Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~ 7~ ~ 7
The pr~sen-t inven-tion relates to a wheel drive mode changeover
apparatus ~or an agricul-tural tractor, and more particularly to
an apparatus for permitting changeover between a two wheel drive
mode and a four wheel drive mode to be effected according to
travelling conditions o~ the tractor such as a sudden sharp turn,
a small turn and bad road conditions.
The above apparatus provided for a four wheel drive vehicle is
well known, which permits the changeover between the two wheel
drive mode and the four wheel drive mode to be effected manually
or automatically according to road conditionsO One such example
is disclosed in United States Patent No. 4,484,653.
An apparatus for use in a four wheel drive vehirle for permitting
changeover between a front wheel accelerating four wheel drive
mods having front wheels driven at a higher peripheral speed than
rear wheels and a standard four wheel drive mode having the front
and rear wheels dr.lven at a substantially equal peripheral speed
is known, for example, from Japanese patent application laid open
under No. 176121/84 (the corresponding UK application being
published under No. Gs 2136784A) and from United States Patent
-- 1 --
~`
71~27
No. 4574910~ In this type of wheel drive mode change
over apparatus, the wheel drive mode changeover is
effected in response to detection of a steering angle
or of braking of a right rear wheel or ]e~t rear
wheel. The traveling conditions and the wheel drive
modes are in one-to-one relations where, as in the
above construction, the wheel drive modes are changed
in response to detection of an amount of disp]acement
of a control device for varying the traveling condi-
tions of the vehicle, such as a steering wheel or aside brake pedal, that is to say where the whe~l drive
modes are changed according to changes in the travel-
ing conditions of the vehicle. Therefore, a desired
wheel drive mode cannot be selected under certain
traveling conditions at will, and a certain wheel
drive mode cannot be retained against changes in the
traveling conditions.
The four wheel drive mode having the front wheels
accelerated is used when a small turn is necessary or
when making a sudden sharp-turn to avert a dangerjust
ahead. For a normal agricultural operation or travel-
ing the four wheel drive mode having the front and
rear wheels driven at a substantially equal peripheral
speed or the two wheel drive mode is used. Therefore,
to establish the one-to-one relations between these
drive modes and the traveling conditions does not
-2-
~Z714~
provide for but rather deviates from the optimal use of these
three drive modes.
The present invention provldes a wheel drive mode
changeover apparatus having a great degree of freedom .in
S swltching between a two wheel drive mode, a four wheel drive mode
with the front and rear wheels driven at a substantially equal
peripheral speed, and a four wheel drlve mode with the front
wheels driven at a higher peripheral speed than the rear wheels.
According to one aspect of the present invention there
is providcd a wheel drive mode changeover apparatus for a vehicle
having at least a first wheel set and a second wheel set driven
by an engine, comprising: changeover means for effecting
changeover between (a) a two wheel drive mode having only the
second wheel set driven, (b) a first four wheel drive mode having
the first wheel set and the second wheel set driven at a
substantially equal peripheral speed, and (c) a second four wheel
drive mode with the first wheel set driven at a higher peripheral
speed than the second wheel set, said changeover means including
first transmission means for effecting said first four wheel
drive mode, second transmission means for effecting said second
four wheel drive mode, a claw clutch for coupling and uncoupling
said first wheel set with said first transmission means, a
friction clutch for coupling and uncoupling said first wheel set
with said second transmission mechanism, and shifting means for
selectively shifting said claw clutch and sald friction clutch;
traveling condition detecting means including means for
generating an output indicative of traveling conditions; first
control means operatively coupled to said traveling condition
detecting means and responsive to said output of said traveling
condition detecting means for actuating said changeover means,
said first control means including means for switching between
said first four wheel drive mode and said second four wheel drive
mode; and second control means for establishing and breaking
operative connection between said changeover means and said first
~ 7~ 7
control means. Suitably the vehicle includes a r:Lght and a left
side brake pedal operatively coupled to said second wheel set,
and wherein said traveling condltion detecting mean.s lncludes
interlock.ing means for providing said first control means with a
kinematic output in response to depression of only one of the
right and left side brake pedals.
In another aspect of the present invention a wheel
drive mode changeover apparatus for a vehicle including at least
a first wheel se-t and a second wheel set driven by an engine,
comprising: changeover means for effecting changeover between ~a)
a two wheel drive mode having only the second wheel set driven,
(b) a first four wheel drive mode having the first wheel set and
the second wheel set driven at substantially the same peripheral
speed, (c) a second four wheel drive mode with the first wheel
set driven at a higher peripheral speed than the second wheel
set, said changeover means including first transmission means for
effecting said first four wheel drive mode, second transmission
means for effecting said second four wheel drive mode, a claw
clutch for coupling and uncoupling said first wheel set with said
first transmission means, à friction clutch for coupling and
uncoupling said first wheel set with said second transmission
means, and shifting means for selectively shifting said claw
clutch and said friction clutch; traveling condition detecting
means for generating an output indicative of traveling condi-
tions; first control means operatively coupled to said travelingcondition detecting means and responsive to an output of said
traveling condition detecting means for actuating said changeover
means, said first control means including means for switching
between said first four wheel drlve mode and said second four
wheel drive mode; and a second control means for actuating said
transmission means to switch between said two wheel drive mode
and said first four wheel drive mode and for establishing and
braking operative connection between said changeover means and
said first control means. Suitabl~ said second control means has
three operative positions including a first operative position
~ ....
.
~'
~ ~ 7~
for causing said changeover means to provide the two wheel drive
mode and prohibit action of said first control means, a second
operative position for caustng said changeover m~ans to provide
the first four wheel drive mode and prshibit action of said flrst
control means, and a third operative position for causing said
changeover means to provide the first four wheel drive mode and
permit actlon of said first control means. ~esirably the vehicle
includes a right and a left side brake pedal operatively coupled
to said second wheel set, and wherein said traveling condition
detecting means includes interlocking means for providing sald
first control means with a kinematic output in response to
depression of only one of said right and left side brake pedals.
This wheel drive mode changeover apparatus permits the
vehicle to travel by a wheel drive mode according to traveling
conditions, and the response to the traveling conditions to be
broXen for a time to retain a desired drive mode such as the four
wheel drive mode having the front and rear wheels driven at a
substantially e~ual peripheral speed.
The degree of freedom in the wheel drive mode
changeover operation may be increased further by providing the
second control means with a function to switch between the two
wheel drive mode and the four wheel drive mode having the front
and rear wheels driven at a substantially equal peripheral speed,
in addition to the function to establish and break operative
connection between the transmission means and the first control
means.
The present invention will be further illustrated by
way of the accompanying drawings in which:-
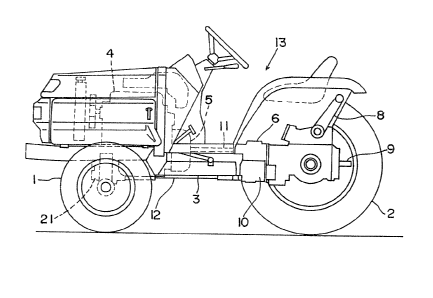
Fig. 1 is a side elevation of an agricultural tractorincluding a wheel drive mode changeover
- 4a -
.~
apparatus embodying the present invention,
Fig. 2 is a schematic plan view of a portion of
transmission including a front wheel change speed
mechanism and an auxiliary change speed mechanism,
FigO 3 is a side view of the front wheel change
speed mechanism,
Fig. 4 is a front view of control means for the
front wheel change speed mechanism,
Fig. 5a is a view showing an interlocking arrange-
ment between a pitman arm and the front wheel change
speed mechanism,
Fig. 5b is a view showing the pitman arm displaced
beyond a predetermined angle,
Fig. 6 is a side view of a steering system extend-
ing from a steering wheel to the pitman arm,
Fig. 7 is a sectional view taken on line Y-Y in
Fig. 4,
Fig. ~ is a sectional view taken on line X-X in
Fig. 4,
Fig. 9a is a schematic plan view showing a
position for shifting the front wheel change speed
mechanism to provide a front wheel accelerating four
wheel drive mode,
Fig. 9b is a schematic plan view showing a
position for shifting the front wheel change speed
mechanism to neutral,
Fig. 9c is a schematic plan view showing a
position for shifting the front wheel change speed
mechanism to provide a standard four wheel drive mode,
and
5Fig. 10 is a view showing an interlocking arrange-
ment between side brakes and the front wheel change
speed mechanism.
Description of the Preferred Embodiment
The invention as embodied in an agricultural
10tractor will be described hereinafter with reference
to the drawings.
Fig. 1 shows a four wheel drive agricultural
tractor having right and left dirigible front drive
wheels 1 and right and left rear wheels 2 supported by
a chassis 3 carrying an engine 4, a main clu~ch 5, a
transmission case 6 and a driver's section 7. The
tractor includes at a rear end thereof a vertically
oscillatable lift arm 8 to which a rotary plow or
other working implement is connected, and a power
takeoff shaft 9 for transmitting power to the working
implement.
This agricultural tractor has a power transmission
system and a front wheel change speed mechanism 10 as
illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2. The power of the engine
4 is transmitted through the main clutch 5, a power
~ ;~714~7
transmission shaft 11 to a main ~hange speed mechanism
(not shown) and to an auxiliary change speed mechanism
7 where the power is changed to varied speeds. The
output o the auxiliary change speed mechanism 7 is
transmitted through an output shaft 70 to a rear
differential mechanism 20b Part of this output is
taken from the output shaft 70 through gears 71a and
71b to be transmitted to the front wheel change speed
mechanism 10 which is operable to effect wheel drive
mode switching. The output of the front wheel change
speed mechanism 10 is transmitted through a front
wheel drive intermediate shaft 12 to a front differen-
tial mechanism 21.
The front wheel change speed mechanism 10 will be
described next. As shown in Figs. 2 and 3, an inter-
mediate transmission shaft 72 is disposed in a region
of the auxiliary change speed mechanism 7 inside the
transmission case 6. The intermediate transmission
shaft 72 carries a first output gear 73 fixed to one
end thereof and a second output gear 74 fixed to the
other end thereof. The first output gear 73 is in
mesh with the gear 71b constituting part of the
mechanism for taking out the power from the auxiliary
change speed mechanism 7. A first driven gear 102 in
25 mesh with the first output gear 73 is freely robatably
mounted on a front wheel drive output shaft 17, and a
' '
~ 7~7
second driven gear 107 in mesh with the second output
gear 74 is fixed to a clutch case 109 freely ro-tatably
mounted on the front wheel drive output shaft 17. The
first driven gear 102 and the clutch case 109 are
interposed by a shift element 104 splined to the front
wheel drive output shaft 101 to be rotatable in unison
and axially slidable thereon. The shift element 104
acts also as piston for a multidisk friction clutch
108. The shift element 104 defines engaging claws 105
opposed to the first driven gear 102 and a piston
portion 106 opposed to the second driven gear 107.
Thus, the multidisk friction clutch 108 is provided
between the shift element 104 and the clutch case 109
and a claw clutch 110 is provided between the shift
element 104 and the first driven gear 102. The
friction clutch 108 is employed at an accelerating
four wheel drive side in order to prevent shoc]cs and
gear noises occurring at times of stopping an acceler~
ating four wheel drive mode. The entire front wheel
change speed mechanism is covered by a case 111.
The first output gear 73 and the first driven gear
102 have a gear ratio to substantially equalize a
peripheral speed of the front wheels 1 effected
through the first output gear 73, first driven gear
102 and claw clutch 110 to a peripheral speed of the
rear wheels 2. The second output gear 74 and the
' .
second driven gear 107 have a gear ratio to make a
peripheral speed of the front wheels 1 efected
through the second output gear 74, second driven gear
107 and friction clutch 108 greatar than, for example
twice, the peripheral speed of the rear wheels 2.
Thus, the tractor is driven by a front wheel acceler-
ating fou~ wheel drive mode when the ~riction clutch
108 is engaged as shown in Fig. 9a, and by a standard
four wheel drive mode with the front and rear wheels
driven at a substantially equal peripheral speed when
the claw clutch 110 is engaged as shown in Fig. 9c.
Fig. 9b shows the shift element 104 in neutxal
position, in which state the tractor is driven by a
two wheel drive mode with the front wheels 1 discon-
nected from the power transmission.
Referring to Fig. 4, the shift element 104 isoperated by a shifter 57 mounted on a support shaft 52
to be movable along the front wheel drive output shaft
101. This shifter 57 is axially movable by a control
element 54 freely rotatably mounted on a control shaft
57 disposed below and extending perpendicular to the
front wheel drive output shaft 101. The control
element 54 includes a boss defining splines 54a at an
end thereof. The control shaft 57 carries a collar 55
~5 at an end thereof adjacent to the end of the boss of
the control element 54. The collar 55 is rotatable in
': :
l~t~
unison with the control shaft 57 and defines splines
S6 equal in shape to the splines 54a. A switching
element 81 is slidably mounted on -the splines 5~a and
56~ When the switching element 81 connects the
control element 54 and the control shaft S7 to be
rotatable in unison, the shift element 104 of the
front wheel change speed mechanism becomes operable by
the control shaft 57. The splines 56 on the collar 55
comprise tapered teeth to be smoothly engageable by
the switching element 81.
The control shaft 57 is connected at the other end
thereof to a control lever 59 carrying an arm 60 to
which a return spring 61 is attached (Fig. 5a) to urge
the control shaft 57 to a position to provide the
standard four wheel drive mode. A stopper 58a and a
roll pin 58b serve to return the control shaft 57 to
the position to provide the standard Eour wheel drive
mode. As particularly described hereinafter, the
control lever 59 is operatively connected to a pitman
arm 68 whereby variations in the front wheel steering
angle are transmitted to the control lever 59 as one
of the factors indicating traveling conditions.
A front wheel steering system will be de,scribed
~irst with reference to Figs. 5 and 6. An output of a
steering wheel 1~1 is transmitted through a steering
shaft 15, a bevel gear mechanism 16 and a joint rod
- 1 0 -
~ 7~
18 to a steering gear mechanism 19. The output is
doubled at the steering gear mechanism 19 for oscil-
lating the pitman arm 68 connected to knucle arms 70
o~ the front wheels 1 through tie rods 69, on a
vertical axis P1.
An interlocking structure between the pitman arm
68 and the control shaft 57 will be described next.
As shown in Fig. 5a, a cam plate 6~ is fixed to the
pitman arm 68, and a cam arm 66 is provided to be
oscillatable on a vertical axis P2 disposed sideways
from the pitman arm 68. The cam arm 66 includes a pin
67 projecting downwardly from an intermediate position
thereof into a cam opening 65 defined in the cam plate
64. A free end of the cam arm 66 is connected to the
control lever 59 through a release wire 63 and a
displacement adjusting spring 62.
The cam arm 66 is not operated by an oscillation
of the pitman arm 68 up to a rightward or leftward
position C. When the pitman arm 68 is oscillated
rightward or leftward beyond the position C as shown
in Fig. 5b, a camming action between the cam opening
65 of the cam plate 6~ and the pin 67 of the cam arm
66 causes the cam arm 66 to draw the release wire 63,
whereby the control lever 59 of the control shaft 57
is moved to a position to provide the front wheel
accelerating drive mode. In other words, an output of
~7~4~7
th~ pitman arm 68 constituting traveling condition
detecting means is transmitted to the control sha~t 57
constituting a first control means 50 for -the front
wheel change speed mechanism 10, and finally to the
S shifter 51 thereby to switch the wheel drive modes.
This first control means 50 functions to switch
between the front wheel accelerating four wheel drive
mode and the standard four wheel drive mode.
A second control means 80 will particularly be
described hereinafter with reference to Figs. 4, 1 and
8. The second control means 80 is operable to estab-
lish and break the connection between the control
shaft 57 of the first control means 50 and the control
element 54 for sliding the shifter 51 for the front
wheel change speed mechanism 10. The transmission
case 6 supports on a lateral wall thereof a pivot
shaft 95 extending transversely of the tractor. The
pivot shaft 95 includes a boss 94 oscillatable on an
axis P3 thereof, and a U-shaped bracket 93 is attached
to the boss 94 to extend normal thereto. The U-shaped
bracket 93 carries at a free end thereof a control arm
85 including a boss 86 oscillatable on an axis P4 of a
pin disposed longitudinally of the tractor. The
control arm 85 has an extreme end thereof extending
into an elongate groove 82 defined in a top portion of
the switching element 81 whereby the control arm 85 is
-12-
~71~;~7
operatively connected to the switching element 81. A
spring 83 is provided to urge the switching elemen-t 81
to the position A for providing the standard four
wheel drive mode. The boss 86 of the control arm 85
carries a lever 87 fixed thereto and defining a slot
88 at an extreme end thereof to receive a pin 89
provided at a lower end of a control rod 90. The boss
94 further carries a connecting member 92 extending
axially thereof. The connecting member 92 carries a
sleeve shaft 91 at one end thereof, and the control
rod 90 is fitted in the sleeve shaft 91. The control
rod 90 has a top end extending tc the driver's section
13 and carries a guide pin 96 in a region of the
driver's section 13. The guide pin 96 extends into an
L-shaped guide groove 97a defined in a cover 97 dis-
posed in the driver's section 13. Number 98 denotes a
retainer comprising a leaf spring for retaining the
control rod 90 in operative positions. Number 99
denotes a switch for detecting the positions of the
control rod 90.
~n interlocking arrangement for the front wheel
change speed mechanism 10, first control means 50 and
second control means 80 will particularly be described
next.
When the control arm 85 is oscillated about the
axis P4 by pulling-the control rod 90 upwardly along
-13-
the guide groove 97a to a position shown at III in
Fi~. ~, the switching element 81 comes into en~agement
with the splines 56 of the collar 55 to place the
control shaft 57, and hence the pitman arm 68, in
operative connection with the shift element 104 of the
~ront wheel change speed mechanism 10 through the
control element 54 and shifter 51. This state permits
the front wheel change speed mechanism 10 to automati-
cally switch to the front wheel accelerating drive
mode with a displacement exceeding a predatermined
amount of the pitman arm 68 which corresponding to the
steering angle which constitutes one of the factors
showing the travelling conditions. In other words,
the upward movement of the control rod 90 along the
guide groove 97a permits the first control means 50 to
control the front wheel change speed mechanism 10.
When the control rod 90 is pushed downwardly along
the guide groove 97a to a position shown at II in Fig.
8, causing the control arm 85 to oscillate clockwise
about the axis P4, the switching element 81 disengages
from the splines 56 o the collar 55 thereby breaking
the operative connection between -the control element
54 and the control shaft 57. Then, the displacement
of the pitman arm 68 or rotation of the control shaft
57 is no longer transmitted to the front wheel change
speed mechanism 10.
-14-
1 ~7~4~
When the control rod 90 is oscillated about the
axis P3 along the lower arm of the L-shaped guide
groove 97a, the control 85 is oscillated in unison
therewith and the control arm 85 and switching element
S 81, respectively, move to positions corresponding to a
position indicated at I in Fig. 8. ~s a result, the
shift element 10~ of the front wheel change speed
mechanism lO moves to neutral position as shown in
Fig. 9~ whereby the tractor is driven by the two wheel
drive mode.
When the second control means 80 is in the
position to permit changeover between the standard
four wheel drive mode and the front wheel accelerating
four wheel drive mode, the switching element 81 and
the collar 55 are connected to each other as noted
above. Therefore, with a counterclockwise rotation of
the control shaft 57 in Fig. 7 resulting from a dis-
placement in a certain amount of the pitman arm 68,
the switching element 81 and the control element 54
also rotate together to switch the wheel drive modes.
At this time the control arm 85 of the second control
means 80 does not interfere with the switching element
81 owing to the elongate groove 82 of the switching
element 81.
~5 As described, the second contro] means 80 has
three operative positions; one corresponding to the
-15-
two wheel drive mode, another corresponding to the
standard four wheel drive mode, and the third position
for permitting the first control means 50 to eEfect
changeover between the standard four wheel drive mode
and the front wheel accelerating four wheel drive
mode. The first control means 50 is adapted to effect
the changeover provided that the second control means
80 is in the position to permit the changeover.
For detecting the traveling conditions, depres-
sions of side brake pedals may be employed in place ofthe displacement of the pitman arm. The side brake
pedals are provided in a pair corresponding to the
right and left wheels, and to enable the tractor to
make a small sharp turn the wheel on the side to which
the tractor turns is braked.
An interlocking arrangement between the side brake
pedals 201 and the control shaft 57 of the first
control means 50 will be described with reference to
Fig. 10. As seen, the side brake pedals 201 have
support bosses from which lever arms 202 extend
upwardly, respectively. The lever arms 202 define
slots 204 through which a pin 203 extends. The pin
203 is supported at opposite ends thereof by a U-
shaped member 206 operatively connected through a
release wire 63 and a spring 62 to the lever 59 at the
end of the control shaft 57. The control shaft 57 is
-16-
4;~
urged by a spring 61 to the s-tandard drive position,
and the rotation beyond the standard drive position is
prevented by a stopper 58a and a roll pin 58b.