Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
,
,
H8324416CA
Sliding sleeve, sliding sleeve connection and method for producing a sliding
sleeve
connection
The present invention relates to a sliding sleeve for pushing or sliding
axially onto an
expanded end of an all-plastic pipe or of a plastic composite pipe, into which
or pushed a
support body of a connecting element, provided with circumferential external
ribs is inserted,
wherein the sliding sleeve is produced from an elastically deformable
polymeric material.
Furthermore, the present invention also relates to a sliding-sleeve connection
between an
end of an all-plastic pipe or a plastic composite pipe and a connecting
element, comprising
the sliding sleeve according to the invention, as well as to a method for
producing such a
sliding sleeve connection.
Pipe connections of the above type are known from prior art. Besides at least
one end of an
all-plastic pipe or a plastic composite pipe, such a pipe connection comprises
a connecting
element having at least one support body, which supporting body, in turn
comprises a
supporting body provided with circumferential external ribs, onto which the
end of the pipe is
sild. Fixing the end of the pipe to the connecting element is effected by
means of a fixing
sleeve arranged above the end of the pipe, through which the end of the pipe
is pressed on
the outer contour of the support body provided with circumferential external
ribs. Depending
on the type of application of the fixing sleeve used, different types of
application techniques
are distinguished. As examples of such connecting techniques are stated
shrinkable sleeve
systems, in which a fixing sleeve with shape memory is expanded together with
the end of
the pipe, the support body is then inserted into the expanded end of the pipe
and the
shrinkable sleeve presses the end of the pipe to the outer contour of the
supporting body by
means of its shrinkage due to the memory effect, as well as axial pressing
systems, in which
the support body is inserted into an expanded end of a pipe and subsequently,
a sliding
1
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
sleeve externally attached to the end of the pipe is pushed in axial direction
onto the pipe
end with the inserted support body of the connecting element. Such an axial
pressing system
with a sliding sleeve is described in DE 101 30 858 Al, for example. The
sliding sleeve
described therein is made of an elastically deformable polymeric material. In
order to achieve
reliable sealing with axial pressing systems of said type, a smaller internal
diameter of the
sliding sleeve relative to the external diameter of the expanded end of the
pipe is required.
However, the smaller the internal diameter of the sliding sleeve relative to
the external
diameter of the expanded end of the pipe, the greater the force to be exerted
for axially
sliding the sliding sleeve onto the expanded end of the pipe with the support
body inserted.
In order to decrease said force to be exerted, a lubricating lacquer is
applied to the internal
surface of the sliding sleeve during the production thereof in practice. This
leads to an
increased method-related effort in the production of the sliding sleeve.
Furthermore,
particularly if a lubricating lacquer is used, particular in the event of
thermal cycling, there
may occur a relative movement of the sliding sleeve on the expanded end of the
pipe,
possibly resulting in that the sealing of the pipe connection is no longer
ensured.
It is therefore the object of the present invention to provide a sliding
sleeve made of an
elastically deformable polymeric material, that overcomes the disadvantages of
prior art. In
particular, the sliding sleeve according to the invention, at a given internal
diameter, is to be
slid onto the expanded end of the pipe with the supporting body inserted by
means of axial
pressing technique with a reduced pressing force when producing the pipe
connection.
Furthermore, the sliding sleeve according to the invention shall have a
reduced tendency for
relative movement of the sliding sleeve on the expanded end of the pipe in the
event of
thermal cycling or such relative movement is to be completely prevented in a
simple manner,
and easy to produce.
According to the present invention the above and other objects are achieved by
means of a
sliding sleeve having the features of claim 1, by means of a sliding-sleeve
connection having
2
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
the features of claim 7, or respectively, by means of a method having the
features of claim 9.
Preferred embodiments of the sliding sleeve, the sliding-sleeve-connection and
the method
according to the invention are described in the respective dependent claims.
According to the present invention, it has been found that an increased
roughness or
irregularity on the internal surface of the sliding sleeve compared to the
smooth internal
surfaces for axial pressing systems so far known from prior art leads to a
reduction of the
force which has to be exerted on the expanded end of the pipe with the support
body
inserted therein. Alternatively, said effect of the reduced force effort when
axially sliding on
the sliding sleeve could as well be caused by unevennesses or irregularities
on the internal
surface, said irregularities, in turn, having a such macroscopic size, that
they can not be
determined by means of the conventional measuring methods for determining the
surface
roughness and thus cannot be characterized by the average roughness value.
These
irregularities are herein described as "macroscopic irregularities".
Accordingly, it is the object of the present invention to provide a sliding
sleeve for axially
sliding onto a widened or expanded end of an all-plastic pipe or a plastic
composite pipe into
which a support body of a connecting element provided with circumferential
external ribs is
inserted, wherein the sliding sleeve is produced from of an elastically
deformable polymeric
material, wherein the internal surface of the sliding sleeve has such a
roughness or
irregularity that the force to be exerted to press-fit the sliding sleeve onto
the expanded end
of the all-plastic pipe or of the plastic composite pipe is reduced compared
with that needed
for a sliding sleeve with a smooth internal surface. The present invention
further relates to a
sliding sleeve connection between an end of an all-plastic pipe or of a
plastic composite pipe
and a connecting element, the sliding sleeve connection comprising a widened
end of an all-
plastic pipe or of a plastic composite pipe, a connecting element having at
least one support
body provided with circumferential external ribs, onto which the expanded end
of the all-
plastic pipe or the plastic-composite pipe is slid in the final sliding sleeve
connection; and a
3
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
,
H8324416CA
sliding sleeve according to the invention, which is axially slid onto the
expanded end. Finally,
the present invention also relates to a method for producing a connection
between an end of
an all-plastic pipe or a plastic composite pipe and a connecting element
having at least one
support body provided with circumferential external ribs, comprising the
following steps of
expanding the end of the all-plastic pipe or the plastic composite pipe,
inserting the support
body of the connecting element into the expanded end of the all-plastic pipe
or plastic
composite pipe and pressing a sliding sleeve made of an elastically-deformable
polymeric
material in axial direction onto the expanded end having the support body
inserted therein,
wherein the internal surface of the sliding sleeve has such a roughness or
irregularity that the
force to be exerted to press-fit the sliding sleeve onto the expanded end of
the all-plastic pipe
or of the plastic composite pipe is reduced compared with that needed for a
sliding sleeve
with a smooth internal surface.
In view of the sliding sleeve according to the invention, it is preferred, if
the roughness or
irregularity of the internal surface of the sliding sleeve is generated by a
plurality of
macroscopic irregularities, the depth of which does not exceed half of the
average wall
thickness of the sliding sleeve.
It may as well be advantageous if the internal surface of the sliding sleeve
has grooves in a
circumferential direction, in longitudinal direction, grooves extending
helically and/or a
combination of the types of grooves mentioned. Such configurations of the
internal surface
have proved to be of particular advantage and are easy to produce. Further
preferred
configurations of the internal surface of the sliding sleeve according to the
invention are an
irregular surface, e.g. produced by filling materials having according
particulate diameters,
diamond patterns, negative shapes of an eroded structure and the like. These
configurations
can preferably be produced in that the quality of the internal surface of the
sliding sleeve
according to the invention has been produced in the course of an extrusion of
a pipe, from
which the sliding sleeve has been obtained by means of cutting the extruded
pipe. As an
4
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
alternative, the respective pipe can be extruded and subsequently the quality
of the internal
surface can be produced afterwards, for example by a suitable brush treatment
and/or
sandpaper treatmentõ and the sliding sleeve according to the invwention can be
obtained by
cutting the pipe to length. Finally, the sliding sleeves can be cut off of the
extruded pipe and
the quality of the internal surface can be produced afterwards. Also cold
forming methods
such as knurling and punching, hot stamping as well as injection molding by
means of a
molding tool having the desired internal surface as a negative form, or the
later production of
the internal surface in injection-molded sleeves, are possible for producing
the surface
roughness of the internal surface of the sliding sleeve.
Advantageously, crosslinked polyethylene (in particular PE-Xa, PE-Xb or PE-Xc)
is used for
the production of the sliding sleeve according to the invention.
Regarding the sliding-sleeve connection according to the invention, it may be
advantageous
if the sliding sleeve encloses the expanded end of the all-plastic pipe or of
the plastic
composite pipe in an elastically expanded manner. This way, sealing of the
sliding sleeve
connection according to the invention is further improved.
According to the present invention, preferred materials for the connecting
element are
polymeric materials such as polypropylene and glass fiber-reinforced
polypropylene,
polyam ides and glass-fiber-reinforced polyam ides, temperature-resistant
thermoplastics such
as polyphenylene sulphone (PPSU), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyether
sulphone
(PES), polysulfone (PSU), polyphenylsulphide (PPS) and polyester carbonate
(PESC) as
well as copolymers and blends of said polymers, wherein the mentioned
polymeric materials
can be implemented fiber-reinforced, in particular glass fiber-reinforced, as
well as metallic
materials such as brass, in particular Ecobrass , red brass and stainless
steel.
Temperature-resistant thermoplastics such as in particular polyphenylene
sulphone and
polyvinylidene fluoride are particularly preferred for the production of the
connecting element
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
used according to the invention. The term "temperature-resistant
thermoplastics" as used
herein relates to the heat resistance and thermal stability of said group of
materials and
designates thermoplastic polymeric materials having a thermal stability at
temperatures of at
least 150 C. The upper limit of the temperature, in which a heat resistant
plastic can be used,
depends of the material used, whereas the implementability of such polymeric
materials ends
with a temperature of 260 C maximum.
According to the present invention, preferably all-plastic pipes are used as
plastic pipes,
preferably made of polyethylene (PE, in particular PE 100 and PE-RT),
crosslinked
polyethylene (PE-X, in particular PE-Xa, PE-Xb or PE-Xc) polypropylene (in
particular
statistic polypropylene PP-R) and polybutylene (PB) as well as plastic-
composite pipes,
preferably with layers of polyethylene (PE, in particular PE 100 and PE-RT)
crosslinked
polyethylene (PE-Xa, PE-Xb or PE-Xc) polypropylene (in particular statistic
polypropylene
PP-R), and/or polybutylene (PB) are used. In addition, a layer of ethylene-
vinyl alcohol
copolymer (EVOH) can be present as an oxygen barrier layer. According to the
present
invention, metal-composite pipes (MCP pipes) preferably include layers of
polyethylene (PE,
in particular PE 100 and PE-RRT), crosslinked polyethylene (PE-X, in
particular PE-Xa, PE,
Xb or PE-Xc), polypropylene (in particular statistic polypropylene PP-R)
and/or Polybutylene
(PB) and at least one layer of metals, preferably aluminum. Layers of adhesive
agents can
be introduced between individual layers in plastic-composite pipes and MPC
pipes.
According to the present invention, all pipes of a pipe connection can be
structured
identically or one or more of the pipes may have different pipe structures.
Furthermore, the
pipes according to the present invention may be fiber-reinforced as well. The
fiber-
reinforcement may be provided in individual pipes or all pipes, over the
entire pipe length or
in sections only. Regarding the plastic pipe or the metal-plastic composite
pipe of the pipe
connection according to the invention, it is particularly preferred that at
least one layer of the
respective pipe includes crosslinked polyethylene (in particular PE-Xa, PE-Xb,
or PE-Xc).
6
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
Crosslinked polyethylene is a material having a shape memory, respectively a
so-called
"memory effect". Such memory effect means that the crosslinked polyethylene
tries to return
to its original shape after any change in its external geometry. During pipe
expansion, this
causes any pipe including PE-X to try to return to the original internal pipe
diameter before
the expansion. As a support body of a connecting element is inserted in the
expanded end of
the pipe after expansion, the memory effect when using a pipe including at
least one layer of
cross-linked polyethylene leads to a particularly high tightness of the
sliding sleeve
connection according to the invention.
The connecting element of the sliding sleeve connection according to the
invention can be a
threaded moulded part or a threadless moulded part, i.e. a connecting element
with no
thread. This in particular includes connecting pieces, connection brackets,
multiple
distributors, t-pieces, wall t-pieces, wall brackets, system transitions,
transition pieces,
angled transition pieces, none of which have a thread. Accordingly, the term
"threaded
moulded part" refers to a connecting element having at least one threaded
moulded part.
This in particular includes connecting pieces, connection brackets, multiple
distributors, t-
pieces, wall t-pieces, wall brackets, system transitions, transition pieces
and angled transition
pieces, all of which have at least one internal and/or external thread.
The sliding sleeve connection according to the present invention is in
particular used in
piping and connection systems in drinking water installation, in sprinkler
systems, in radiator
connections, in concrete core temperature controls as well as in surface
heating or surface
cooling systems.
The features deemed to be advantageous related to the sliding sleeve according
to the
invention as well apply accordingly for the sliding sleeve connection
according to the
invention and the method according to the invention.
Description of preferred embodiments
7
. CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
In the following, the invention is to be described in detail with reference to
the embodiments
illustrated in the figures. The figures show in:
Fig.1 an illustration of a longitudinal section of a sliding sleeve according
to an embodiment
of the present invention;
Fig. 2 an illustration of a longitudinal section of a sliding-sleeve
connection according to an
embodiment of the present invention, in which an expanded end of a plastic
pipe is slid onto
a support body of the connecting element and is fixed by means of a sliding
sleeve according
to the invention; and
Fig. 3 a perspective view of a sliding sleeve according to another embodiment
of the present
invention.
Fig. 1 shows an illustration of a longitudinal section of an embodiment of a
sliding-sleeve 1
according to the invention. The sliding-sleeve 1 is made of crosslinked
polyethylene (PEXa).
The internal surface 1 is irregular-structured and has an average roughness
value Ra of 5
pm. As used herein, the term "average roughness value" or "average roughness"
(indicated
by the symbol "Ra ") of a surface means the arithmetic average of the
variation on the mount
of all measurement points on the surface from the central line of the surface.
The average
roughness depth Rz of the sliding-sleeve 1 according to the invention which is
illustrated in
Fig. 1 is 40 pm. As used herein, the term "averages roughness depth"
(indicated by the
symbol "Rz") of a surface the roughness depth in accordance with DIN EN ISO
4287/4288.
The sliding sleeve 1 according to the invention illustrated in Fig. 1 has been
produced in that
a respective pipe made of crosslinked polyethylene had been extruded, the pipe
has been
cut to obtain pieces and the irregular structure of the internal surface 2 of
a piece has been
produced subsequently by implementation of a steel brush, thereby obtaining
the sliding
sleeve 1 according to the invention.
8
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
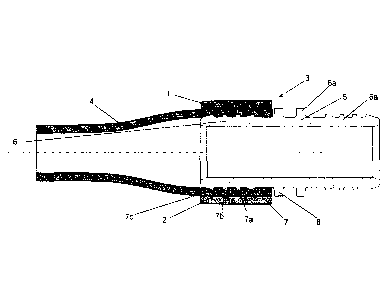
Fig. 2 is an illustration of a longitudinal section of an embodiment of a
sliding sleeve
connection 3 according to the invention with a sliding sleeve 1 according to
the invention.
The sliding sleeve connection 3 according to the invention in this case
comrises an
expanded end of a plastic pipe 4 as well as a connecting element 5.
The connecting element 5 is a connecting piece having two support bodies 6,
6a, wherein an
end of a plastic pipe 4 is only slid onto the support body 6. Each of the
support bodies 6, 6a
here comprises four circumferential external ribs 7, 7a, 7b, 7c, wherein these
four
circumferential ribs are arranged in axial direction starting from the end of
the connecting
element 4 in such a way, that a rib 7c having a sawtooth-like cross-section is
follwoed by two
subsequent external ribs 7b, 7a having a rectangular cross section and that
another external
rib 7 having a sawtooth-like cross-section subsequently follows. Furthermore,
the connecting
element 5 has a circumferential collar 8, 8a for every support body 6, 6a,
which closes off the
respective support body 6, 6a.
In the illustrated embodiment, the connecting element 5 is a component made of
polyphenylene sulphone (PPSU). Also usable in alternative embodiments of the
pipe
connection 3 according to the invention are connecting element 5 made of
polypropylene and
glass fiber reinforced polypropylene, polyamides and glass fiber reinforced
polyamides,
polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyether sulfone (PES), polysulfone (PSU),
polyphenyl
sulphide (PPS), polyester carbonate (PESC), as well as copolymers and blends
of said
polymers, wherein said polymer materials can also be used fiber reinforced, in
particular
glass fiber reinforced, or metallic materials, such as brass, particularly
Ecobrass , red brass
and stainless steel.
The pipe according to this embodiment of the present invention is an all-
plastic pipe made of
crosslinked polyethylene (PE-X). All-plastic pipes made of different materials
as well as
plastic composite pipes and metal-plastic composite pipes can alternatively be
used in other
9
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
embodiments of the present invention. Preferred, however, when using plastic
composite
pipes and metal-plastic composite pipes is a layer of cross-linked
polyethylene (PE-X), in
particular PE-Xa, PE-Xb and PE-Xc as the layer facing the internal diameter of
pipe.
According to the invention, another pipe can be connected to the sliding
sleeve connection 3
according to the invention at the second support body 6a. The further pipe can
have an
identical or different construction to the pipe 4 of the support body 6.
Fixing the expanded end 4 to the support body 6 is effected by means of the
sliding sleeve 1
according to the invention. In the embodiment shown in Fig.2, the sliding
sleeve 1 according
to the invention is a sleeve made of crosslinked polyethylene (in particular
PE-Xa, PE-Xb or
PE-Xc) having an internal surface 2 with a combination of longitudinal grooves
and radial
grooves, leading to an average roughness value Rain a range of 3.4 pm and an
averaged
roughness depth IR, in a range of 33.
For producing the sliding sleeve-connection 3 according to the invention, the
sliding sleeve 1
according of the invention is initially slid over the end of the plastic pipe
4. Then, an
expansion tool is inserted into the end of the plastic pipe 4 and the plastic
pipe 4 expanded
on one end by means of the expansion tool, without expanding the sliding
sleeve 1. The
support body 6 of the connecting element 5 is inserted into the expanded end
of the plastic
pipe 4, until the end of the plastic pipe 4 is approximately attached to the
circumferential
collar 8 of the connecting element 5. Due to the memory effect of the pipe
material, the
expanded end of the plastic pipe 4 shrinks, wherein the synthetic material of
the plastic pipe
4 is pressed into the outer contour of the support body 6 of the connecting
element 5. Finally,
the sliding sleeve 1 according to the invention is slid onto the end of the
plastic pipe 4 having
the supporting body inserted therein in axial direction by means of an
appropriate sliding tool,
such that the end of the plastic pipe 4 is fixed to the support body 6.
Eventually further plastic
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
pipes 4 or metal-plastic composite pipes can be connected to further support
bodies 6a of
the connecting element 5.
Figure 3 shows a sliding-sleeve 1 according to another embodiment of the
present invention
in a perspective view. The sliding sleeve 1 according to the invention is made
of crosslinked
polyethylene (PE-Xa) in this embodiment, too. The internal surface 2 of the
sliding sleeve 1
according to the invention has a plurality of macroscopic grooves 9, extending
in longitudinal
direction of the sliding sleeve 1. Additionally or as an alternative, the
grooves 9 may as well
extend in circumferential direction of the sliding sleeve 1 and/or helically.
In the embodiment
shown, the depth of the grooves 9 is approximately 10 A of the wall thickness
of the sliding
sleeve. In alternative embodiments, the depth of the grooves 9 might be
smaller or bigger.
According to the invention, it cannot exceed half of the average wall
thickness of the sliding
sleeve 1.
The sliding sleeve 1 illustrated in Fig. 3 has been produced in that the pipe
made of
crosslinked polyethylene having the respective grooves 9 has been extruded and
the pipe
has been cut, thereby obtaining sliding sleeves 1 according to the invention.
Measurements concerning pressing force
For measuring the forces required for sliding sliding sleeves made of
crosslinked
polyethylene onto expanded ends of pipes having a support body of a connecting
element
inserted therein, an extruded plastic pipe made of crosslinked polyethylene
having an
external diameter of 38.8 mm has been cut in portions of 34 mm length each.
The portions were subjected to a treatment of the internal surface by means of
a steel brush,
such that the internal surfaces of the resulting sliding sleeves according to
comparative
examples and examples according to the invention have the roughness values
shown in
Table 1. The roughness values were determined by means of a Perthometer S2
with
11
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
H8324416CA
PURV3-100, obtained from Mahr GmbH, Gottingen, having an inductive mobile
sensor
system with interchangeable sensor probe and a 2 pm probe tip in accordance
with DIN EN
ISO 4288.
The sliding sleeves according to comparative examples and according to
examples
according to the invention were slid onto the ends of a plastic pipe made of
crosslinked
polyethylene having an external diameter of 25.8 mm. In each case one support
body of
identical connecting pieces has been slid into the expanded ends and the
sliding sleeves
according to comparative examples have been slid onto the expanded end having
the
supporting body inserted therein by means of a tensile testing machine of the
Zwick
company, wherein the force exerted upon sliding onto has been measured by
means of a
load cell. The values obtained are as well indicated in Table 1 and represent
average values
of three measurements.
Table 1
Ra [pm] R2 [pm] Pressing force [kN]
Comparative example 1 0.5 2.2 6.0
Comparative example 2 0.8 3.5 5.9
Example 1 1.3 7 5.7
Example 2 3.8 31 5.1
Example 3 7.1 39 4.7
The obtained values clearly show that the rough internal surfaces of the
sliding sleeves
according to the examples 1 to 3 compared to smooth surfaces of sliding
sleeves according
to the comparative examples 1 and 2 have led to reduced sliding forces.
The present invention has been described in detail with reference to the
examples shown in
the figures and described in the embodiments of the present invention. It is
to be understood,
12
CA 03009423 2018-06-21
,
H8324416CA
that the present invention is not exclusively limited to the embodiments
shown, but that the
scope of the present invention results from the attached claims.
13