Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
r'
~26~;53
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
- This invention relates to a connector for
fiber optic cables.
Fiber optic cables are well known in the art.
Such cables consist of very small diameter glass or
plastic fibers independently buffered and covered with
opague cladding material and are used for conducting
optical signals from one place to another. Because the
optic signal carried is immune to elect:rlcal noise and
other interference, fiber optic cables are increasingly
being used as a substitute for high speed data
transmission and as we~l as audio and video
transmission.
When it is desired to separ~bly connect two
fiber optic cable ends, it i5 necessry to secure the
ends of fibers in exact axial alignment with one
another, or with the focal point of a lens, in the case
of lens-type connectors, in order to achieve maximum
signal transmission. The holding device for the ends of
the fiber must be able to be easlly assembled onto the
delicate fibers and must be capable of holding the
fibers straight, secure, and concentric with ~ach other
without undue pressure. Most prior art connectors
employ drilled holes or channels between rods to
position the ~ibers. Tolerance variations in the fiber
; diameters and drill diameters adversely affect the
ability to easily assemble the fiber while maintaining
absolute fiber concentricity with such prio~ art
constructions.
SUMMARY AND OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION
According to the invention, a connector for
fiber optic cables comprises a tubular housing and a
pair of multi-part termination assemblies. Each
termination assembly receives the end of a fiber optic
cable, and is mounted in the connector housing. A pair
;.
, ~ .
.
. .
,: :
, :
~ ~L2~5S3 ~
of lens elements are located within the housing by
sleeves which coaxially align the lens elements one with
the other. The metal sleeves also receive the forward 4
end of the termination assemblies to align the optic
fiber mounted in the termination assembly with the focal
point of the lens element.
It is, therefore, an object of the invention
to provide a connector for f iber optic cables which
comprises multi-part termination assemblies which mount
on the cable ends and are received by a tubular
housing.
It is another object of the in~ention to
provide a connector for fiber optic cables which
comprises opposed lens elements held ~n axial alignment
by sleeves which are mounted in a housing and which
additionally receive the end of termination as~emblies
attached to the flber optic cable.
These and other objects of the invention will
become apparent from the following detailed description,
of the drawings, wherein reference numerals used
throughout the description designate like or
corresponding parts shown on the drawing figures.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION O~ THE DRAWINGS
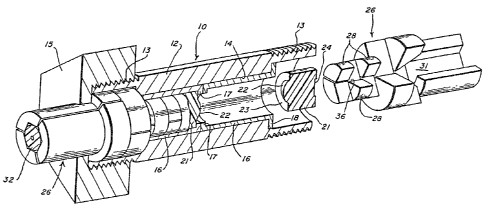
Figure 1 is a partial sectional view exploded
of a fiber optic connector according to the invention.
~igure 2 is an exploded view of the
termination assembly shown in Figure 1.
DESCRITPI~N OF THE PREFERRED EMBODI~ENT
Turning now to the drawing figures there is
shown in Figure 1 a fiber optic connector generally
designated by the reference numeral 10. The connector
comprises an elongated tubular housing 12 which may be
treaded at each end 13 as shown for reception of a
~:~ reta.ining nut 15. The housing 12 includes a through
;
- ~ ' ' .
~'
-- 4 --
bore 14 which extends from one threaded end 13 to the
other.
The connector additionally comprises a pair of
sleeves 16 which are inserted into the through bore 14
from either end of the housing, Each sleeve 16 may
comprise a precision drawn metal shell which includes a
lip 17 on one end and a flange 18 on the other end. The
sleeves 16 are di~ensioned to receive a lens e~ement 21
which may comprise molded plastic. The front surface of
each lens element 21 comprises a convex Iens 22 which is
surrounded by a seating surface 23. The back of each
lens element 21 is formed with a circular recess 24.
The fiber optic connector additionally
includes two termination assemblies 26~ Each
termination assembly 26 compr~ses three identical
termination portions 27. Each termlnation portion
comprises a forward section including a plurality of
angularly dlsplaced arcuate lobes 28, and a rear arcuate
portion 29 which when the termination portions 27 are
assemhled with one another form an entry port 31 on one
`~ end and a small fiber positioning channel 36 on the
other end. The entry port 31 is dimensioned to receive
the end of a fiber optic cable 32. Between the entry
port 31 and the fiber positioning channel 36 is a
tapered guideway 34 which diminishes in size from the
size of the entry port 31 to the size of the Eiber
positioning channel 36 formed by the lobes 28.
METHOD OF USE OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Three termination portions may be grouped as
shown in Figure 1 to form a termination asse~bly 26
including an entry port 31 at one end thereof and a
fiber positioning channel 36 at the other end. Once
three termination portions have been assembled~ 2 fiber
optic cable having a short length of the protective
:: ~
, .
f~ ~
i3
-- 5 --
cladding removed from the end thereof may be inserted
into the entry port 31. The tapered guideway 34 feeds
the optic fiber 33 into the fiber positioning channel 36
until the end of the optic fiber is flush with the front
face of the termination assembly 26.
The use of three termination portions 27 to
form the fiber positioning channel 36 obviates the need
to drill a long, thin bore in the term;ination assembly
to receive the optic fiber. Also, because the lobes 28
of the several termination portions interlock with one
- another, there is no gap or slot along the fiber
positioning channel 36 into which the optic fiber can
slip. If desired, the fiber optic cable 32 can be
positioned in the termination assembly so that the optic
fiber 33 protrudes slightly from the fiber positioning
channel 36. The end of the optic fiber can then be
ground down and polished ~lush with the end of the
termination assembly or, in the alternative, the fiber
may be cleaved flush with the end of the termination
assembly. A small amount of adhesive ~e may used to
secure the portions 27 of the termination assembly to
one another and to secure the fiber optic cable 32 in
: place within the assembly.
The sleeve 16 surrounds each lens element 21
and abutting termination assembly 26 within the housing
- . 12. A precision drawn metal sleeve is preferred since
tolerances can be held very exact for such a
construction, and the alignment and spacing ~of the lens
elements and termination asemblies are controlled by the
sleeve. The lip 17 on the forward portion of each
sleeve 16 provides a reerence plane against which the
seating surface 23 of the lens element 21 abuts, and the
precise fit of the two sleeves 16 in the bore 14 acts to
coaxially align the lens elements 21 with one another.
.
, ~ .
:
~L2~ 3
~ 6 --
The forward lobe o the termination assembly 26 butts
against the rear surface of the lens e~.ement 21. The
recess 24 formed in the rear surface of the lens ele~ent
21 prevents the optic fiber held by the termination
assembly from coming into contact with and scratching or
being scratched by the lens element 21~ A pair of
threaded fasteners (only one shown) may be tightened
onto the threaded surfaces 13 to hold the termination
assemblies within the housing 12.
Having thus described the invention, various
modifications and alterations thereof will become
apparent to those skil~ed in the art, which
modifications and alterations are intended to be within
the scope of the invention as de~ined by the appended
claims.
What is claimed is:
. . .
. ~
..