Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
lZ~6~6
--2--
State of the Art
Laminated sheets of synthetic resin of the kind described above,
as well as methods for hot-forming such sheets are known from
German patent 28 23 669. In this known ~ethod, the bending.
plate executes during the bending operatlon a rotary motion.
around an axis that coincides with the'axis of the cylindrical
surface around which the sheet is being bent, with the bending
plate performing a slidlng motion relative to the surface of
the border region of the sheet that is to be bent, and with
which it is in constant planar contact. The'frictional forces
acting during this sliding motion on the surface of the border-
range of the sheet that is to be bent counteract a tendency
of the sheet to split in the bending regionalong the bonding
agent seams., as the applicant found out later. This splitting
is also counteracted in the aforementioned known methods by
form-holding parts which after the bending operation hold the
bending region or the border region, respectively, in its bent
or deformed form, at least until the resolidification of the
bonding agent. As a form-holding agent, e.g., a strip-shaped
press die with a concave cylindrical pressure surface may be
used, which after the bending operation is pressed against
the convex surface of the bent sheet region.
Experience has shown that in the aforementioned known'methods
the pressure surface of the form-holding parts must very precisely
match the sheet surface that has a convex bend in the bending region.
,, . q
lZ916iS
-3- 26129-16
with greater thickness tolerances of the sheet, the risk obtains
that in the event of a greater thickness deviation upwards,
the edges of the pressure surface of the form-holding part will
press against the sheet surface in an undesirable manner. In
addition, a separate form-holding part is required for each
bending radius and each sheet thickness.
Description of the Invention
It is the object of the invention to indicate a method
of the kind mentioned above for the hot-forming of laminated
sheets of synthetic resin, which are composed of several hot-
forming laminate layers containing a duromer plastic and planar
carrier materials, between which are inserted layers of a thermo-
plastic bonding agent, with the method of the invention making
do without the use of special form parts matching the convexly
curved sheet surface.
The problem set the invention is solved by a method
for hot-forming a laminated sheet of synthetic resin which is
composed of several hot-forming laminate layers containing a
duromer plastic material and planar carrier materials, between
which are inserted layers of a thermoplastic bonding agent,
by which method the sheet in at least its region that is to
be deformed is heated to the forming temperature which is equal
to or higher than the melting temperature of the thermoplastic
bonding agent, and whereupon, for the purpose of bending a border
region of the sheet that in its final form is flat, it is bent
around a cylindrical surface with the aid of a movably guided
bending plate, and is cooled; the bending occurring in such a
manner that at least during a large part of the bending operation
~2~
-3a- 26129-16
the bending plate will be in planar contact with the border
region of the sheet that is to be bent, and the individual
laminate layers will be mutually displaced in the bending region
and in the border region in the direction of the sheet's surface,
and whereat, after the bending operation, the bending plate
holds the border region in its bent position at least until
the resolidification of the thermoplastic bonding agent, wherein
in a last phase of the bending operation the bending plate is
constantly guided in such a manner that each point of its bending
surface has an essential component of mot.ion in a direction
parallel to the plane of the bent border region, and that,
appropriately, a prebending element is provided connected with
the bending plate, which in its motion during a first phase
of the bending operation presses against the border region of
the sheet to be bent and thereby prebends it.
' - 1;~6~ , ,
By guiding the bending plate according to the method of the
invention, a substantial sliding motion between the bending
plate and the sheet's border region to be bent obtains also
shortly before the end position of the bending plate is reached,
. whereby the frictional forces transferred to the outer laminate
. layer of the sheet such a great traction in the direction of
the sliding motion acts on this laminate layer that it surely
prevents a splitting of the sheet along the bonding agent seams
In the bending plate's end position, it presses the bent border
region of the sheet against a counterpressure surface, whereby
the bending region and the bent border region of the sheet
are fixed in the final form until the resolidification of the
thermoplastic bonding agent.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the method
of the invention is characterized by that the motion executed
by the bending plate in a last portion of the bending operation
is a rotary motion. During this rotary motion of the bending
plate, an angle of rotation between 15 and 45 is advantageously
covered.
In a further preferred embodiment of the invention, the method
of the inventlon is also characterized by that during an ini~ial
phase of this rotary motion, a translational motion is superimposed
on it in an at least nearly parallel direction to the plane
of the bent border region of the sheet.
lZ916~6
-5- 26129-16
According to a further preferred embodiment of the
invention, the method of the invention is additionally charac-
terized by that during the bending of the border region of the
sheet by about ~0, this rotary motion takes place at least
during a final period of this rotary motion around an axis of
rotation the distance of which from the plane of that surface
of the undeformed region of the sheet that changes over into
the convex surface of the bent sheet region is smaller than
half the distance of this plane from the bending surface axis,
and the distance of which from the plane of the outer surface
of the bent border region of the sheet is greater than double
the distance of this plane from the bending surface axis.
According to another preferred embodiment of the inven-
tion, the method of the invention is characterized by that the
prebending element performs a translational motion during its
engagement with the bent border region of the sheet in an at
least nearly parallel direction to the plane of the bent border
region of the sheet.
It is a further object of the invention to indicate
a device for bending a border region of a sheet by about 90,
which has a clamping device with flat clamping surfaces serving
to hold the undeformed sheet, wit}l one of the flat clamping
surfaces chanying over into a counterpressure surface by way
of an appropriately circular-cylindrical bending surface, and
which also has a bending plate that is pivoted on a mounting
for rotation around an axis parallel to the axis of the cylin-
drical bending surface and has a plane pressure surface and
J~
.i."'~t~
lZ916~6
-6- 26129-16
an adjusting mechanism, characterized by a cradle or sliding
carriage adjustable by one or more adjusting mechanisms, in
the direction that is at least nearly parallel to the counter-
pressure surface, in which cradle or sliding carriage the bend-
ing plate mounting is pivoted, so that in an end position of
the cradle or sliding carriage the distance of the axis of
rotation of the bending plate from the plane of that surface
of the undeformed region of the sheet that changes over into
the convex surface of the bent sheet region is smaller than
half the distance of this plane from the bending surface axis,
while the distance from this axis of rotation from the plane
of the outer surface of the bent border region of the sheet
is greater than the distance of this plane from the bending
surface axis, by one or more adjusting mechanisms to adjust
the cradle or sliding carriage, and a special pressure mechanism
for pressing the bending plate against the bent border region
of the sheet.
On the bending plate or on its mounting, a prebending
element appropriately shaped as a cylindr.ical body may be attached
or supported.
In a preferred embodiment of the device according
to the invention, it is characterized by that the adjusting
element for the bending plate is formed by a hydraulic adjusting
device engaging the bending plate or its mounting, which forces
on the bending plate a translational and/or rotary motion against
the resistance of the border region of the sheet that is to be
~X~6~6
-6a- 26129-16
bent. Advantageously, a stop is provided to limit the trans-
lational motion of the cradle or sliding carriage, which is
actuated even before the end of the rotary motion.
According to a further embodiment, the device
according to the invention serving to bend a border region of
a sheet by
16~6
- 7 - 26129-16
90 and which is provided with a clamping element with clamping
surfaces that is displaceable in a direction at least approximately
parallel to the counterpressure surface, is characterized by
that the hydraulic adjusting mechanism engaging at the bending
plate or its mounting is supported by the displaceable clamping
element.
According to a preferred embodiment oE the device of
the invention, the prebending element is formed by one or several
rollers or cylinders pivoted on the bending plate or its mounting,
and/or the plane of the pressure surface of the bending plate cuts
the body or bodies of the prebending element.
In the drawings which illustrate the embodiment of the
invention,
Figure 1 is a schematic section of the device in the
rest position;
Figures 2 through 4, also schematic sections, show the
device executing the steps of hot-forming a laminated sheet of
synthetic resin.
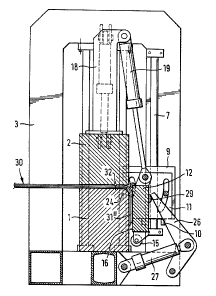
This device, shown in Figure 1 in its rest position,
is constructed substantially symmetrically to the plane of the
drawing. It shows a clamping mechanism in the nature of a down
stroke press, with two clamping bars 1 and 2, the longitudinal
extension which runs vertically to the plane of the drawing. The
lower clamping bar 1 is mounted in a bedplate which essentially
consists of two frames 3 arranged at both ends of clamping bars
1, 2, which
1291~16
frames are connected to each other by a base grate 4 with side
bars 5. At each of the two frames 3, two guide c~lumns 6 are
arranged to guide the upper, vertically adjustable clamping
bar 2, and guide column 7 to guide a base plate 9 provided
with blocks 8, wlth the vertical motion of said base plat~
downwards being defined by stops 10. :~ :
Guide plates 11 are pivoted on the blocks 8 of the base plates
9. The two guide plates 11 are connected by a beam-shaped
bending plate 12 whose longitudinal extension runs vertically
to the plane of the drawing. In the vicinity of the lo.wer
longitudinal edge 13 of the bending plate, rollers 15 serving
as prebending element are pivoted on several base supports
14 arranged along the bending plate 12, in such a ~anner that
the roller surfaces will project somewhat beyond the plane
of the bending plate pressure surface 16, which me~ns that
the plane oE this pressure surface 16 cuts through the ~odies
of these rollers 15.
Two hydraulic adjusting devices 17 acting between the two frames
3 and the upper clamping bar 2 serve to move the upper clamping
bar 2. In addition, two uprights 18 are mounted on the upper
side of the upper clamping bar, which at their upper ends are
pivoted on one end of the hydraulic adjusting devices 19, while
the other ends of these adjusting devices 19 are pivoted on
base supports 20 which are connected to the bending plate 12.
~29~61~i
g
The clamping bars 1, 2 have flat.clamping surfaces 21, 22,
with the clampiny surface 21 of the lower clamping bar 1 changing
over, through a circular cylindrical bending surface 23 wh~se
axis is indicated with 24, into a counterpressure surface
25 which is bent by 90 in relation to this clamping surface 21_
The clamping surfaces 21, 22, the bending surface ~3 and the
counterpressure surface 25 are cooled with the aid of a
cooling medium which circulates in suitable cooling channels
arranged in clamping bars 1, 2, which are not shown in the
figures for reasons of better clarity.
In addition, the device contains a pressure mechanism consisting
of two pressure levers 26 pivoted on the base grate 4, which,
with the aid/hydraulic adjusting mechanisms 27 acting between
the base grate ~ and the pressure levers 26, can be moved from
the rest position shown in Fig. 1 in the direction of arrow
28 and which are intended to work together with the stops 29
arranged at the back of bending plate 12.
To carry out the method for bending the border region of a
laminated sheet of synthetic resin, as described in German
patent 28 23 669, the sheet 30 is first heated in a separate
device /the forming temperature of about 160-170C and then
placed on the clamping surface 21 of the lower clamping bar 1
in such a manner that - as can be seen in Fig. 1 - it will
protrude with its border region 31 that is to be bent beyond
the edge of the clamping bar 1. By actuating the hydraulic adjusting
mechanisms 17, the upper clamping bar 2 is lowered and the sheet 30
~9~6~6
--1 o--
is wedged between the two clamping bars 1, 2 (see Fig. 2).
Together with the upper clamping bar 2, there is also lowered
the unit connected with it by way of the brackets 18 and the
hydraulic adjustment mechanisms 19, and consisting of the
base plates 9, guide plates 11, the bending plate 12 and the
rollers 15, and which unit is vertically displaceable along -
the guide columns 7, in such a manner that/the phase of the
method of the invention shown in Fig. 2, the rollers 15 serving
as prebending element contact the sheet's border region 31 that
is to be bent~
Subsequently, the hydraulic adjustment mechanisms 19 are acLuated,
as a result of which the bending plate 12 together with the
base plates 9 guided along the guide columns 7 and the rollers
15 that are connected to the bending plate 12 is lowered further
and the rollers 15 then prebend the sheet 30 o~er the circular
cylindrical bending surface 23, the radius of which is, e.g.,
30 mm, whereat the rollers 15 roll off along the sheet surface,
until the bending plate pressure surface 16 thereupon comes
into contact with the prebent border region 31' of the sheet
(see Fig. 3). In the course of the further thrust of the hydraulic
adjustment mechanisms 19, this bending plate pressure surface 16
adjoins the border region 31 of the sheet under pressure, and
slides along the surface of the border region and - by virtue
of the sliding friction - there applies on the upper laminate
layer of the sheet a force in the direction towards the edge
of the sheet, whereby a splitting of the sheet along the bonding
agen~ seams is prevented.
1~:916~6
~ 26129-16
Upon establishment of the planar contact between the pressure
surface of the bending plate and the prebent border region 31' of
the sheet, a rotary motion is superimposed on the translational
motion of the bending plate 12, whereat the relation between
translational and rotary motion results quite automatically from
that the pressure area 16 oE the bending plate is in constant
planar contact with the sheet's border region that is to be bent.
Fig. 3 shows the position of the device during this phase of the
bending operation.
During the further thrust of the adjustment mechanisms
19, the vertical translational motion of the bending plate 12 is
initially stopped by virtue of the base plates 9, on which the
bending plate 12 is pivoted, run up against the stops 10 and the
further thrust of the adjustment mechanisms 19 then serves exclu-
sively to continuing the rotary motion of the bending plate 12.
In this last phase of the bending operation, the bending
plate thus executes a purely rotary motion around an axis 32 (see
Fig. 4) which lies approximately in that surface of the undeformed
region of the sheet, which changes over into the convex surface of
the bent region of the sheet and whose distance from the plane of
the outer surface of the bent border region of the sheet is
greater than the distance of this plane from the bending surface
axis 24. From this it results that also in this last phase of the
bending operation, each point of the pressure surface 16
'`1
129~6~6
-12-
of the bending plate, in particular also just b~fore the bending
plate comes to a halt at the end of the bending operation,
has an essential motion component in the direction parallel
to the plane of the bent border region 31" (see ~ig. 4), which
means that also immediately before he end of the bending operation,
the pressure sur~ace 16 of the bending~plate and the surface
of the p~ebent border region 31' of the sheet slide towards
each other and by virtue of the forces acting on the uppermost
laminate layer in the direction of the laminate surface by
virtue of the sliding friction prevent a splitting of the sheet
at its bonding agent seams.
To support the momentum of the rotary motion of the bending
plate 12 during this last phase o~ the bending operation 9,
the hydraulic adjusting mechanisms 27 are actuated immediately
after the base plates 9 run up against the stops 1~, pressing
the pressure levers 26 against the stops 29 mounted on the
rear side of the bending plate 12 and pressing the bending
plate 12 - after ending its xotary motion during a resolidifcation
period for the bonding agent seams - to the bent border region
31" of the sheet ~see Fig. 4).
Depending on the thickness of the sheet to be bent, the bending
operation lasts between 5 and 15 seconds, the resolidification
period between 4 and 6 minutes.
129~6~6
-13-
Commercial Usability
The bent laminated sheets of synthetic resin produced with
the aid of the method of the invention as well as with the
device according to the invention are used above all as self- .
supporting sheet parts provided with decorative surfaces, mainly
for furniture and the inside finishing and panelling of rooms,
especially for hospitals, L lumbing unit ~ and sanitary cabins,
~,