Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1315118
COMPACT PRESSURE GAUGE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a pressure gauge, and
more particularly to a compact pressure gauge.
A conventional pressure gauge generally has a
structure similar to that illustrated as Prior Art and
described below. The Prior Art constructions generally
incorporate a toothed sector-like member, and the accuracy
of the pressure gauge depends on the precision of the small
teeth of the sector-like member, the fineness of which
create difficulties in their manufacture. Furthermore,
once dust deposits on the small teeth, undesired errors
will be caused in measurement. Therefore, I disclosed an
improved pressure gauge U.S. in Patent No . 4,715,222, which
issued on December 29, 1987. In this improved pressure
gauge, the sector-like member is replaced with a movable
rack member. The rack member has an end portion movable in
a cylinder, and the opposite end portion thereof is provid-
ed with a toothed rack. Although it is easier to manu-
facture the rack member than a sector-like member, the rack
member occupies more space due to its linear arrangement
and movement.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore the feature of this invention to
provide a compact pressure gauge with a short rack member.
~k '
131~118
According to this invention, a compact gauge
includes a generally U-shaped rack member which has
generally parallel first and second arms. The first
arm extends into a cylinder and thus acts as a piston
5rod. The second arm has a rack.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Other features and advantages of this invention
will become apparent in the following detailed
description of the preferred embodiments of this
10invention with reference to the accompanying drawings
in which:
Fig. 1 is a sectional view of a conventional
pressure gauge;
Fig. 2 is a sectional view of another
15conventional pressure gauge;
Fig. 3 is an exploded view of a compact pressure
gauge in accordance with a first embodiment of this
invention;
Figs. 4 and 5 are schematic views illustrating
20the operation of the compact pressure gauge in
accordance with the first embodiment of this invention;
Fig. 6 is a sectional view showing the cylinder
of the compact pressure gauge in accordance with a
second embodiment of this invention; and
25Fig. 7 is an exploded view of a compact pressure
gauge in accordance with a third embodiment of this
invention.
-2A- 131~118
Referring to the Prior Art ~igure 1, which
illustrates a conventional pressure gauge, the operation of
the gauge results in angular displacement of the arcuate,
toothed sector 10. My later developed gauge, shown in
Figure 2, incorporates a toothed rack 20 which is displaced
linearly along cylinder 30.
The Figure 1 prior art device is difficult to
manufacture in view of the curved sector 10, with its small
teeth. The teeth are susceptible to becoming dust laden,
with diminution in accuracy.
The Figure 2 linear rack 20, owing to its.aligned
relation and linearity of movement, requires greater space
provision than the arcuate toothed section 10, of Figure
1.
. ~
, ;~
t~
_ETAILED DESC~IPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
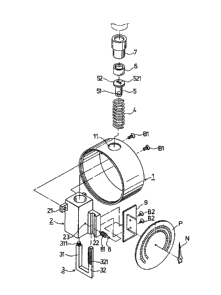
Referring to Figs. 3-6, a compact pressure gauge
of this invention is shown. The compact pressure gauge
includes an outer housing 1 which looks like a circular
barrel. The outer housing 1 is formed in its upper
surface with a circular hole 11. A cylinder body 2 is
provided with two lugs 21, each of which has a threaded
hole opposite a circular hole (not shown) in the outer
housing 1, so that the cylinder body 2 is screwed to
the outer housing 1 by two first lock bolts Bl. In
addition, the cylinder body 1 has a cylindrical bore in
its upper end surface and a square lower end opening
formed in its bottom wall.
A channel member 22 of a U-shaped cross-section
lS is integrally formed with the cylinder body 1 at a side
wall thereof and has an open-ended guide slot. A U-
shaped piston rod 3 has a first arm 31 of a square
cross-section with an externally threaded upper end
311, and a second arm 32 of a rectangular cross-section
including a rack 321 formed thereon. The first arm 31
extends into the bore in the cylinder body 1 through
the square lower end opening of the cylinder body 2 so
that a first compression spring 4 is sleeved on the
first arm 31 in the cylinder body 1. The second arm 32
is received slidably in the guide slot in the channel
member 22. An abutment element 5 has an internally
threaded lower end 51 engaged threadably with the upper
,, ,,.. ", . ",.,,, . ,.,~,,, ,. ,.~ , .,,,, . , 1 ; , ,
131S118
end of the first arm 31 of the piston rod 3, and an
outward flange 52 formed in its upper end surface with
a screwdriver hole 521. With the screwdriver hole 521
provided in the upper end surface of the abutment
element 5, the abutment element 5 can be screwed to the
first arm 31 of the piston rod 3. After a seal 6 is
placed into a cylinder cover 7, the lower end of th~
cylinder cover 7 is inserted tightly into the upper end
of the cylinder body 1 so that the cylinder body 1 and
the cylinder cover 7 form together a cylinder, as shown
in Figs. 4 and 5. Consequently r the abutment element 5
is biased by the first spring 4 to abut against the
seal 6 so that the seal 6 acts as a piston.
A pivot hole 23 is formed in a side wall of the
cylinder body 1 so that a rotating shaft 8 is mounted
rotatably on the cylinder hody 1 at an end thereof.
The opposite end of the rotating shaft 8 is inserted
through a circular hole in a L-shaped positioning plate
9. The positioning plate 9 has two circular holes
therein opposite two threaded holes (not shown) in the
back of the channel member 22 so that the positioning
plate 9 is screwed to the channel member 22 by two
second lock bolts B2. After the rotating shaft 8 has
been inserted through the positioning plate 9, it is
also inserted through the central hole in a circular
indicating plate P while permitting an indicating
needle N to be secured thereto.
131~118
A pinion 81 is secured to the rotating shaft 8
for meshing with the rack 321 of the piston rod 3.
When the compact pressure gauge is idle, the seal 6 is
pressed by the first spring 4 to abut against the upper
wall of the cylinder cover 7, as shown in Fig. 5. When
the compact pressure gauge is in use, compressed gas
enters the cylinder cover 7 in a direction indicated by
an arrow A to impel the seal 6, abutment element 5, and
piston rod 3 downwardly. Because the pinion 81 always
meshes with the rack 321, the downward movement of the
piston rod 3 permits the rotating shaft 8 and the
indicating needle N to be rotated.
As explained in the foregoing, the pressure gauge
of this invention has a relatively small volume and a
simple structure.
The bottom wall of the cylinder body 2 is
provided on its inner surface with a stepped
cylindrical spring seat 24. If necessary, referring to
Fig. 6, an additional compression spring 4' may be
located on the spring seat 24 around the first spring 4
to increase the spring pressure against the abutment
element 5 and the seal 6.
Alternatively, referring to Fig. 7, the
compressed gas inlet of the compact pressure gauge may
be provided in the back of the outer housing, for
convenience in reading. In this embodiment, the
compact pressure gauge includes a cylinder body C with
'. '.. -.. '.. ' ~'.'.. ' .
1315118
a cylindrical internal space (not shown) for receiving
a piston, a piston rod, and at least one spring therein
in the aforesaid manner. For clarity, the piston,
piston rod, and spring are not shown in Fig. 7. The
cylinder body C has a large threaded hole Cl formed in
its upper surface and engaged sealingly with a large
bolt B3, and a small threaded hole C2 formed in its
inclined side surface and engaged sealingly with a
small bolt B4. The inner end portion of the large
threaded hole Cl is communicated with the inner end
portion of the small threaded hole C2 through a
straight gas passage Pl. The inner end portion of the
small threaded hole C2 is communicated with the
exterior of the outer housing H through a V-shaped gas
passage P2. Certainly, O rings (not shown) may be
sleeved on the large and small bolts B3 and B4 to
ensure an air-tight seal between the cylinder body C
and the bolts B3 and B4.
~ith this invention thus explained, it is
apparent that numerous modifications and variations can
be made without departing from the scope and spirit of
this invention. It is therefore intended that this
invention be limited only as indicated in the appended
claims.
.