Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
3~i
ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INV~NTION
This invention relates generally to an
electromagnetic clutch, and more particularly, to an
improved connecting structure between an armature plate
and a hub of an electromagnetic clutch, for transmitting
rotational force supplied by a pulley to the drive shaft
of a compressor.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure l is a cross-sectional view of a
conventional electromagnetic clutch.
Figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a second
conventional electromagnetic clutch.
Figure 3 is a cross-sectional view of an
electromagnetic clutch in accordance with the present
invention.
Figure 4 is a front view of the electromagnetic
clutch of Figure 3.
BACKGROUND OF l~E INVENTION
A conventional electromagnetic clutch with an
elastic member for easing the impact force transmitted
to the drive shaft of a compressor is disclosed in U.S.
Patent No. 3,774,739 to Higuchi, and is illustrated in
Figure 1. The clutch comprises pulley l which is
supported on bearing 2 and is rotated by an automotive
engine through a belt (not shown). Pulley 1 is formed
of a magnetic material in which one or more concentric
arcuate or annular slits 3 are formed to define a
plurality of concentric annular magnetic poles. Hub 5
is fixed on the terminal end of drive shaft 4. Holder
plate 8 and the outer end portion of hub 5 are formed
with concentrically disposed cylindrically shaped
flanges 81 and 51. Rubber member 9 is disposed in the
space defined between axial flanges 81 and 51.
Therefore, armature plate 6 is connected to hub 5
through holder plate 8 and rubber member 9. Rubber
member 9 therefore functions to ease the transmission of
~'i'
~'
~ 3 ~ ~
sudden torque changes to the drive shaft. These sudden
torque changes impart an impact force on rubber member 9
which induces a bending or shearing stress on the rubber
member. This intermittently applied stress to the
rubber member may cause the rubber member to crack and
eventually be destroyed.
One solution to overcome the above mentioned
disadvantages is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,624,354
to Koitabashi and is illustrated in Figure 2. This
electromagnetic clutch comprises holder plate 8' and
outer end hub 5' both of which are provided with
concentrically positioned polygonally shaped axial
flanges 81' and 51', and rubber member 9' which is
disposed between axial flanges 81' and 51'. The
polygonal shape reduces the shearing stress in the
rubber member and the durability of the rubber member is
thus improved.
However, the rubber member used in both of these
conventional electromagnetic clutches is affixed on the
axial flanges 81' and 51' by adhesive materials, and the
adhesive strength of the adhesive material fails with
the passing of time. As a result, the rubber member
becomes detached from the surface of axial flanges 81'
and 51'. Also, the adhesive portion of the rubber
member may be damaged.
SUM~ARY OF THE INVENTIO~
It is an object of an aspect of this invention to
provide an electromagnetic clutch with a mechanism for
easing the impact force transmitted to the drive shaft.
It is an object of an aspect of this invention to
provide an electromagnetic clutch with improved
durability of an elastic member which connects the drive
shaft to the clutch.
An electromagnetic clutch according to an aspect of
the present invention includes a first rotatable member
with an axial end plate of magnetic material, and a
~ 3~ ~
second rotatable member se.cured on a hub. The hub
includes a radially extending flange portion~ An
annular armature plate is concentrically disposed on and
radially surrounds the outer peripheral portion of the
hub with a gap therebetween. The armature plate faces
the axial end plate of the first rotatable member with
an axial air gap therebetween. An electromagnetic means
is disposed within the first rotatable member for
attracting the armature plate to the axial end plate of
the first rotatable member. A holder plate is fixed on
an axial end surface of the armature plate and is formed
with a first axially extending flange portion. The
radial flange portion o~ the hub has a second axially
extending flange portion. The first and second axial
flanges are polygonally shaped and face one another with
a radial gap therebetween. An elastic member is
disposed in the radial gap and, therefore, the impact
force is eased by the compressive deformation of the
elastic membex when the clutch is engaged. Excessive
twisting deformation of the elastic member is thus
prevented.
Another aspect of this invention is as follows:
In an electromagnetic clutch comprising a first
rotatable member having an axial end plate of magnetic
material, a second rotatable member and an armature
plate of magnetic material joined to the second
rotatable member so as to be capable of limited axial
movement, said armature plate facing said axial end
plate of said first ro~atable member with an axial air
gap therebetween, and an electromagnetic means
associated with said axial end plate for attracting said
armature plate into engagement with said axial end plate
whereby the rotation of said first rotatable member can
be transmitted to said second rotatable member through
said armature plate by the operat:ion of said
electromagnetic means, the improvement comprising: a
3S
holder plate affixed to the outer axial surface of said
armature plate and formed with a first axial flange
portion ext~nding outwardly from said armature plate,
said first axial flange portion having a configuration
including at least one straight line, said second
rotatable member having a second axial flange portion
extending outwaxdly from said armature plate, said first
and second axial flange portions having inner and outer
surfaces facing one another with a radial gap
therebetween, said first axial flange portion having a
radial flange at one end thereof extending toward said
second axial flange portion, said second axial flange
portion having a radial flange at an end opposite said
one end of said first axial flange portion extending
toward said first axial flange portion, and elastic
means disposed between the inner and outer surfaces of
said axial flange portions and said radial flanges
within the radial gap for limiting the relative rotation
between said first and second axial flange portions by
the compression of said elastic means when said armature
plate engages said axial end plate upon operation of
said electromagnetic means.
Further objects, features and other aspects of this
invention will be understood from the following detailed
description of the preferred embodiment of this
invention while referring to the annexed drawings.
DETAIIED DESC,'RIPTION
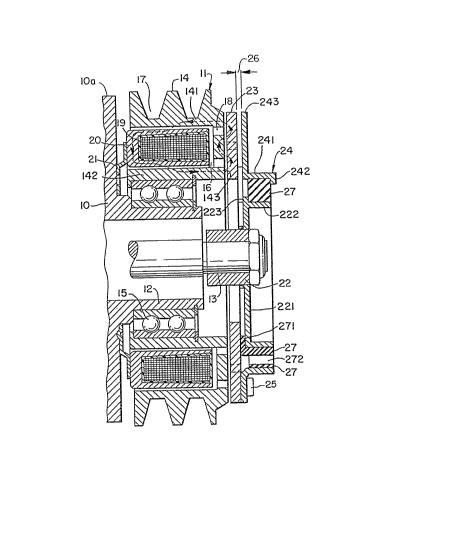
Referring to Figures 3 and 4, which illustrate an
electromagnetic clutch 1~ in accordance with the present
invention, the clutch is shown assembled on compressor
10 for an automotive air conditioning system.
Compressor housing lOa is provided with cantilevered
tubular extension 12 surrounding drive shaft 13 of the
compressor. Drive shaft 13 is rotatably supported in
the compressor housing lOa by a bearing (not shown).
~,7 9 ~t3
4a
Pulley 1~ is rotatably supported on tubular
extension 12 through bearing 15 which is mounted on the
outer peripheral surface of tubular extension 12.
Pulley ~4 is made of magnetic material, such as steel,
and comprises outer annular cylindrical portion 141,
inner annular cylindrical portion 142 and axial end
plate portion 143 connecting outer and inner cylindrical
portions 141, 142. Annular U shaped cavity 16 is thus
defined between these three portions 141, 142 and 143.
Annular V-shaped grooves 17 are provided on the outer
peripheral surface of cylindrical portion 141 of pulley
14 for receiving a V-belt (not shown) for coupling the
compressor to the output shaft of an automobile enyine
(not shown).
Axial end plat~ portion 143 includes one or more
concentric slits 18 which are disposed on one or more
concentric circles, so that a plurality of annular or
arcuate magnetic portions are defined, with the magnetic
surfaces being on the axial end surface of axial end
plate portion 143.
33~
Electromagnetic coil 19 is dispoæd in annular cavity 16 OI
pulley 1~. Coil 19 35 contained within annular magnetic coll
housing 20 having a U-shaped cross section. Coil housing 20 is ~ixed
to supporting plate 21 which is secured to compressor housing lOa.
Coil housing 2(l is thus maintained within cavity 16 out oi contact
wlth pulley 14 by a small gap.
A hub 22 is secured to an ex~ending terminal end OI shaft 13.
Hub 22 has a radial Ilange portion 221 extending radially outward.
Ring plate or armature plal:e 23 is disposed ad~acent the outer
peripheral sur~ace OI flange por~ion 221 with an annular radial gap
therebetween~ Armature plate 23 iaces the axial end plate
portion 143 o~ pulley 14 with a predetermined axial air gap
~herebetween.
In this construction, holder plate 24 Is fixsd o~ the outer a~dal
end su~ace of armature plate 23 by a plurality oi rivets 25. Holder
plate 24 is provided with a first a~al Ilange 241 whi~h extends
axially outward irom the inner end portion oi plate 24 and is formed
in a triangula~ shape. An arc shaped disc portion 243 extends radi-
ally outward at one side oi trlangular flange 241, as shown ln Figure
4. Each straight ~ne portion of triangular Slange 241 is connected
with on~ another through an arc~haped corner. The configuration
OI ~lange 241 thus consls~s oE a plurality of line and arc portions.
Axlal gap 26 is Iormed betwe~n the axial end surface OI armature
plate 23 and the axial end portion of flange 241, as shown in
Figure 3.
Hub 22 is iormed wlth second axial flange portion 222 which
extends axially outward from the outer end portion oI radial flange
portlon 221. Second axial flange portlon 222 corresponds in shape to
9~35
Ilange portion 241 and Iaces ~lange 2~1 with a radial gap
therebetween.
Elastic member 27, i.e., a rubber member, is dispo~ed in the
gap deIined betwe~n the inner suriaces OI flange portions 222 and
241. The lnner surfa~e oi elastic member 27 is fixed on the outer
sur~a¢e o~ axial ilange portion 222 o~ hub 22 by vulcani ation, and
elastic member 27 is fixectly dispoæd within the gap so as to
urged radially inward by axial flange 241. Alternatlvely, iY first and
s~cond fixed ~lange portions ?42, 223 are Yormed on the outer te~
minal end m first a2~a~ Ilange 241 and the outer termin31 end ot
radial ~lange 221, respectively, to restrl~t the axial movement o~
elastic membsr 2~, elastlc member 27 will be able to maintain its
position in the radial gap without the use any special a~fixing
method. Ther~ore, armature plate 23 maintains its static position
to i ace the a~al end plate portion 143 with an axial air gap
there~etween by the recoil strength oi elastic member 27.
In thi~ construction, if coil 19 is not energi~ed, armature
plate 23 Is separated irom pulley 14 by the reeoil strength of elastis~
member 27 and maintain~ the desired air gap. Thereioret only
puUey 14 w~ be driven by the engine oî the automob~e, and the
compressor wlll not be operated. When coil lg is energized, how-
ever, armature plate 23 is attracted to pulley 14 by the magnetic
Il~ which is created by the energization o~ ~o~ 19 and indicated by
th2 dotte~l lina ln Flgure 3 and elastic m~mber 27 is bent ln the axial
direction. The rotating motion o~ the au~omotive engine ls transmit-
ted to drive shait 13 OI the compressor through puL~ey 14, armature
plate 23, holder plate 24, elastic member 27 and hub 22.
At the moment armature plate 23 contact~ the axial end plate
portion 143 oi pulley 14, elastic member 27 receives an impact iorce
,., ~
.~..v' ;
,..
7~3~
causecl by the torque o~ holder plate 24. However, the lmpact rOrce
is eased by the deIormatlon o~ elastic member 27. That ~s, relative
rotating motion ~etween the a~cial rlanges is limited and excessive
shearing stress actlng on the rubber member wlll be reduced to
thereby prevent the rubber member irom becoming damaged.
Elastic mernber 27 ~s provided with extended portions 271
whlch extend radially inward at each corner thereoI. Extendlng
portions 271 ar~ ~ixedly disposed between iirst radial ~lange
pornon 2~1 o~ hu~ 22 and the outer end sur~ac~ of armature plate 23
by se~uring rivets 25~ These portions help to ensure tha~ the rubber
member w~ not move. ~ order to redu~e the temperature o~ rubber
member 27 during operation ~ the devlce, communicat1ng holes 272
are iormed through each corner to allow air to ~low bgtwe~D the
axial gap a6 and ambient space. ThereIore, heat iatigue OI rubber
member 2~ wlll be reduced.
Thi~ lnvention has been des~ribed in detail in connection with
the preferred embodlments only and the inv~ntion is not r~tricted
thereto. It ~rlll be easily unde~stoodl by those skllled in the art that
other variations can be made within ths scope oi the lnven~ion.
. . .
, .... .