Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1~79~46
This invention relates to a stretch control device for
use when laminatinq or joining two strip materials, the modulus of
elasticity of one material beinq greater than the other.
In a disposable diaper assembly line, two webs of
materials, each of which has a different modulus of elasticity,
are fed to means for joining or laminating the web materials. The
material having less elasticity or otherwise designated master
material is drawn off its supply roll and fed to the laminating
means and has a predetermined stretch.
The use of the material having less elasticity as the
master material is a desirable compromise which permits a greater
range of elasticity in the materials being used without
necessitating critical adjustments in the feed of the materials
being joined or laminated.
The prior art shows use of control systems to achieve
constant tension on individual or all materials to be laminated
and required operator skill and careful monitoring of quality of
the final laminate. This is disclosed in an article entitled "The
Art of Roll to Roll Adhesive Laminating", as published in
Converter magazine, December, 1981.
12~79246
Load cells and dancer arms have been used in the past
to control the tension on a web being fed as disclosed in United
States Patent No. 2,753,128, as well as Japanese Patent No.
44-12163 and British Patent No. 1,371,760.
United States Patent No. 2,627,296 to Secrest dis-
closes an apparatus including means for adjusting the tension in
a web of fabric.
United States Patent No. 3,239,161 to Dutro et al
; discloses a drive control mechanism which dispenses an elongated
web of material with the speed and tension thereof being adjust-
able.
The United States Patent No. 3,510,374 to Walker
discloses a control apparatus for sensing a property of a moving
web and adjusting the moving web so that the desired property is '
~ uniform throughout the web.
'¦ United States Patent No. 3,107,679 to Pawlowski
j discloses an automatic tension control device which utilizes
either pneumatic or electrical circuitry to maintain the tension ¦
in a web of material substantially constant.
Ij In United States Patent No. 3,762,125 to Prena, there
¦l is disclosed a device for controlling the lamination of one
material onto another material which utilizes a photocell 50,
which is responsive to indicia 48 on the film "F" which sends
¦~ the information to a control box 34 of a clutch 39 which controls
the stretch rollers 38a and 38b to thereby keep the two webs
lined up with one another.
-3-
1~7~46
62301-1353
Un1ted ~tates Patent No. 4,34~,g93 to Leonard discloses
a tension monitoring and controlling means which includes a
controller responsive to outputs of the tension sensing transducer
thereof a reference tension selector for controlling torque
applied to the tension control roll to thereby control the web
tension.
~IU~ AI~ U~ ITII`~
It is, therefore, the primary object of this invention
to achieve equal stretch on two materials being laminated or
joined as they are pulled off their supply rolls and fed to be
laminated.
The invention provides a method of laminating a first or
master material and a second material of greater elasticity than
the master material which comprises feeding the materials to
laminating means and determining the stretch in each material as
it is laminated and applying a variation in tension to the second
material so that it arrives at the laminating means with
substantially the same tension as the master material.
The invention also provides a stretch control device for
material to be laminated comprising means for feeding a master
material at a fixed tension to laminating means, a supply roll of
a second material havlng greater elasticity than the said master
material, means for feeding the said second material to the said
laminating means, means for measuring and calculating the amount
of stretch in each material, and means for varying and applying a
calculated tension on the said second material as it is fed to the
said laminating means so that the stretch on the second material
,
1 279246
62301-1353
will be the same as that on the said master material.
From another aspect, the invention provides laminating
apparatus for laminating a master material and a second material,
each of unknown modulus of elasticity, including laminating rolls,
means for feeding each material along its own flow path to the
laminating rolls, and, for each material, in its flow path,
tension measuring means, and spaced linear speed measuring means
located at different positions in the respective flow path,
microprocessor means for receiving at least one tension signal and
two linear speed signals for each material from which the modulus
of elasticity of each material can be calculated, and means
responsive to an output from the microprocessor for varying the
tension, and hence the degree of stretch, of said second material
to match its stretch to that of the master material at the
laminating rolls.
4a
~`..
1'~79246
By way of illustration but not limitation, an embodiment
of this invention will be hereinafter described with reference to
the drawing, in which:
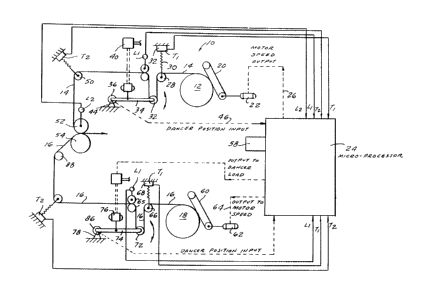
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a stretch control
device according to the present invention.
With continuing reference to the accompanying drawing,
wherein there is shown a schematic representation of a stretch
control device 10 according to the present invention, a supply
roll 12 of a master material 14 is provided. The modulus of
elasticity of the master material 14 is unknown but the master
material 14 is less elastic than a second material 16 to be
delivered from its supply roll 18. The modulus of elasticity of
material 16 is also unkown.
A friction belt assembly 20 driven by motor 22 is
provided for providing initial tension on the master material 14
as it unwinds the master material 14 from the feed roll 12.
The speed of motor 22 is controlled by a microprocessor
(computer) 24 as an output 26, based on the position of dancer arm
34.
The master material then passes over roll 28 which
may be spring mounted as at 30 from a load cell 32. The master
material 14 is fed over an idler roll 32 of adjustable dancer
arm 34 which is pivotally mounted at 36. At equilibrium, the
1~'79Z46
tension in the web at 30 is created by the moment of the load on
the dancer arm as manually set or controlled by a pneumatic or
hydraulic assembly 40 connected to the dancer arm 34. A potentio-
meter or rotational sensor 44 measures the position of the dancer
arm 34 and provides an input 46 to the micro-processor 24 which
is used to determine a speed correction for the unwind motor 22.
The master material 14 is then fed over another roll 50 and then
between laminating rolls 52 and 54 where it meets with the web
material 16.
The second material 16 is of greater elasticity than
the first material and the micro-processor provides for auto-
matically controlling the feed system for the second material 16.
These outputs of the micro-processor 24 are readable off the
micro-processor portion 58.
An endless belt assembly 60 driven by a motor 62
feeds the material 16 as it is fed from its supply roll 18. The
speed of the motor 62 is one of the outputs 64 of the micro-pro-
cessor 24 and is automatically controlled by the micro-processor
24. The material 16 is entrained about roll 66 which is connected~
;I to a load cell 68 for measuring tension on material 16. The ten-
l sion in material 16 is created by the load necessary to lift the
dancer arm to a stable position. The load setting is an output
of the micro-processor 24. The material 16 is entrained about the
jl idler roll 72 of dancer arm 74, whose position is determined by
the amount of material in the machine between the s~pply roll 18
-6-
1.
1279Z46
and the first set of rolls 65 and the elasticity of that material
for the tension level required to support the dancer arm. The
control method for keeping the dancer arm stable or at mid-range
is to adjust the unwind motor speed automatically to correct
the dancer arm position. For a given material, tension and
feed roll setting, there will be only one correct unwind speed
at stability. ~he dancer arm is pivotally mounted as at 78 and
its position may be monitored by a potentiometer or rotary sensor,
or other means. The dancer arm may be of any of the well-known
recognized types, such as pivoted vertically or multi-pass units
or linearly-transported dancer rolls.
The material 16 is then passed to the laminating
rolls 52 and 54 where the material 16 will join the master
material 14 with the same stretch thereon so that, when these
materials are laminated or joined together, there will be little I
or no warping or breakage and there will be no curling at relaxa-¦
tion after cut-off.
From a consideration of the arrangement of parts,
either feed system heretofore described can be used for the
master material, the inputs to the micro-processor being set
dependent on the system used for the master material. This
provides for a greater range of materials since the stretch on
the more elastic material can best be adjusted to equal the
stretch on the master material as the resulting change in total
tension in the laminate of the two webii will be reduced.
~1
I! ~ ~