Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
~3~ 7~
EXPANDING PROBE WITH EXPANDABLE SEALS
--1--
Descr ! et ion
The invention relates to a fluld pressure loaded probe for
expanding a tube in portions and for slmultaneously fixing
several outer design elements such as cams, bearingsand gear
wneels, comprising a basic cylTndrical member as well as
sealing elements and spacer sleeves slId on alternately,
with the tube port70ns to be expanded belng marked off from
tube portions remaining undeformed, by the sealing elements.
A probe of the above-mentioned type is proposed In EP-A-
0 213 529 describing a process for simultaneously fixing several
drive elments, especlally cams, on a tube member by stmul-
taneously expanding the tube member In portions. The problems
connected with suitable sealing members are not dealt with in
detail; the seals referred to are slmple O-rlngs made of
rubber-elastic materials. Practical experience has shown that
for
such seals are not suitable/maklng probes available on a
production basis because when pressure is applied, the seal-
ing elements are squeezed Into the annular gap between
the tube member and the basTc probe member, and In consequence
they survive only a small nember of expanding operations.
There are various prior art probes for hydrau1ically ex-
panding tubes for fixing them in tube bases, in the case of
which O-rtngs of rubber-elastic materials, prior to being
pressure-loaded, are radially expanded in order to bring the
O-rings into sealing contact with the wall of the tube before
the annular space occurring is loaded with a pressure fluid.
, ,.~ .
-2-
For instance, frorn DE 33 12 073 C2 a probe is known in the
casa of which 0-rings are arranged in pairs and spaced apart
by a spacer sleeve slid onto the probe body, with the 0-rings
being able to stop against tensioning cones which may be brought
closer to each other. Tapered rings which are positioned on
the expanding cones and which may also be expanded radially
serve as additional supporting rings. Because of the necessary
length of the tensioning cones, such an expanding device is
not really suitable for being used in connaction with probes
for fixing several external design elements, nor are the 0-rings
suitable as sealing elements, even with a greater Shore hardness.
As the 0-rings are fr~ely movable on the expanding cones in
the axial direction, it~not possible accuractaly to determlna
the position of the seals when final seal1ng contact has to
be established. Therefore, in DE 34 08 8b3 C1, dealing with
the same probe, both tensioning cones facing each other are
unmovably fixed to the basic probe member, there is an additional
pretensioning cone facing in the opposite direction and arranged
on the basic probe member, and the spacer sleeve, the seals
and the supporting rings are jointly movable in one direction
relative to the basic probe member. The complicated shape
of the basic probe member represents a disadvantage, and it
is not possible to arrange multiple devices of this design
on one probe. Tne 0-rings used are not suitable for the
application mentioned ini~ially. Finally, EP 00 55 101 B1
discloses a probe which, similar to previously mentioned
probes,operates with 0-rings which are to run up against
expanding cones. This happens exclusively as a result of
the internal pressure applied. In this case, too, the
uncertain axial position of the seal when achieving the
sealing effect relative to the tube body is disadvantageous.
The rubber-elastic 0-rings are unsuitable for the reasons
mentioned above.
It is the object of the present invent70n to provide â probe
for simultaneously hydraulically expanding several individual
longitudinal portlons for the purpose of fixing design elements
of the above-clescribed type, which simultaneously permits
~ . .
L
--3--
position-accura~e expansion of the individual tube portions
so that they are accurately associated with the slid-on design
elements and which, while haviny a simple design, provides
improved sealing as compared to prior art probes for expanding
several longitudinal portions, ensures stable positioning of
the seals and an easy introduction of the probe into the tube.
The objective is achieved by providing a probe which is character-
ised by a device for bringing the spacer sleeves closerto each
other axially while simultaneously compressing and radially
expanding the sealing elements for pressing them against the
inside of the tube,and by means for limiting the axial travel
of at least part of the spacer sleeves relative to the basic
probe member. Such a probe design ensures that in a pre-
determined position with a small axlal tolerance, the sealing
elements arranged in pairs can be brought into sealing contact
with the tube and that the forces applied to the sealing elements
for expanding purposes remain within certain narrow limits.
According to a first preferred embodiment, a spacer
sleeve positioned between the regions to be expanded comprises
means for limiting the axial travel, which may consist of
radially inserted pins engaging axial grooves of limited length
in the basic probe member. Easy assembly of the modular probe
is essentially not adversely affected as the stop pins may be
threaded for example. According to a further advantageous
embodIment, the said pins may contain bores, thereby being
suitable for feeding pressure fluid into the portions to be
expanded and marked off by the sealing elements and/or for
draining leaking fluid from the portions positioned in between
and remaining unde-formed.
In a further advantageous embodiment, the seals are axially
layered, with the outwardly facing part viewed from the
pressure loaded annular space having a greater hardness in
order to avoid the familiar feature of material flowing away
into the annular gap, thereby embracing~inner more flexible
part so as to produce an approximately U-shaped cross-section.
,
~3~7~
--4--
According to a second preferred embodIment, the means for
limiting the axial travel comprise pressure spring elements
which are positioned wlthin the sealing elements and which have to be
wlth each other,
brought into to contact /thereby limiting the travel of the
spacer sleeves relative to each other and thus relative to
the basic member. In an advantageous embodiment, these
elements are designed as conical annulardiscs which, due to
axial compression, are at the same time increased in their
radial size and act as sealing elements themselves.
A preferred embodiment comprises a package of several such
discs the interior of which comprises a harder material
producing the returning forces and whose exterior is provided
with a softer sealing support. The conical rings are arranged
that
in such a way/in the load-relieved condition, as viewed from
the fluid pressure loaded annular chamber, they comprise
outwardly positioned Imaginary conical points.
The device for bringing the spacer sleeves axially closer
together preferably comprises a stop which~axially movable
on the basic member and which cooperates with a stop which
is axially fixed relative to the basic member, with both of
them embracing the sealing elements and the spacer sleeve.
It is particularly advantageous for the spacer sleeves of
the probe to be designed as straight tubular pieces with
axially normal end faces. Whereas the axially movable stop
may directly act on an outer spacer sleeve, it is possible
for the axially fixed stop to act on a specially designed
design element slid on to the tube end, for example a
driving pinion with a sleeve-shaped projection.
Preferred embodiments of the invention are illustrated in
the drawing wherein
Fig. 1 is a longitudinal section of a probe in
accordance with the invention.
. . ~ ..
~ r~
--5~
Fig. 2 shows a probe portion to Fig. 1 in a first
embodiment in a larger scale.
Fig. 3 gives details to Fig. 2 in a larger scale.
Fig. 4 shows a probe portion to Fig. 1 in a second
embodiment in the course of being expanded,
in a larger scale.
ig. 5 illustrates details to Fig. 4 in a larger scale.
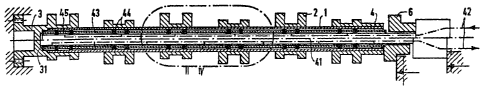
Fig. 1 shows a probe wtth a slid-on camshaft for a six
cylinder engine, with the camshaft consisting of a tube 1,
double cams 2 to be fixed on it and a drive plnion 3
combined with a double cam, with the drive pinion 3 being
slid on to the tube end in a sleeve-like way.
As can be seen in Fig. 2, the probe consists of a bas;c
member 41 with axially extending channels 42 for 5uppl y i ng
pressure fluid and draining off fluid leakages,as well as
slid-on spacer sleeves 43 and sealing assemblies 44. In
accordance with the positions of the portions to be expanded pre-
determTned by the positions of the cams 2, spacer sleeves 43, 45
of changing lengths have been slid on between which the seals 44
arranged in pairsare positioned. The last of the spacer sleeves
is axially supported on a shoulder 31 of the pinion 3 which
itself rests against a fTxed stop, and the device further
comprises a stop 6 which is axially movable relative to the
basic probe member and which is shown in two positions. Dis-
placement of the stop 6 results in the chain of spacer sleeves
43, 35 coming closer to each other, thereby causTng the sealIng
elements to be compressed and expanded, as can be seen in the
following Figures.
The details to Fig. 3 indicate that the seals 44 consists of
a first ring 441 made of a harder, more resistant material
and of a second ring 441 made of a rubber-elastic material
and positioned towards the pressure loaded annular space.
~ 3 ~
-6-
Whereas the sealing element illustrated on the left indicates
the condition prior to pretensioning the sealIng elements with
a greater axial length, the sealing element shown on the right
is shortened, which results in a radial expansion and firm
contact with the wall of the tube 4. As far as the spacer
sleeve 43 is concerned it can be seen that a sleeve-like pin
431 has been inserted into a bore which engages an axial
gr~ove 411 in the basic probe member 41, thereby lImiting
axial travel. The inner bore of the pin 431 is connected to
the discharge channel 42 for rernoving fluid leakages.
Fig. 4 which is otherwise similar to Fig. 2 shows a probe
with sealing elements 46 consisting of individual annular
discs which in the positions shown limit the movement of
the spacer sleeves 43, 45 towards each other.
As can be seen in the detail to Fiy. 5, the sealing elements 46,
as shown on the left, consist of individual conical annular
discs 461 and outer sealing supports 462, with the inner rings
of a greater radial diameter producing returning forces in
the course of deformation and accurately limiting axial approach
of the spacer sleeves because of their greater strength. This
can be seen in the compressed conditton shown on the right:
the originally conical discs 461 now have an essentially planar
shape, whereas the outer supports 462 sealingly rest against
the tube body 1.
.