Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
GEARLESS TRANSMISSION
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention is directed to a gearless
transmission and to a power transfer system. The system is
of particular utility in the hoisting field.
BACKGROUND TO THE INVENTION
Hoist systems are frequently used wherein a
plurality of shaft drlven winding drums carry the cable by
which the platforms or cars are raised and lowered. The
required synchronization of drive shaft rotations is provided
by a geared t~ransmisslon, having a series of gears in meshing
relation connecting the respective shafts.
Such prior art arrangements suffer from a number of
disadvantages. Gears inherently generate vibration and, due
to the provlsion of necessary tooth clearances, restrictions
on tooth profiIes and~the occurrence of wear, almost
inevitably develop signlflcant backlash. This adds to the
generation of friction and noise, while reducing the
efficiency of the system.
Owing to the limits~imposed by the cable fleet
angle, that is, the angle at which a~cable~is wound upon a
drum, it is; customary in many instances to install the
hoisting machinery and cable drums in a penthouse or machine
room, at the head of the elevator shaft. This necessitates
mounting the gear devices in a fashion such that vibration
therefrom~ lS transmitted to the structural steelwork of the
shaft and is fre~uently~ heard~ on many floors of the building
-- 1 --
.
:
- : , .. .
.
. , . . ~ ~ , ,
. - ~, ' '.' ', ' :, ; . .
~ . ' . '
4~9
as an objectionable noise and/or vibration.
Certain aspects of prlor art gearless transmissi.ons
are to be found in the following listed United States
patents; 327,741 Oct. 1880 True; 2,003,317 June 1935
Strandgren; 3,443,083 March 1969 Pope et al; 3,791,170 Feb.
1974 Schmidt; 4,072,061 Feb. 1978 Caflisch.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with the present invention there is
provided a gearless, multi-shaft synchronized transmission
using a displaceable force transfer plate in orbital force
transfer, synchronizing relation between the plurality of
shafts.
In order to avoid the possibility of jamming of the
transmission, or the creation of instability in the operation
of the transmission it lS necessary for the use of at least
three such shafts, the shafts being mutually parallel in side
by side misaligned relation, such that the respective polar
axes do not all lie in a common plane.
The present invention thus provides at least three
working shafts, one of which is externally driven, the
remaining shafts of the device being driven by a force
transfer plate. ~ ~
Thus there is provided a gearless transmission
having at least three parallel working shafts rotatably
mounted in bearings, for rotatlon in working relation about
their respective p~olar a~xis; each shaft having offset
connection means located adiacent one end of the
- 2 -
,'
transmission, the connection means each having an axle exten-
ding therefrom, projecting beyond the adjacent shaft end,
being parallel with and offset from the respective shaft
axis; a drive plate extending substantially normally to the
polar axes of the shafts and carrying at least three rotary
bearings, each bearing being connected in force transfer
relation with a respective axle; and, drive means connected
in force transfer relation with a shaft in rotational rela-
tion therewith, whereby in use, operation of the drive means
in force transfer rotational relation with that shaft pro-
duces orbital displacement of the drive plate about the
respective offset axles, and rotation of the working shafts
in mutually synchronized rotational relation.
In a preferred arrangement four such working shafts
are provided in mutually parallel, laterally spaced relation,
grouped about an axis located therebetween, with the drive
means connected in force transfer relation with a selected
one of the four shaft.
It will be appreciated that the drive means connec-
ted in rotational driving relation may comprise any suitabletorque transmitting agency connectable with the selected
shaft.
In the preferred embodiment a motor having a rotary
output shaft has that shaft directly connected in rotational
torque transfer relation with the selected shaft.
In many instances the drive means comprises an
electric motor.
-- 3 --
. .
-. .. . . . . . ... .
. .
?4~
In the case of a hoisting mechanism the rotatable
shafts are each provided with a drum portion to receive a
cable in wound relation thereon.
Reference hereinafter may be made to shafts having
a cable wound thereon. Such reference generally imputes the
provision of a drum portion upon the shaft by which to
receive the cable, in a taking-up and paying-out relation.
In the above recited four shaft arrangement, in use
each shaft has a cable wound thereon.
In one embodiment a level wind guide means is
located between the working shafts for axial displacement
relative thereto in cable guiding relation with the
respective shafts.
The level wind guide means has a plurality of guide
sheaves mounted thereon in mutually spaced relation
thereabout, and shaft means supporting the level wind guide
means between the working shafts for displacement along the
shaft means parallel wlth the worklng shafts.
The wind guide supporting shaft means is rotatable,
~0 being in threaded relation with a nut portion of the level
wind guide means, to selectlvely drive the wind guide means
in controlled axial displacement along its supporting shaft.
In a side delivery embodiment of the invention the
wind guide means incorporates a plurality of sheaves, one for
each working shaft, to receive a cable in axial positioned
relation, relative to a respective working shaft. The
pulleys are arranged by mountlng on the level wlnd guide
means to provide an off-going and on-coming cable guide
: - 4 -
:: :
. . .
,
:
- ~2~4~9
directed axially of the transmission. For that purpose cable
passage means are provided through the axial end structure
portions of the transmission, at one end thereof. ~o that
end, a centre portion of the drive plate is removed, to
permit unrestricted passage for the cables therethrough.
In one embodiment at least one of the offset
connection (crank) means may be provided with a counter
balance weight extending outwardly therefrom in at least
partial balancing relation with unbalanced portions of the
transmission. In a preferred embodiment, in addition to
balancing the out-of-balance mass of each of the cranks and
its related axle portion, an additional balance mass may be
provided, to at least partially off-set the out-of-balance
mass of the drive plate. This provision may be used to
further enhance the fly wheel effect provided by the drive
plate.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Certain embodiments of the present invention are
~0 described by way of illustration, without limitation of the
invention thereto, reference being made to the accompanying
drawings, wherein;
Figure 1 is a schematic plan view of a 4-shaft
gearless transmission in accordance with the present
invention;
Figure 2 is a front elevation of the Figure
arrangement;
... ~ `:
,
Figure 3 appears with Figure 7, and is a schematic
perspective view, partially in phantom of a 3-shaft gearless
transmission;
Figure 4 is a schematic plan view taken at the mid
section, as at 4-4 of Figure 2, showing further detail of a
hoist embodiment;
Figure 5 is a front end elevation of the Figure 4
embodiment;
Figure 6 is an enlarged view taken at 5-5 of Figure
4; and,
Figure 7 is an enlarged side elevation of a shaft
end detail.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
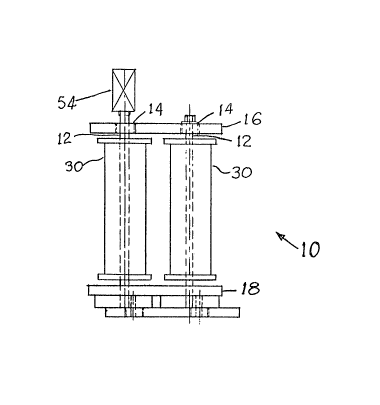
Referring to Figure 1 and 2, the gearless
transmission 10 has four shafts 12 rotatably supported by
bearings 14 betwe:en end plate 16, 18.
Referr1ng also to the Figure 3 embodiment 20, this
is illustrated as having three shafts 12 in bearings 14, with
end plates 22, 24.
:Each shaft 12 has an offset axle portion 26 each in
radially offset relation from the respective shaft axis 28.
The offset axis of axle portion 26 relative to the shaft axis
28 constitutes in effect a crank portion, from which the axle
25 26 extends. The axle portions 26 engage bearings 27 of drive
plate 29 :(shown in phantom in Figure 3, and shown in full
line in Figure 7).
.
: - 6 -
.
,
Referring to the Figures 5 and 7 embodiment, it
will be seen that each shaft 12 supports a ~rum 30.
The outer end 32 o~ each shaft 12 has a crank
member 34 from which an axle 26 extends, to engage the
respective bearing 27 of drive plate 29.
An aperture 38 in drive plate 29, and apertures 40
in end plate 18, in the Figure 7 embodiment, permit the
endwise, axial passage of wire ropes 42 from off the
respective drums 30, in winding and unwinding relation, by
way of the level wind guide means 44.
Referring to Figure 6, the level wind guide means
44 comprises a body 46 having four adjoining lobe portions,
with sheaves 48 rotatably mounted therebetween, in guiding
relation with wire ropes 42.
1~ A centrally located hollow nut portion 50 is
internally threaded, to receive a lead screw 52 (Figure 4) in
driving relation therewith. Rotation of the lead screw 52
serves to displace wire gui.de means 44 and its guide sheaves
48 axially in predetermined relation within the transmission
10.
A reversible motor 54 connects in rotational
driving relation with one of the shafts 12. Intermediate
reduction gears 56, 58 connect the drive motor 54 with the
lead screw 54 of the level wind guide means 44.
The horizontally extending wire ropes, of the
Figures 4 through 7 embodiments, may be trained about
intermediate guide sheaves, external to the transmission 10,
to hoist a cage or perform other useful work.
- 7 -
~.2~3~4~9
In operation, with the wire cables 42 carrying a
tensile load, operation of the motor 54 in an in-winding
sense produces rotation of shaft 12 and lead screw 52.
The rotation of the driven shaft 12 displaces drive
plate 29, by way of the respective offset axle portion 26, to
move the plate 29 in an orbital rotation of fixed
orientation,
The orbital rotation of plate 29 drives the
remaining three shafts 12 in precisely synchronized, in-phase
relation with the motor driven shaft 12.
The drum portions 30, having wire ropes 42 wound
thereon, rotate in synchronized relation, to wind-on or
pay-out the ropes 42, in accordance with the direction of
rotation of motor 54. The orderly winding of the ropes 42 is
controlled by the synchronized axial displacement of the
level wind guide means 44, which feeds the wire ropes 42 in
precisely controlled relation on and off the drums 30, by the
precise axial placement of sheaves 48.
The transmission is usually set up to provide a
wire rope fleet angle substantially of zero. That is to say,
the wire ropes extend tangentially from their respective
drums, and in a plane or planes normal to the main axes of
the drums.
In the absence of load transfer gears, the
mechanism operates substantially with no backlash, with
little noise and a-t high efficiency.
The inherent out-of-balance of the orbital drive
plate 29 may be counterbalanced, at least in part, by balance
masses 39, secured to and forming part of the cranks 34.
:
. . .
s9
It will be understood that the subject transmission
has a wide utility, and that the illustrated winding
mechanisms may be used in more orthodox fashion, with the
direct wire rope attachment, between load and drum, in
accordance with the invention.
- _ g _
'
- -