Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
9 ~40
'OATER
This application is a division of application Serial No.
480,403 filed April ~n, 1985.
The invention relates to a coater for coating a running paper or
cardboard web.
When coating a running paper or cardboard web with pigment coating,
the quality of the coating is improved and the operation of the
coater becomes easier, if the application of coating substance on
the web and the forming of the coating layer are carried out very
close to each other. Due to this, application of coating substance
and the actual coating are nowadays usually carried out in the same
device, for example, as described in Patent Specification US
4250211. In devices of this kind, there is a problem with
stationary vortices generated in the coating chamber of the
applicator. Impurities occurring in the coating substance easily
accumulate in the vortices, thus decreasing the purity of the
coating substance in the coating chamber. At the same time the dry
solids content of the coating substance in the coating chamber
increases, because water is continuously absorbed by the running
web. Due to the vortices the desired substituting of new coating
substance for the old coating substance is not effective enough in
the coating chamber. The phenomena described above have a
deteriorating influence on the coater operation and on the coating
quality.
An object of the invention is to avoid the drawbacks
mentioned above and to provide a coater which gives a better
coating quality and is easier to operate than known coaters. This is
obtained by improving the flow pattern of the coating substance in
the coating chamber.
:
~69~
More specifically, the invention consists of a coater for coating a
running paper or cardboard web, comprising wall means defining a
coating chamber having an inlet end and an opposite outlet end, the
chamber having an inlet opening at its inlet end for introducing
coating substance into the chamber and being open against the web at
its outlet end, the wall means including a web entrance wall that
bounds the chamber in the upstream direction with respect to the
path of movement of the weh and is spaced from the web so as to
lo define a slot for the web to enter the chamber, and a back wall
structure that bounds the chamber in the opposite, downstream
- direction, said back wall structure including a doctor member that
engages the web for forming a coating layer on the web, and the
coater also comprising supply means connected to the inlet opening
of the coating chamber for delivering pressurized coating substance
into the coating chamber, the supply means including an inlet
conduit which terminates at said inlet opening and which defines a
flow path along which coating substance that is delivered into the
coating chamber passes, the flow path having at least one sharp
change of direction a short distance upstream of the inlet opening,
the slot defined between the web entrance wall and the web being
sufficiently narrow to limit the flow of coating substance from the
coating chamber and thereby maintain the coating substance in the
coating chamber under pressure, and the distance between the web
entrance wall and the doctor member at the outlet end of the cnamber
being such that,at normal web running speed, the web moves from the
entrance wall to the doctor member in a time of at most 0.3 s, the
inlet opening being positioned to introduce coating substance into
the coating chamber at a position that is closer to the web
entrance wall than to the back wall structure, whereby the flow of
1~9 >~
2a
coating substance in the co~ting chamber is, at a position close to
the web entrance wall, divided into two branches, of which a first
( branch follows the web in its running direction toward the back wall
S structure and a second branch, which is of a considerably greater
volume flow rate than the first branch, flows out from the coating
chamber through the slot.
By applying the invention it is possible to keep the coating
substance in the coating chamber clean and homogeneous, because the
flow in the chamber is so directed, that the coating substance in
the chamber is continuously and effectively replaced by new coating
substance. The flow out from the coating chamber through the web
entrance slot, that is, the slot through which web enters into the
chamber, prevents air from entering into the chamber together with
the web. In order to maintain this flow as steady and undisturbed
as possible it is of advantage that the web entrance slot converges
in the direction of movement of the web. For the same reason it is
of advantage that the slot side facing the web joins the outside of
the web entrance wall of the coating ehamber in the form of a smooth
continuous eurve.
In order to to be able to control the flow pattern in the coating
chamber, the height of the web entranee slot between the web
entrance wall of the coating chamber and the web should be made
adjustable. This can be obtained, as known per se, by making the
coating chamber wall movable or by making the entire coating chamber
angularly adjustable relative to the web. In the latter case,
adjustment will also change the angle of the doctor blade at the
coating
1~)9~40
nip, which i~ not always desired. In order to maintain the
angular po~ition of the doctor blade unchanged, the blade
and its holder may be connected to stationary portions of
the coating chamber, whereas resilient members are arranged
to allow small angular adjustments of the rest of the
coating chamber.
In a preferred embodiment of the inven~ion, the web entrance
wall of the coating chamber comprises a protrusion extending
towards the interior of the coating chamber. It has been
found that a protrusion of this kind improve~ the flow
pattern in the coating chamber.
In order to maintain the homogeneity of the coating
substance, it i~ favourable that the flow speed varies in
the inlet duct oP the coating chamber. In this way
continuous stirring of the coating substance is
accomplished. Close before the coating chamber the inlet
duct usually has a throttled passage, where the ~low speed
of the coating substance considerably increases. In order to
insure the homogeneity of the coating substance~ it is also
favourable that the inlet duct makes at least one,
preferably two abrupt direction changes. The increased flow
speed and the abrupt direction changes accomplish that the
coating ~ubstance supplied to the coating chamber is
effectively homogenized.
In order to obtain a desired flow pattern in the coating
1~9;~
(
chamber, it is favourable that the depth of the coating
chamber measured perpendicularly to the web is about equal
to or greater than the distance, in the web running
direction, between the web entrance wall and the opposite
wall, that is, the back wall of the coating chamber.
A coater according to the invention may be further improved
by providing the coating chamber with a partition wall,
which leads the flow of the coating substance entering the
coating chamber first mainly along the web entrance wall of
the coating chamber towards the web, thereafter in the web
running direction, and finally along the back wall of the
coating chamber away from the web. The partition wall may be
so arranged, that the coating substance can freely ~low
around the partition wall, but it is al~o possible to
provide the coating chamber with an outlet opening close to
its back wall, that is, at the opposite side of the
partition wall relative to the inlet opening of the coating
chamber. The latter arrangement provides a possibility to
control the flow in the coating chamber with great accuracy.
The control may be improved by providing the outlet opening
of the coating chamber with an adjustable flow throttling
device.
With regard to flow control, it i~ also favourable that the
position of the partition wall is adjustable, so that the
height of the slot between the partition wall and the web
can be varied. The adjustment range should preferably
~X~24~
include slot heights of 0.1 to 5 mm. When a partition wall
is used, the throttled pas3age of the inlet duct may be
positioned in the coating chamber itself or a second
throttled pas~age may be formed therein, in which the flow
speed somewhat increases and possible pressure differences
are equalized.
Because it is important to prevent air from entering the
coating chamber together with the web, the adjustment of the
partition wall mu~t be made so, that the flow out through
the web entrance slot remains sufficiently strong. This can
be obtained by keeping the slot between the partition wall
and the web narrower than the slot between the web entrance
wall of the coating chamber and the web.
Even if the outlet opening of the coating chamber is located
at the opposite side of the partition wall than ~he inlet
opening, it might be useful to arrange, in the partition
wall, a pressure equalizing opening, which preferably is
located at a distance from the web greater than the distance
between the web entrance wall and the back wall of the
coating chamber measured along the web. Such an opening
increases the possibilitie~ to control the flow in the
coating chamber.
A still more effective control of the flow in the coating
chamber may be obtained by arranging a wall outside the web
entrance wall of the coating chaMber, thereby forming a
substantially closed outlet duct for the coating sub~tance
flowing out through the web entrance slot of the coating
chamber. In this duct a ~referably controllable partial
vacuum may be maintained, in order to further improve the
flow control.
Especially at high web speeds it is important, that the web
is firmly supported at the position of the coating chamber.
For this purpose a conventional rotating support drum may be
used, the peripheral speed and rotation direction of which
follows the web movement. The support element also gives the
advantage that, in the event of web rupture, only limited
spla~hing of coating substance occurs.
The invention will now be described, by way of example, with
reference to the accompanying drawing, in which
- Figure 1 schematically shows a section in the web
running direction of a coater according to the
invention,
- Figure 2 shows, on a smaller scale, the general
arrangement of a coater according to Figure 1,
- Figure 3 shows a ~ectional view, corresponding to
the one of Figures 1 and 2, of a second embodiment
of the invention,
- Figure 4 shows a sectional view, corresponding to
the one of Figures 1 and 2, of a third embodiment
of the invention.
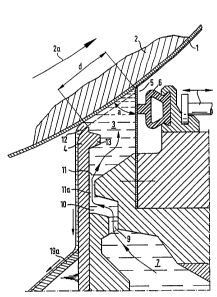
In the drawing, numeral 1 refers to a running paper or
cardboard web and 2 to a support drum carrying the web. An
arrow 2a refers to the moving direction of the drum 2. There
is a coating chamber 3 having a web entrance wall 4 and a
back wall 5. The back wall is formed by a flexible doctor
blade, which forms an angle a with the web 1 and which is
pressed against the web by a controllable force, acting over
one or several pneumatic control elements 6 of rubber. The
doctor blade pressure is controllable mechanioally by screw
means shown only schematically and also pneumatically by
varying the pressure inside the element 6, thereby obtaining
fine adjustment of the blade pressure. Instead of the doctor
blade 5, a doctor rod arrangement may be used as well, for
instance, generally of the kind shown in Patent
Specification US 3245377.
Below the coating chamber 3 there is a pressure equalizing
chamber 7, to which coating 3ubstance is supplied through a
duct 8. From t~e chamber 7 the coating substance flows via a
throttled passage 9 to another smaller pressure equalizing
chamber ~0, fro~ which it flows via an inlet duct 11 into
the coating chamber 3. The inlet duct 11 is in the vicinity
of the web entrance wall 4 of the coating chamber. The
throttling and flow direction alteration passages 9,10,11a
of the inlet duct provide an effective stirring of the
coating substance, so that it remains as homogeneous as
possible.
l~ti~:40
The preqsure in the coating chamber 3 is usually kept at a
level of 2 to 12 kPa above atmospheric pressure. Due to this
pressure, a portion of the coating substance flows out from
the coating chamber through a slot 12 between the web
entrance wall 4 and the web 1. This flow prevents air from
entering the coating chamber together with the running web
1. The web pas~es the distance d between the web entrance
wall 4 and the back wall 5 of the coating chamber in a time
which should be at the most 0.3 s, preferably at the most
0.03 s. Cardboard webs are usually coated at substantially
lower speeds than paper webs. A typical paper coating speed
is about 1000 m/min, which speed may be doubled or reduced
by 50 % or even more depending on the circumstances. During
the passage of the web over the coating chamber a portion of
the coating substance adheres to the web and is levelled and
smoothed out in a coating nip between the edge of the doctor
blade 5 and the web. A protrusion 13 at the inside of the
web entrance wall 4 leads the coating substance flow in the
coating chamber, so that stationary vortices are generally
avoided. The extension of the protrusion 13 from the inner
surface of the wall 4 towards the interior of the coating
chamber is 5 to 15 mm, the dis~ance d is 20 to 30 mm, and
the angle a is usually between 30 and 60. The depth of the
coating chamber measured perpendicularly to the web 1 is
about equal to the distance d. The diameter of the support
drum 2 may be about 1 m.
Figure 1 shows how, in the web entrance slot 12, the side
i9~
( ~urface facing the web forms a conti~uou~ curve joining the
outer surface of the wall element 4.
The embodiment ~hown in Figure 3 differs from the embodiment
shown in Figures 1 and 2 in that the de?th of the coating
chamber in a direction away from the web is greater, and, in
addition, a partition wall 14 is provided in the middle of
the coating chamber. As in the embodiment according to
Figure l, coating substance is fed through pipes 8 to a
pressure equalizing chamber 7, wherefrom it flows through an
inlet duct 11 into the coating chamber 3. The coating
chamber has an outlet duct 15 having downstream of the
coating chamber an enlargement 16 and thereafter continuing
in the form of several parallel pipes 17. These pipes are
provided with an adjustable throttle valve 18, by means of
which the pressure in the outlet duct 15 can be adjusted.
Coating substance flowing through the web entrance slot 12
is collected in a spac~ t9, from where it flows away through
a pipe 20 to a coating substance container 21, either
directly or as shown by joining a pipe 22, to which also the
coating chamber outlet pipes 17 are connected. Additional
coating substance is continuously supplied to the coating
substance contai~er 21 through a pipe 23 to insure that a
sufficient amount of coating substance is always available.
Coating substance is pumped from the container 21 to the
coating chamber 3 through a pipe 24 by means of a pump 25
and through a filter 26 and pipes 8 connected to the
~ L~()
pressure equalizing chamber 7.
The partition wall 14 of the coating chamber is preferably
made adjustable relative to the web. Adjustment means are
indicated by arrows 44. The position of the partition wall
i9 SO adjusted, that there is a slot 27 between the edge of
the partition wall and the web, which slot is smaller than
the web entrance slot 12. The height of the slot 27 is
adjustable within a range of 0.1 to 5 mm.
There is a pressure equalizing opening 28 in the partition
wall 14. This opening interconnects the two portions of the
coating chamber that are at opposite sides of the ~artition
wall. Measured along the partition wall, the opening 28 is
at a distance b from the web 1. This distance is greater
than the distance d between the opposite walls of the
coating chamber in the web running direction. A portion of
coating substance in the cha~ber 3 can return through the
opening 28 to the inlet side of the coating chamber, as
indicated by an arrow 29. This flow is increased if there is
a throttled passage 11a in the inlet duct 11 close in front
of the opening 28. The cross section area of the opening 28
may be adjusted within the li~its of the partition wall
position adjustment 44. It is also possible to use separate
adjustment means for varyir.g the size of the opening 28
independently of the adjustment of the slot Z7.
In the embodiment shown in Figure 4, a wall 30 is located
~,,9,'~
outside the web entrance wall 4 of the coating chamber 3.
This wall forms together with the web entrance wall 4 a flow
duct 31 for the coating substance flowing out through the
web entrance slot 12. The flow in the flow duct 31 may be
increased by providing partial vacuum in the duct and the
flow may be influenced by adjusting this vacuum. In this way
an additional possibility to influence the flow pattern in
the coating chamber is provided. The device for providing a
partial vacuu~ in the duct 31 is shown as a vacuum pump 32
with control means 33.
Numeral 34 refers to the basic support member of the coating
device and 35 to a conventional doctor blade 5 support beam.
Normally, about 2 to 5 liter per second coating substance is
fed to the coating chamber 3 for each meter of tranverse
width of the web 1. This means that a 5 m wide web reqires a
of flow of about 10 to 25 l/s. The flow out through the web
entrance slot 12 is usually at least 20 times the flow out
through the coating nip.
The invention is not limited to the emdodiment shown, but
several modifications thereof are feasible with-n the scope
of the attached claims. For example, means corresponding to
the flow direction alteration and throttling arrangements
9,10,11a shown in Figure 1 may be arranged between the
chamber 7 and the chamber 3 shown in Figure 3.
.. ..