Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
This inventior~ relates to an apparatus and a method
of fabricating plate web girders. The invention was
developed primarily for fabricating girders of the kind
which comprise a corrugated web interposed between a pair
of flanges, and will be described hereinafter with
reference to that use. However, it may be used to
fabricate any type of plate web girder. As used herein
the term corrugated web means a web corrugated in any
manner so as to have crests and troughs formed therein
including webs with non-parallel corrugations.
Hitherto, the method utilized for fabricating such
girders comprises the step of tack welding the flanges to
the web in an appropriate configuration, followed by the
step of continuously welding the tack welded girder from
a central location towards its respective ends.
Such a method overcomes the problem of buckling
which is a result of thermal stresses caused by isolated
heat inputs during welding.
Whilst being suitable for overcoming the
aformentioned buckling problem, the fabrication of a
girder according to the method is time consuming.
It is an object of this invention to provide an
apparatus and a method for fabricating a plate web
girder, which will be overcome or at least ameliorate
this disadvantage.
Accordingly, in one aspect this invention consists
in an apparatus for fabricating a plate wab girder of the
kind comprising two flanges spaced apart by a web, said
-2-
r~ 7
apparatus comprising a plurality of welding devices e~ch
mounted on respective spaced-apart guides to follow a
respective portion of a weldiny pa-th defined by the
intersection of said web and a flange; and means to move
said girder longitudinally relative to said weldiny
devices.
In a second aspect this invention consists in a
method of fabricating a plate web girder of the kind
comprising two flanges spaced apart by a web, said method
comprising the steps of positioning said flanges relative
to said web, positioning a plurality of welding devices
-at spaced-apart locations along said girders, said
devices being adapted to follow a respective portion of a
welding path defined by the intersection of said web and
a flange; actuating said devices and simultaneous moving
said girder longitudinally relative to said devices.
In one embodiment it is preferred that the girder is
moved at a substantially constant rate. However, it is
also within the scope of this invention to vary the rate
to achieve a constant speed of the welding device along
the welding path for corrugated web girders.
Preferably, the welding devices are positioned
in a linear array at equallyspaced-apart locations and
the girder is moved for a distance equal to the distance
between adjacent devices.
It is also preferred that each guide bears against
the web adjacent the respective welding path to main-tain
the welding device at a predetermined distance from the
-3~
d
web at each poin-t alony the path.
Each yuide preferably also includes rneans to bear
against the flange -to main-tain the welding device at a
predetermined distance from said Elanye adjacent the
respective welding path.
The apparatus and method of this invention have been
found to be suitable for fabricating plate web girds
having corrugated webs, although the welding angle between
the welding path varies as the guide traverses the crests
and troughs of the corrugations.
Accordingly, it is further preferred that the
welding angle between the respective weld path and the
respective welding device is maintained substantially
constant for each point along the path. Preferably, the
welding angle is less than 15 degrees from vertical in
a direction forward of the weld.
In one embodiment the welding angle is maintained by
adjusting the respective welding devices in response to
movement of the guide over the corrugations of the web.
One embodiment of this invention will now be described,
by way of example only with reference to the accompanying
drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a schematic perspective view of part of
the apparatus according to this invention; and
Figure 2 is an enlarged exploded, perspective view,
partly in dotted lines, of part of the apparatus of
Figure 2.
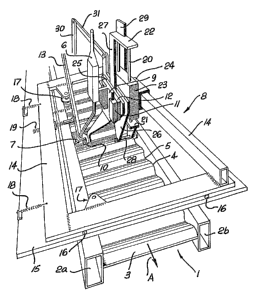
Figures 1 and 2 show part of the apparatus for
fabricating a plate web girder 1 comprising two flanges
~2~
2a, 2b spaced apart by a eorrugated web 3. The
corrugated web 3 is formed with successive crests 4 and
troughs 5.
The apparatus comprises a plurality of welding
devices equally spaced apart in linear array. Figure 1
illustrates only one such device which takes the orm of
a welding gun 6 which is connected with a MIG wire feed
welder (not shown) in the conventional manner. Each gun
6 has a welding tip 7 and is mounted on a respective
spaced apart guide indicated generally at 8. Again
Figure 1 shows only one such guide, however, each guide
is identical.
Witn the ai~ of guide ~ the wel~ing tip 7 of gun 6
follows a portion of the welding path defined by the
intersection of web 3 and flange 2a. The apparatus
includes an electrically driven worm screw (not shown)
which is connected to the girder 1 and constitutes means
to move the girder longitudinally in the direction shown
by arrow A relative to the gun 6 at a substantially
constant rate.
The gun 6 is clamped to a mounting bracket 9 forming
part of guide 8. Mounting bracket 9 i5 fitted with a
roller 10 which bears against the web 3 adjacent the
welding path and weIding tip 7. Bracket 9 is slideably
mounted in grooved blocks 11 in turn mounted on a support
plate 12. Thi allows roller 10 to follow the surfa~e of
web 3 by bracket 9 liding in blocks 11 as the girder
moves past the roller. In this way the welding tip is
6~7
maintained at a predetermined distance from the web 3 at
each point along the welding ~ath.
A support arm 13 is used to locate welding tip 7.
Although not shown in figure 1 this arm 13 extends toward
the remote end of the girder 1 sufficiently to suit the
sharpness of the corrugations in web 3 and is hingedly
mounted. The arm 13 has a comparatively long length so
that movement of the welding tip 7 up and down as roller
10 passes over web 3 is not inhibited.
Guide 8 also includes a frame 14 which rests on a
base plate 15 above flanges 2a, 2b. Rollers 16 are
provided between the frame 14 and ba~e plate 15. Two
further rollers 17 are mounted on frame 14 and held in
contact with flange 2a under the action of two springs 18
acting on frame 14. An adjustable stop 19 extends from
frame 14 and arm 13 is held against stop 19 by a spring
connected between arm 13 and frame 14. The welding tip 7
is thus maintained at a predetermined distance from the
flange 2a adjacent the welding path at each point along
the path by rollers 17 bearing against flange 2a. The
distance is adjusted by ad]usting the length of stop 19.
The angle between the welding tip 7 and the welding
path is preferably less than 15 degrees from vertical in
a direction forward of the weld. As the gun 6 moves over
the web 3 this angle will change as the path follows the
crests and troughs of the web. To improve the quality of
the weld this welding angle is maintained substantially
constant by moving the mounting ~racket 9 to which
welding gun 6 is clamped. The means to maintain the
welding angle comprises a member formed by a pair of rods
20 supported by a roller arrangement 21. Roller
arrangement 21 follows the corrugations of web 3 and the
upper ends o~ rods 20 are joined by a bracket 22. Rods
20 pass through a mounting block 23 which is in turn
mounted with frame 14 by means of a sliding sleeve 24
over the frame. This ensures the rods 20 are free to
m~ve up ana down as roller arrangement 21 passes over web
3. The sleeve 24 allows the whole member to move
longitudinally of the girder.
The roller arrangement 21 is connected to support
plate 12 by means of connecting plates 25,26. Plate 25
is bolted to plate 12 through slotted bolt holes to allow
relative movement between the plates. Plate~ 25 and 26
are bolted together and by means of lock nuts and
suitable spacers the angles between the planes of the
plates can be varied to correctly orient slotted blocks
11 with bracket 9. An upright bar 27 extends between
plates 25 and 26 and is joined at its upper end to
bracket 22. The lower end of bar 27~ is fixed to roller
arrangement 21 by means of a bolt 28 extending through
plate 26. This serves to keep plate 26 upright between
block 23 and bar 27.
The bracket 22 secured to the top of rods 20 serves
two purposes. Firstly it actuates two limit switching
devices on a bar 29 fixedly extending ~rom block 23. The
limit switching devices are positioned on bar 2g so as to
be respectively actuated when crests and troughs of the
web 3 are encountered by roller arrangement 21. That is,
when the bracket 22 is at its lowermost and uppermost
positions with respect to bar 29 respectively.
The limit switching devices can be any suitable
position sensitive switching device and operate a
modulating motor (not shown) of any suitable type. The
moduLating motor acts via arms 30 and 31 on plate 26 to
which arm 31 is bolted at 32 (shown in Figure 2). The
motor moves arm 31 longitudinally backward or forward so
that plate 26 pivots about the bolt 28 holding it to
rolLer arrangement 21. In this way plate 25, plate 12
and slotted blocks 11 can be inclined at different
angles. Because bracket 9 holding welding gun 6 is held
by blocks 11 the welding gun can in this manner be
adjusted to maintain the welding angle constant. In
operation the limit switches are respectively operated as
the roller arrangement reaches the bottom of each trough
and the top of each crest. The limit switches in turn
operate to reverse the direction of the modulating motor
which adjusts the position of the welding gun at a
selected rate corresponding to the changing direction of
the welding path as it follows the corrugations. By
positioning the roller arrangement 21 to encounter
the corrugations ahead of the guide roller 10 it is
possible to compensate for lag in the adjusting
i26~
of the welding g~n to maintain the welding angle
constant. In addition, suitable adjustment of the
position at which the roller arrangement forming part of
the member to follow the corrugations encounters each
corrugation with respect to the position at which roller
10 encounters the same corrugation allows girders
comprising webs with non-parallel corrugations to be
fabricated.
The. foregoing descri~es only one embodiment of this
invention and modifications may be made thereto without
departing from the scope of the invention. For example,
the mechanical sensing, switching and adjusting
mechanisms described above can equally be replaced with
electric, electronic or electro-mechanical devices or a
combination of such devices.