted by the adjustment of the opening of the flow rate adjustment valves
18v so that no impact is applied to the middle trunk section 110. Furthermore,
the descending speed of the support members 17 is preferably adjusted by the
adjustment of the opening of each of the flow rate adjustment valves 18v so
that the support members 17 of the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20,
20
descend simultaneously.
In the first jig 10, when the support member 17 descends, the lower end
portion of the skirt portion 17b interferes with the tapered surface 14a of
the
tapered guide 14, thereby guiding the center of the skirt portion 17b of the
support member 17 to the center of the tapered surface 14a, as illustrated in
FIGS. 4C and 4D. Then, the skirt portion 17b of the support member 17 is
ultimately placed on the top surface 12a of the casing 12 and, in this state,
the
center of the support member 17 is aligned with the center of the tapered
guide
14.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 16
PCT/JP2014/062969
Further, in the second jig 20, when the support member 17 descends, the
lower end portion of the skirt portion 17b interferes with the slanted
surfaces
25, 25 of the tapered block 24, thereby guiding the center of the skirt
portion
17b of the support member 17 to the center of the block members 24b, 24b
facing each other, as illustrated in FIGS. 7C and 7D. Then, the skirt portion
17b of the support member 17 is ultimately placed on the top surface 12a of
the
casing 12 and, in this state, the center of the support member 17 is aligned
with
the center of the block members 24b, 24b facing each other.
[0045]
Thus, the supporting concave portion 19 of the support member 17 of
each of the first jigs 10, 10 and the second jigs 20, 20 is guided to and
positioned in a specific position.
At this time, the spherical portion 135e fitted within the supporting
concave portion 19 moves following the support member 17 that descends
along the slanted surfaces 25, 25 of the tapered block 24 by the changing of
the
angle of the leg member 135. Accordingly, even if there is a manufacturing
error of the middle trunk section 110, the spherical portion 135e is supported
while kept within the supporting concave portion 19 by the swing movement of
the leg member 135.
Further, when the middle trunk section 110 deviates in the horizontal
direction from the predetermined reference position with the support member
17 lowered to the lower end, it is also possible to finely adjust the position
of
the middle trunk section 110 by adjusting the screwing amount of the fixing
bolts 139b of the fixing members 139 on the outer peripheral side of the lower
sliding member 134.
[0046]
Thus, the middle trunk section 110 is positioned in the longitudinal
direction S and the horizontal direction W of the fuselage 100 by each jig of
the
pair of the first jigs 10, 10, and positioned in the longitudinal direction S
of the
fuselage 100 by each jig of the pair of the second jigs 20, 20.
In this state, the tip portion of the fixing bolt 139b of each of the fixing
members 139 is butted against the lower sliding member 134 to fix the
position,
and the upper fixing screw 137 and the lower fixing screw 138 are tightened,
thereby fixing the angle of the leg member 135.
It should be noted that the middle trunk section 110 can also be
supported at a location other than the above-described first jigs 10, 10 and
second jigs 20, 20 and, in such a case, only a height needs to be aligned with
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
A
WO 2014/203660 Al 17
PCT/JP2014/062969
the middle trunk section 110 at the location other than the first jigs 10, 10,
and
the second jigs 20, 20.
[0047]
Thereafter, the fuselage 100 is assembled by the attachment of
predetermined components to the middle trunk section 110 thus positioned,
such as the attachment of a main wing, and the attachment of a front trunk
section and a rear trunk section that constitute the fuselage 100 to the front
and
back of the middle trunk section 110.
[0048]
As described above, the leg member 135 of the support leg 120 mounted
to the middle trunk section 110 is capable of swinging, making it possible to
efficiently position the middle trunk section 110 with respect to the assembly
reference position with high precision. At this time, the support leg 120 can
be
easily and quickly mounted to the middle trunk section 110 without adjusting
the position using a shim plate, resin, or the like.
[0049]
Further, the middle trunk section 110 can be positioned in the
longitudinal direction S and the horizontal direction W of the fuselage 100 by
the first jig 10 by simply lowering the support member 17 after the middle
trunk section 110 is placed, and positioned in the longitudinal direction S of
the
fuselage 100 by the second jig 20. Accordingly, the middle trunk section 110
is
easily and reliably positioned, making it possible to perform work
efficiently.
Moreover, in the first jig 10 and the second jig 20, the flow rate of the
hydraulic oil pushed out by the hydraulic cylinder 13 is controlled by
adjusting
the opening of the flow rate adjustment valve 18v, making it possible to
prevent
the middle trunk section 110 from being impacted when the support member 17
descends after the middle trunk section 110 is placed.
[0050]
It should be noted that, in the above embodiment, the configuration of
the supported portion 130 may be changed to a suitable configuration other
than that described above as long as the leg member 135 is capable of
swinging.
Further, the configuration of the support leg body 121 is not limited, and
may be changed to a suitable configuration corresponding to the object to be
supported that is to be mounted.
Furthermore, while the middle trunk section 110 is placed on the first jig
and the second jig 20, the configuration of the jigs that support the middle
trunk section 110 may be replaced with any other configuration.
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
A
WO 2014/203660 Al 18
PCT/JP2014/062969
=
Reference Signs List
[0051]
First jig (jig)
11 Base
12 Casing
13 Hydraulic cylinder
14-Tapered guide
14a Tapered surface
Receiving portion
15a Plate portion
15b Peripheral wall
16 Rolling element
17 Support member
18 Hydraulic pump
18v Flow rate adjustment valve
19 Supporting concave portion
Second jig (jig)
22 Guide member
24 Tapered block
24b Block member
Slanted surface
28 Fall prevention block
100 Fuselage
110 Middle trunk section (object to be supported)
111 Attaching portion
120, 120A, 120B Support leg
121 Support leg body
122 Base block
123 Attachment bracket
124 Baseplate
125 Rising wall
126 Upper plate
127 Attachment plate
128 Reinforcement plate
130 Supported portion
131 Upper sliding base (support member)
131a Concave support surface (sliding surface)
132 Lower sliding base (support member)
CA 02912516 2015-11-13
WO 2014/203660 Al 19
PCT/JP2014/062969
132a Convex support surface (sliding surface)
133 Upper sliding member (sliding member)
133a Convex sliding surface (sliding surface)
133c Through-hole (second through-hole)
134 Lower sliding member (sliding member)
134a Concave sliding surface (sliding surface)
134c Through-hole (second through-hole)
134d Outer peripheral surface
135 Leg member
135e Spherical portion (positioning portion)
136 Through-hole (first through-hole)
137 Upper fixing screw
138 Lower fixing screw
139 Fixing member
139a Fixing block
139b Fixing bolt